1. Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J, Haber DA. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007; 7:169–81.

2. Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, Vergnenegre A, Massuti B, Felip E, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012; 13:239–46.
3. Kobayashi S, Boggon TJ, Dayaram T, Janne PA, Kocher O, Meyerson M, et al. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:786–92.
4. Engelman JA, Zejnullahu K, Mitsudomi T, Song Y, Hyland C, Park JO, et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science. 2007; 316:1039–43.

5. Wu SG, Chang YL, Yu CJ, Yang PC, Shih JY. The role of PIK3CA mutations among lung adenocarcinoma ptients with primary and acquired resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:35249.
6. Gammelgaard KR, Vad-Nielsen J, Clement MS, Weiss S, Daugaard TF, Dagnaes-Hansen F, et al. Up-regulated FGFR1 expression as a mediator of intrinsic TKI resistance in EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Transl Oncol. 2019; 12:432–40.

7. Mao C, Liao RY, Chen Q. Loss of PTEN expression predicts resistance to EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibodies in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2010; 102:940.

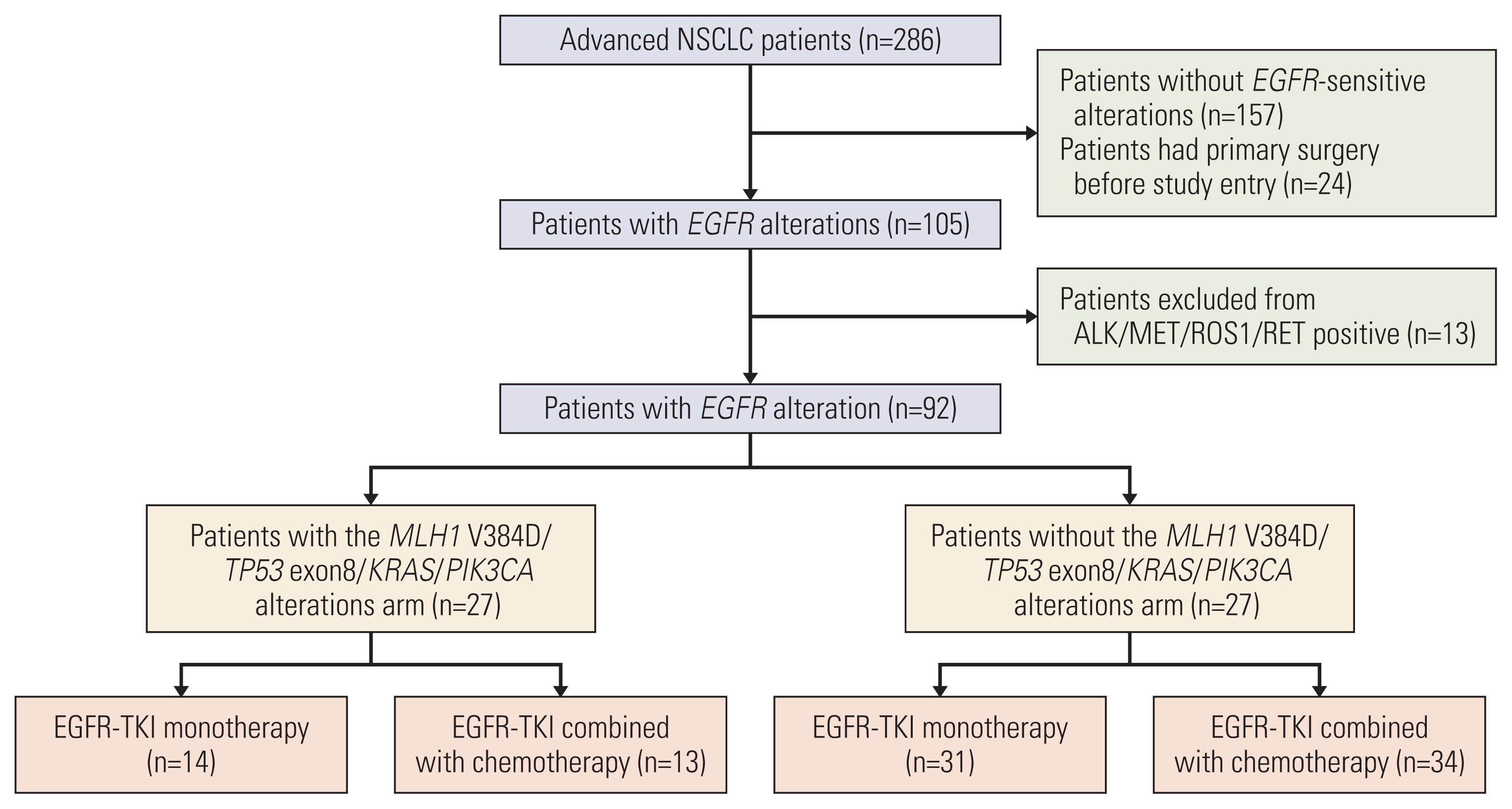
8. Duan J, Xu J, Wang Z, Bai H, Cheng Y, An T, et al. Refined stratification based on baseline concomitant mutations and longitudinal circulating tumor DNA monitoring in advanced EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma under gefitinib treatment. J Thorac Oncol. 2020; 15:1857–70.

9. Chiu CH, Ho HL, Doong H, Yeh YC, Chen MY, Chou TY, et al. MLH1 V384D polymorphism associates with poor response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR L858R-positive lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:8407–17.
10. Canale M, Petracci E, Delmonte A, Bronte G, Chiadini E, Ludovini V, et al. Concomitant TP53 mutation confers worse prognosis in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with TKIs. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:1047.

11. Nardo G, Carlet J, Marra L, Bonanno L, Boscolo A, Dal Maso A, et al. Detection of low-frequency KRAS mutations in cfDNA from EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients after first-line EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:607840.

12. Deng LL, Gao G, Deng HB, Wang F, Wang ZH, Yang Y. Co-occurring genetic alterations predict distant metastasis and poor efficacy of first-line EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019; 145:2613–24.

13. Guo Y, Song J, Wang Y, Huang L, Sun L, Zhao J, et al. Concurrent genetic alterations and other biomarkers predict treatment efficacy of EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a review. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:610923.

14. Canale M, Petracci E, Delmonte A, Chiadini E, Dazzi C, Papi M, et al. Impact of TP53 mutations on outcome in EGFR-mutated patients treated with first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 2017; 23:2195–202.
15. Scagliotti GV, Ceppi P, Capelletto E, Novello S. Updated clinical information on multitargeted antifolates in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 2009; 10(Suppl 1):S35–40.

16. La Monica S, Madeddu D, Tiseo M, Vivo V, Galetti M, Cretella D, et al. Combination of gefitinib and pemetrexed prevents the acquisition of TKI resistance in NSCLC cell lines carrying EGFR-activating mutation. J Thorac Oncol. 2016; 11:1051–63.
17. Cheng Y, Murakami H, Yang PC, He J, Nakagawa K, Kang JH, et al. Randomized phase II trial of gefitinib with and without pemetrexed as first-line therapy in patients with advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer with activating epidermal growth factor receptor mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:3258–66.

18. Lu N, Pan Y, Han X. A retrospective study on the efficacy and prognostic factors of three EGFR-TKI drugs. Mod Oncol. 2018; 26:2362–7.
19. Griesinger F, Korol EE, Kayaniyil S, Varol N, Ebner T, Goring SM. Efficacy and safety of first-line carboplatin-versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 2019; 135:196–204.

20. Li C, Zhang B, Guo J, Hu F, Nie W, Zheng X, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) combined with chemotherapy delay brain metastasis in patients with EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Target Oncol. 2019; 14:423–31.

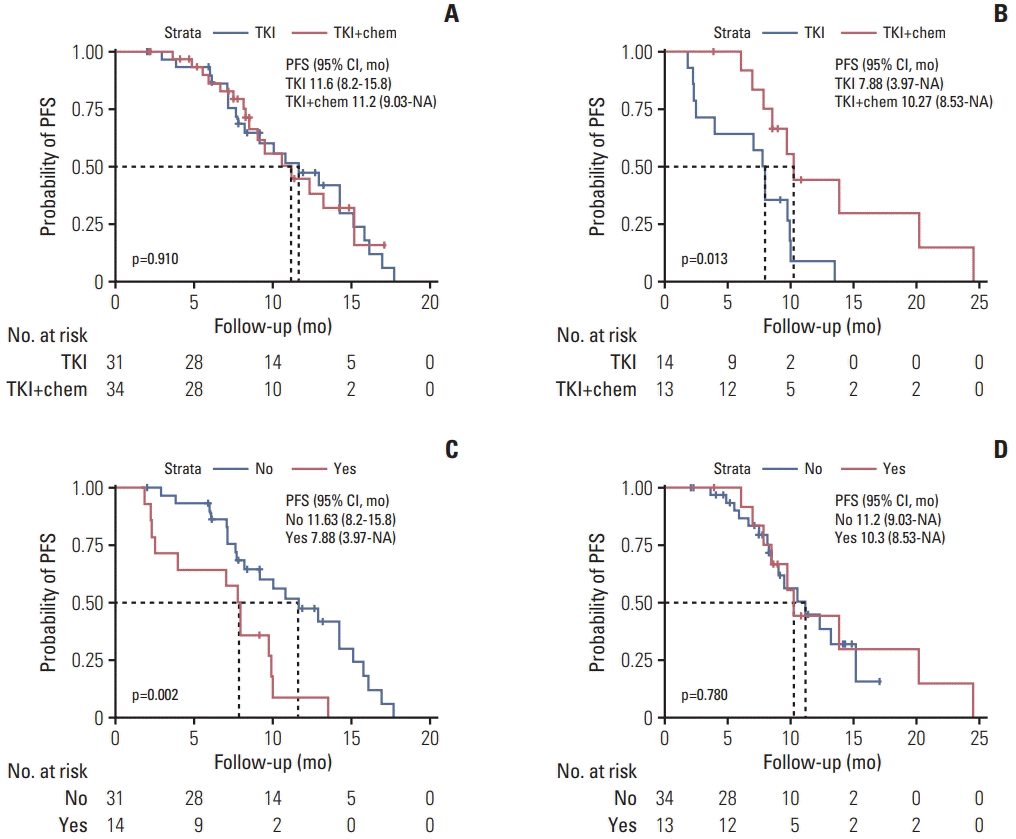
21. Rebuzzi SE, Alfieri R, La Monica S, Minari R, Petronini PG, Tiseo M. Combination of EGFR-TKIs and chemotherapy in advanced EGFR mutated NSCLC: review of the literature and future perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020; 146:102820.

22. Mok TS, Wu YL, Yu CJ, Zhou C, Chen YM, Zhang L, et al. Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II study of sequential erlotinib and chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:5080–7.
23. Wu Q, Luo W, Li W, Wang T, Huang L, Xu F. First-generation EGFR-TKI plus chemotherapy versus EGFR-TKI alone as first-line treatment in advanced NSCLC with EGFR activating mutation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Oncol. 2021; 11:598265.

24. Liu S, He Y, Jiang T, Ren S, Zhou F, Zhao C, et al. EGFR-TKIs plus chemotherapy demonstrated superior efficacy than EGFR-TKIs alone as first-line setting in advanced NSCLC patients with EGFR mutation and BIM deletion polymorphism. Lung Cancer. 2018; 120:82–7.

25. Gatzemeier U, Pluzanska A, Szczesna A, Kaukel E, Roubec J, De Rosa F, et al. Phase III study of erlotinib in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the Tarceva Lung Cancer Investigation Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:1545–52.

26. Wang Y, Yuan X, Yang M, Shen Z, Chen H, He X, et al. Efficacy of icotinib, an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer patients with exon 19 deletion and exon 21 L858R: a retrospective analysis in China. Pharmacology. 2021; 106:658–66.

27. Huang L, Fu L. Mechanisms of resistance to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015; 5:390–401.

28. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aggarwal C, Aisner DL, Akerley W, Bauman JR, et al. NCCN guidelines insights: non-small cell lung cancer, version 1.2020. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019; 17:1464–72.
29. Vendrell JA, Mau-Them FT, Beganton B, Godreuil S, Coopman P, Solassol J. Circulating cell free tumor DNA detection as a routine tool for lung cancer patient management. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18:264.

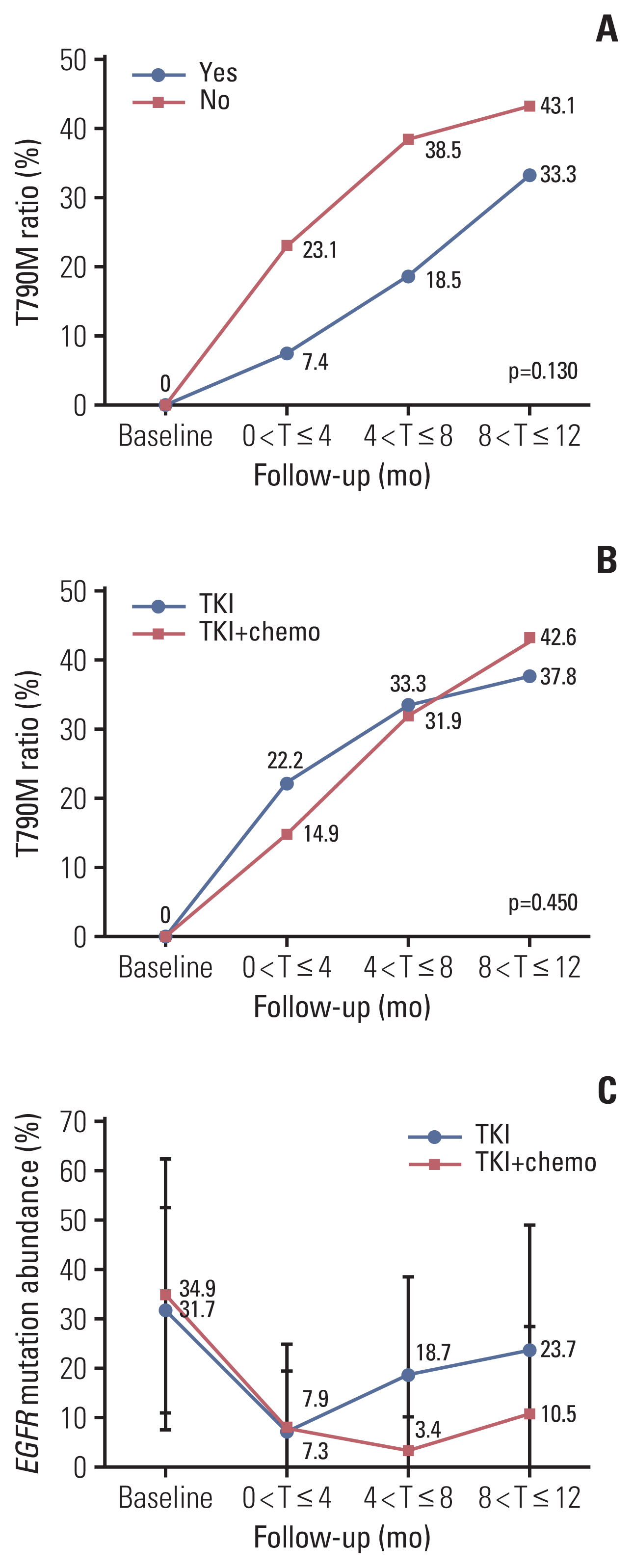
30. Ni J, Weng L, Liu Y, Sun Z, Bai C, Wang Y. Dynamic monitoring of EGFR mutations in circulating cell-free DNA for EGFR-mutant metastatic patients with lung cancer: early detection of drug resistance and prognostic significance. Oncol Lett. 2017; 13:4549–57.

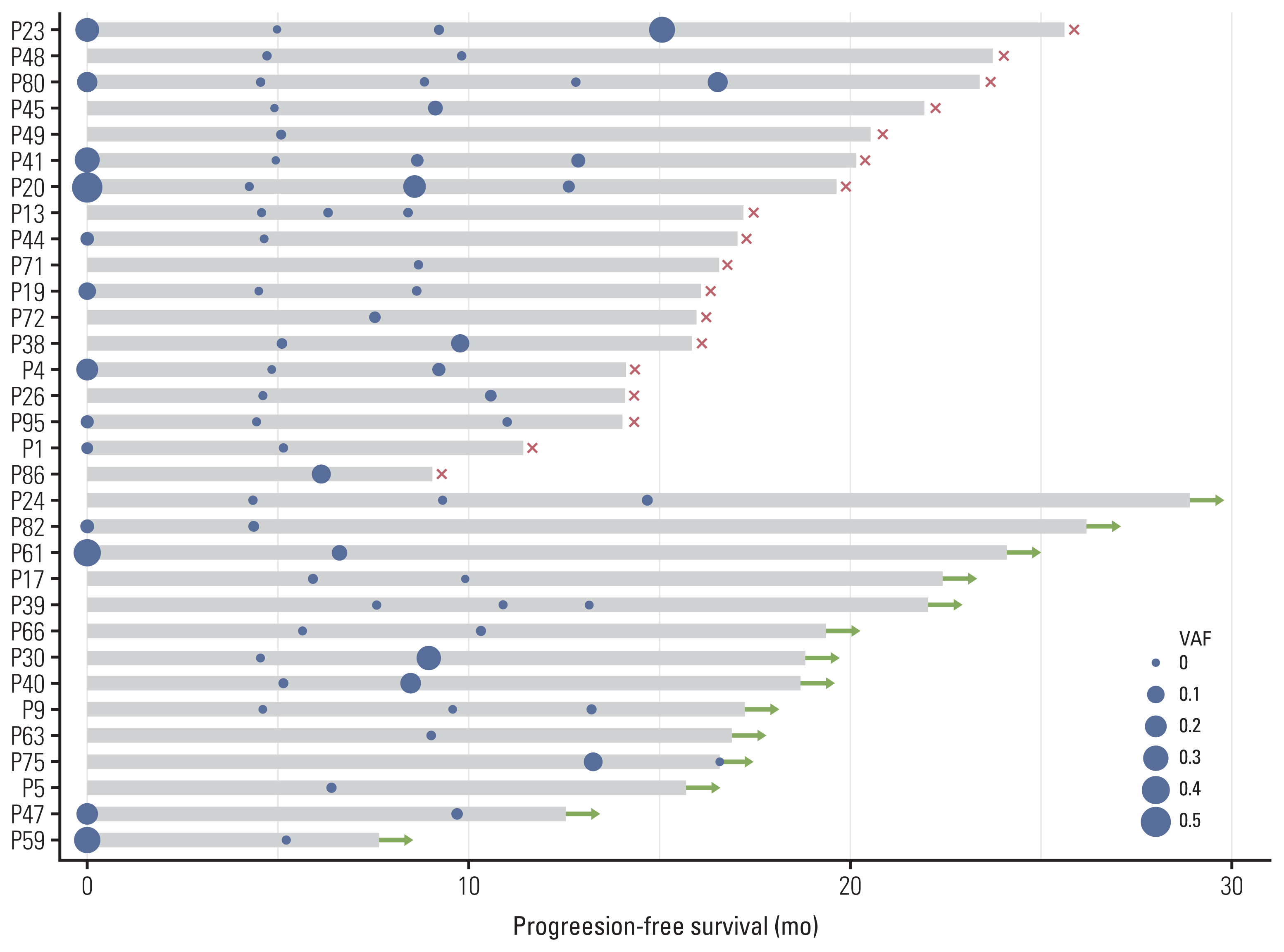
31. Li X, Cai W, Yang G, Su C, Ren S, Zhao C, et al. Comprehensive analysis of EGFR-mutant abundance and its effect on efficacy of EGFR TKIs in advanced NSCLC with EGFR mutations. J Thorac Oncol. 2017; 12:1388–97.

32. Li N, Wang BX, Li J, Shao Y, Li MT, Li JJ, et al. Perioperative circulating tumor DNA as a potential prognostic marker for operable stage I to IIIA non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer. 2022; 128:708–18.
33. Lim ZF, Ma PC. Emerging insights of tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance mechanisms in lung cancer targeted therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2019; 12:134.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download