Abstract
Background/Aims
Among the many complications that can occur following therapeutic endoscopy, bleeding is the most serious, which occurs in 1.0-6.1% of all colonoscopic polypectomies. The aim of this study was to identify risk factors of delayed post-polypectomy bleeding (PPB).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the data of patients who underwent colonoscopic polypectomy between January 2003 and December 2012. We compared patients who experienced delayed PPB with those who did not. The control-to-patient ratio was 3:1. The clinical data analyzed included polyp size, number, location, and shape, patient' body mass index (BMI), preventive hemostasis, and endoscopist experience.
Results
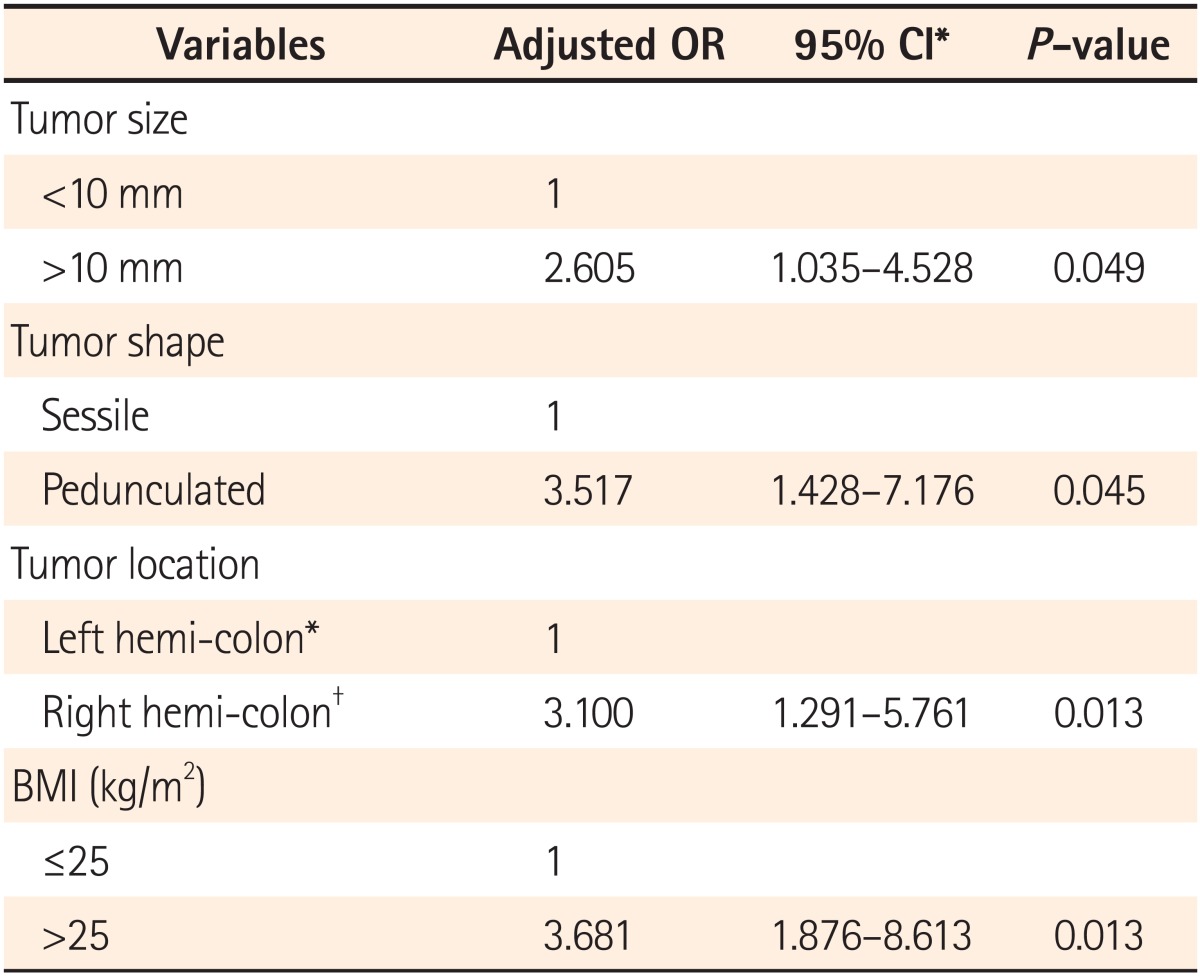
Of 1,745 patients undergoing colonoscopic polypectomy, 21 (1.2%) experienced significant delayed PPB. We selected 63 age- and sex-matched controls. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that polyps >10 mm (odds ratio [OR], 2.605; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.035-4.528; P=0.049), a pedunculated polyp (OR, 3.517; 95% CI, 1.428-7.176; P=0.045), a polyp located in the right hemicolon (OR, 3.10; 95% CI, 1.291-5.761; P=0.013), and a high BMI (OR, 3.681; 95% CI, 1.876-8.613; P=0.013) were significantly associated with delayed PPB.
Colorectal cancer is the third and second most common cancer in men and women worldwide, respectively. In 2008, approximately 608,000 deaths from colorectal cancer were estimated worldwide, accounting for 8% of all cancer deaths, and making it the fourth most common cause of death from cancer.1 In Korea, the colorectal cancer incidence rates in 2008 were 54.7 and 36.9 per 100,000 individuals among men and women, respectively.2 A recent study showed an increase in the incidence of colon cancer among younger population and that more than one quarter (28.2%) of patients in South Korea were asymptomatic.3
Colonoscopic polypectomy for adenomas reduces the mortality rates of colorectal cancer.4,5,6 However, it is not completely free from complications. Bleeding is one of the most serious complications of endoscopic polypectomy, reported in approximately 1.0-6.1% of all cases.7,8,9
Bleeding can occur during the procedure (immediate post-polypectomy bleeding [PPB]) or after hospital discharge (delayed PPB). Several studies have demonstrated that the incidence of delayed PPB ranges from 0.4% to 1.1%.9,10,11,12,13,14,15 Clinically delayed PPB may be more serious because the volume of blood loss is more than that in immediate PPB, and appropriate treatment may be delayed.16 Therefore, delayed PPB is a serious complication that usually requires hospitalization, transfusion, and repeat endoscopy.
We retrospectively reviewed the data from patients who underwent colonoscopic polypectomy at Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, between January 2003 and December 2012. Patients with IBD, non-epithelial neoplasms, or familial adenomatous polyposis were excluded from this study. In addition, patients with a bleeding tendency (e.g., ongoing anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy, prothrombin time >30% of the normal range, or a platelet count <100×103/mm3) and those with a history of colon surgery were also excluded. If anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents such as aspirin or ticlopidine had been prescribed, they were discontinued at least 7 days before the procedure. These patients restarted anticoagulant or antiplatelet agents 3-5 days after the procedure.20
Delayed PPB was defined as lower gastrointestinal bleeding that occurs between 24 hours and 14 days after the procedure.11 Patients who underwent polypectomy without delayed PPB were randomly selected among those who had been admitted during the polypectomy procedure. Patients who were age- and sex-matched were selected as a control group. The control-to-case ratio was 3:1.
The baseline characteristics of the patients and their polyps (tumor size, tumor location, tumor shape, and histopathological findings) were compared between the two groups. We also compared endoscopist experience (≥10 years' experience) and preventive prophylaxis between the groups. The primary goal of this study was to evaluate the risk factors of delayed PPB after colonoscopic polypectomy. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul Paik Hospital. A consent waiver was granted for this database study.
Polypectomies were performed by using a standard flexible colonoscope (CFH260AL/CFH260AI; Olympus Optical Co., Tokyo, Japan). Snare polypectomy was most frequently used as either en bloc or piecemeal resection. Routine preinjection of the polyp base with saline was performed (Fig. 1A and 1B). An electrosurgical unit (VIO 300D; ERBE, Tübingen, Germany) was set according to the manufacturer's instructions, and mixed current was used at the time of resection. Delayed PPB was treated by transfusion, if needed, and endoscopic interventional procedures such as argon plasma coagulation or hemoclips to achieve hemostasis (Fig. 1C and 1D).
Results of the comparisons of characteristics between cases and controls were analyzed by using the t-test for continuous variables and the chi-square test for categorical variables. All statistical analyses were performed by using the SPSS version 16 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted for the adjusted factors that affected delayed PPB. A P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
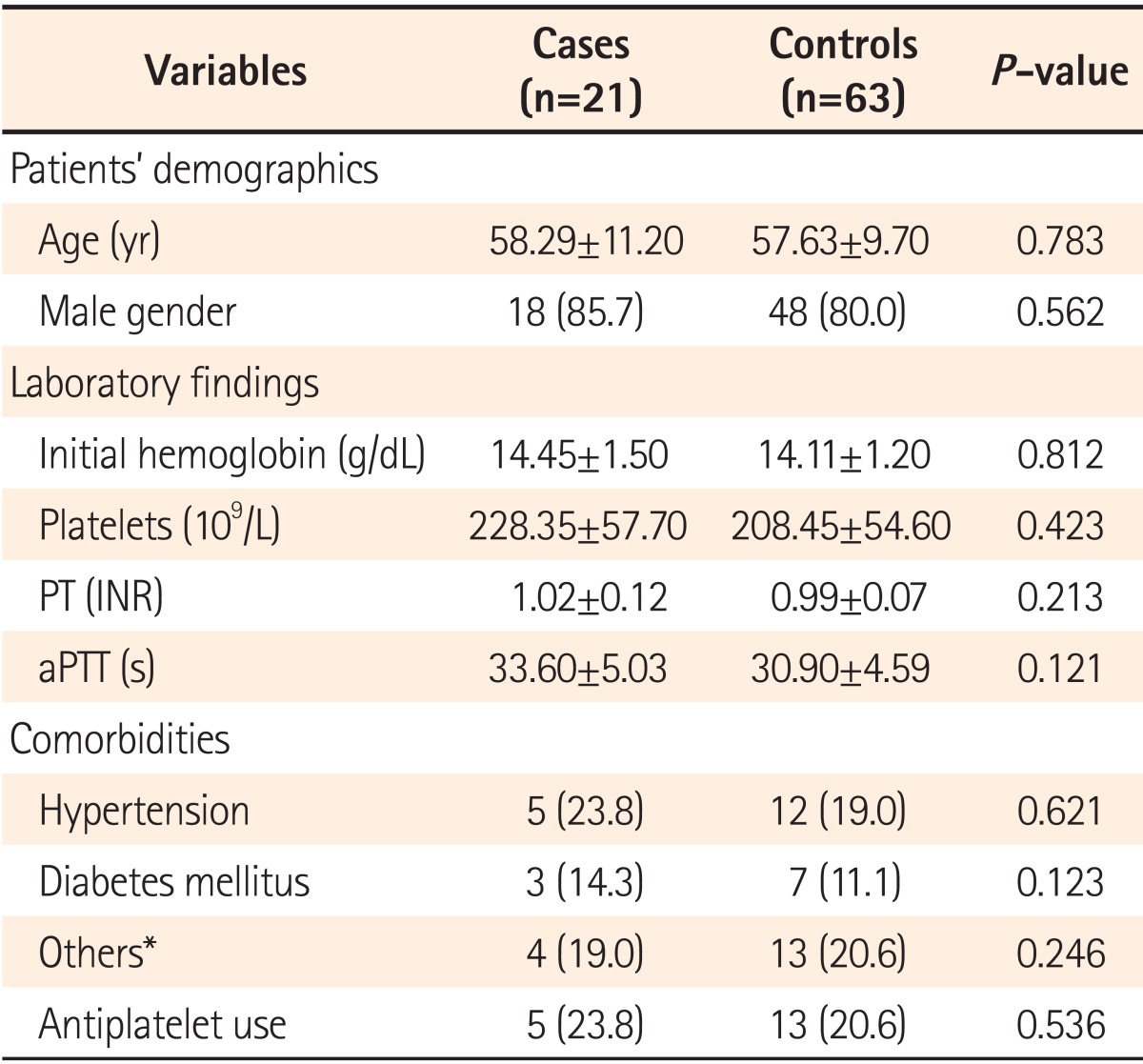
Of the 1,745 patients who underwent colonoscopic polypectomy, 21 (1.2%) experienced delayed PPB. These patients were age- and sex-matched to 63 randomly selected control patients. The baseline characteristics of the case and control groups were similar. The male-to-female ratio and mean age did not differ between delayed PPB and control groups. The mean platelet count was 228.35±57.7 ×103/mm3 in the bleeding group and 208.45±54.6 ×103/mm3 in the control group (P=0.423). The mean international normalized ratio was 1.02±0.12 in the bleeding group and 0.99±0.07 in the control group (P=0.213). No significant differences were identified between the two groups of patients in terms of demographic characteristics, laboratory findings, and comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, cerebrovascular disease, and chronic liver disease (Table 1).
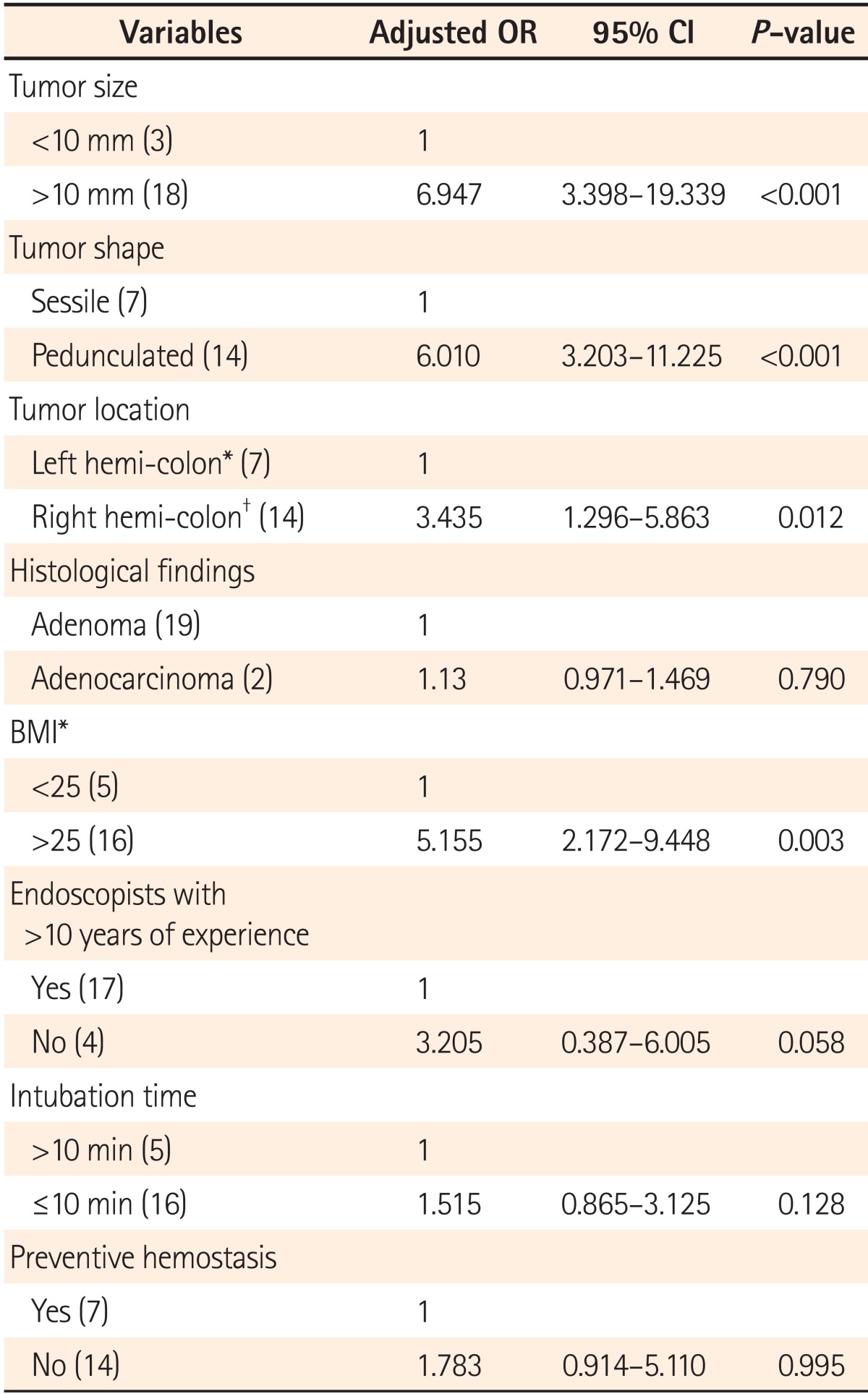
By using the univariate logistic regression analysis, we found no significant differences in tumor histology, endoscopist experience, intubation time, or preventive prophylaxis such as hemoclip use and argon plasma coagulation between the case and control groups. However, significant differences in polyp size, shape, location, and patient's BMI were found between the two groups (Table 2).
The multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that polyp size, shape, and location, and patient BMI were consistently associated with delayed PPB. Patients with polyps >10 mm had 2.6 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.035-4.528; P=0.049) than those with smaller polyps. In addition, patients with pedunculated polyps had 3.5 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.428-7.176; P=0.045) than those with sessile polyps. Patients with polyps located in the right hemicolon had 3.1 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.291-5.761; P=0.013) than those with polyps located in the left hemicolon. Patients with higher BMI had 3.7 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.876-8.613; P=0.013) than those with lower BMI (Table 3).
Many studies have reported that colonoscopic polypectomy reduces the incidence of colon cancer. It is well documented that most colonic adenocarcinomas arise from preexisting adenomatous colonic polyps.21,22
As a result of improvements in hemostatic instruments and techniques, hemorrhagic complications after colonoscopic polypectomies can be well controlled. However, PPB is still the most significant complication of endoscopic polypectomy.23,24,25,26,27
PPB is generally divided into 2 types, namely immediate bleeding after polypectomy and delayed bleeding that can occur up to 2 weeks after the procedure.7,11 Immediate bleeding following colonoscopic polypectomies can be easily detected and controlled, but delayed bleeding can have serious outcomes. In this study, delayed PPB was defined as lower gastrointestinal bleeding that occurred between 24 hours and 14 days after the procedure, because most cases of delayed PPB are reported during this period.11 In our study, the rate of delayed PPB is 1.2%, which is similar to that reported in a recent study.14
Previous studies have shown polyp size to be the most predictive factor of PPB. A retrospective cohort study showed that patients with polyps >10 mm had 4.5 times higher risk of PPB (95% CI, 2.0-10.3; P=0.003) than those with smaller polyps.18 Bae et al. also demonstrated that the risk of delayed PPB increased by 11.6% for every 1-mm increase in resected polyp diameter.13 Similarly, Sawhney et al. calculated a 9% increase in the risk of secondary PPB for every additional millimeter in polyp size.10 In our study, patients with polyps >10 mm also had 2.6 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.035-4.528; P=0.049) than those with smaller polyps. Although some studies yielded conflicting results, patients with sessile polyps have also been reported to be at increased risk of delayed PPB compared to patients with pedunculated ones. However, in our study, patients with pedunculated polyps had 3.5 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.428-7.176; P=0.045) than those with sessile polyps, which is not consistent with results from other studies.7,12,14,28 A recent study, however, has shown that protruding polyps (Ip, Isp) were associated with increased risk of delayed PPB,14 which is consistent with the results of our study. This observation could be associated with the blood vessels inside the stalk, which are exposed during the procedure. We assumed that the lower incidence of delayed PPB in patients with sessile polyps than in patients with pedunculated polyps could be attributable to more caution during procedures. As the procedures for pedunculated polyp removal are relatively simple compared with sessile polyps, the former may be performed, inadvertently, with less caution.
Polyp location is another factor of delayed PPB. A multicenter case-control study demonstrated that polyp localization to the right hemicolon is an independent risk factor of delayed PPB.29 Our study similarly showed that patients with polyps located in the right hemi-colon had 3.1 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.291-5.761; P=0.013) than those with polyps located in the left hemicolon. This risk may be associated with the thinner wall of the cecum, which increases vessel damage in the deeper submucosal layer.17 The histological properties of polyps were not significantly associated with delayed PPB, similar to the observation of another study.15
Of interest are the patients with BMI >25 kg/m2 had 3.7 times higher risk (95% CI, 1.876-8.613; P=0.013) than those with BMI <25 kg/m2. This finding of our study is quite unique; however, the biological mechanisms by which obesity increases the risk of PPB are unclear. We assumed that various adaptations and/or alterations in the cardiovascular system and its functioning may occur in obese individuals. These events might be modulated by substances (interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α) released from adipocytes, such as those in adipose tissue, that are excessively accumulated.15,30 More studies should be performed to analyze the association of obesity with delayed PPB.
This study has several limitations. This study was retrospective and based on existing medical records. In addition, the sample size was relatively small. Although the control group was randomly assigned, selection bias might have affected the validity of our study. For instance, interindividual variation in the techniques employed, which may play an important role in the incidence of delayed PPB, was not analyzed.
In conclusion, the incidence of delayed PPB was 1.2% in this study, and patients with large polyps, pedunculated polyps, or polyps located in the right hemicolon showed an increased risk of delayed PPB. In addition, patients with higher BMI also showed a higher risk of delayed PPB. Therefore, more caution is needed during polypectomies in patients with these risk factors.
References
1. Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010; 127:2893–2917. PMID: 21351269.
2. Lee BI, Hong SP, Kim SE, et al. Korean guidelines for colorectal cancer screening and polyp detection. Clin Endosc. 2012; 45:25–43. PMID: 22741131.
3. Park SH, Song CW, Kim YB, et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of colon cancer diagnosed at primary health care institutions. Intest Res. 2014; 12:131–138. PMID: 25349580.
4. Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Ho MN, et al. The National Polyp Study Workgroup. Prevention of colorectal cancer by colonoscopic polypectomy. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:1977–1981. PMID: 8247072.
5. Manser CN, Bachmann LM, Brunner J, Hunold F, Bauerfeind P, Marbet UA. Colonoscopy screening markedly reduces the occurrence of colon carcinomas and carcinoma-related death: a closed cohort study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:110–117. PMID: 22498179.
6. Zauber AG, Winawer SJ, O'Brien MJ, et al. Colonoscopic polypectomy and long-term prevention of colorectal-cancer deaths. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:687–696. PMID: 22356322.
7. Rosen L, Bub DS, Reed JF 3rd, Nastasee SA. Hemorrhage following colonoscopic polypectomy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1993; 36:1126–1131. PMID: 8253009.
8. Dobrowolski S, Dobosz M, Babicki A, Glowacki J, Nalecz A. Blood supply of colorectal polyps correlates with risk of bleeding after colonoscopic polypectomy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:1004–1009. PMID: 16733117.
9. Kim HS, Kim KU, Park WK, et al. Delayed bleeding in a colonoscopic polypectomy: an experience with 5,236 polypectomies. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2000; 16:462–468.
10. Sawhney MS, Salfiti N, Nelson DB, Lederle FA, Bond JH. Risk factors for severe delayed postpolypectomy bleeding. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:115–119. PMID: 18253906.
11. Singaram C, Torbey CF, Jacoby RF. Delayed postpolypectomy bleeding. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995; 90:146–147. PMID: 7801918.
12. Kim DH, Lim SW. Analysis of delayed postpolypectomy bleeding in a colorectal clinic. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2011; 27:13–16. PMID: 21431091.
13. Bae GH, Jung JT, Kwon JG, et al. Risk factors of delayed bleeding after colonoscopic polypectomy: case-control study. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2012; 59:423–427. PMID: 22735875.
14. Choung BS, Kim SH, Ahn DS, et al. Incidence and risk factors of delayed postpolypectomy bleeding: a retrospective cohort study. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014; 48:784–789. PMID: 24231934.
15. Wu XR, Church JM, Jarrar A, Liang J, Kalady MF. Risk factors for delayed postpolypectomy bleeding: how to minimize your patients' risk. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013; 28:1127–1134. PMID: 23440363.
16. Waye JD, Lewis BS, Yessayan S. Colonoscopy: a prospective report of complications. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992; 15:347–351. PMID: 1294644.
17. Sorbi D, Norton I, Conio M, Balm R, Zinsmeister A, Gostout CJ. Postpolypectomy lower GI bleeding: descriptive analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51:690–696. PMID: 10840301.
18. Watabe H, Yamaji Y, Okamoto M, et al. Risk assessment for delayed hemorrhagic complication of colonic polypectomy: polyp-related factors and patient-related factors. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:73–78. PMID: 16813806.
19. Bourke MJ. Bleeding following wide-field endoscopic resection in the colon. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2011; 7:814–817. PMID: 22347820.
20. Pan A, Schlup M, Lubcke R, Chou A, Schultz M. The role of aspirin in post-polypectomy bleeding-a retrospective survey. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012; 12:138. PMID: 23046845.
21. Jass JR. Do all colorectal carcinomas arise in preexisting adenomas? World J Surg. 1989; 13:45–51. PMID: 2658353.
22. Morson B. President's address. The polyp-cancer sequence in the large bowel. Proc R Soc Med. 1974; 67:451–457. PMID: 4853754.
23. Hachisu T. A new detachable snare for hemostasis in the removal of large polyps or other elevated lesions. Surg Endosc. 1991; 5:70–74. PMID: 1948617.
24. Pontecorvo C, Pesce G. The 'safety snare'-a ligature-placing snare to prevent haemorrhage after transection of large pedunculated polyps. Endoscopy. 1986; 18:55–56. PMID: 3956439.
25. Binmoeller KF, Thonke F, Soehendra N. Endoscopic hemoclip treatment for gastrointestinal bleeding. Endoscopy. 1993; 25:167–170. PMID: 8491134.
26. Hachisu T. Evaluation of endoscopic hemostasis using an improved clipping apparatus. Surg Endosc. 1988; 2:13–17. PMID: 3051463.
27. Parra-Blanco A, Kaminaga N, Kojima T, et al. Hemoclipping for postpolypectomy and postbiopsy colonic bleeding. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000; 51:37–41. PMID: 10625793.
28. Heldwein W, Dollhopf M, Rosch T, et al. The Munich Polypectomy Study (MUPS): prospective analysis of complications and risk factors in 4000 colonic snare polypectomies. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:1116–1122. PMID: 16281142.
29. Buddingh KT, Herngreen T, Haringsma J, et al. Location in the right hemi-colon is an independent risk factor for delayed post-polypectomy hemorrhage: a multi-center case-control study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:1119–1124. PMID: 21266961.
30. Shoelson SE, Herrero L, Naaz A. Obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology. 2007; 132:2169–2180. PMID: 17498510.
Fig. 1
(A) Colon polypectomy. Snare closed at the base of the polyp. (B) Base of the polyp after polypectomy. No immediate bleeding occurred. (C) Delayed post-polypectomy bleeding. Three days later, the patient complained of hematochezia, and fresh blood and clots were observed on endoscopy. (D) Endoscopic treatment. Endoscopic clipping for the treatment of delayed post-polypectomy bleeding was performed.





 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download