1. Xi HQ, Wu XS, Wei B, Chen L. Aberrant expression of EphA3 in gastric carcinoma: Correlation with tumor angiogenesis and survival. J Gastroenterol. 2012; 47(7):785–94.

2. Yamamoto VN, Thylur DS, Bauschard M, Schmale I, Sinha UK. Overcoming radioresistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2016; 63:44–51.

3. Kaidar-Person O, Gil Z, Billan S. Precision medicine in head and neck cancer. Drug Resist Updat. 2018; 40:13–6.

4. Goldstein M, Kastan MB. The DNA damage response: Implications for tumor responses to radiation and chemotherapy. Annu Rev Med. 2015; 66:129–43.

5. Larionova I, Rakina M, Ivanyuk E, Trushchuk Y, Chernyshova A, Denisov E. Radiotherapy resistance: Identifying universal biomarkers for various human cancers. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022; 148(5):1015–31.

6. Qin CJ, Song XM, Chen ZH, Ren XQ, Xu KW, Jing H, et al. XRCC2 as a predictive biomarker for radioresistance in locally advanced rectal cancer patients undergoing preoperative radiotherapy. Oncotarget. 2015; 6(31):32193–204.

7. Bhattacharya P, Shetake NG, Pandey BN, Kumar A. Receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in cancer radiotherapy and its targeting for tumor radiosensitization. Int J Radiat Biol. 2018; 94(7):628–44.

8. Nam HY, Han MW, Chang HW, Lee YS, Lee M, Lee HJ, et al. Radioresistant cancer cells can be conditioned to enter senescence by mTOR inhibition. Cancer Res. 2013; 73(14):4267–77.

9. Hill RM, Rocha S, Parsons JL. Overcoming the impact of hypoxia in driving radiotherapy resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14(17):4130.

10. Jackson RK, Liew LP, Hay MP. Overcoming radioresistance: small molecule radiosensitisers and hypoxia-activated prodrugs. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2019; 31(5):290–302.

11. Moreno Roig E, Groot AJ, Yaromina A, Hendrickx TC, Barbeau LMO, Giuranno L, et al. HIF-1α and HIF-2α differently regulate the radiation sensitivity of NSCLC cells. Cells. 2019; 8(1):45.

12. Rankin EB, Giaccia AJ. Hypoxic control of metastasis. Science. 2016; 352(6282):175–80.

13. Vilaplana-Lopera N, Besh M, Moon EJ. Targeting hypoxia: Revival of old remedies. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(11):1604.

14. Stakheyeva M, Riabov V, Mitrofanova I, Litviakov N, Choynzonov E, Cherdyntseva N, et al. Role of the immune component of tumor microenvironment in the efficiency of cancer treatment: Perspectives for the personalized therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2017; 23(32):4807–26.

15. Biffi G, Tuveson DA. Diversity and biology of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Physiol Rev. 2021; 101(1):147–76.

16. Chen Y, McAndrews KM, Kalluri R. Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021; 18(12):792–804.

17. Larionova I, Cherdyntseva N, Liu T, Patysheva M, Rakina M, Kzhyshkowska J. Interaction of tumor-associated macrophages and cancer chemotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 2019; 8(7):1596004.

18. Boutilier AJ, Elsawa SF. Macrophage polarization states in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(13):6995.

19. Lee WH, Kim SH, An JH, Kim TK, Cha HJ, Chang HW, et al. Tristetraprolin regulates phagocytosis through interaction with CD47 in head and neck cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2022; 24(3):541.

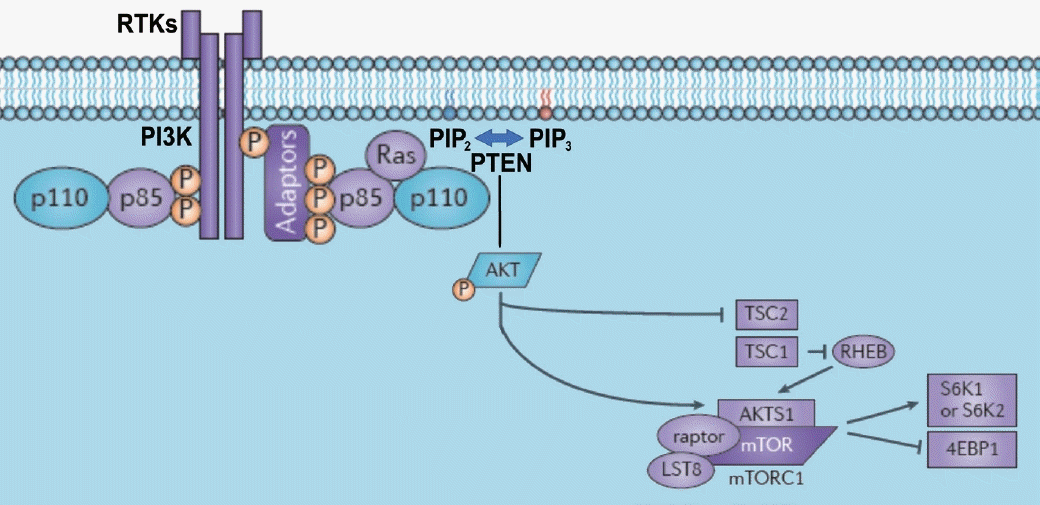
20. Mardanshahi A, Gharibkandi NA, Vaseghi S, Abedi SM, Molavipordanjani S. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway inhibitors enhance radiosensitivity in cancer cell lines. Mol Biol Rep. 2021; 48(8):1–14.

21. Simpson DR, Mell LK, Cohen EE. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 2015; 51(4):291–8.

22. Huo X, Li Z, Zhang S, Li C, Guo M, Lu J, et al. Analysis of the expression level and methylation of tumor protein p53, phosphatase and tensin homolog and mutS homolog 2 in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced thymic lymphoma in C57BL/6 mice. Oncol Lett. 2017; 14(4):4339–48.

23. Madsen RR. PI3K in stemness regulation: From development to cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020; 48(1):301–15.

24. Massacesi C, Di Tomaso E, Urban P, Germa C, Quadt C, Trandafir L, et al. PI3K inhibitors as new cancer therapeutics: Implications for clinical trial design. Onco Targets Ther. 2016; 9:203–10.

25. Marquard FE, Jücker M. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling as a molecular target in head and neck cancer. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020; 172:113729.

26. Burris HA 3rd. Overcoming acquired resistance to anticancer therapy: Focus on the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2013; 71(4):829–42.

27. Horn D, Hess J, Freier K, Hoffmann J, Freudlsperger C. Targeting EGFR-PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling enhances radiosensitivity in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015; 19(6):795–805.

28. Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X, Peng J. Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: The framework of malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep. 2020; 47(6):4587–629.

29. Han MW, Ryu IS, Lee JC, Kim SH, Chang HW, Lee YS, et al. Phosphorylation of PI3K regulatory subunit p85 contributes to resistance against PI3K inhibitors in radioresistant head and neck cancer. Oral Oncol. 2018; 78:56–63.

30. Worby CA, Dixon JE. PTEN. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014; 83:641–69.

31. Leslie NR, Downes CP. PTEN function: How normal cells control it and tumour cells lose it. Biochem J. 2004; 382(Pt 1):1–11.

32. Papa A, Pandolfi PP. The PTEN–PI3K axis in cancer. Biomolecules. 2019; 9(4):153.

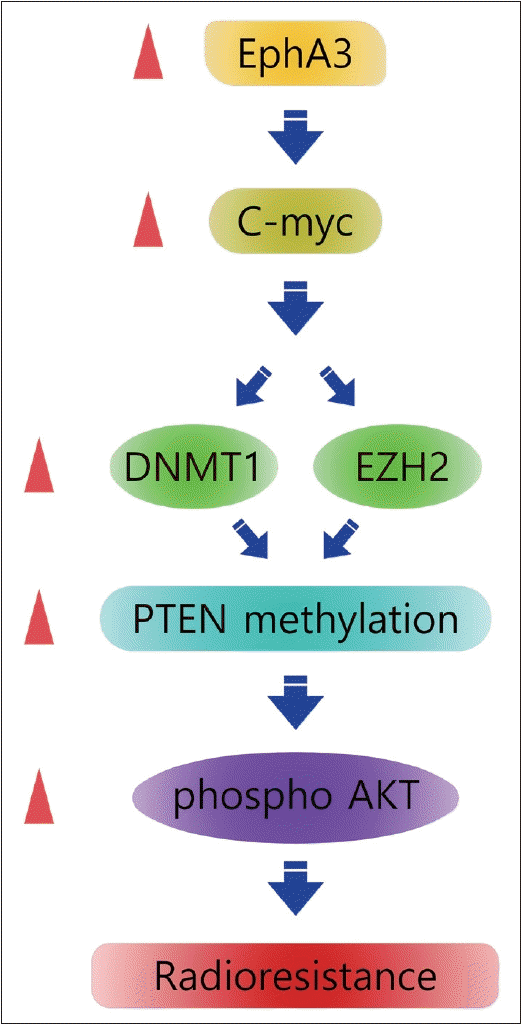
33. Kim SH, Kang BC, Seong D, Lee WH, An JH, Je HU, et al. EPHA3 contributes to epigenetic suppression of PTEN in radioresistant head and neck cancer. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(4):599.

34. Héroult M, Schaffner F, Augustin HG. Eph receptor and ephrin ligand-mediated interactions during angiogenesis and tumor progression. Exp Cell Res. 2006; 312(5):642–50.

35. Brantley-Sieders D, Schmidt S, Parker M, Chen J. Eph receptor tyrosine kinases in tumor and tumor microenvironment. Curr Pharm Des. 2004; 10(27):3431–42.

36. Keane N, Freeman C, Swords R, Giles FJ. EPHA3 as a novel therapeutic target in the hematological malignancies. Expert Rev Hematol. 2012; 5(3):325–40.

37. Charmsaz S, Al-Ejeh F, Yeadon TM, Miller KJ, Smith FM, Stringer BW, et al. EphA3 as a target for antibody immunotherapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 2017; 31(8):1779–87.

38. Janes PW, Slape CI, Farnsworth RH, Atapattu L, Scott AM, Vail ME. EphA3 biology and cancer. Growth Factors. 2014; 32(6):176–89.

39. Kim SH, Lee WH, Kim SW, Je HU, Lee JC, Chang HW, et al. EphA3 maintains radioresistance in head and neck cancers through epithelial mesenchymal transition. Cell Signal. 2018; 47:122–30.

40. Day BW, Stringer BW, Boyd AW. Eph receptors as therapeutic targets in glioblastoma. Br J Cancer. 2014; 111(7):1255–61.

41. Day BW, Stringer BW, Al-Ejeh F, Ting MJ, Wilson J, Ensbey KS, et al. EphA3 maintains tumorigenicity and is a therapeutic target in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Cell. 2013; 23(2):238–48.

42. Vail ME, Murone C, Tan A, Hii L, Abebe D, Janes PW, et al. Targeting EphA3 inhibits cancer growth by disrupting the tumor stromal microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(16):4470–81.

43. Chang HW, Kim SY, Yi SL, Son SH, Song DY, Moon SY, et al. Expression of Ku80 correlates with sensitivities to radiation in cancer cell lines of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 2006; 42(10):979–86.

44. Lodola A, Giorgio C, Incerti M, Zanotti I, Tognolini M. Targeting Eph/ephrin system in cancer therapy. Eur J Med Chem. 2017; 142:152–62.

45. Xi HQ, Wu XS, Wei B, Chen L. Eph receptors and ephrins as targets for cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 2012; 16(12):2894–909.

46. La Rocca F, Airoldi I, Di Carlo E, Marotta P, Falco G, Simeon V, et al. EphA3 targeting reduces in vitro adhesion and invasion and in vivo growth and angiogenesis of multiple myeloma cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2017; 40(5):483–96.

47. Swords RT, Greenberg PL, Wei AH, Durrant S, Advani AS, Hertzberg MS, et al. KB004, a first in class monoclonal antibody targeting the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA3, in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies: Results from a phase 1 study. Leuk Res. 2016; 50:123–31.

48. Perri F, Pacelli R, Della Vittoria Scarpati G, Cella L, Giuliano M, Caponigro F, et al. Radioresistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Biological bases and therapeutic implications. Head Neck. 2015; 37(5):763–70.

49. de Jong MC, Pramana J, van der Wal JE, Lacko M, Peutz-Kootstra CJ, de Jong JM, et al. CD44 expression predicts local recurrence after radiotherapy in larynx cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16(21):5329–38.






 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download