1. Luntz M, Barzilai R. Middle ear cholesteatoma. Harefuah. 2021; May. 160(5):316–22.
2. Rutkowska J, Ozgirgin N, Olszewska E. Cholesteatoma definition and classification: a literature review. J Int Adv Otol. 2017; Aug. 13(2):266–71.

3. Castle JT. Cholesteatoma pearls: practical points and update. Head Neck Pathol. 2018; Sep. 12(3):419–29.

4. Maniu A, Harabagiu O, Perde Schrepler M, Catana A, Fanuta B, Mogoanta CA. Molecular biology of cholesteatoma. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014; 55(1):7–13.
5. Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet. 2006; Apr. 15. (Spec 1):R17–29.

6. Siomi MC, Sato K, Pezic D, Aravin AA. PIWI-interacting small RNAs: the vanguard of genome defence. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011; Apr. 12(4):246–58.

7. Park JL, Lee YS, Kunkeaw N, Kim SY, Kim IH, Lee YS. Epigenetic regulation of noncoding RNA transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase III. Epigenomics. 2017; Feb. 9(2):171–87.

8. Panni S, Lovering RC, Porras P, Orchard S. Non-coding RNA regulatory networks. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020; Jun. 1863(6):194417.

9. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; Jan. 116(2):281–97.
10. Jing Q, Huang S, Guth S, Zarubin T, Motoyama A, Chen J, et al. Involvement of microRNA in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA instability. Cell. 2005; Mar. 120(5):623–34.
11. Budakoti M, Panwar AS, Molpa D, Singh RK, Busselberg D, Mishra AP, et al. Micro-RNA: the darkhorse of cancer. Cell Signal. 2021; Jul. 83:109995.

12. Yeo JH, Chong MM. Many routes to a micro RNA. IUBMB Life. 2011; Nov. 63(11):972–8.

13. Wang KC, Chang HY. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 2011; Sep. 43(6):904–14.

14. Bai Y, Dai X, Harrison AP, Chen M. RNA regulatory networks in animals and plants: a long noncoding RNA perspective. Brief Funct Genomics. 2015; Mar. 14(2):91–101.

15. Lasda E, Parker R. Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. RNA. 2014; Dec. 20(12):1829–42.

16. Chen LL, Yang L. Regulation of circRNA biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2015; Apr. 12(4):381–8.

17. Liang ZZ, Guo C, Zou MM, Meng P, Zhang TT. circRNA-miRNA-mRNA regulatory network in human lung cancer: an update. Cancer Cell Int. 2020; May. 20:173.

18. He YD, Tao W, He T, Wang BY, Tang XM, Zhang LM, et al. A urine extracellular vesicle circRNA classifier for detection of high-grade prostate cancer in patients with prostate-specific antigen 2–10 ng/mL at initial biopsy. Mol Cancer. 2021; Jul. 20(1):96.
19. Zang J, Lu D, Xu A. The interaction of circRNAs and RNA binding proteins: an important part of circRNA maintenance and function. J Neurosci Res. 2020; Jan. 98(1):87–97.

20. Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP. A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell. 2011; Aug. 146(3):353–8.

21. Zhang J, Liu L, Xu T, Zhang W, Li J, Rao N, et al. Time to infer miRNA sponge modules. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2022; Mar. 13(2):e1686.

22. Lu TX, Rothenberg ME. MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018; Apr. 141(4):1202–7.

23. Croset M, Pantano F, Kan CW, Bonnelye E, Descotes F, Alix-Panabieres C, et al. miRNA-30 family members inhibit breast cancer invasion, osteomimicry, and bone destruction by directly targeting multiple bone metastasis-associated genes. Cancer Res. 2018; Sep. 78(18):5259–73.

24. Liao Z, Chen Y, Duan C, Zhu K, Huang R, Zhao H, et al. Cardiac telocytes inhibit cardiac microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis through exosomal miRNA-21-5p-targeted cdip1 silencing to improve angiogenesis following myocardial infarction. Theranostics. 2021; Jan. 11(1):268–91.

25. Kanlikilicer P, Bayraktar R, Denizli M, Rashed MH, Ivan C, Aslan B, et al. Exosomal miRNA confers chemo resistance via targeting Cav1/p-gp/M2-type macrophage axis in ovarian cancer. EBioMedicine. 2018; Dec. 38:100–12.

26. Xu J, Li Y, Lu J, Pan T, Ding N, Wang Z, et al. The mRNA related ceRNA-ceRNA landscape and significance across 20 major cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; Sep. 43(17):8169–82.

27. Tay Y, Kats L, Salmena L, Weiss D, Tan SM, Ala U, et al. Coding-independent regulation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by competing endogenous mRNAs. Cell. 2011; Oct. 147(2):344–57.

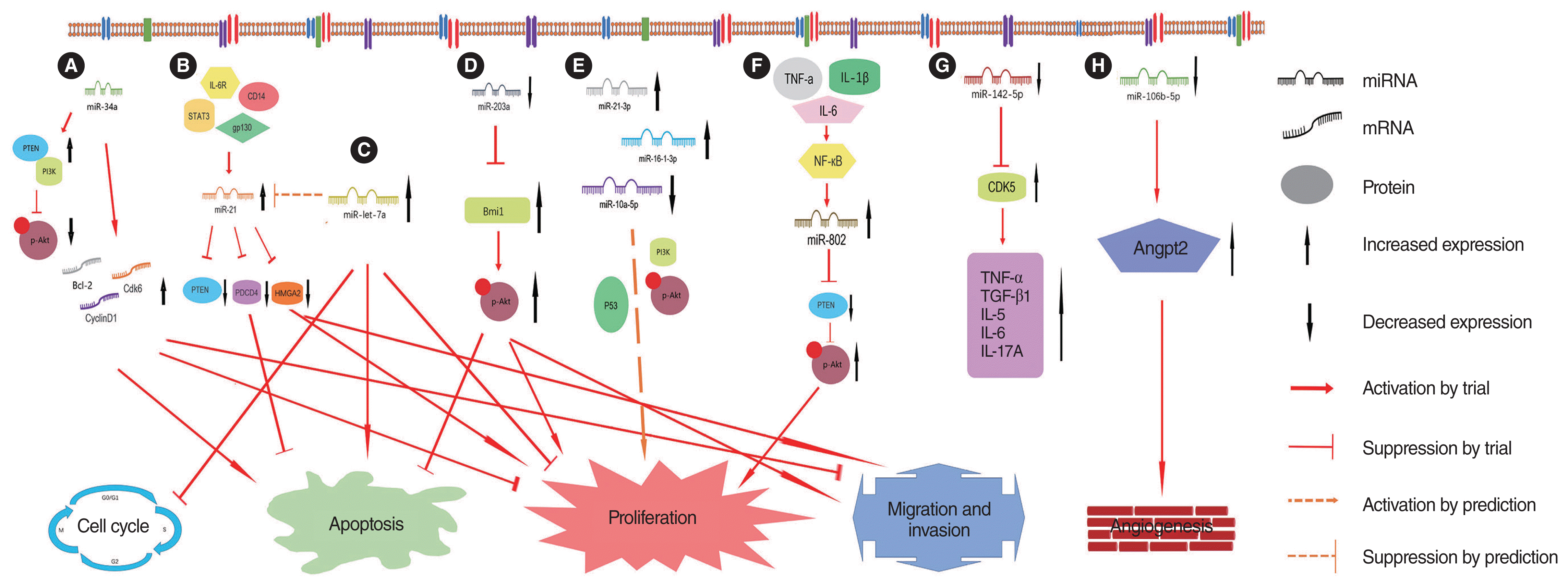
28. Zheng H, Wang W, Li S, Han L. The effect of Zbxz23ir-21 NANO (nanomaterials) delivery vector on apoptosis and PTEN(phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten)/PI3K(Intracellular phosphatidylinositol kinase)/AKT(related to the A and C kinase) in children with cholesteatoma in middle ear. Bioengineered. 2021; Dec. 12(1):8809–21.

29. Friedland DR, Eernisse R, Erbe C, Gupta N, Cioffi JA. Cholesteatoma growth and proliferation: posttranscriptional regulation by microRNA-21. Otol Neurotol. 2009; Oct. 30(7):998–1005.
30. Chen X, Li X, Qin Z. MicroRNA-21 promotes the proliferation and invasion of cholesteatoma keratinocytes. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016; Dec. 136(12):1261–6.

31. Li Y, Liang J, Hu J, Ren X, Sheng Y. Down-regulation of exosomal miR-106b-5p derived from cholesteatoma perimatrix fibroblasts promotes angiogenesis in endothelial cells by overexpression of Angiopoietin 2. Cell Biol Int. 2018; Sep. 42(10):1300–10.

32. Zang J, Hui L, Yang N, Yang B, Jiang X. Downregulation of MiR-203a disinhibits Bmi1 and promotes growth and proliferation of keratinocytes in cholesteatoma. Int J Med Sci. 2018; Mar. 15(5):447–55.

33. Xie S, Liu X, Pan Z, Chen X, Peng A, Yin T, et al. Microarray analysis of differentially-expressed microRNAs in acquired middle ear cholesteatoma. Int J Med Sci. 2018; Oct. 15(13):1547–54.

34. Zhang W, Chen X, Qin Z. MicroRNA let-7a suppresses the growth and invasion of cholesteatoma keratinocytes. Mol Med Rep. 2015; Mar. 11(3):2097–103.

35. Chen X, Qin Z. Post-transcriptional regulation by microRNA-21 and let-7a microRNA in paediatric cholesteatoma. J Int Med Res. 2011; 39(6):2110–8.

36. Li N, Qin ZB. Inflammation-induced miR-802 promotes cell proliferation in cholesteatoma. Biotechnol Lett. 2014; Sep. 36(9):1753–9.

37. Sui R, Shi W, Han S, Fan X, Zhang X, Wang N, et al. MiR-142-5p directly targets cyclin-dependent kinase 5-mediated upregulation of the inflammatory process in acquired middle ear cholesteatoma. Mol Immunol. 2022; Jan. 141:236–45.

38. Li Q, Wang HQ, Chen YQ, Xiong S, Zeng L. Study of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR expression in middle ear cholesteatoma. Lin Chung Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2017; Feb. 31(4):250–3.
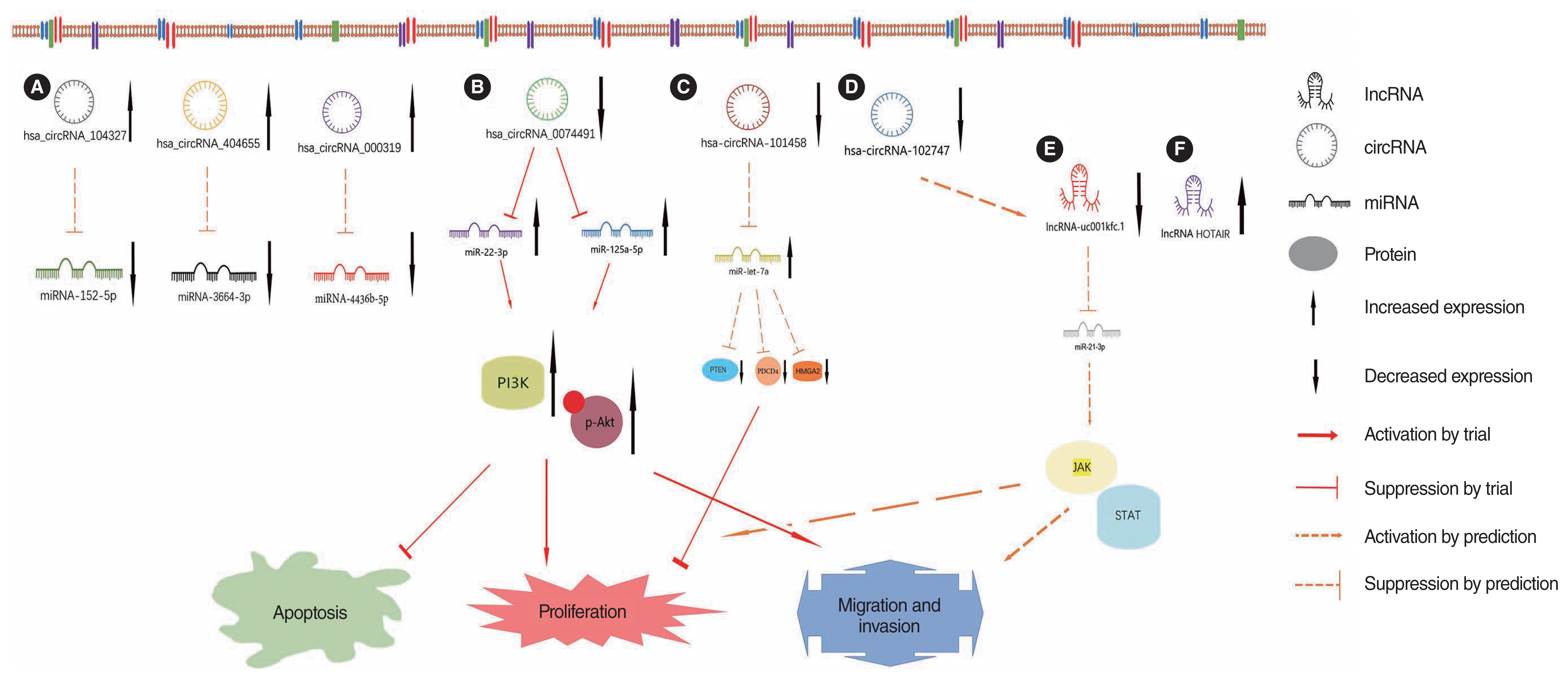
39. Gao J, Tang Q, Zhu X, Wang S, Zhang Y, Liu W, et al. Long noncoding RNAs show differential expression profiles and display ceRNA potential in cholesteatoma pathogenesis. Oncol Rep. 2018; May. 39(5):2091–100.

40. Hu Y, Qian X. Hsa_circ_0074491 regulates the malignance of cholesteatoma keratinocytes by modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway by binding to miR-22-3p and miR-125a-5p: an observational study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021; Sep. 100(37):e27122.
41. Xie S, Jin L, Yin T, Ren J, Liu W. Microarray analysis and functional prediction of differentially expressed circular RNAs in acquired middle ear cholesteatoma. Biomed Eng Online. 2021; Dec. 20(1):129.

42. Gao J, Tang Q, Xue R, Zhu X, Wang S, Zhang Y, et al. Comprehensive circular RNA expression profiling with associated ceRNA network reveals their therapeutic potential in cholesteatoma. Oncol Rep. 2020; Apr. 43(4):1234–44.

43. Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993; Dec. 75(5):843–54.

44. Denli AM, Tops BB, Plasterk RH, Ketting RF, Hannon GJ. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature. 2004; Nov. 432(7014):231–5.

45. Glaich O, Parikh S, Bell RE, Mekahel K, Donyo M, Leader Y, et al. DNA methylation directs microRNA biogenesis in mammalian cells. Nat Commun. 2019; Dec. 10(1):5657.

46. Leclercq M, Diallo AB, Blanchette M. Computational prediction of the localization of microRNAs within their pre-miRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013; Aug. 41(15):7200–11.

47. Treiber T, Treiber N, Meister G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019; Jan. 20(1):5–20.

48. Mathonnet G, Fabian MR, Svitkin YV, Parsyan A, Huck L, Murata T, et al. MicroRNA inhibition of translation initiation in vitro by targeting the cap-binding complex eIF4F. Science. 2007; Sep. 317(5845):1764–7.

49. Rebane A, Akdis CA. MicroRNAs: essential players in the regulation of inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; Jul. 132(1):15–26.

50. Amador-Canizares Y, Panigrahi M, Huys A, Kunden RD, Adams HM, Schinold MJ, et al. miR-122, small RNA annealing and sequence mutations alter the predicted structure of the Hepatitis C virus 5′ UTR RNA to stabilize and promote viral RNA accumulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; Oct. 46(18):9776–92.

51. Lee I, Ajay SS, Yook JI, Kim HS, Hong SH, Kim NH, et al. New class of microRNA targets containing simultaneous 5′-UTR and 3′-UTR interaction sites. Genome Res. 2009; Jul. 19(7):1175–83.

52. Orom UA, Nielsen FC, Lund AH. MicroRNA-10a binds the 5′UTR of ribosomal protein mRNAs and enhances their translation. Mol Cell. 2008; May. 30(4):460–71.

53. Quinn JJ, Chang HY. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Genet. 2016; Jan. 17(1):47–62.

54. Kaessmann H. Origins, evolution, and phenotypic impact of new genes. Genome Res. 2010; Oct. 20(10):1313–26.

55. Fedoseyeva V, Zharinova I, Alexandrov A. Secondary structure-stretched forms of long intron RNA products from the view point of initiation of chromosome homologs somatic pairing. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2015; 33(4):869–76.

56. Zucchelli S, Cotella D, Takahashi H, Carrieri C, Cimatti L, Fasolo F, et al. SINEUPs: a new class of natural and synthetic antisense long non-coding RNAs that activate translation. RNA Biol. 2015; Aug. 12(8):771–9.

57. Kopp F, Mendell JT. Functional classification and experimental dissection of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 2018; Jan. 172(3):393–407.

58. Jin JJ, Lv W, Xia P, Xu ZY, Zheng AD, Wang XJ, et al. Long noncoding RNA SYISL regulates myogenesis by interacting with polycomb repressive complex 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018; Oct. 115(42):E9802–11.
59. Mathy NW, Burleigh O, Kochvar A, Whiteford ER, Behrens M, Marta P, et al. A novel long intergenic non-coding RNA, Nostrill, regulates iNOS gene transcription and neurotoxicity in microglia. J Neuroinflammation. 2021; Jan. 18(1):16.

60. Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y, Song Y. Long non-coding RNAs: a new frontier in the study of human diseases. Cancer Lett. 2013; Oct. 339(2):159–66.

61. Dykes IM, Emanueli C. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017; Jun. 15(3):177–86.

62. Sun Q, Hao Q, Prasanth KV. Nuclear long noncoding RNAs: key regulators of gene expression. Trends Genet. 2018; Feb. 34(2):142–57.

63. Hainer SJ, Pruneski JA, Mitchell RD, Monteverde RM, Martens JA. Intergenic transcription causes repression by directing nucleosome assembly. Genes Dev. 2011; Jan. 25(1):29–40.

64. McHugh CA, Chen CK, Chow A, Surka CF, Tran C, McDonel P, et al. The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3. Nature. 2015; May. 521(7551):232–6.

65. Engreitz JM, Haines JE, Perez EM, Munson G, Chen J, Kane M, et al. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nature. 2016; Nov. 539(7629):452–5.

66. Sun TT, He J, Liang Q, Ren LL, Yan TT, Yu TC, et al. LncRNA GClnc1 promotes gastric carcinogenesis and may act as a modular scaffold of WDR5 and KAT2A complexes to specify the histone modification pattern. Cancer Discov. 2016; Jul. 6(7):784–801.

67. Huang W, Li H, Yu Q, Xiao W, Wang DO. LncRNA-mediated DNA methylation: an emerging mechanism in cancer and beyond. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022; Mar. 41(1):100.

68. Wen Z, Lian L, Ding H, Hu Y, Xiao Z, Xiong K, et al. LncRNA ANCR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through upregulating HNRNPA1 expression. RNA Biol. 2020; Mar. 17(3):381–94.

69. Wu SK, Roberts JT, Balas MM, Johnson AM. RNA matchmaking in chromatin regulation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2020; Dec. 48(6):2467–81.

70. Yu B, Qi Y, Li R, Shi Q, Satpathy AT, Chang HY. B cell-specific XIST complex enforces X-inactivation and restrains atypical B cells. Cell. 2021; Apr. 184(7):1790–803.

71. Wan G, Hu X, Liu Y, Han C, Sood AK, Calin GA, et al. A novel non-coding RNA lncRNA-JADE connects DNA damage signalling to histone H4 acetylation. EMBO J. 2013; Oct. 32(21):2833–47.

72. Guil S, Esteller M. RNA-RNA interactions in gene regulation: the coding and noncoding players. Trends Biochem Sci. 2015; May. 40(5):248–56.

73. Erdmann VA, Barciszewska MZ, Hochberg A, de Groot N, Barciszewski J. Regulatory RNAs. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001; Jun. 58(7):960–77.

74. Cui M, Zheng M, Sun B, Wang Y, Ye L, Zhang X. A long noncoding RNA perturbs the circadian rhythm of hepatoma cells to facilitate hepatocarcinogenesis. Neoplasia. 2015; Jan. 17(1):79–88.

75. Sanger HL, Klotz G, Riesner D, Gross HJ, Kleinschmidt AK. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976; Nov. 73(11):3852–673.

76. Hsu MT, Coca-Prados M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1979; Jul. 280(5720):339–40.

77. Cocquerelle C, Mascrez B, Hetuin D, Bailleul B. Mis-splicing yields circular RNA molecules. FASEB J. 1993; Jan. 7(1):155–60.

78. Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F, Krueger J, Rybak A, et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature. 2013; Mar. 495(7441):333–8.

79. Mehta SL, Dempsey RJ, Vemuganti R. Role of circular RNAs in brain development and CNS diseases. Prog Neurobiol. 2020; Mar. 186:101746.

80. Liu X, Hu Z, Zhou J, Tian C, Tian G, He M, et al. Interior circular RNA. RNA Biol. 2020; Jan. 17(1):87–97.

81. Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LV, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019; Nov. 20(11):675–91.

82. Li J, Xu Q, Huang ZJ, Mao N, Lin ZT, Cheng L, et al. CircRNAs: a new target for the diagnosis and treatment of digestive system neoplasms. Cell Death Dis. 2021; Feb. 12(2):205.

83. Xie S, Chang Y, Jin H, Yang F, Xu Y, Yan X, et al. Non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020; Nov. 493:55–70.

84. Zhang C, Han X, Yang L, Fu J, Sun C, Huang S, et al. Circular RNA circPPM1F modulates M1 macrophage activation and pancreatic islet inflammation in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Theranostics. 2020; Aug. 10(24):10908–24.

85. Xu H, Wang C, Song H, Xu Y, Ji G. RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers. Mol Cancer. 2019; Jan. 18(1):8.

86. Gu Y, Wang Y, He L, Zhang J, Zhu X, Liu N, et al. Circular RNA circIPO11 drives self-renewal of liver cancer initiating cells via Hedgehog signaling. Mol Cancer. 2021; Oct. 20(1):132.

87. Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013; Mar. 495(7441):384–8.

88. Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glazar P, Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, et al. Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant, conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell. 2015; Jun. 58(5):870–85.

89. Chen J, Chen T, Zhu Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, et al. circPTN sponges miR-145-5p/miR-330-5p to promote proliferation and stemness in glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019; Sep. 38(1):398.

90. Zheng X, Huang M, Xing L, Yang R, Wang X, Jiang R, et al. The circRNA circSEPT9 mediated by E2F1 and EIF4A3 facilitates the carcinogenesis and development of triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020; Apr. 19(1):73.

91. Xu JZ, Shao CC, Wang XJ, Zhao X, Chen JQ, Ouyang YX, et al. circTADA2As suppress breast cancer progression and metastasis via targeting miR-203a-3p/SOCS3 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2019; Feb. 10(3):175.

92. Mugoni V, Ciani Y, Nardella C, Demichelis F. Circulating RNAs in prostate cancer patients. Cancer Lett. 2022; Jan. 524:57–69.

93. Yao Y, Chen X, Yang H, Chen W, Qian Y, Yan Z, et al. Hsa_circ_ 0058124 promotes papillary thyroid cancer tumorigenesis and invasiveness through the NOTCH3/GATAD2A axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019; Jul. 38(1):318.
94. Bi W, Huang J, Nie C, Liu B, He G, Han J, et al. CircRNA circRNA_ 102171 promotes papillary thyroid cancer progression through modulating CTNNBIP1-dependent activation of β-catenin pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018; Nov. 37(1):275.
95. Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Veno MT, Kjems J. Circular RNAs in cancer: opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene. 2018; Feb. 37(5):555–65.

96. Zhou X, Zhan L, Huang K, Wang X. The functions and clinical significance of circRNAs in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2020; Oct. 13(1):138.

97. Suenkel C, Cavalli D, Massalini S, Calegari F, Rajewsky N. A highly conserved circular RNA is required to keep neural cells in a progenitor state in the mammalian brain. Cell Rep. 2020; Feb. 30(7):2170–9.

98. Sheng JQ, Liu L, Wang MR, Li PY. Circular RNAs in digestive system cancer: potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Am J Cancer Res. 2018; Jul. 8(7):1142–56.
99. Hu W, Bi ZY, Chen ZL, Liu C, Li LL, Zhang F, et al. Emerging landscape of circular RNAs in lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018; Jul. 427:18–27.

100. Tang X, Ren H, Guo M, Qian J, Yang Y, Gu C. Review on circular RNAs and new insights into their roles in cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021; Jan. 19:910–28.

101. Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong F, et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2018; Apr. 17(1):79.

102. Fontemaggi G, Turco C, Esposito G, Di Agostino S. New molecular mechanisms and clinical impact of circRNAs in human cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021; Jun. 13(13):3154.

103. Karreth FA, Pandolfi PP. ceRNA cross-talk in cancer: when ce-bling rivalries go awry. Cancer Discov. 2013; Oct. 3(10):1113–21.

104. Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang L, Yang H, Wang Q, Qi H, et al. MicroRNA response elements-regulated TRAIL expression shows specific survival-suppressing activity on bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2013; Feb. 32(1):10.

105. Chen L, Li W, Li Z, Song Y, Zhao J, Chen Z, et al. circNUDT21 promotes bladder cancer progression by modulating the miR-16-1-3p/MDM2/p53 axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021; Sep. 26:625–36.

106. Hollensen AK, Andersen S, Hjorth K, Bak RO, Hansen TB, Kjems J, et al. Enhanced tailored MicroRNA sponge activity of RNA Pol II-transcribed TuD hairpins relative to ectopically expressed ciRS7-derived circRNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2018; Dec. 13:365–75.

107. Pan Z, Cai J, Lin J, Zhou H, Peng J, Liang J, et al. A novel protein encoded by circFNDC3B inhibits tumor progression and EMT through regulating Snail in colon cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020; Apr. 19(1):71.

108. Yang Y, Gao X, Zhang M, Yan S, Sun C, Xiao F, et al. Novel role of FBXW7 circular RNA in repressing glioma tumorigenesis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2018; Mar. 110(3):304–15.

109. Xia X, Li X, Li F, Wu X, Zhang M, Zhou H, et al. A novel tumor suppressor protein encoded by circular AKT3 RNA inhibits glioblastoma tumorigenicity by competing with active phosphoinositide-dependent Kinase-1. Mol Cancer. 2019; Aug. 18(1):131.

110. Nabet BY, Qiu Y, Shabason JE, Wu TJ, Yoon T, Kim BC, et al. Exosome RNA unshielding couples stromal activation to pattern recognition receptor signaling in cancer. Cell. 2017; Jul. 170(2):352–66.

111. Pefanis E, Wang J, Rothschild G, Lim J, Kazadi D, Sun J, et al. RNA exosome-regulated long non-coding RNA transcription controls super-enhancer activity. Cell. 2015; May. 161(4):774–89.

112. Zheng R, Du M, Wang X, Xu W, Liang J, Wang W, et al. Exosome-transmitted long non-coding RNA PTENP1 suppresses bladder cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 2018; Oct. 17(1):143.

113. Huang X, He M, Huang S, Lin R, Zhan M, Yang D, et al. Circular RNA circERBB2 promotes gallbladder cancer progression by regulating PA2G4-dependent rDNA transcription. Mol Cancer. 2019; Nov. 18(1):166.

114. Yang F, Hu A, Li D, Wang J, Guo Y, Liu Y, et al. Circ-HuR suppresses HuR expression and gastric cancer progression by inhibiting CNBP transactivation. Mol Cancer. 2019; Nov. 18(1):158.

115. Ding L, Zhao Y, Dang S, Wang Y, Li X, Yu X, et al. Circular RNA circ-DONSON facilitates gastric cancer growth and invasion via NURF complex dependent activation of transcription factor SOX4. Mol Cancer. 2019; Mar. 18(1):45.

116. Du WW, Yang W, Li X, Awan FM, Yang Z, Fang L, et al. A circular RNA circ-DNMT1 enhances breast cancer progression by activating autophagy. Oncogene. 2018; Nov. 37(44):5829–42.

117. Chen Y, Yang F, Fang E, Xiao W, Mei H, Li H, et al. Circular RNA circAGO2 drives cancer progression through facilitating HuR-repressed functions of AGO2-miRNA complexes. Cell Death Differ. 2019; Jul. 26(7):1346–64.

118. Hua JT, Ahmed M, Guo H, Zhang Y, Chen S, Soares F, et al. Risk SNP-mediated promoter-enhancer switching drives prostate cancer through lncRNA PCAT19. Cell. 2018; Jul. 174(3):564–75.

119. Moison M, Pacheco JM, Lucero L, Fonouni-Farde C, Rodriguez-Melo J, Mansilla N, et al. The lncRNA APOLO interacts with the transcription factor WRKY42 to trigger root hair cell expansion in response to cold. Mol Plant. 2021; Jun. 14(6):937–48.

120. Hu X, Li F, He J, Yang J, Jiang Y, Jiang M, et al. LncRNA NEAT1 recruits SFPQ to regulate MITF splicing and control RPE cell proliferation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021; Nov. 62(14):18.

121. Muller V, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Steinbach B, Pantel K, Schwarzenbach H. Interplay of lncRNA H19/miR-675 and lncRNA NEAT1/miR-204 in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 2019; May. 13(5):1137–49.

122. Yan J, Yang Y, Fan X, Tang Y, Tang Z. Sp1-mediated circRNA circHipk2 regulates myogenesis by targeting ribosomal protein Rpl7. Genes (Basel). 2021; May. 12(5):696.

123. Du WW, Zhang C, Yang W, Yong T, Awan FM, Yang BB. Identifying and characterizing circRNA-protein interaction. Theranostics. 2017; Sep. 7(17):4183–91.

124. Ma XL, Zhan TC, Hu JP, Zhang CL, Zhu KP. Doxorubicin-induced novel circRNA_0004674 facilitates osteosarcoma progression and chemoresistance by upregulating MCL1 through miR-142-5p. Cell Death Discov. 2021; Oct. 7(1):309.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download