INTRODUCTION
METHODS
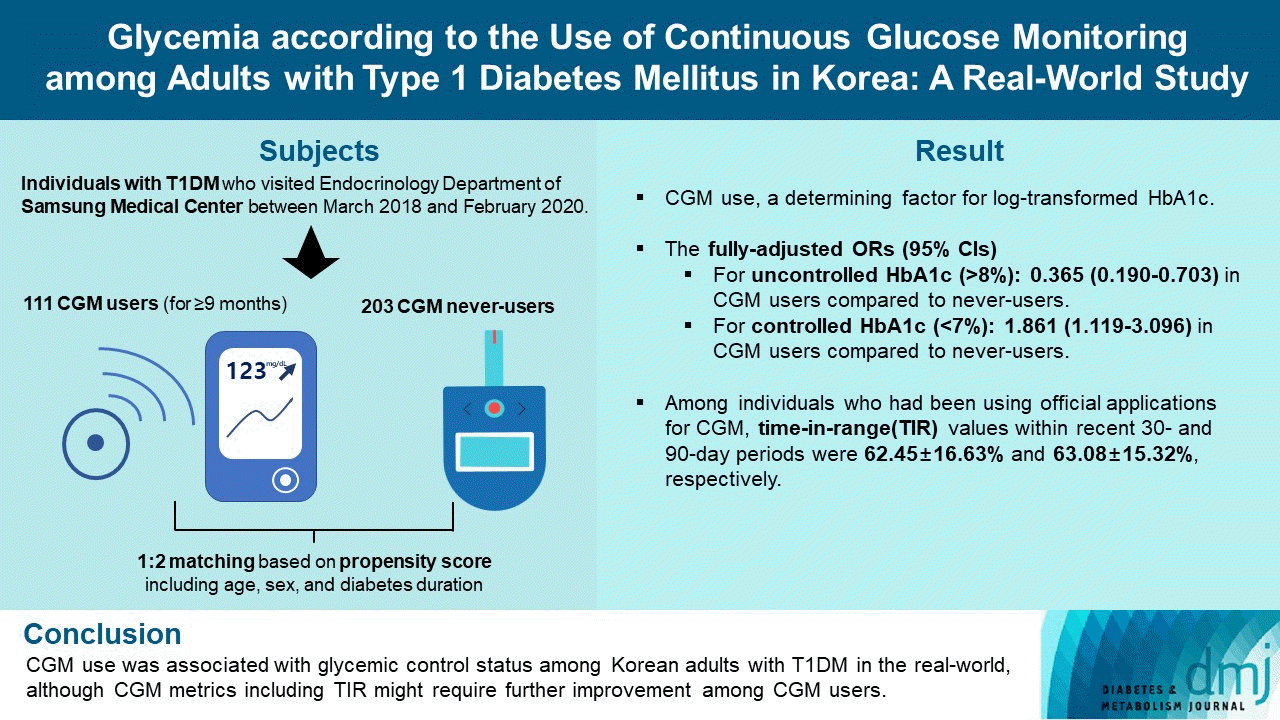
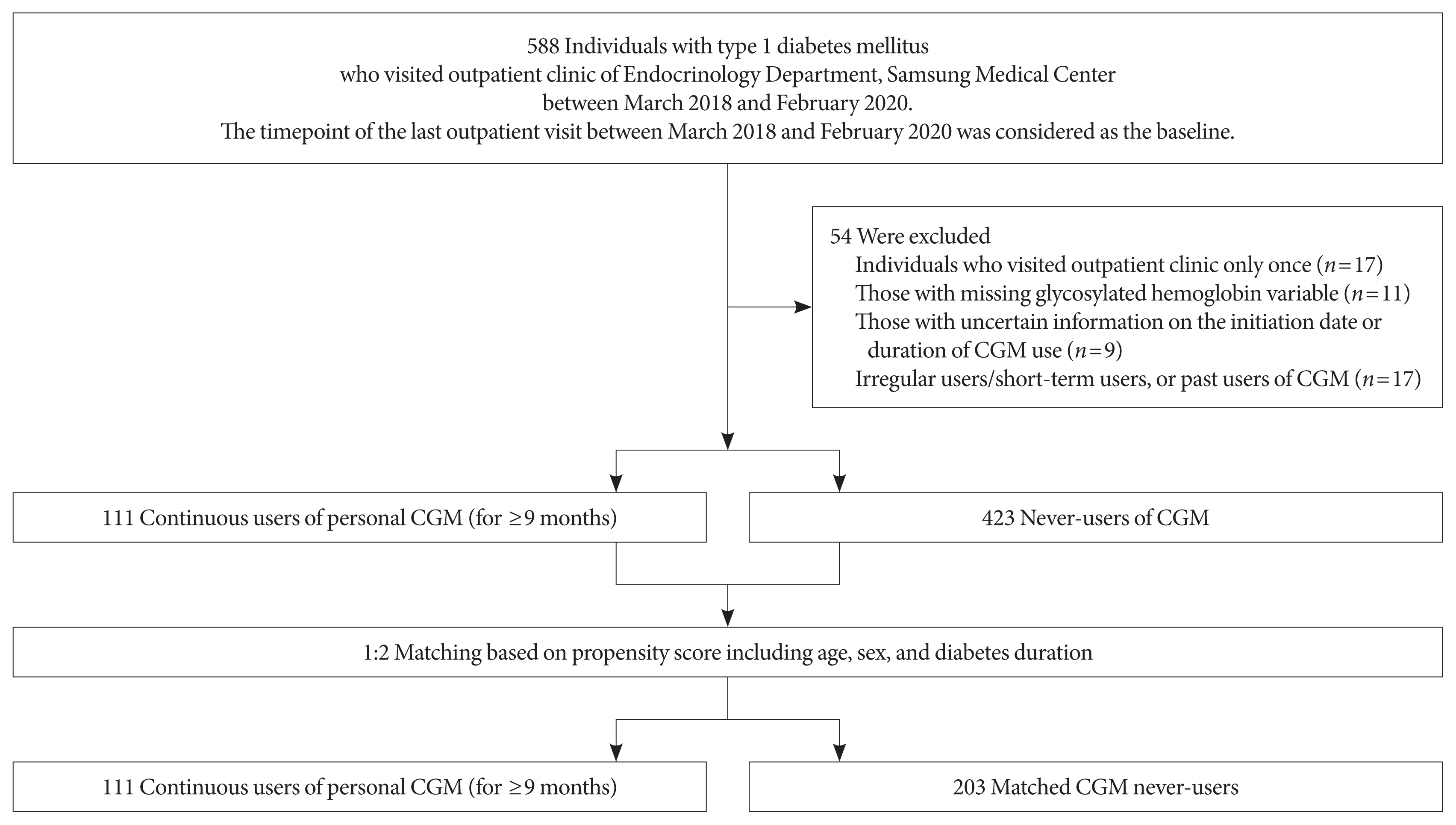
Study population and design
Data collection
Statistical analysis
Subgroup and sensitivity analyses
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics
Table 1
| Characteristic | Total (n=314) | CGM never-users (n=203) | CGM users (n=111) | P value | SMD before matching | SMD after 1:2 PS matching |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matching variables | ||||||
| Ageb, yr | 38.00 (31.00–49.00) | 38.00 (31.00–50.00) | 38.00 (30.00–48.00) | 0.7072 | 0.664 | 0.037 |
| Male sex | 137 (43.63) | 91 (44.83) | 46 (41.44) | 0.5630 | 0.194 | 0.068 |
| Diabetes durationb, yr | 10.00 (4.00–18.00) | 10.00 (4.00–18.00) | 10.00 (5.00–18.00) | 0.8739 | 0.352 | 0.073 |
|
|
||||||
| Other variables | Missing (n) in CGM never-users | Missing (n) in CGM users | ||||
| BMIb, kg/m2 | 22.47 (21.02–24.14) | 22.47 (21.02–24.02) | 22.47 (20.92–24.20) | 0.7339 | 0 | 0 |
| Systolic BPa, mm Hg | 121.88±16.28 | 121.62±16.51 | 122.34±15.94 | 0.7230 | 25 | 12 |
| Diastolic BPa, mm Hg | 69.66±11.67 | 68.98±11.71 | 70.88±11.55 | 0.1957 | 25 | 12 |
| Total daily dose of insulinb, IU | 40.00 (28.10–54.00) | 40.00 (28.00–55.00) | 40.00 (29.00–50.00) | 0.8746 | 1 | 12 |
| Use of insulin pump | 16 (5.10) | 12 (5.91) | 4 (3.60) | 0.4341 | 0 | 0 |
| Total cholesterolb, mg/dL | 161.00 (141.50–185.00) | 159.00 (142.00–185.00) | 166.00 (141.00–187.00) | 0.2511 | 5 | 1 |
| Triglyceridesb, mg/dL | 69.00 (54.00–90.00) | 71.00 (54.00–96.00) | 65.50 (53.00–85.00) | 0.2413 | 6 | 1 |
| HDL-Cb, mg/dL | 66.00 (55.00–81.00) | 65.00 (54.00–80.00) | 67.50 (56.00–81.00) | 0.3493 | 6 | 1 |
| LDL-Cb, mg/dL | 89.00 (72.00–114.00) | 89.00 (72.00–110.00) | 93.00 (76.00–120.00) | 0.1822 | 6 | 1 |
| ASTb, U/L | 20.00 (16.00–24.00) | 20.00 (17.00–25.00) | 19.00 (16.00–23.00) | 0.1078 | 5 | 1 |
| ALTb, U/L | 16.00 (11.00–22.50) | 17.00 (11.00–23.00) | 15.00 (10.00–22.00) | 0.1423 | 5 | 1 |
| BUNb, mg/dL | 12.90 (10.80–16.80) | 13.05 (10.80–17.10) | 12.80 (10.50–16.20) | 0.3756 | 5 | 1 |
| Creatinineb, mg/dL | 0.77 (0.65–0.90) | 0.77 (0.66–0.90) | 0.77 (0.64–0.90) | 0.4402 | 10 | 8 |
| eGFRb,c, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 108.70 (92.20–117.40) | 107.80 (91.80–117.20) | 109.80 (95.40–119.20) | 0.3515 | 10 | 8 |
| Glycosylated hemoglobinb, % | 7.20 (6.70–8.00) | 7.40 (6.90–8.30) | 7.00 (6.50–7.60) | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 |
| Fasting plasma glucoseb, mg/dL | 146.00 (114.00–190.00) | 144.00 (111.00–188.00) | 149.50 (122.00–193.00) | 0.2313 | 40 | 5 |
| Glycated albuminb, % | 21.55 (18.60–25.10) | 21.80 (18.90–25.80) | 20.80 (18.50–23.60) | 0.0387 | 26 | 2 |
| Cerebral infarction | 1 (0.32) | 0 | 1 (0.90) | 0.3535 | 0 | 0 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 1 (0.32) | 0 | 1 (0.90) | 0.3535 | 0 | 0 |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 69 (21.97) | 49 (24.14) | 20 (18.02) | 0.2106 | 0 | 0 |
| End-stage renal disease | 23 (7.32) | 15 (7.39) | 8 (7.21) | 0.9528 | 0 | 0 |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range), number (%), or mean±standard deviation. Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test was applied for categorical variables.
CGM, continuous glucose monitoring; SMD, standardized mean difference; PS, propensity score; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
CGM use was independently associated with log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin level
Table 2
Association of uncontrolled (>8%) or controlled (<7%) glycosylated hemoglobin with CGM use
Table 3
Logistic regression analysis with uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin (>8%) as a dependent variable was performed to identify whether CGM use could influence this outcome variable. Model 1: Adjusted for age, sex, diabetes duration and body mass index; Model 2: Adjusted for model 1 plus history of cerebral infarction and acute myocardial infarction during the previous 5 years from baseline, and presence of diabetic retinopathy and end-stage renal disease at baseline; Model 3: Adjusted for model 1 plus use of insulin pump, and estimated glomerular filtration rate.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download