INTRODUCTION
The gastrointestinal tract, or gut, is a crucial component of the digestive system responsible for the breakdown of food and absorption of essential nutrients required for human survival {(1)}. However, the gut also serves as a point of entry for external substances, including pathogenic microorganisms that can cause various diseases (2). In response to such threats, the epithelial cells at the intestinal tract act as primary physical barriers, while immune cells in lymphoid tissues provide defensive mechanism against invading pathogens (3). Despite these defenses, various viruses, such as astrovirus, rotavirus, norovirus, enterovirus, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and influenza A virus (IAV), use the gut as a site for replication or fecal-oral transmission (4).
Viruses are intracellular pathogens that rely on host cell surface receptors for entry and take over host cellular machineries for their life cycle such as replication, assembly, and release of new virus particles (5). In contrast, host cells evolved to detect and counteract viral invasion by recognizing pathogen-associated molecular patterns, such as nucleic acids, peptidoglycan (6). While antiviral drugs targeting viral proteins have shown efficacy, their effectiveness is limited by the emergence of drug-resistant viral strains and the outbreak of new viruses. However, drugs targeting host factors that are essential for viral replication are less susceptible to drug resistance. Therefore, identifying such host factors that either promote host defense mechanism or restrict viral replication can provide insights into host-virus interactions and novel targets for antiviral drug development.
Studies of viral pathogenesis typically utilize in vitro cell culture systems of transformed human cell lines such as immortalized cell lines or cancer cell lines, which are simple and cost-effective. However, these cell lines frequently fail to accurately mimic the characteristics and signaling pathways of normal human cells or in vivo condition, and they are not suitable for modeling the interactions between different cell types in complex tissue architecture since they have cellular heterogeneity. To address these limitations, animal models, including rodents and primates, have been utilized for studying viral pathogenesis. However, many human viruses do not infect or reproduce human pathophysiology in these animal models, limiting their usefulness in understanding host-virus interactions and molecular mechanisms of human viral diseases. In addition, primate model is cost-inefficient and hard to handle (7).
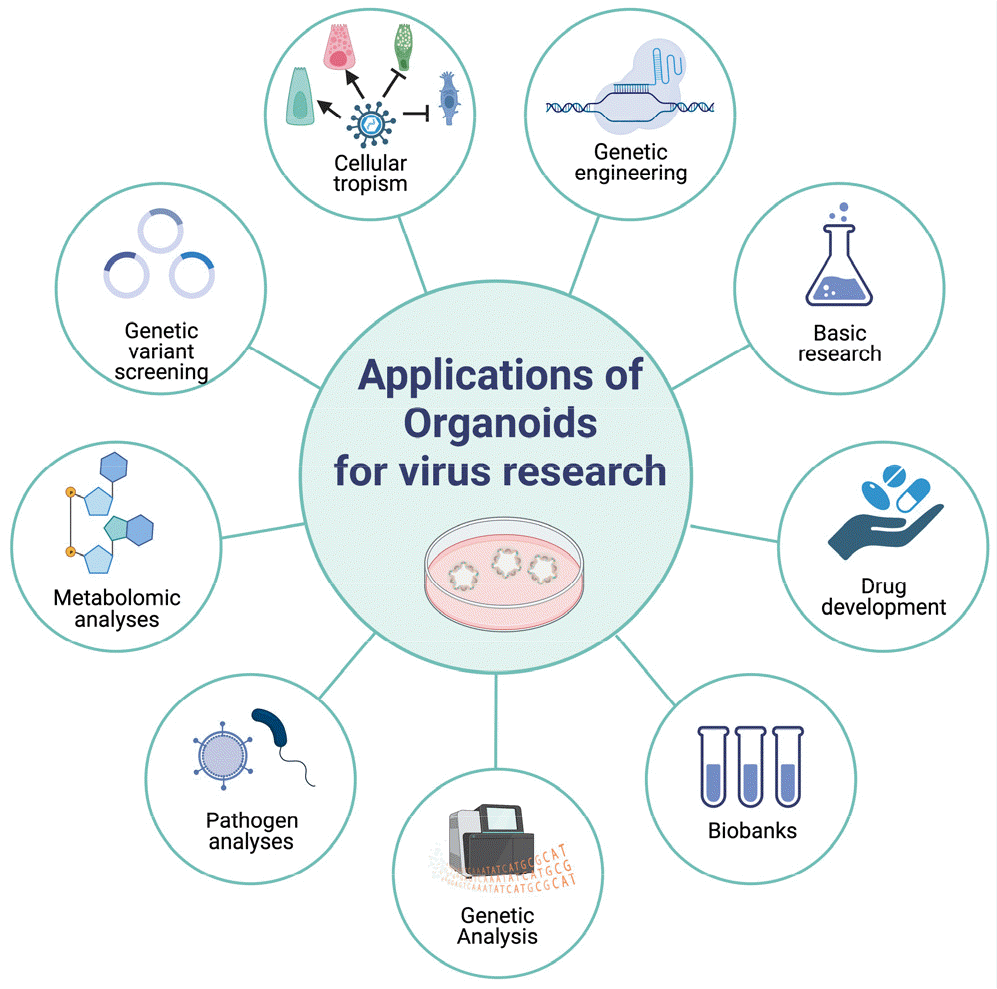
Recently, 3D organoid models have emerged as a promising in vitro system that closely resembles in vivo organs (8). Organoids are self-organized 3D constructs derived from stem cells, either pluripotent (embryonic or induced) or adult stem cells, and differentiated into organ-specific cell types with similar in vivo architecture. These cells self-organize into aggregates via cell sorting and spatially restricted lineage commitment, recapitulating the architecture and functionality of the organ. Organoids are more physiologically relevant and maintain experimental tractability, making them ideal for modeling human infectious diseases and establishing a more accurate mechanistic understanding of human immunity and host-pathogen interactions (Fig. 1).
In this review, we will summarize recent findings using adult stem cell derived intestinal organoid for the host-pathogen interaction.
BODY
Rotavirus
Rotavirus is a prevalent causative agent of gastroenteritis, especially in infants and young children (9). However, the incidence of the disease is not limited to children as patients who have undergone organ transplants are at an increased risk of rotavirus infection (10). Although vaccines have been developed to prevent rotavirus infection, the resources required for vaccine distribution and administration are not fully equipped, particularly in developing countries. Therefore, alternative therapeutic strategies are being developed to counter rotavirus by identifying anti-viral targets through extensive research (11). However, the existing 2D cell line model used for rotavirus research has several limitations in exploring patient-derived rotavirus. As a result, research has shifted towards utilizing gut organoids with heterogeneous characteristics to improve rotavirus research (12).
In 2015, two groups demonstrated the potential of 3D primary human intestinal organoid cultures as a platform for studying viral infections (13, 14). Rapid replication of both laboratory and patient-derived strains in human intestinal organoids was observed within 24 h of inoculation. The study by Yin et al. revealed that the antiviral cytokine interferon (IFN)-α-, a VP7-targeted neutralizing antibody, and the nucleoside analog ribavirin exhibited virus-suppressive activity in the organoid system (14). Interestingly, patient-derived strains grown in organoids exhibited varying sensitivity to IFN-α and ribavirin, suggesting that this organoid model system could be used in a personalized medicine setting for identifying the most effective, strain-specific therapeutic interventions. In a separate report, Saxena et al. demonstrated that rotavirus infection in intestinal organoids led to water influx into the lumen, mimicking rotavirus-induced diarrhea in vitro (13). The study further revealed that the rotavirus enterotoxin NSP4 peptide could also cause water influx in intestinal organoids. Additionally, Pan and colleagues confirmed the ability of the organoid system to accurately mimic physiological responses during rotavirus infection and demonstrated the therapeutic potential of different IFNs (14). To extend the existing rotavirus research, primary human intestinal organoids isolated from crypt have been demonstrated to be susceptible to rotavirus (15). Both experimental strain SA11 and patient-derived rotavirus strains from stool samples of infected patients have shown kinetics of viral replication in human intestinal organoids. Unlike the 2D cell line model, organoids provide a more reliable platform for evaluating the interaction between the host and virus during rotavirus infection. The authors have shown that the IFN stimulating gene (ISG) production, which is associated with host-pathogen interaction, is induced during rotavirus infection. Additionally, they have suggested that human intestinal organoids can be used to evaluate anti-viral drugs for rotavirus.
Through this platform, the hypothesis that the enzyme which supplies nucleosides in the host is utilized for viral replication has been tested (16, 17). By targeting IMPDH enzymes and DHODH enzymes which suppress purine and pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis, respectively, it is reasonable to target enzymes that supply nucleosides for anti-rotavirus replication. Hakim et al. proposed that rotavirus infection could be overcome with the addition of exogenous IFN because the endogenous IFNs is insufficient to produce the necessary amount of anti-viral ISG (17). Furthermore, the PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in rotavirus infection, has been suggested as another potential anti-viral target (18). Finally, Chen et al. used intestinal organoids to identify the mode of action of existing anti-viral drugs, and they found that 6-thioguanine (6-TG), a drug used for organ transplantation, inhibited rotavirus replication by suppressing Rac1 (19).
Norovirus
Norovirus, a prevalent gastroenteric virus, is transmitted via the fecal-oral route, and young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals are at a heightened risk of infection (20). In developing countries, preventing norovirus infection caused by contaminated food and water is a major challenge. However, research on norovirus has been hindered by limitations in establishing in-vitro culture systems, similar to those encountered in rotavirus research.
In 2016, Ettayebi et al. demonstrated that norovirus can infect enterocytes of human intestinal organoids and replicate successfully (21). By utilizing a human intestinal organoid that mimics the in vivo host environment, the authors showed that bile and FUT2 were necessary for the successful replication of multiple human norovirus strains, in a strain-dependent manner. The use of bile proved essential during or after virus adherence to the target cell, mimicking the human replication niche. Furthermore, the FUT2 enzyme enhanced the replication of GⅡ.4 norovirus.
Subsequently, Hosmillo et al. investigated the replication cycle of norovirus by genetically modifying intestinal epithelial organoids to repress IFN production (22). The authors found that modified intestinal organoids were more susceptible to norovirus infection and demonstrated that IFN responses, type Ⅰ and type Ⅲ, inhibited norovirus replication in intestinal epithelial cells.
Enterovirus
Enterovirus is a non-enveloped, single-stranded, positive RNA virus that belongs to the Picornaviridae family. The enterovirus genome contains a single long open reading frame (ORF) that encodes viral and non-structural proteins. Human pathogenic enteroviruses mainly belong to groups A-D and rhinovirus A-C among the 15 species of enterovirus. Enterovirus replication occurs in small intestinal submucosal lymphoid tissues, respiratory mature polarized enterocytes, and gastrointestinal pharynx and is mainly transmitted through the fecal-oral route. While patients often have asymptomatic or mild symptoms, some serotypes can cause severe symptoms leading to death in severe cases.
Lulla et al. demonstrated the conservation of upstream ORF (uORF) between major enterovirus groups and observed the expression of uORF translation in enterovirus-infected cells using echovirus 7 and poliovirus 1 for the first time (23). Moreover, the authors used differentiated organoids from the terminal ileum of patients mainly composed of absorptive enterocytes to reveal the function of uORF. Using echovirus, the authors confirmed that enterovirus proliferation in human intestinal organoids decreases when the uORF protein is knocked out. The study highlights the critical role of uORF in the release of enterovirus beyond the limitations of low viral sensitivity when using the mouse model.
Tsang et al. demonstrated the human intestinal organoids as a suitable enterovirus research model for identifying viral replication kinetics and antiviral sensitivity compared to existing in vitro cell line models, RD cells, and Caco-2 cells (24). A71, coxsackievirus B2, and poliovirus 3, which are representative enteroviruses, can replicate in human intestinal organoids, except for EV-D68 respiratory infections (24). Evaluation of the mRNA transcript expression level of the enterovirus receptor within the human intestinal organoids revealed that only the EV-D68 receptor is expressed at a low level. The use of human intestinal organoids in enterovirus research could lead to more effective antiviral therapies and a better understanding of the virus's replication cycle.
Coronavirus
Coronaviridae, a positive-strand RNA virus family, is enveloped and known to cause infections in birds and mammals, including humans. Among the pathogenic viruses that affect humans, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 are noteworthy (25).
MERS-CoV is a zoonotic virus, primarily transmitted via contact with dromedary camels (26). Although human-to-human transmission is possible, it is less efficient without close contact (27, 28). The entry receptor for MERS-CoV is dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) (29), and the respiratory symptoms range from mild to severe acute pneumonia, often leading to multiorgan failure (30, 31). The virus may also cause gastrointestinal symptoms, including diarrhea.
SARS-CoV-2 caused the worldwide COVID-19 pandemic. It uses angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) as an entry receptor on the surface of host cells (32), which is activated by the transmembrane protease serine 2 (TMPRSS2), a host protease (33). The virus causes inflammation and can lead to severe COVID-19 cases, with the virus transmitting primarily through the respiratory tract. Still, multiple organ involvement is observed in COVID-19 patients, with some experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms as well (34, 35). The virus may also be detected in feces, with patients experiencing gastrointestinal symptoms taking more time to recover than those shedding the virus through the respiratory tract. Since COVID-19 continues to cause deaths, virology and host immune response research on SARS-CoV-2 are crucial for developing new treatments.
Giobbe et al. demonstrated that SARS-CoV-2 can infect gastric epithelium, and pediatric and late fetal intestinal organoids are more permissive to SARS-CoV-2 than early fetal and adult organoids (36). The authors found that the reverse polarity organoid model increased the infection rate against SARS-CoV-2. Furthermore, the study suggests the fecal-oral pathway is a potential alternative transmission route for SARS-CoV-2, particularly in children. Similarly, human intestinal organoids were found to be susceptible to MERS-CoV, and Zhou et al. confirmed that the gastrointestinal tract may be an alternative route of transmission (37).
Intestinal organoids are modified with CRISPR/Cas9 to establish a knockout biobank. Beumer and colleagues select a therapeutic target by genetically engineering host factors such as entry receptors and proteases (38). The study reveals that ACE2 is the entry receptor for SARS-CoV/SARS-CoV-2, and TMPRSS2 contributes to viral replication. Furthermore, the previously known receptor of MERS-CoV, DPP4, is confirmed again through CRISPR/Cas9 knockout in the intestinal organoid. The author proposes targeting TMPRSS2 as an antiviral strategy due to its requirement by SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and the SARS-CoV-2 vsriant alpha (B.1.1.7).
Triana and colleagues investigated the host immune responses caused by SARS-CoV-2 by performing single-cell analysis of organoids from colon and ileum (39). The study suggested that immature enterocytes 2 is the main target cell, and the expression of ACE2 decreases after infection. Comparing the two types of organoids, the ileum-derived organoid is more immunoresponsive and produces more ISG in the bystander cell. Infected cells activate NFκB/TNF pro-inflammatory responses and produce IFN, but IFN-related responses are limited to bystander cells. The study shows that SARS-CoV-2 inhibits the host immune response in a paracrine manner and that susceptibility varies depending on the cell types.
Heuberger et al. investigate the increased levels of IFN-γ in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and its relation to ACE2 (40). The authors select a human colon organoid as a research model to study differentiation and its impact on infection. The study reveals that IFN-γ, commonly used as an antiviral mediator, promotes differentiation into enterocytes and improves ACE2 expression of the organoid. The study also suggests that IFN-γ becomes more active when infected with the virus. The study shows that infection of epithelial cells against SARS-CoV-2 mounts due to the increased IFN-γ expression that makes mature enterocytes. The author speculates that high expression of IFN-λ represses Wnt signaling activity and increases differentiation into the enterocyte. The study suggests that this may be the cause of severe SARS-CoV-2 symptoms and chronic inflammatory reactions.
Astrovirus
Astrovirus is a positive-stranded RNA virus that commonly infects the gastrointestinal tract (41). Human astrovirus (HAstV) typically causes mild or asymptomatic diarrhea lasting for a few days, with occasional cases exhibiting acute symptoms such as fever, vomiting, and abdominal pain (42). Immunocompromised individuals are particularly susceptible to severe systemic symptoms such as encephalitis and meningitis. The prevalence of astrovirus infection is high, with 90% of children under the age of 5 exhibiting serum antibodies for at least one HAstV genotype (43, 44, 45).
In a recent study, Triana and colleagues investigate the response of individual cell types to astrovirus infection (46). Using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) of infected organoids, the authors first generate an annotated reference of multiple cell types within organoids by performing scRNA-seq on human ileum biopsies. With the exception of paneth and tuft cells, all the other cell types in biopsies were identified in human ileum organoid. The authors also utilize high multiplex RNA in situ hybridization to determine the spatial distribution of viral nucleic acid. The results of the study indicate that infection by HAstV1 is controlled through an increase in IFN and induces expression of MKI67, a marker of cell proliferation. In addition, the authors identify distinct basal ISG expression in each epithelial cell lineage and show that the expression is increased in the infected cell compared to bystander cells during infection.
Influenza A virus
IAVs are known for their diverse subtypes classified according to the hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) surface molecules they express. The low fidelity of the viral RNA polymerase allows for the generation of various combinations of these two molecules, which ultimately define the host range of the virus from avian to mammalian species. In the past, outbreaks of highly virulent IAV have been reported, such as the Spanish flu caused by the H1N1 subtype, the Hong Kong flu by the H3N2 subtype, and the Chinese flu by the H7N9 subtype (47, 48). Despite continuous outbreaks, it remains challenging to predict which subtype will result in high virulence. Therefore, it is critical to establish an in vitro system that accurately recapitulates the in vivo pathophysiology. These efforts will aid in the development of effective treatments and preventative measures against IAV infections.
In a study by Huang et al., the interaction between H9N2 avian influenza and intestinal epithelial cells was investigated using mouse intestinal organoids (49). The infection with H9N2 avian influenza resulted in morphological damage in mouse intestinal organoids, causing a loss of highly specialized secretory Paneth cells, which function as an intestinal stem cell niche and contribute to damage in stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Furthermore, down-regulation of Wnt and Notch signaling, which regulate intestinal stem cell and Paneth cells proliferation and differentiation, was observed. These findings provide insights into the pathogenesis of H9N2 avian influenza in the gastrointestinal tract and may inform the development of novel therapies targeting the intestinal epithelium.
Mammalian reoviruses
Mammalian reoviruses (MRVs) are a group of double-stranded RNA viruses that can infect various mammalian hosts, including humans (50). These viruses have been implicated in a range of human diseases, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract, with the colon being a primary target. Although reovirus infection is usually asymptomatic or causes mild symptoms, recent studies suggest that it may play a role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer (51). MRVs have been shown to infect and replicate in human colon cancer cell lines, and their replication has been observed in colonic tissues of patients with IBD (52). Additionally, reovirus has been investigated as an oncolytic agent for the treatment of colorectal cancer, showing promising results in preclinical studies. Therefore, understanding the biology and pathogenesis of MRVs in the context of human disease, particularly in the colon, is essential for developing effective treatment strategies against reovirus infections and exploring their potential as novel therapeutic agents for colorectal cancer and IBD. Upon infecting human intestine and colon organoids with MRV, both type Ⅰ (β1) and type Ⅲ (γ1-3) IFNs were observed, with IFNⅠ being more highly expressed than IFNⅢ (53). The induction of these IFNs subsequently led to the production of ISGs, which resulted in the prevention of viral infection of the organoids. These findings highlight the antiviral innate immune response of type Ⅰ and type Ⅲ IFNs in the human gut. These results have significant implications for understanding the pathogenesis of MRV infections in the human gut and the development of novel therapeutic approaches against reovirus infections.
CONCLUSION
Pathogenic diseases have been a persistent threat to humanity for centuries, with the recent outbreak of new viruses such as SARS-CoV-2 causing unprecedented disruptions to global health and social systems. The development of effective strategies to combat viral pathogens requires a comprehensive understanding of the interactions between these pathogens and their host systems. A deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis can provide crucial insights into potential targets for intervention, paving the way for the development of new and effective treatments for viral diseases. Therefore, a concerted effort is required to accelerate the pace of research into viral pathogenesis and to develop innovative approaches to combat these pathogens.
The development of intestinal organoid culture systems has significantly advanced the field of viral pathogen research, particularly in understanding the interaction between viruses and the human gut. These 3D organoid models provide a more physiologically relevant and accurate representation of human organs compared to traditional in vitro cell culture systems. The studies discussed in this review have demonstrated the utility of intestinal organoids for investigating the replication, pathogenesis, and immune response of various viral pathogens, including rotavirus, norovirus, enterovirus, and coronaviruses.
The use of intestinal organoids has enabled researchers to study the dynamics of viral replication, evaluate the efficacy of antiviral drugs, and identify host factors that are essential for viral infection and replication. The organoid models have been particularly valuable in understanding the complex host-virus interactions and the mechanisms underlying viral pathogenesis. By using patient-derived strains and primary human intestinal organoids, researchers have been able to personalize therapeutic interventions and explore strain-specific responses to antiviral treatments.
Overall, the advances in intestinal organoid culture systems have overcome the limitations of traditional cell culture models and animal models, providing a valuable tool for studying viral pathogenesis in a more physiologically relevant and clinically available.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download