Abstract
Purpose
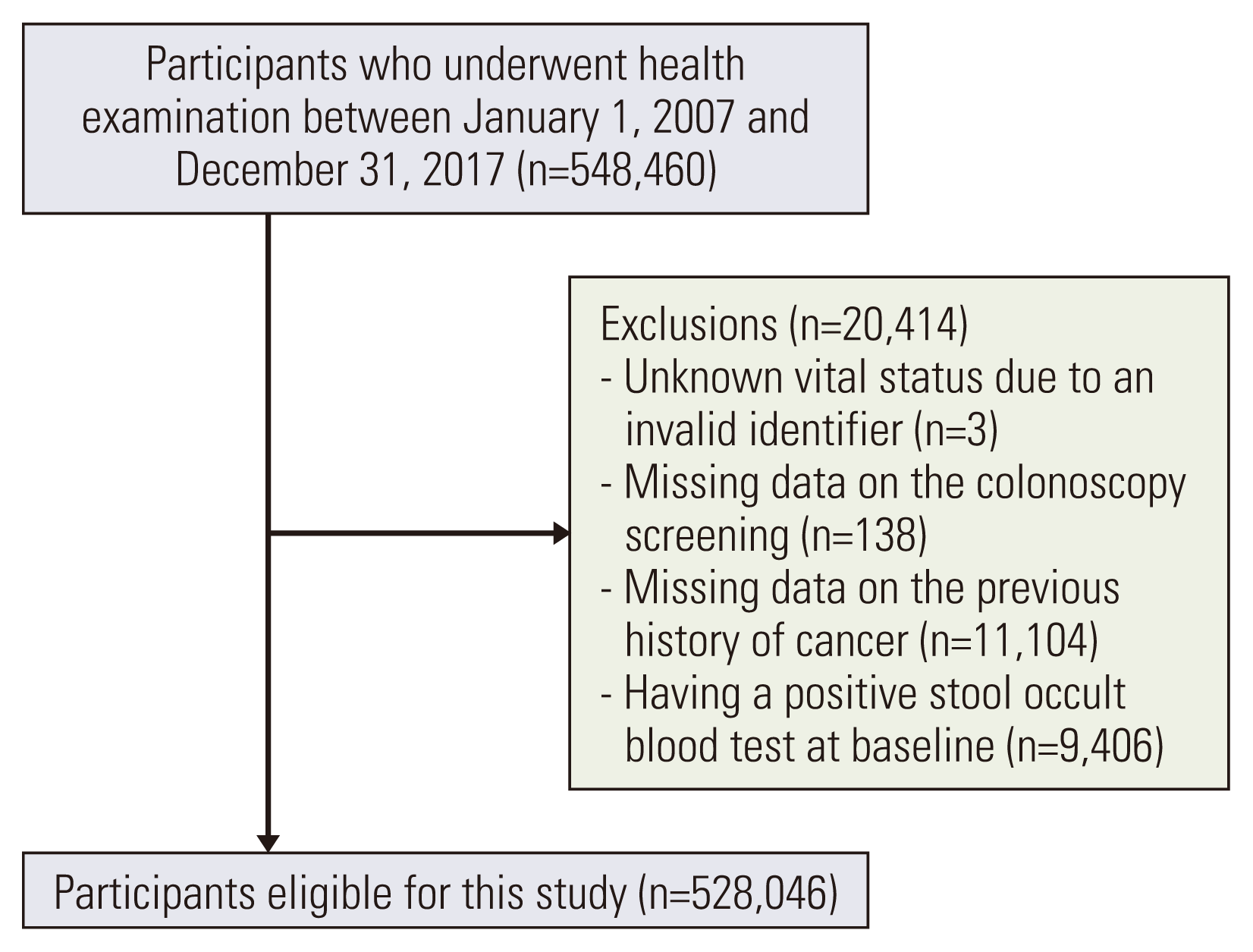
Materials and Methods
Results
Electronic Supplementary Material
Notes
Ethical Statement
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, which waived the requirement for informed consent due to the use of anonymized data routinely collected as part of a health check-up program and already linked to mortality data from the Korea National Statistical Office (IRB No. 2011-01-030-005 for the general Kangbuk Samsung Health Study protocol and 2021-10-032 for the present study).
Author Contributions
Conceived and designed the analysis: Lee JA, Chang Y, Ryu S.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Lee JA, Chang Y, Kim Y, Park DI, Park SK, Park HY, Koh J, Lee SJ, Ryu S.
Wrote the paper: Lee JA, Chang Y.
Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: Lee JA, Chang Y, Kim Y, Park DI, Park SK, Park HY, Koh J, Lee SJ, Ryu S.
Statistical analysis: Chang Y, Ryu S.
Obtained funding: Chang Y, Ryu S.
Supervision: Chang Y, Ryu S.
Acknowledgments
References
Table 1
| Characteristic | Colonoscopic screening | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Never | Ever | ||
| No. | 357,325 | 170,721 | |
| Age (yr) | 38.1 (38.0–38.1) | 43.5 (43.5–43.6) | < 0.001 |
| Male sex (%) | 48.3 (48.1–48.4) | 61.6 (61.4–61.9) | < 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.3 (23.3–23.3) | 23.4 (23.4–23.4) | < 0.001 |
| Current smoker (%) | 22.8 (22.7–23.0) | 21.0 (20.8–21.2) | < 0.001 |
| Alcohol intake (%)b) | 18.0 (17.9–18.1) | 22.8 (22.6–23.0) | < 0.001 |
| Regular exercise (%)c) | 15.3 (15.1–15.4) | 16.4 (16.2–16.6) | < 0.001 |
| Highest education level (%)d) | 78.2 (78.0–78.3) | 75.8 (75.5–76.0) | < 0.001 |
| Obesity (%)e) | 28.2 (28.1–28.4) | 29.5 (29.3–29.7) | < 0.001 |
| Diabetes (%) | 4.4 (4.4–4.5) | 4.6 (4.5–4.7) | 0.013 |
| Hypertension (%) | 14.1 (14.0–14.2) | 13.4 (13.2–13.5) | < 0.001 |
| History of CVD (%) | 5.6 (5.5–5.6) | 4.5 (4.4–4.6) | < 0.001 |
| Medication for hyperlipidemia (%) | 2.6 (2.5–2.6) | 3.5 (3.5–3.6) | < 0.001 |
| Family history of cancer | 22.8 (22.6–22.9) | 27.9 (27.6–28.1) | < 0.001 |
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 111.7 (111.6–111.7) | 110.6 (110.5–110.6) | < 0.001 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 71.6 (71.6–71.7) | 70.8 (70.7–70.8) | < 0.001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 95.9 (95.9–96.0) | 93.3 (93.2–93.3) | < 0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 192.0 (191.9–192.1) | 193.9 (193.8–194.1) | < 0.001 |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 115.3 (115.2–115.4) | 120.0 (119.8–120.1) | < 0.001 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 57.2 (57.1–57.2) | 57.9 (57.9–58.0) | < 0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 117.5 (117.2–117.7) | 106.7 (106.4–107.1) | < 0.001 |
| ALT (U/L) | 23.5 (23.4–23.5) | 26.2 (26.1–26.3) | < 0.001 |
| hsCRP (mg/L) | 1.1 (1.1–1.1) | 1.1 (1.1–1.1) | < 0.001 |
| HOMA-IRb) | 1.76 (1.76–1.77) | 1.45 (1.44–1.46) | < 0.001 |
Table 2
| Colonoscopy screening | Person-years | No. of events | Mortality rate (per 105 PY) | Age and sex-adjusted HR (95% CI) | Multivariable-adjusted HRa) (95% CI) | HR (95% CI)b) in the model using time-dependent variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | ||||||
| Never | 12,775,275.0 | 6,790 | 53.1 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Ever | 4,034,204.7 | 3,257 | 80.7 | 0.87 (0.81–0.95) | 0.89 (0.82–0.96) | 0.67 (0.62–0.73) |
| Age < 45 yr | ||||||
| Never | 11,295,458.0 | 3,681 | 32.6 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Ever | 2,873,664.7 | 1,075 | 37.4 | 1.01 (0.87–1.17) | 1.02 (0.88–1.18) | 0.86 (0.75–0.99) |
| Age ≥ 45 yr | ||||||
| Never | 1,479,817.2 | 3,109 | 210.1 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Ever | 1,160,540.0 | 2,182 | 188.0 | 0.80 (0.73–0.86) | 0.81 (0.75–0.89) | 0.71 (0.65–0.78) |
p=0.021 for the overall interaction between age and colonoscopic screening for all-cause mortality (time-dependent model). CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HR, hazard ratio; PY, person-years.
a) Cox proportional hazard models with inverse probability weights with age as a time scale were used to estimate HRs and 95% CIs. The multivariable-adjusted model was adjusted for age (time scale), sex, year of screening examination, study center, obesity, smoking status, regular exercise, alcohol intake, educational level, family history of cancer, medication for hyperlipidemia, history of diabetes, history of hypertension, and history of CVD,
b) Estimated from Cox proportional hazard models with inverse probability weights with colonoscopic screening, obesity, smoking status, regular exercise, alcohol intake, educational level, medication for hyperlipidemia, history of diabetes, history of hypertension, and history of CVD as time-dependent variables and baseline age, sex, study center, year of screening examination, education level, and family history of cancer as time-fixed variables.
Table 3
| Colonoscopy screening | Person-years | No. of events | Mortality rate (per 105 PY) | Age and sex-adjusted HR (95% CI) | Multivariable-adjusted HRa) (95% CI) | HR (95% CI)b) in the model using time-dependent variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | ||||||
| Never | 12,775,275.0 | 165 | 1.3 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Ever | 4,034,204.7 | 61 | 1.5 | 0.63 (0.34–1.17) | 0.68 (0.36–1.30) | 0.50 (0.31–0.80) |
| Age < 45 yr | ||||||
| Never | 11,295,458.0 | 64 | 0.6 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Ever | 2,873,664.7 | 17 | 0.6 | 0.95 (0.24–3.76) | 1.09 (0.26–4.59) | 0.47 (0.15–1.44) |
| Age ≥ 45 yr | ||||||
| Never | 1,479,817.2 | 101 | 6.8 | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) | 1.00 (reference) |
| Ever | 1,160,540.0 | 44 | 3.8 | 0.53 (0.30–0.93) | 0.57 (0.32–1.00) | 0.52 (0.31–0.87) |
p=0.931 for the overall interaction between age and colonoscopic screening for colorectal cancer mortality (time-dependent model). CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; HR, hazard ratio; PY, person-years.
a) Cox proportional hazard models with inverse probability weights with age as a time scale were used to estimate HRs and 95% CIs. The multivariable-adjusted model was adjusted for age (time scale), sex, year of screening examination, study center, obesity, smoking status, regular exercise, alcohol intake, educational level, family history of cancer, medication for hyperlipidemia, history of diabetes, history of hypertension, and history of CVD,
b) Estimated from Cox proportional hazard models with inverse probability weights with colonoscopic screening, obesity, smoking status, regular exercise, alcohol intake, educational level, medication for hyperlipidemia, history of diabetes, history of hypertension, and history of CVD as time-dependent variables and baseline age, sex, study center, year of screening examination, education level, and family history of cancer as time-fixed variables.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download