INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Participants
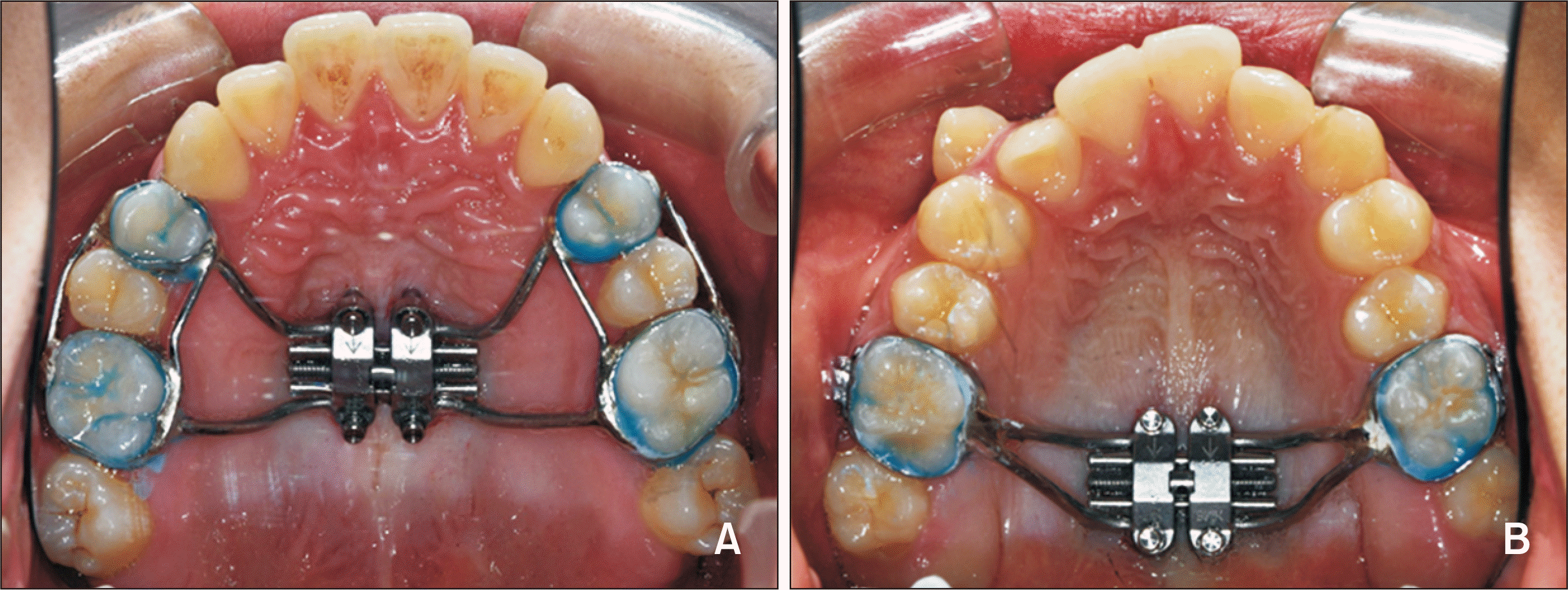
Treatment protocol
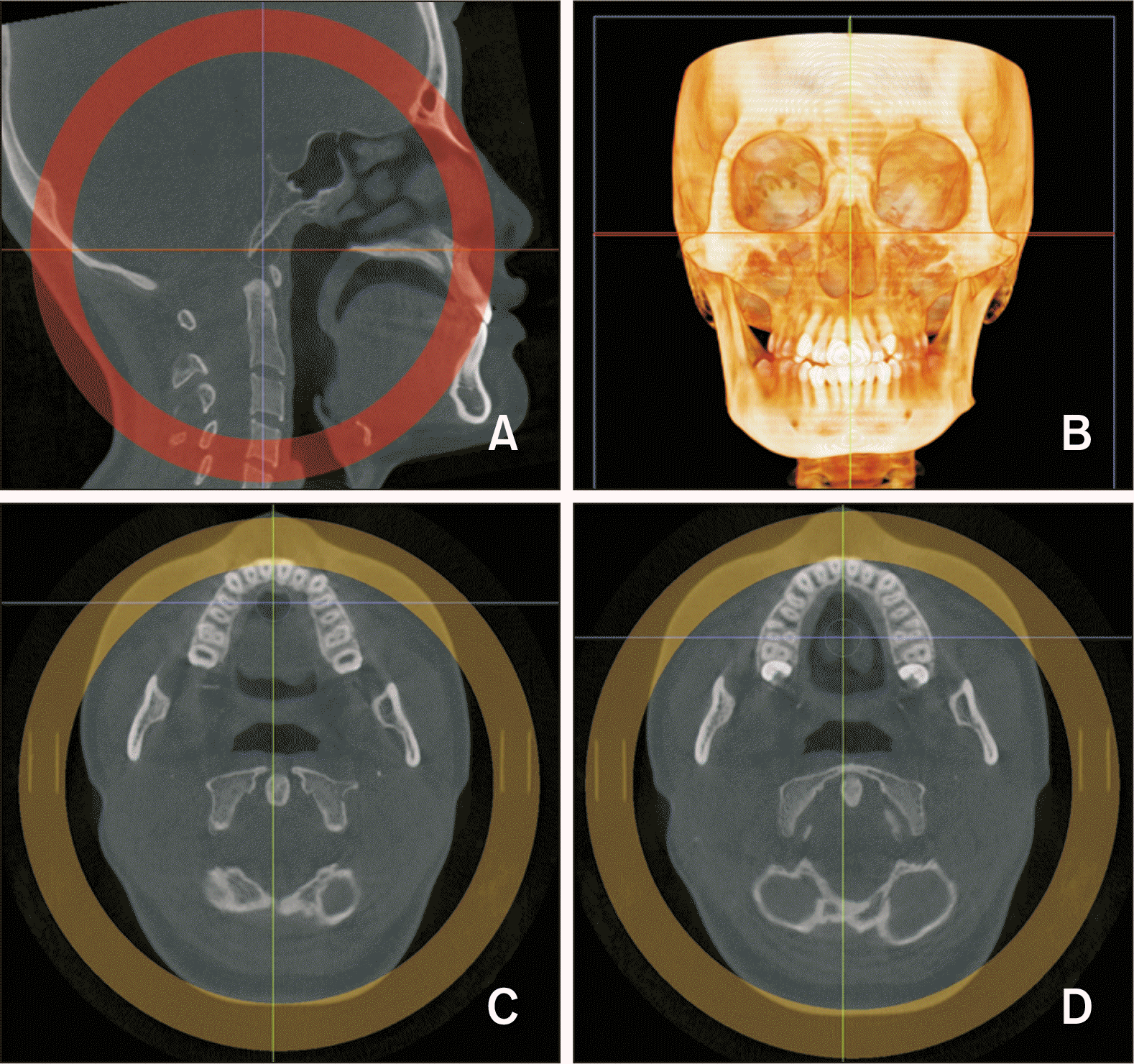 | Figure 2Re-orientation A, Sagittal view: palatal plane is parallel to the axial plane. B, Coronal view: 3D image, the line joining the lower margins of the orbits is parallel to the axial plane. C, D, Axial view: Lines passing through the palatal root canals of the bilateral maxillary first premolars (C) and first molars (D). |
Measurements
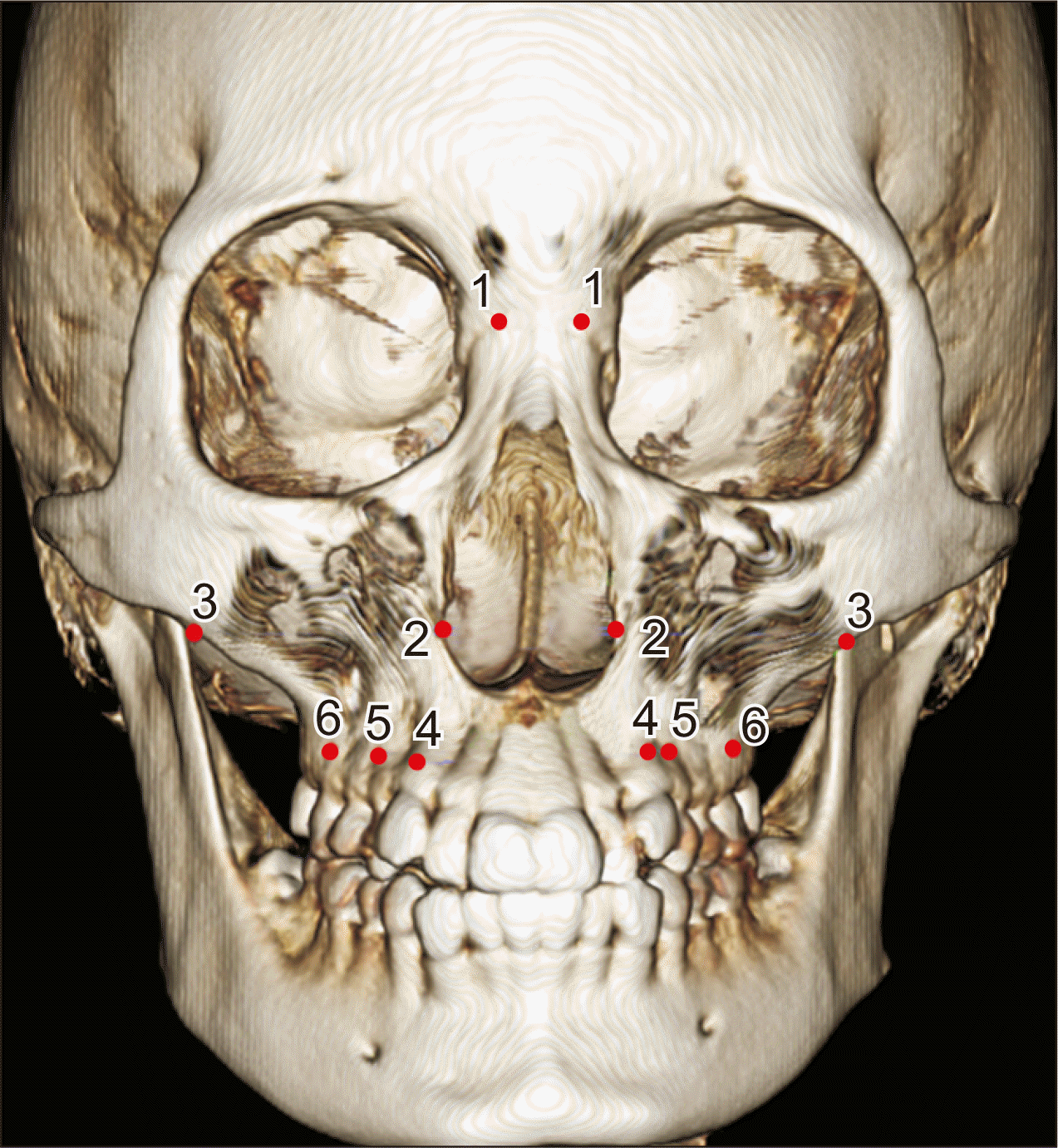 | Figure 3Landmarks used in this study. 1, The most lateral point of the nasofrontal suture. 2, The most lateral point of the nasal cavity. 3, The most inferolateral point of the zygomaticomaxillary suture. 4, Ectocanine, the most inferolateral point on the alveolar ridge at the center of the maxillary canine. 5, Ectopremolare, the most inferolateral point on the alveolar ridge at the center of the maxillary first premolar. 6, Ectomolare, the most inferolateral point on the alveolar ridge at the center of the maxillary first molar. The measurement definitions are presented in Table 1. Table 1Definition of skeletal and dental measurements |
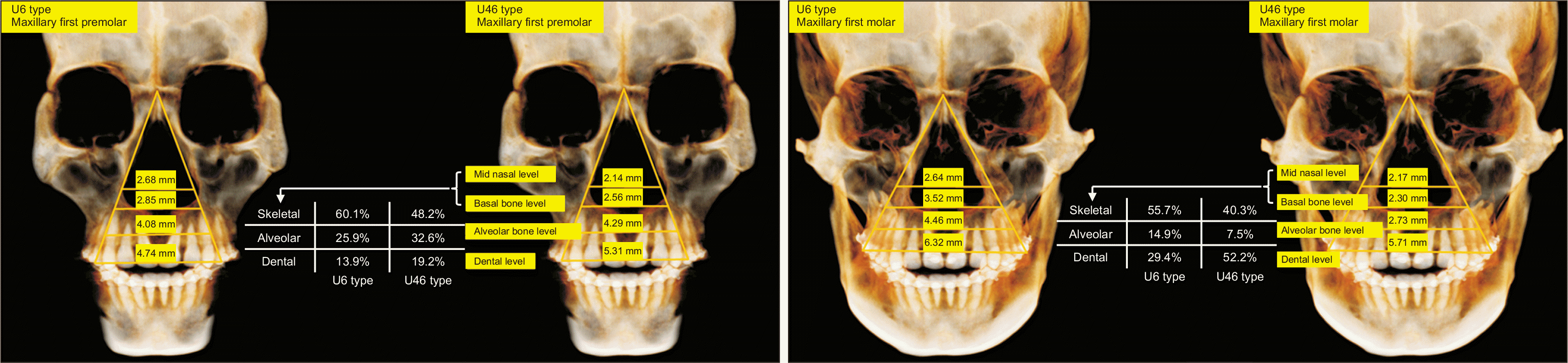
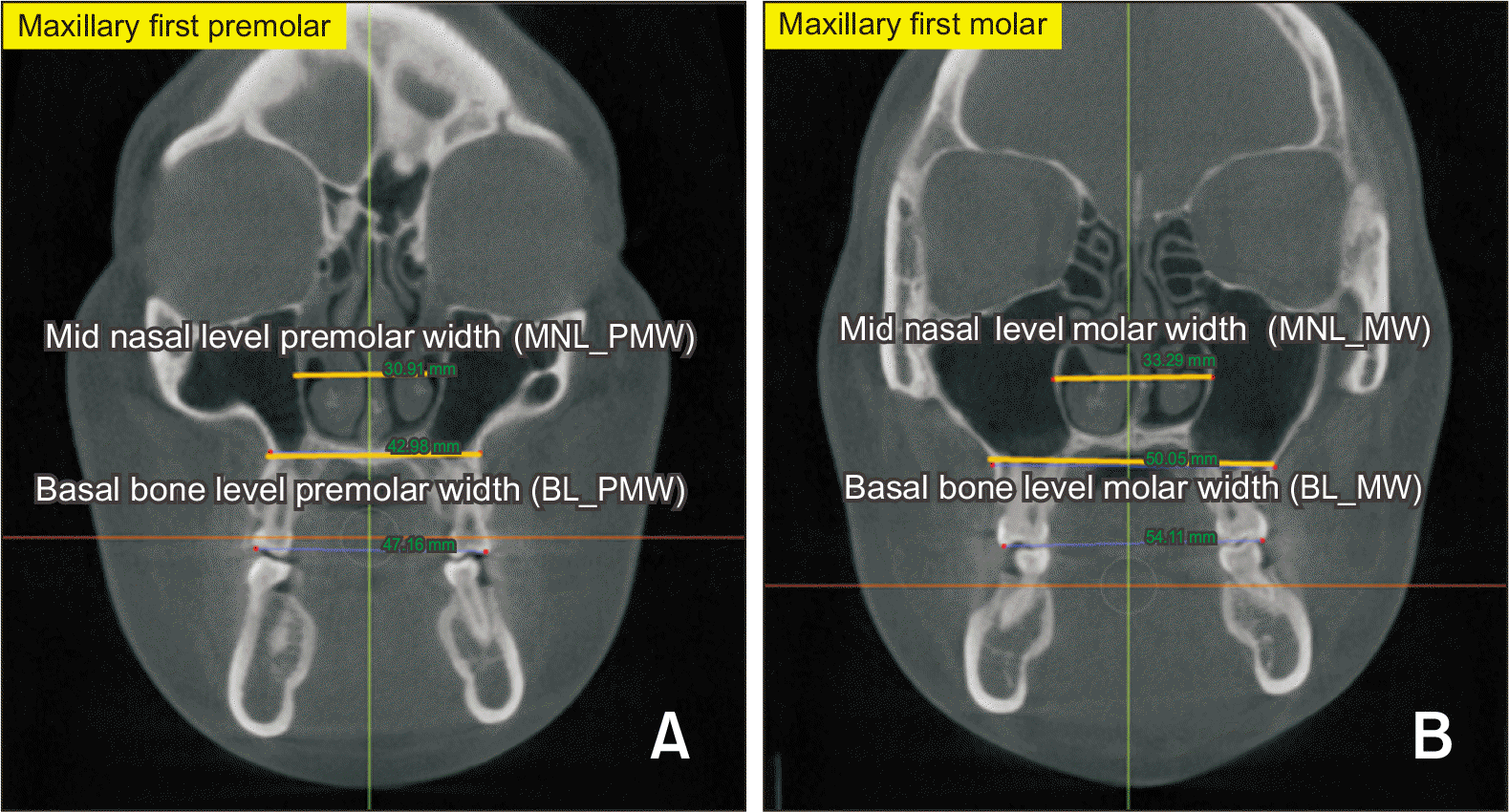 | Figure 4Skeletal expansion measurement. A, The distance between the most lateral points of the nasal cavity was measured for the midnasal-level premolar width. The distance between the most medial points on the basal bone at the junction of the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus and the buccal cortex of the maxillary alveolar bone was measured for the basal-bone-level premolar width. B, The distance between the most lateral points of the nasal cavity was measured for the midnasal-level molar width. The distance between the most medial points on the basal bone at the junction of the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus and the buccal cortex of the maxillary alveolar bone was measured for the basal-bone-level molar width.
BL_PMW, basal bone level premolar width; BL_MW, basal bone level molar width; MNL_PMW, midnasal level premolar width; MNL_MW, midnasal level molar width.
|
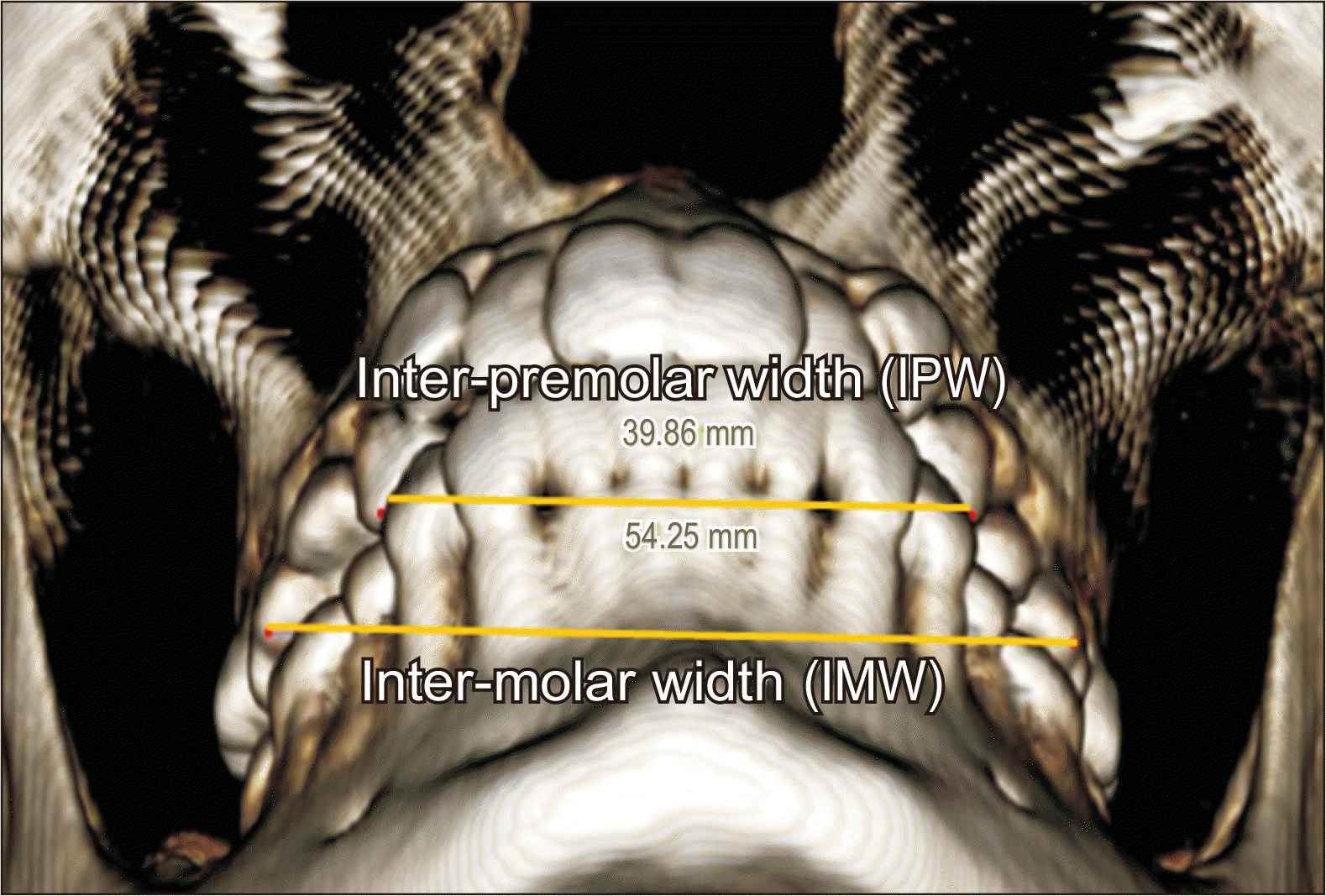 | Figure 5Linear dental measurement. IPW, and IMW were measured using a 3D coordinate system.
3D, three-dimensional; IPW, inter-premolar width; IMW, inter-molar width.
|
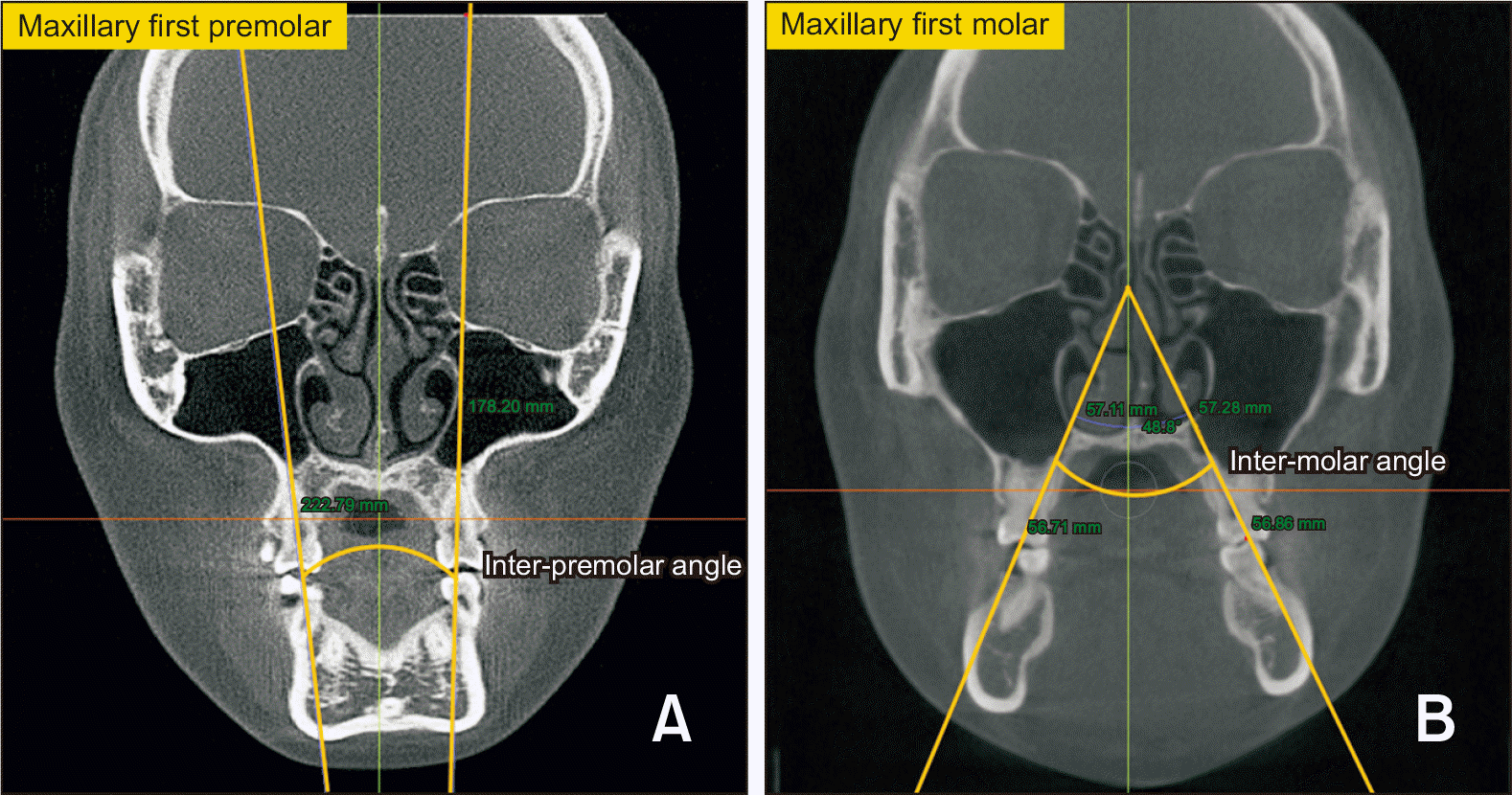 | Figure 6Dental angular measurement. A, The angle between the lines joining the bilateral fossa and palatal root apices of the maxillary first premolars was measured as the inter-premolar angle. B, The angle between the lines joining the bilateral fossa and palatal root apices of the maxillary first molars was measured as the inter-molar angle. |
Table 2
BNSW, bilateral nasofrontal suture width; NCW, nasal cavity width; ZD, zygomaticomaxillary suture distance; AP_den, difference in anterior and posterior dental width expansion; AP_alv, difference in anterior and posterior alveolar width expansion; AP_basal, difference in anterior and posterior basal width expansion; AP_mid, difference in anterior and posterior midnasal width expansion; IPW, inter-premolar width; IMW, inter-molar width; EPMW, ectopremolare width; EMW, ectomolare width; BL_PMW, basal bone level premolar width; BL_MW, basal bone level molar width; MNL_PMW, midnasal level premolar width; MNL_MW, midnasal level molar width; MARPE, microimplant-assisted rapid palatal expansion.
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Table 3
Table 4
| Measurement | Landmark | U6 type | U46 type | U6 type vs. U46 type | p-value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean difference | SD | p-value | Mean difference | SD | p-value | Comparison | |||||
| Skeletal | ∆BNSW | 0.47 | 0.83 | 0.039 | 0.67 | 0.91 | 0.01 | 0.525 | |||
| ∆NCW | 2.68 | 1.97 | < 0.001 | 2.31 | 1.61 | < 0.001 | 0.724a | ||||
| ∆ZD | 3.07 | 1.77 | < 0.001 | 2.68 | 2.16 | < 0.001 | 0.578 | ||||
| A_mid | 2.69 | 1.43 | < 0.001 | 2.14 | 1.35 | < 0.001 | 0.184a | ||||
| P_mid | 2.64 | 1.25 | < 0.001 | 2.17 | 1.11 | < 0.001 | 0.239a | ||||
| A_basal | 2.85 | 1.82 | < 0.001 | 2.56 | 2.02 | < 0.001 | 0.402a | ||||
| P_basal | 3.53 | 2.01 | < 0.001 | 2.31 | 1.43 | < 0.001 | U6 type > U46 type | 0.043a,* | |||
| Alveolar | A_alv | 4.08 | 2.03 | < 0.001 | 4.29 | 1.69 | < 0.001 | 0.745 | |||
| P_alv | 4.46 | 2.23 | < 0.001 | 2.73 | 2.22 | < 0.001 | U6 type > U46 type | 0.036* | |||
| Dental | A_den | 4.77 | 2.22 | < 0.001 | 5.32 | 2.41 | < 0.001 | 0.505 | |||
| P_den | 6.33 | 2.19 | < 0.001 | 5.65 | 2.57 | < 0.001 | 0.428 | ||||
Table 5
| Measurement | U6 type | U46 type | p-value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |||
| AP_den (mm) | 1.58 | 2.47 | 0.33 | 1.99 | 0.138 | |
| AP_alv (mm) | 0.69 | 1.43 | −1.56 | 2.09 | 0.001a,*** | |
| AP_basal (mm) | 0.68 | 0.88 | −0.22 | 1.67 | 0.077 | |
| AP_mid (mm) | −0.05 | 1.09 | 0.04 | 0.96 | 0.818 | |
AP_den, difference in anterior and posterior dental width expansion; AP_alv, difference in anterior and posterior alveolar width expansion; AP_basal, difference in anterior and posterior basal width expansion; AP_mid, difference in anterior and posterior midnasal width expansion; SD, standard deviation.
Table 6
| Measurement | U6 type (SD) | U46 type (SD) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPA (T1–T0) | 2.64 (5.88) | 6.04 (5.18) | 0.036* |
| IMA (T1–T0) | 7.06 (5.27) | 5.88 (6.49) | 0.752a |
DISCUSSION
Table 7
| Measurement | U6 type (SD) | U46 type (SD) | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of bicortically engaged microimplants | 3.88 (0.5) | 2.56 (0.96) | 0.001a,*** |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download