1. O'Duffy JD. Behçet's disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1994; 6:39–43. PMID:
8031678.
2. Kaklamani VG, Vaiopoulos G, Kaklamanis PG. Behçet's disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1998; 27:197–217. PMID:
9514126.

3. Sakane T, Takeno M, Suzuki N, Inaba G. Behçet's disease. N Engl J Med. 1999; 341:1284–1291. PMID:
10528040.

4. Baba S, Maruta M, Ando K, Teramoto T, Endo I. Intestinal Behçet's disease: report of five cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1976; 19:428–440. PMID:
939158.
5. Kasahara Y, Tanaka S, Nishino M, Umemura H, Shiraha S, Kuyama T. Intestinal involvement in Behçet's disease: review of 136 surgical cases in the Japanese literature. Dis Colon Rectum. 1981; 24:103–106. PMID:
7215071.
6. Bayraktar Y, Ozaslan E, Van Thiel DH. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Behcet's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2000; 30:144–154. PMID:
10730919.

7. Grigg EL, Kane S, Katz S. Mimicry and deception in inflammatory bowel disease and intestinal Behçet disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y). 2012; 8:103–112. PMID:
22485077.
8. Kim DH, Cheon JH. Intestinal Behçet's disease: a true inflammatory bowel disease or merely an intestinal complication of systemic vasculitis? Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:22–32. PMID:
26632379.

9. Yang SK. Intestinal Behcet's disease. Intest Res. 2005; 3:1–10.
10. Kim SU, Cheon JH, Lim JS, et al. Massive gastrointestinal bleeding due to aneurysmal rupture of ileo-colic artery in a patient with Behcet's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007; 49:400–404. PMID:
17641560.
11. Jung YS, Cheon JH, Park SJ, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. Long-term clinical outcomes of Crohn's disease and intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:99–105. PMID:
22508364.

12. Lakhanpal S, Tani K, Lie JT, Katoh K, Ishigatsubo Y, Ohokubo T. Pathologic features of Behçet's syndrome: a review of Japanese autopsy registry data. Hum Pathol. 1985; 16:790–795. PMID:
4018777.

13. Cheon JH, Shin SJ, Kim SW, et al. Diagnosis of intestinal Behçet's disease. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009; 53:187–193. PMID:
19835220.
14. Cheon JH, Kim WH. An update on the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of intestinal Behçet's disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015; 27:24–31. PMID:
25405821.

15. Criteria for diagnosis of Behçet's disease. International Study Group for Behçet's Disease. Lancet. 1990; 335:1078–1080. PMID:
1970380.
16. Mizushima Y, Inaba G, Mimura Y, Ono S. Diagnostic criteria for Behçet's disease in 1987, and guidelines for treating Behçet's disease. Saishin Igaku. 1988; 43:382–391.
17. Lee CR, Kim WH, Cho YS, et al. Colonoscopic findings in intestinal Behçet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2001; 7:243–249. PMID:
11515851.

18. Kim JS, Lim SH, Choi IJ, et al. Prediction of the clinical course of Behçet's colitis according to macroscopic classification by colonoscopy. Endoscopy. 2000; 32:635–640. PMID:
10935793.

19. Shepherd NA. Pathological mimics of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Pathol. 1991; 44:726–733. PMID:
1918397.

20. Ebert EC. Gastrointestinal manifestations of Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2009; 54:201–207. PMID:
18594975.

21. Kobayashi K, Ueno F, Bito S, et al. Development of consensus statements for the diagnosis and management of intestinal Behçet’s disease using a modified Delphi approach. J Gastroenterol. 2007; 42:737–745. PMID:
17876543.

22. Cheon JH, Celik AF, Kim WH. Behçet's disease: gastrointestinal involvement. In : Yazici Y, Yazici H, editors. Behçet's syndrome. New York: Springer;2010. p. 165–188.
23. Lee SK, Kim BK, Kim TI, Kim WH. Differential diagnosis of intestinal Behçet's disease and Crohn's disease by colonoscopic findings. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:9–16. PMID:
19160153.

24. Lee YJ, Yang SK, Byeon JS, et al. Analysis of colonoscopic findings in the differential diagnosis between intestinal tuberculosis and Crohn's disease. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:592–597. PMID:
16673312.

25. O'Duffy JD. Vasculitis in Behçet's disease. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1990; 16:423–431. PMID:
2189158.
26. Shin SJ, Lee SK, Kim TI, et al. Chronological changes in the systemic manifestations of intestinal Behcet's disease and their significance in diagnosis. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2010; 25:1371–1376. PMID:
20533055.

27. Muto T. Historical review of so called “simple ulcer” of the intestine. Stomach Intestine. 1979; 14:739–748.
28. Jung HC, Rhee PL, Song IS, Choi KW, Kim CY. Temporal changes in the clinical type or diagnosis of Behçet's colitis in patients with aphthoid or punched-out colonic ulcerations. J Korean Med Sci. 1991; 6:313–318. PMID:
1844639.

29. Cheon JH, Kim ES, Shin SJ, et al. Development and validation of novel diagnostic criteria for intestinal Behçet's disease in Korean patients with ileocolonic ulcers. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009; 104:2492–2499. PMID:
19532129.

30. Jung YS, Cheon JH, Park SJ, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH. Clinical course of intestinal Behcet's disease during the first five years. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:496–503. PMID:
22899244.

31. Cheon JH, Kim WH. Recent advances of endoscopy in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut Liver. 2007; 1:118–125. PMID:
20485627.

32. Lee HJ, Kim YN, Jang HW, et al. Correlations between endoscopic and clinical disease activity indices in intestinal Behcet's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:5771–5778. PMID:
23155319.

33. Rutgeerts P, Vermeire S, Van Assche G. Mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease: impossible ideal or therapeutic target? Gut. 2007; 56:453–455. PMID:
17369375.

34. Frøslie KF, Jahnsen J, Moum BA, Vatn MH. IBSEN Group. Mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel disease: results from a Norwegian population-based cohort. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:412–422. PMID:
17681162.

35. Rutgeerts P, Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, et al. Infliximab for induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 353:2462–2476. PMID:
16339095.

36. Schnitzler F, Fidder H, Ferrante M, et al. Mucosal healing predicts long-term outcome of maintenance therapy with infliximab in Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2009; 15:1295–1301. PMID:
19340881.

37. Yim SM, Kim DH, Lee HJ, et al. Mucosal healing predicts the long-term prognosis of intestinal Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2014; 59:2529–2535. PMID:
24838499.

38. De Cruz P, Kamm MA, Hamilton AL, et al. Crohn's disease management after intestinal resection: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2015; 385:1406–1417. PMID:
25542620.

39. Vermeire S, Van Assche G, Rutgeerts P. Laboratory markers in IBD: useful, magic, or unnecessary toys? Gut. 2006; 55:426–431. PMID:
16474109.

40. Sands BE. Biomarkers of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2015; 149:1275–1285.e2. PMID:
26166315.

41. Müftüoğlu AU, Yazici H, Yurdakul S, et al. Behçet's disease: relation of serum C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rates to disease activity. Int J Dermatol. 1986; 25:235–239. PMID:
3710672.
42. Coskun B, Saral Y, Gödekmerdan A, Erden I, Coskun N. Activation markers in Behçet's disease. Skinmed. 2005; 4:282–286. PMID:
16282749.

43. Jung YS, Hong SP, Kim TI, Kim WH, Cheon JH. Long-term clinical outcomes and factors predictive of relapse after 5-aminosalicylate or sulfasalazine therapy in patients with intestinal Behcet disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012; 46:e38–e45. PMID:
22298088.

44. Jung YS, Yoon JY, Lee JH, et al. Prognostic factors and long-term clinical outcomes for surgical patients with intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:1594–1602. PMID:
21674717.

45. Choi CH, Kim TI, Kim BC, et al. Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibody in intestinal Behçet's disease patients: relation to clinical course. Dis Colon Rectum. 2006; 49:1849–1859. PMID:
17080284.

46. Shin SJ, Kim BC, Kim TI, Lee SK, Lee KH, Kim WH. Anti-alpha-enolase antibody as a serologic marker and its correlation with disease severity in intestinal Behçet's disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:812–818. PMID:
20632102.
47. Bouchon A, Dietrich J, Colonna M. Cutting edge: inflammatory responses can be triggered by TREM-1, a novel receptor expressed on neutrophils and monocytes. J Immunol. 2000; 164:4991–4995. PMID:
10799849.
48. Jung YS, Kim SW, Yoon JY, et al. Expression of a soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 (sTREM-1) correlates with clinical disease activity in intestinal Behcet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:2130–2137. PMID:
21910175.
49. Lee HW, Chung SH, Moon CM, et al. The correlation of serum IL-12B expression with disease activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3772. DOI:
10.1097/MD.0000000000003772. PMID:
27281077.
50. Chung SH, Lee HW, Kim SW, et al. Usefulness of measuring serum procalcitonin levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Gut Liver. 2016; 10:574–580. PMID:
26780089.
51. Wei SC. Could fecal calprotectin enter mainstream use for diagnosing and monitoring inflammatory bowel disease? Intest Res. 2016; 14:293–294. PMID:
27799878.
52. Kim DH, Park Y, Kim B, et al. Fecal calprotectin as a non-invasive biomarker for intestinal involvement of Behçet's disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 32:595–601. PMID:
27521492.

53. Cheon JH, Han DS, Park JY, et al. Development, validation, and responsiveness of a novel disease activity index for intestinal Behçet's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011; 17:605–613. PMID:
20848515.

54. Best WR, Becktel JM, Singleton JW, Kern F Jr. Development of a Crohn's disease activity index: National Cooperative Crohn's Disease Study. Gastroenterology. 1976; 70:439–444. PMID:
1248701.
55. Turner D, Otley AR, Mack D, et al. Development, validation, and evaluation of a pediatric ulcerative colitis activity index: a prospective multicenter study. Gastroenterology. 2007; 133:423–432. PMID:
17681163.

56. Cellier C, Sahmoud T, Froguel E, et al. Correlations between clinical activity, endoscopic severity, and biological parameters in colonic or ileocolonic Crohn's disease: a prospective multicentre study of 121 cases. The Groupe d'Etudes Thérapeutiques des Affections Inflammatoires Digestives. Gut. 1994; 35:231–235. PMID:
7508411.

57. Kim ES, Chen M, Lee J, Lee CK, Kim YS. Diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease in Asia: the results of a multinational web-based survey in the 2(nd) Asian Organization for Crohn's and Colitis (AOCC) meeting in Seoul. Intest Res. 2016; 14:224–230. PMID:
27433144.

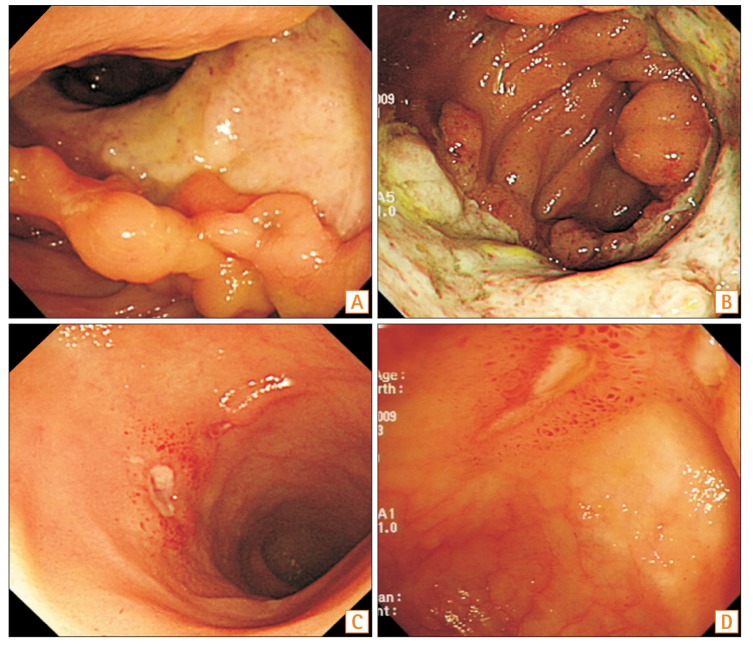
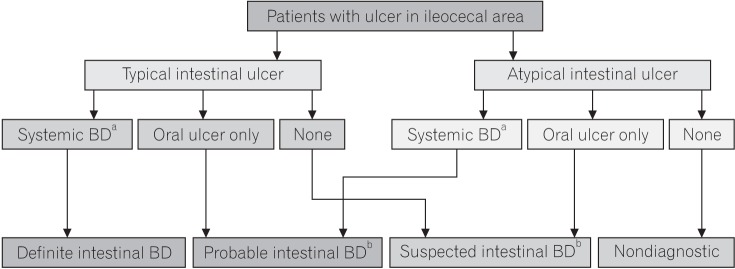
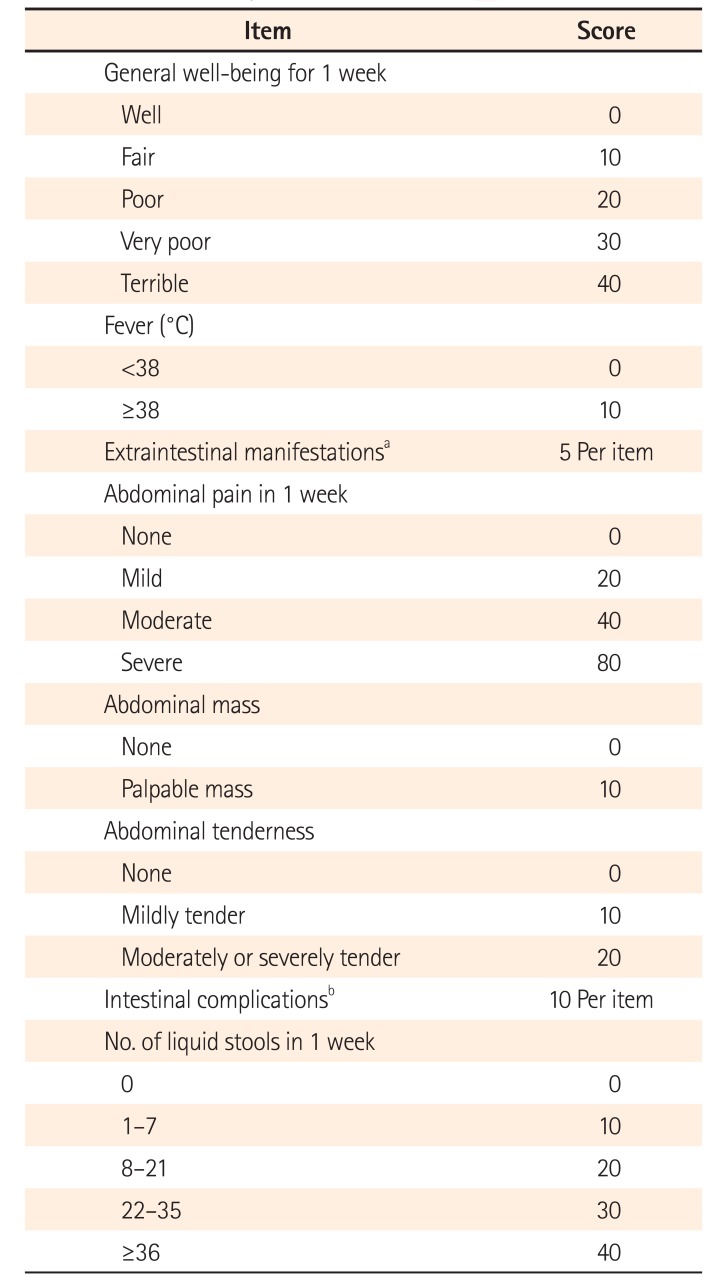
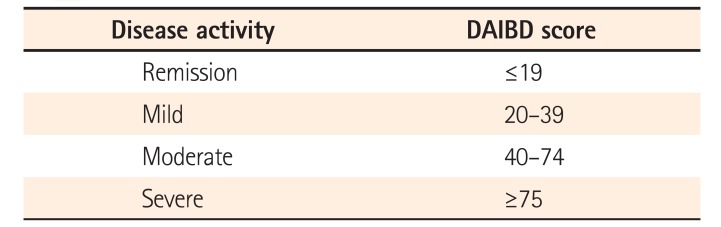




 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download