Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to verify the utility of simple, safe, and effective venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis and implement it with few adverse events during cesarean delivery.
Methods
This single-center, prospective study involved pregnant women who underwent cesarean deliveries from August 3, 2020 to March 31, 2022. Patients with VTE risk factors were initially administered unfractionated heparin (5,000 international unit [IU] subcutaneously, twice daily), 6 hours after cesarean delivery. Subsequently, they were administered enoxaparin (2,000 IU subcutaneously, twice daily). They were not administered anticoagulants if one or more of the exclusion criteria were met. The primary efficacy outcome was the incidence of symptomatic VTE. The primary safety outcome was the incidence of major bleeding.
Results
Out of the 850 women eligible for this study, 551 (64.9%) had one or more VTE risk factors and 299 (35.1%) had no risk factors. Of the 551 women with one or more VTE risk factors, 15 met one or more exclusion criteria for enoxaparin administration. A total of 314 women received only perioperative mechanical prophylaxis, including 15 who met the exclusion criteria for anticoagulants and 299 without VTE risk factors. During implementation of the protocol, no woman developed symptomatic VTE after cesarean delivery. Major bleeding occurred in only one woman who received postoperative anticoagulants.
Go to : 
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) consists of pulmonary thromboembolism (PE) and deep venous thrombosis (DVT). VTE is one of the serious complications of cesarean delivery [1]. Approximately 2 out of 10,000 women develop VTE annually [2]. In pregnant women, the incidence of VTE has been reported to be around 6 to 18 per 10,000 deliveries [3]. Consequently, pregnant women are about five times more likely to develop VTE than non-pregnant women [4]. The frequency of VTE after a cesarean delivery is 0.5% [5], and women undergoing cesarean deliveries are at high risk for VTE. Since the average age at the time of childbirth has increased, a corresponding increase in complications and high-risk cesarean deliveries are expected. Therefore, it is important to implement further measures to prevent postoperative VTE and reduce maternal mortality. Over the past decade, we have developed at our institution, a strategy for preoperative VTE screening in patients undergoing gynecologic surgery using serum D-dimer measurements and lower extremity venous ultrasonography [6]. However, serum D-dimer levels in pregnant women are significantly higher than those in non-pregnant women; furthermore, in contrast to that of non-pregnant women, the cutoff value for VTE for pregnant women is unclear. Therefore, preoperative screening for DVT is not available for women undergoing cesarean delivery.
Meta-analyses have not confirmed the efficacy of anticoagulants for the prevention of VTE after cesarean delivery compared to no treatment [7]. Therefore, the American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) guidelines of 2012 recommended postoperative prophylaxis for VTE and additional risk factors during cesarean delivery [8]. Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) while wearing elastic stockings (ES) or anticoagulant therapy has been used to prevent thrombosis. Anticoagulant therapy via drug administration is extremely effective for preventing VTE compared to physical prophylaxis; however, the risk of adverse events, such as bleeding and hematoma formation, remains. Therefore, the ACCP guidelines of 2012 suggest that mechanical prophylaxis, including IPC, can also be used for VTE prophylaxis without anticoagulant therapy [8].
Postpartum anticoagulant therapy, including unfractionated heparin (UFH), should be initiated 6 to 12 hours after cesarean delivery [9]. Although in Japan, low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) and selective factor Xa inhibitors (fondaparinux) are only approved for use 24 hours after surgery.
When administering anticoagulants, patients should be closely monitored for the occurrence of postoperative bleeding. To address this concern, an elective and individualized VTE prophylaxis strategy-was designed for cesarean deliveries that did not undergo preoperative DVT screening. This strategy determines whether mechanical prophylaxis or additional anticoagulants should be used based on the individual’s risk factors for VTE. Additionally, to avoid the complications of severe bleeding, exclusion criteria and dose reduction/discontinuation criteria for anticoagulants should be examined. Therefore, we established a perioperative VTE prevention program for cesarean deliveries. This study aimed to implement and verify the utility of a simple, safe, and effective VTE prophylaxis with few adverse events during cesarean delivery.
Go to : 
This single-center, prospective study included pregnant women who underwent cesarean delivery at the Department of Obstetrics, Nara Medical University Hospital, Kashihara, Japan.
From August 3, 2020 to March 31, 2022, 2,509 deliveries were performed at our hospital. During this period, 856 (34.1%) women underwent cesarean deliveries at our institution.
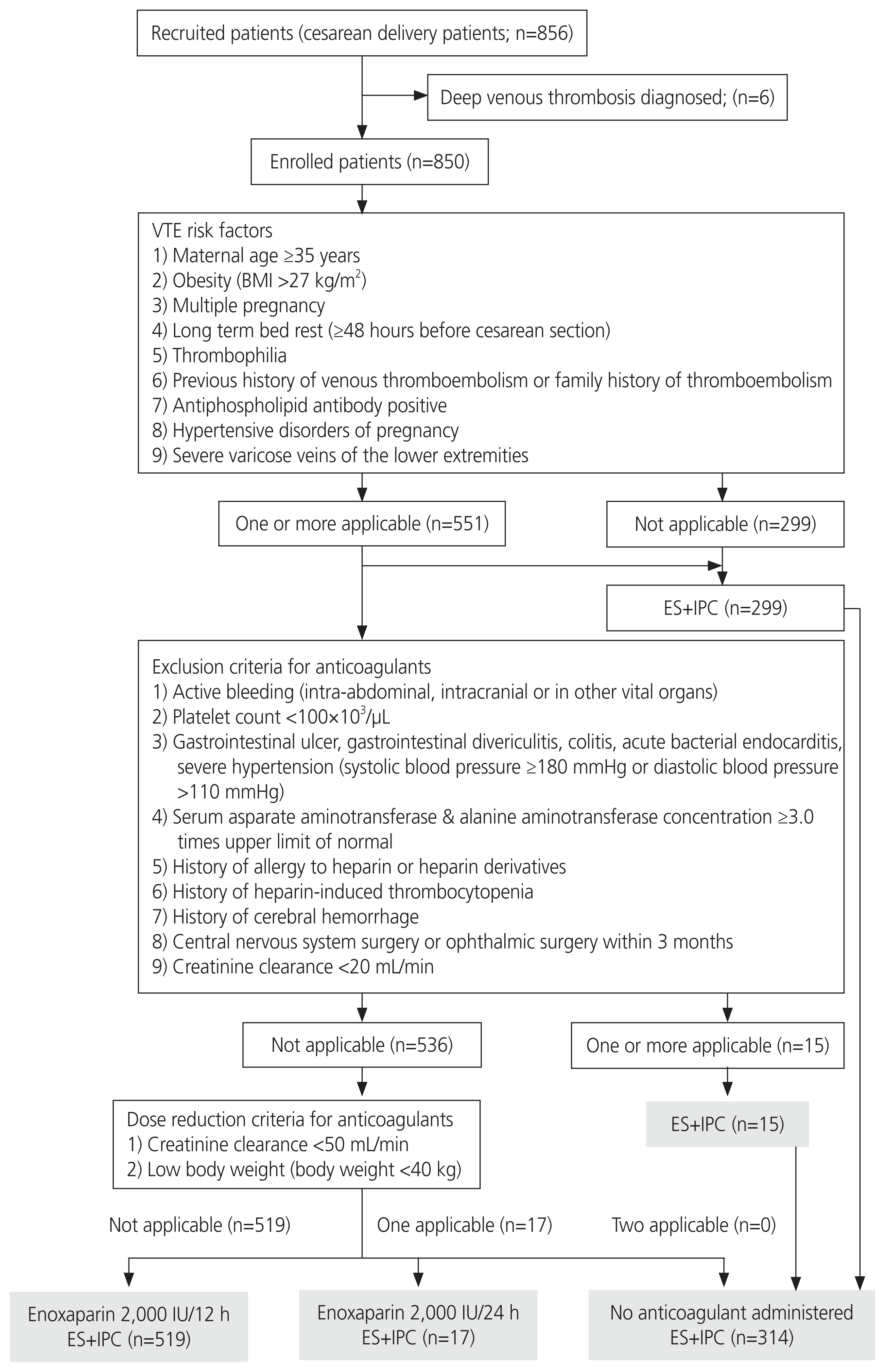
Risk factors for VTE were defined as follows: maternal age, 35 years or older; body mass index, 27 kg/m2 or more before cesarean delivery; multiple pregnancies; long-term bed rest (≥48 hours before cesarean delivery); thrombophilia; history of VTE or family history of VTE; antiphospholipid antibody positivity; hypertensive disorders of pregnancy; and severe varicose veins of the lower extremities (Fig. 1).
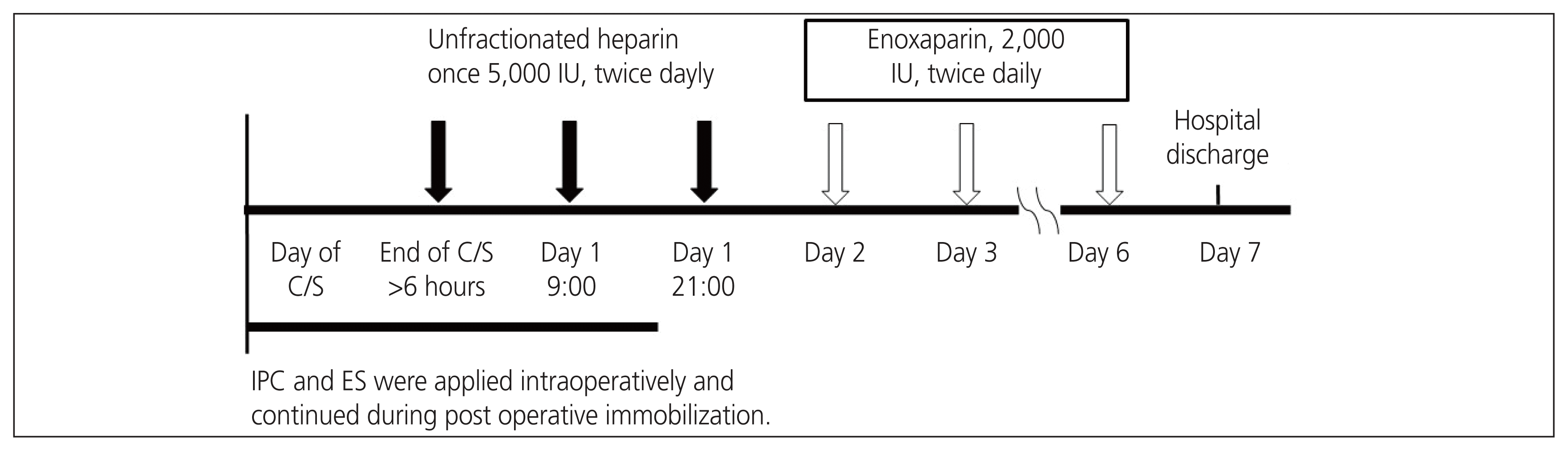
The anticoagulant dosing schedule is shown in Fig. 2. Patients initially received UFH (5,000 international unit [IU] subcutaneously, twice daily) 6 hours after cesarean delivery, and this was continued for 24 hours. Subsequently, they were administered LMWH (enoxaparin; 2,000 IU subcutaneously, twice daily) for 5 days. IPC and ES were placed on the patients’ legs at the beginning of cesarean delivery and worn continuously postoperatively until the patients were ambulatory. In the Japanese drug package insert for enoxaparin, the dose of enoxaparin should be reduced or it should not be administered to patients with a creatinine clearance of 50 mL/min or low body weight, as these patients have increased blood levels of enoxaparin. Anticoagulants were not administered if one or more of the exclusion criteria were met (Fig. 1). When one dose reduction criterion for anticoagulants was applicable, the dose of enoxaparin was reduced, and it was administered subcutaneously (2,000 IU once daily for 5 days). When two or more of the dose reduction criteria were applicable, anticoagulants were not administered (Fig. 1).
Blood count and liver function enzymes (aspartate aminotransferase [AST] and alanine aminotransferase [ALT]) were measured upon entry into the study (preoperatively) and on postoperative day 6. Additional blood tests were performed based on each patient’s general condition after cesarean delivery.
The primary efficacy outcome of this protocol was the incidence of symptomatic VTE (PE or DVT) after cesarean delivery until 4 weeks after cesarean delivery. Color Doppler ultrasound and/or dynamic computed tomography were performed for patients who were clinically suspected with DVT or PE. Enoxaparin was discontinued if symptomatic VTE or major bleeding was confirmed.
The primary safety outcome was established as the onset of major bleeding after the administration of anticoagulants. Major bleeding was defined as follows: fatal hemorrhage (intracranial, intra-abdominal, intraocular); bleeding requiring surgery; or decreased blood hemoglobin level (<5.0 g/dL) up to 4 weeks postoperatively.
Secondary safety outcomes included the incidence of minor bleeding, which was defined as bleeding other than major bleeding within 4 weeks of surgery. We also evaluated the women to determine the presence of liver dysfunction (AST or ALT three-time or higher than the upper limit of normal [ULN]) on postoperative day 6. In our institution, values that were up to or greater than three-time the upper limit of normal for AST and ALT were 93 IU/L and 72 IU/L, respectively. Furthermore, we examined the incidence of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) in women who received anticoagulant therapy. The diagnostic criteria for HIT are as follows [9]: normal platelet count before anticoagulant administration; thrombocytopenia (platelet count decreased by 30% to <100×1,000/μL or decreased by more than 50% from the baseline platelet count); acute thrombotic events; and HIT antibody seroconversion.
The participants’ data were recorded in a computer system to facilitate data collection and analysis. SPSS version 28.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, USA) was used to analyze the data. Differences between the observed results were evaluated using Fisher’s exact test and the paired t-test. Statistical significance was calculated at P<0.05.
Go to : 
Cesarean delivery was performed on 856 patients from August 3, 2020 to March 31, 2022. Six patients were excluded because they had preoperative DVT, and the remaining 850 were enrolled in this study. Table 1 describes the characteristics of the 850 pregnant women involved in this study.
Characteristic of 850 patients
Fig. 1 shows the flowchart of the study protocol. Of the 850 women enrolled in the study, 551 (64.9%) had one or more VTE risk factors and 299 (35.1%) had no risk factors. Of the 551 women with one or more VTE risk factors, 15 met one or more of the exclusion criteria for enoxaparin administration (one had a history of cerebral hemorrhage; two had prior heparin hypersensitivities; seven had preoperative platelet counts <100×1,000/μL; six had liver function enzyme levels ≥100 IU; some overlapping occurred). A total of 314 women (including the aforementioned 15 women who met the exclusion criteria for anticoagulants and 299 women without VTE risk factors) received perioperative mechanical prophylaxis (ES and IPC) without anticoagulant therapy. Of the 536 women who did not meet the exclusion criteria for anticoagulants, 519 patients who did not meet the anticoagulant dose reduction criteria received 2,000 units of enoxaparin every 12 hours in addition to mechanical prophylaxis during the perioperative period. For the 17 women who met one criterion for enoxaparin dose reduction (all weighing less than 40 kg), 2,000 units of enoxaparin were administered every 24 instead of every 12 hours in addition to mechanical prophylaxis during the perioperative period.
All women were discharged by postoperative day 7 and followed-up for 4 weeks postoperatively for the development of symptomatic VTE. None of the women experienced symptomatic VTE up until 4 weeks after cesarean delivery using this protocol.
Table 2 shows the frequency of bleeding complications. A total of 37 out of 850 women (4.4%) experienced a bleeding event postoperatively. Of these 37 women, 30 received anticoagulants for VTE and 7 received only mechanical prophylaxis after cesarean delivery. The non-anticoagulant group (7/314, 2.2%) experienced fewer bleeding complications than did the anticoagulant group (30/536, 5.6%) (P=0.022). A total of 36 out of the 37 women who had bleeding events experienced only minor bleeding. Specifically, minor subcutaneous bleeding at the wound site occurred, which did not require surgical treatment and blood transfusions. Enoxaparin was discontinued in 8 women due to a slight increase in the amount of subcutaneous hemorrhage observed during visual inspection. Major bleeding occurred in only one woman who received postoperative enoxaparin; a subfascial hematoma at the wound site was noted, along with a decrease in hemoglobin levels to 4.8 g/dL on postoperative day 3. Consequently, reoperation and blood transfusion were performed.
In the anticoagulant group, liver function enzyme (AST and ALT) levels on day 6 after cesarean delivery were significantly higher than those before cesarean deliver (P<0.001) (Table 3). Similarly, in the non-anticoagulant group, AST and ALT levels were significantly increased on postoperative day 6 compared with levels measured before cesarean delivery (P<0.001) (Table 3). Five women (5/536, 0.9%) in the anticoagulant group and 4 women (4/314, 1.3%) in the non-anticoagulant group had AST levels that were more than three times the ULN on postoperative day 6 (not statistically significant, P=0.732). Similarly, 18 women (18/536, 3.4%) in the anticoagulant group and 16 women (16/314, 5.1%) in the non-anticoagulant group had ALT levels that were more than three times the ULN on postoperative day 6 (no significant difference, P=0.276). All increased liver enzyme levels returned to normal ranges within 2 weeks after surgery.
Results of laboratory examinations before and 6 days after cesarean section
Additionally, in both the anticoagulant and non-anticoagulant groups, platelet counts on day 6 after cesarean delivery were significantly increased compared to preoperative levels (P<0.001) (Table 3). Furthermore, no incidence of HIT was observed among the 536 women treated with anticoagulation therapy.
Go to : 
VTE is likely to occur during the perioperative period, and the prevention of DVT is central to preventing the development of PE. The risk of VTE increases approximately five-fold in pregnancy compared to the risk in non-pregnant women [4]. During the puerperium period, the VTE risk is thought to exponentially increase by 30- to 60-fold [10]. Furthermore, a meta-analysis published in 2016 revealed a more than four-fold increase in VTE incidence after cesarean delivery compared with vaginal delivery [11]. Thus, when anticoagulants are administered to prevent the onset of VTE after cesarean delivery, it is important to balance the beneficial effects of VTE prophylaxis with adverse events, especially bleeding. Since anticoagulants are administered solely for the prevention of VTE, complications should be reduced as much as possible.
During our single-center prospective study of 850 cesarean deliveries, none of the women, who were administered prophylaxis based on the risk factors for VTE, developed symptomatic VTE after cesarean delivery. This may indicate that our thromboprophylaxis protocol can reduce the risk incidence of VTE after cesarean delivery. In the course of this study, 551 (64.8%) pregnant women had one or more VTE risk factors preoperatively. Fifteen out of these 551 pregnant women met the exclusion criteria for anticoagulants and received only mechanical prophylaxis for VTE during the perioperative period.
As aforementioned, anticoagulants are associated with potential complications, such as an increased risk of bleeding and hepatotoxicity. Therefore, when using anticoagulants, it is important to confirm whether the anticoagulant exclusion criteria or dose reduction criteria are met before surgery. Using these criteria, women can be appropriately selected to receive anticoagulant therapy. If the criteria for exclusion of anticoagulants are met, then only mechanical prophylaxis should be administered; however, if the criteria for dose reduction are met, then a reduced dose of anticoagulants should be administered.
Anticoagulants may cause adverse events such as bleeding, hepatotoxicity and HIT. In our study, adverse bleeding events after cesarean delivery occurred in 37 women (4.4%), yet only 1 woman (0.1%) in this group experienced major bleeding. The remaining 36 women experienced subcutaneous bleeding. All subcutaneous hemorrhages were minor and did not require treatment. Therefore, after cesarean delivery, it is important to check the surgical wound daily for subcutaneous bleeding. There have been few reports of subcutaneous hemorrhage associated with LMWH used for VTE prophylaxis after cesarean delivery. A non-randomized controlled trial in 1,600 pregnant women showed that LMWH administration after cesarean delivery increased the risk of bleeding at the wound site (absolute risk increase, 3.8%) [12].
The serum levels of liver enzymes usually increase with the use of anticoagulants [13]. Increases in liver enzyme levels occur not only with the use of UFH but also with the use of LMWH. Heparin-induced hepatotoxicity is often defined as AST or ALT levels that are up to three-time the ULN [14,15]. With this definition in mind, the incidence of heparin-induced hepatotoxicity has been observed in approximately 5% of cases involving UFH administration and in 5% to 10% of cases involving LMWH administration [16,17]. In our study, AST and ALT levels were also significantly increased after surgery. However, no significant differences in the incidence of AST and ALT levels over three-time the ULN were observed between the anticoagulant group and the non-anticoagulant group. Previous studies have reported the use of therapeutic doses of UFH or LMWH; however, our study reported on the use of prophylactic doses. This may explain the lower incidence of hepatotoxicity. Furthermore, these values were not significantly different from those of the non-anticoagulant group. Various medications (e.g., analgesics and antibiotics) were administered before and after cesarean delivery; therefore, there may have been no difference in the incidence of hepatotoxicity between the two groups. Increases in serum AST or ALT levels occur within 4 to 5 days after the initiation of LMWH therapy; however, they are rarely symptomatic [18]. These increases in AST or ALT levels normalize approximately 7 days after heparin therapy is discontinued [19]. LMWH, similar to standard unfractionated heparin, is considered toxic to hepatocytes [18]. However, the detailed mechanism underlying its hepatotoxicity remains unclear. Increased serum AST or ALT levels are rarely associated with increased bilirubin levels [17]. Moreover, hepatotoxicity caused by enoxaparin is reversible [20].
HIT is a serious iatrogenic disease that causes thrombocytopenia and thromboembolism. Although its incidence is low (0.5–5%) [21–23], it is a serious disease that is associated with heparin administration and causes a variety of thromboembolic events. Administration of UFH/LMWH produces antibodies (HIT antibodies) against complexes of heparin and platelet factor 4 [24]. HIT antibodies activate platelets and monocytes, which results in excessive thrombin production. In particular, HIT is a severe complication leading to thrombocytopenia and arteriovenous thromboembolism [25], producing a hypercoagulable condition which decimates platelet count to less than 50% within 5 to 10 days after heparin administration [25,26]. In this study, no cases of HIT were observed in patients who received anticoagulants.
Our study had some limitations. First, the use of enoxaparin was not allowed until 24 hours after surgery due to medical insurance stipulations in Japan. Therefore, we used unfractionated heparin until enoxaparin was administered. Therefore, adverse events may have been attributable not only to enoxaparin but also to unfractionated heparin. Second, the absence of abnormal blood test results on day 6 after surgery indicated that no further blood tests were required. Therefore, it is unknown whether there were any abnormalities in platelet counts or liver function enzymes after day 7. Third, although no cases of VTE occurred after cesarean delivery, the number of enrolled women was small. Therefore, in the future, a large randomized controlled trial should be conducted to validate our findings.
Although there are limitations as described above, this protocol, with clear criteria for anticoagulant administration and dose reduction/exclusion, may be effective in preventing VTE after cesarean delivery.
Go to : 
Notes
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee at Nara Medical University (approval number 2704), and the study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Patient consent
Informed consent was obtained from the participants before their participation in this study.
Funding information
This research was supported by the Japan Society for Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI (grant number 219K10488).
Go to : 
References
1. Anderson FA Jr, Spencer FA. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2003; 107:I9–16.

2. Lidegaard Ø, Edström B, Kreiner S. Oral contraceptives and venous thromboembolism: a five-year national case-control study. Contraception. 2002; 65:187–96.

4. Sia WW, Powrie RO, Cooper AB, Larson L, Phipps M, Spencer P, et al. The incidence of deep vein thrombosis in women undergoing cesarean delivery. Thromb Res. 2009; 123:550–5.

5. Giannubilo SR, Tranquilli AL. Anticoagulant therapy during pregnancy for maternal and fetal acquired and inherited thrombophilia. Curr Med Chem. 2012; 19:4562–71.

6. Haruta S, Kawaguchi R, Hirai T, Kobayashi H. Sequential screening to predict symptomatic pulmonary thromboembolism after gynecologic surgery in Nara, Japan. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2016; 132:42–5.

7. Bain E, Wilson A, Tooher R, Gates S, Davis LJ, Middleton P. Prophylaxis for venous thromboembolic disease in pregnancy and the early postnatal period. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; (2):CD001689.

8. Bates SM, Greer IA, Middeldorp S, Veenstra DL, Prabulos AM, Vandvik PO. VTE, thrombophilia, antithrombotic therapy, and pregnancy: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Ches. 2012; 141:e691S–736S.
9. Ahmed I, Majeed A, Powell R. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia: diagnosis and management update. Postgrad Med J. 2007; 83:575–82.

10. Jackson E, Curtis KM, Gaffield ME. Risk of venous thromboembolism during the postpartum period: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 117:691–703.
11. Blondon M, Casini A, Hoppe KK, Boehlen F, Righini M, Smith NL. Risks of venous thromboembolism after cesarean sections: a meta-analysis. Chest. 2016; 150:572–96.

12. Ferres MA, Olivarez SA, Trinh V, Davidson C, Sangi-Haghpeykar H, Aagaard-Tillery KM. Rate of wound complications with enoxaparin use among women at high risk for postpartum thrombosis. Obstet Gynecol. 2011; 117:119–24.

13. Bounameaux H. Unfractionated versus low-molecular-weight heparin in the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Vasc Med. 1998; 3:41–6.

14. Stricker BHC, Spoelstra P. Drug-induced hepatic injury. 2nd. New York: Elsevier;1992. p. 339–40.
15. Harrill AH, Roach J, Fier I, Eaddy JS, Kurtz CL, Antoine DJ, et al. The effects of heparins on the liver: application of mechanistic serum biomarkers in a randomized study in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2012; 92:214–20.

16. Carlson MK, Gleason PP, Sen S. Elevation of hepatic transaminases after enoxaparin use: case report and review of unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacotherapy. 2001; 21:108–13.

17. Arora N, Goldhaber SZ. Anticoagulants and transaminase elevation. Circulation. 2006; 113:e698–702.

18. Livertox: clinical and research information on drug-induced liver injury [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases;c2012. [cited 2023 Mar 2]. Abailable from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK548009/
.
19. Hahn KJ, Morales SJ, Lewis JH. Enoxaparin-induced liver injury: case report and review of the literature and FDA adverse event reporting system (FAERS). Drug Saf Case Rep. 2015; 2:17.

20. Mehershahi S, Mantri N, Kumar A, Danial S, Harish P. Enoxaparin-induced liver injury. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2020; 14:315–19.

21. Martel N, Lee J, Wells PS. Risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with unfractionated and low-molecular-weight heparin thromboprophylaxis: a meta-analysis. Blood. 2005; 106:2710–5.

22. Girolami B, Prandoni P, Stefani PM, Tanduo C, Sabbion P, Eichler P, et al. The incidence of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia in hospitalized medical patients treated with subcutaneous unfractionated heparin: a prospective cohort study. Blood. 2003; 101:2955–9.

23. Warkentin TE, Sheppard JA, Sigouin CS, Kohlmann T, Eichler P, Greinacher A. Gender imbalance and risk factor interactions in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2006; 108:2937–41.
24. Warkentin TE. The paradox of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Haemost. 2009; 7:1472–3.

Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download