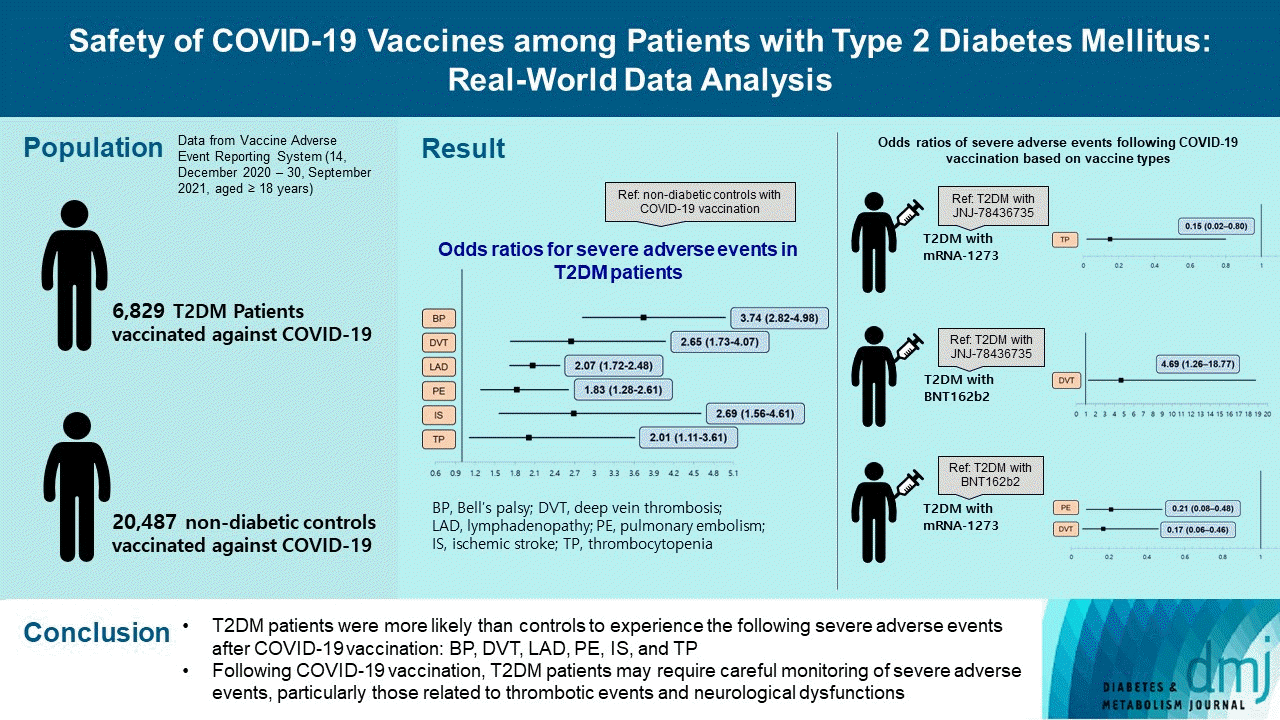
Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Fig. 1.
Supplementary Fig. 2.
Supplementary Fig. 3.
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Table 4.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: H.J.K., S.J.L., M.H., H.W.H.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: H.J.K., S.J.L., S.S., J.H.B., G.S., C.W.L., J.H.K., S.R.S., M.H., H.W.H.
Drafting the work or revising: H.J.K., S.J.L.
Final approval of the manuscript: H.J.K., S.J.L., S.S., J.H.B., G.S., C.W.L., J.H.K., S.R.S., M.H., H.W.H.
FUNDING
This research was supported by the Bio Industry Technology Development Program (No. 20015086) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry, & Energy (MOTIE, Korea), as well as supported by a grant from the Information and Communications Promotion Fund through the National IT Industry Promotion Agency (NIPA), funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), Republic of Korea.
This research was partly supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No.2020-R1F1A1068423, NRF-2019M3C7A1032262), as well as by an Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No.2019-0-00224, AIM: AI based Next-generation Security In-formation Event Management Methodology for Cognitive Intelligence and Secure-Open Framework). This research was partly supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (No. HC20C0118).
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
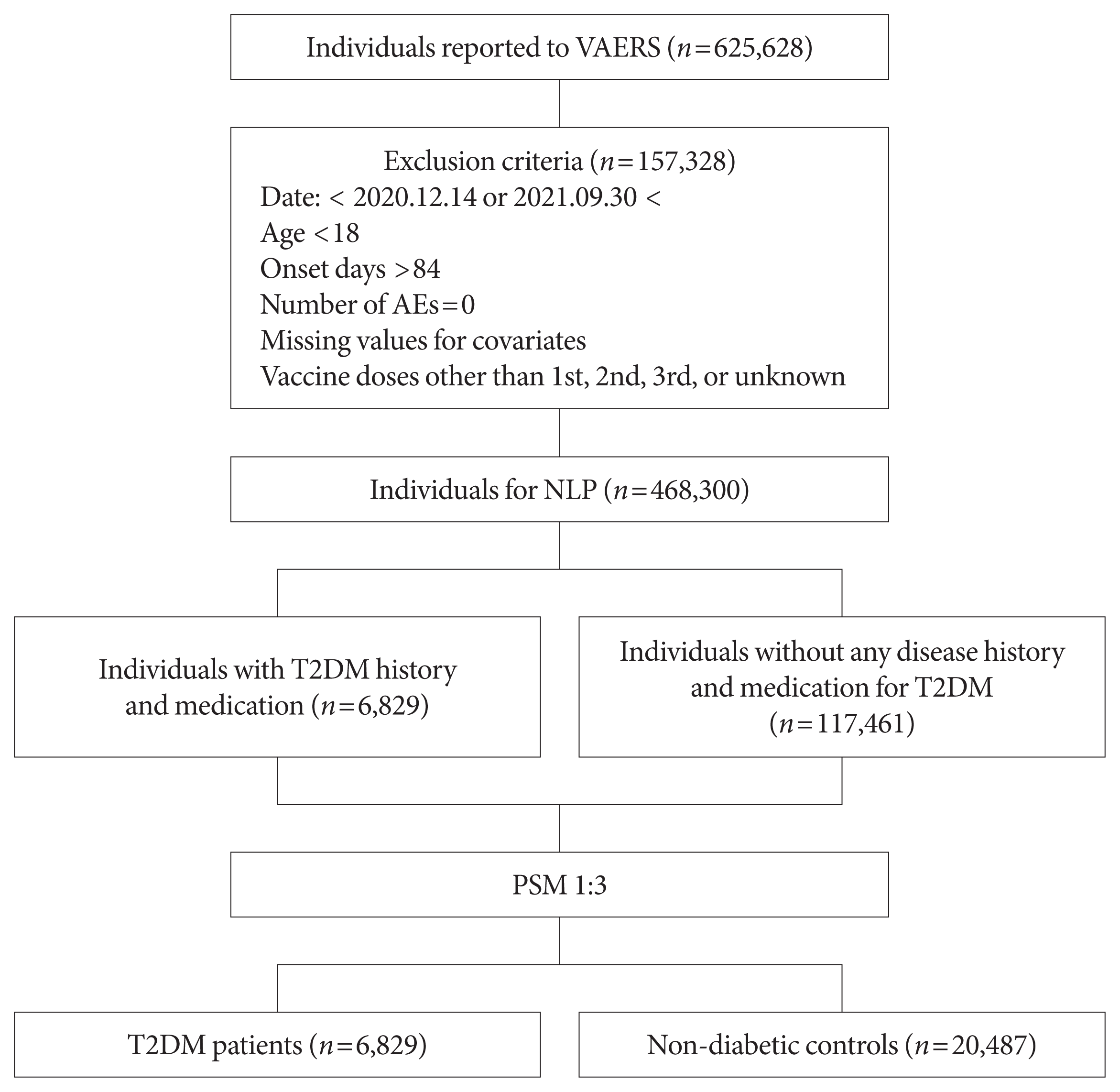
Fig. 2
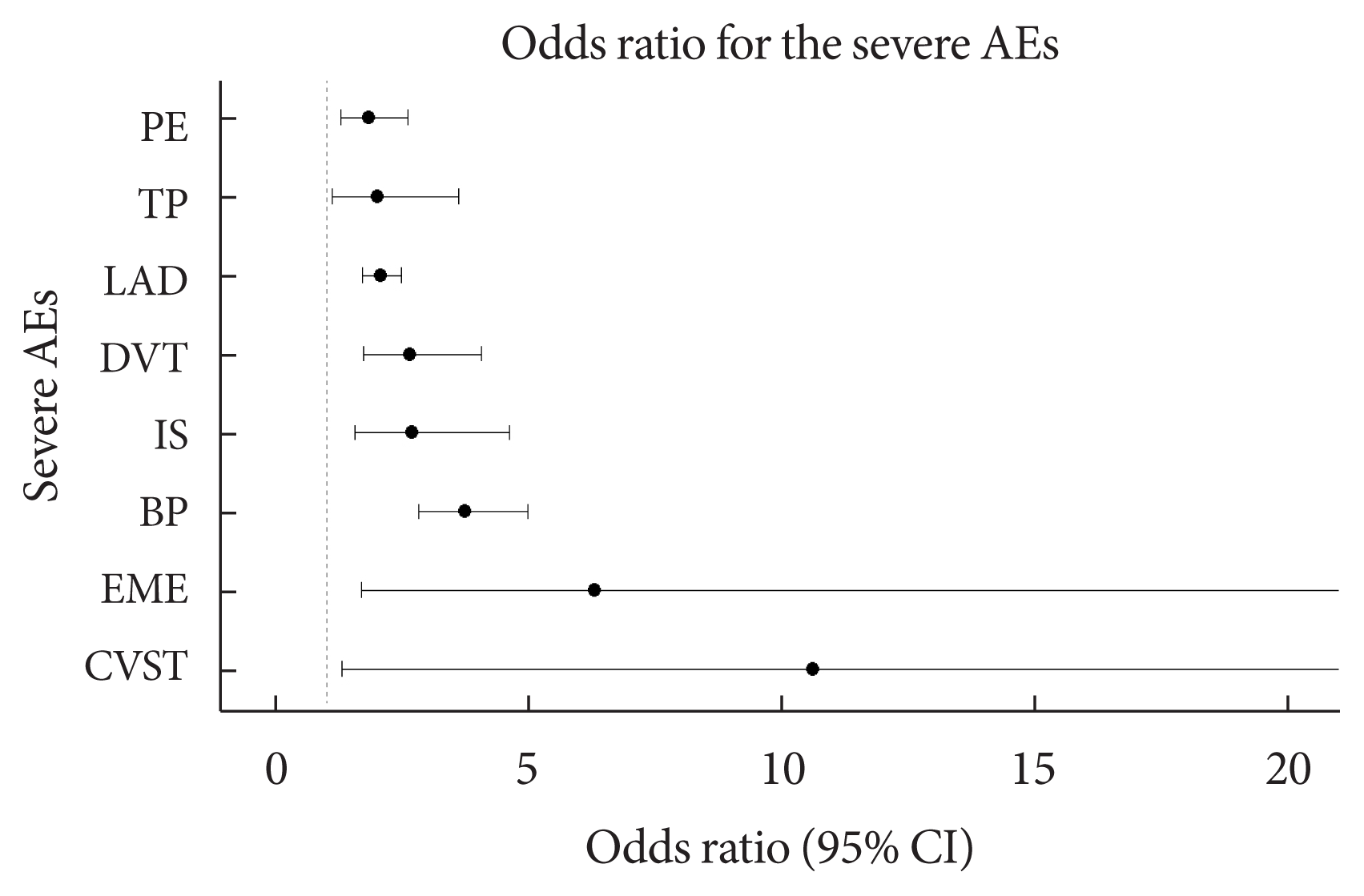
Table 1
| Variable | Before matching | After matching | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| T2DM | Non-diabetic | P value | T2DM | Non-diabetic | P value | |
| Number | 6,829 | 117,461 | 6,829 | 20,487 | ||
|
|
||||||
| Sexa | 1.000 | |||||
| Female | 4,443 (65.1) | 78,857 (67.1) | <0.001 | 4,443 (65.1) | 13,329 (65.1) | |
| Male | 2,386 (34.9) | 38,604 (32.9) | 2,386 (34.9) | 7,158 (34.9) | ||
|
|
||||||
| Age, yra | 1.000 | |||||
| 18–24 | 18 (0.3) | 10,520 (9.0) | <0.001 | 18 (0.3) | 54 (0.3) | |
| 25–39 | 377 (5.5) | 30,946 (26.3) | 377 (5.5) | 1,131 (5.5) | ||
| 40–49 | 893 (13.1) | 19,506 (16.6) | 893 (13.1) | 2,679 (13.1) | ||
| 50–64 | 2,811 (41.2) | 28,812 (24.5) | 2,811 (41.2) | 8,433 (41.2) | ||
| 65–74 | 1,852 (27.1) | 15,692 (13.4) | 1,852 (27.1) | 5,556 (27.1) | ||
| ≥75 | 878 (12.9) | 11,985 (10.2) | 878 (12.9) | 2,634 (12.9) | ||
|
|
||||||
| Vaccine typea | 1.000 | |||||
| JNJ-78436735 | 453 (6.6) | 7,326 (6.2) | <0.001 | 453 (6.6) | 1,359 (6.6) | |
| mRNA-1273 | 3,625 (53.1) | 60,298 (51.3) | 3,625 (53.1) | 10,875 (53.1) | ||
| BNT162b2 | 2,751 (40.3) | 49,837 (42.4) | 2,751 (40.3) | 8,253 (40.3) | ||
Table 2
Table 3
| Variable | BP (n=201) | DVT (n=89) | LAD (n=509) | PE (n=132) | IS (n=58) | TP (n=47) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM | 3.74 (2.82–4.98)c | 2.65 (1.73–4.07)c | 2.07 (1.72–2.48)c | 1.83 (1.28–2.61)c | 2.69 (1.56–4.61)c | 2.01 (1.11–3.61)a |
| Male sex | 2.34 (1.76–3.11)c | 1.95 (1.27–3.00)b | 0.65 (0.52–0.79)c | 2.01 (1.42–2.87)c | 1.29 (0.76–2.17) | 2.83 (1.57–5.29)c |
| Age | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 1.02 (1.01–1.04)a | 0.97 (0.96–0.97)c | 1.01 (0.99–1.02) | 1.04 (1.02–1.06)c | 1.02 (0.99–1.04) |
| Vaccine type (mRNA-1273) | 1.14 (0.67–2.10) | 0.38 (0.21–0.73)b | 2.24 (1.36–4.05)b | 0.50 (0.31–0.85)b | 0.43 (0.21–1.02)a | 0.38 (0.18–0.88)a |
| Vaccine type (BNT162b2) | 1.03 (0.60–1.91) | 0.44 (0.24–0.87)a | 3.16 (1.91–5.69)c | 0.36 (0.21–0.63)c | 0.38 (0.17–0.94)a | 0.24 (0.10–0.60)b |
The odds ratio was calculated by multiple logistic regression analysis for each severe adverse event after adjusting for sex (reference: female), age, onset days, and vaccine type (reference: JNJ-78436735) as covariates. In the case of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and encephalitis myelitis encephalomyelitis, the frequency of occurrence was very small (10 or less); therefore, the results of logistic regression were not presented in the table.
Table 4
| Interaction effects | BP | DVT | LAD | PE | IS | TP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2DM×(mRNA-1273) (reference: T2DM× JNJ-78436735) | 1.26 (0.40–3.97) | 0.80 (0.22–2.91) | 1.44 (0.46–5.42) | 0.58 (0.20–1.65) | 1.68 (0.32–10.16) | 0.15 (0.02–0.80)a |
| T2DM×(BNT162b2) (reference: T2DM× JNJ-78436735) | 2.17 (0.67–7.08) | 4.69 (1.26–18.77)a | 1.67 (0.54–6.24) | 2.78 (0.90–8.86) | 2.54 (0.45–16.84) | 0.21 (0.02–1.34) |
| T2DM×(mRNA-1273) (reference: T2DM× BNT162b2) | 0.58 (0.31–1.07) | 0.17 (0.06–0.46)b | 0.87 (0.60–1.25) | 0.21 (0.08–0.48)b | 0.66 (0.19–2.18) | 0.72 (0.17–3.08) |
The odds ratio was calculated by multiple logistic regression analysis for each severe adverse event after adjusting for sex (reference: female), age, onset days, and vaccine type (reference: JNJ-78436735) as covariates. In the case of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and encephalitis myelitis encephalomyelitis, the frequency of occurrence was very small (10 or less, respectively); therefore, the results are not presented in the table.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download