Abstract
In rare cases, antiresoprtive medications for osteoporosis cause osteonecrosis. Necrotic bone lesions localized at the jaw after the use of antiresorptive medications is named medicationrelated osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ). Although some cases with MRONJ affect the paranasal sinus, inferior turbinate necrosis have not been reported in South Korea yet. Here, we report a case of inferior turbinate osteonecrosis that developed after denosumab had been used.
Go to : 
골다공증, 골결핍증, 악성종양의 골전이 시 사용되는 denosumab은 골흡수 억제제로, 파골세포를 자극하는 중간 매개체인 receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand 수용체를 표적으로 파골세포의 기능과 생존을 억제함으로써 골 흡수를 막는 약제이다. Denosumab은 골다공증 환자에서 6개월마다 피하주사로 투여 시 척추, 골반의 골절 위험도를 낮춘다고 알려져있다[1,2]. Bisphosphoneate, denosumab, romosozumab 같은 골흡수 억제제는 드물게 뼈의 혈액 공급 저하를 발생시켜 뼈괴사를 유발할 수 있고, 특히 턱뼈가 괴사되는 약물성 턱뼈괴사(medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw)를 유발하기도 한다.
국내에서 대한구강악안면외과학회나 대한내분비학회 등에서 약물성 턱뼈괴사에 대한 연구 및 발표가 꾸준히 이루어지고 있고, 상악에 약물성 턱뼈괴사 발생 시 부비동염이 동반되는 경우가 44% 정도로, 부비동 합병증이 흔하다고 알려진것에 비해 국내 이비인후과학회에서는 본 질환에 대한 증례 보고가 2012년과 2021년에 각각 한 건의 증례만 보고되었을 정도로, 이비인후과 의사에게는 생소한 질환이다[3]. 이전 보고된 두 증례는 각각 bisphosphonate 계열의 약물과 denosumab 투여 이후 발생한 약물성 턱뼈괴사 환자였고 부비동염이 동반되어 이에 대한 부비동 내시경수술과 치과 치료 후 회복되었다[4,5]. 본 증례는 국내 최초로 보고하는 denosumab 투여 후 발생한 하비갑개 골괴사 증례이다. 본 증례는 denosumab 투여 후 발생한 하악의 약물성 턱뼈괴사로 치과에서 치료하였지만 지속되는 상악동염으로 본원 이비인후과에 의뢰되었던 환자에서 부비동 내시경수술 중 악골괴사와 연관된 병변 없이 하비갑개 괴사가 발견되어 이에 대해 부분 하비갑개 절제술 후 효과적으로 치료된 바, 본 증례에 대해 공유하여 임상적인 도움을 주고자 한다.
Go to : 
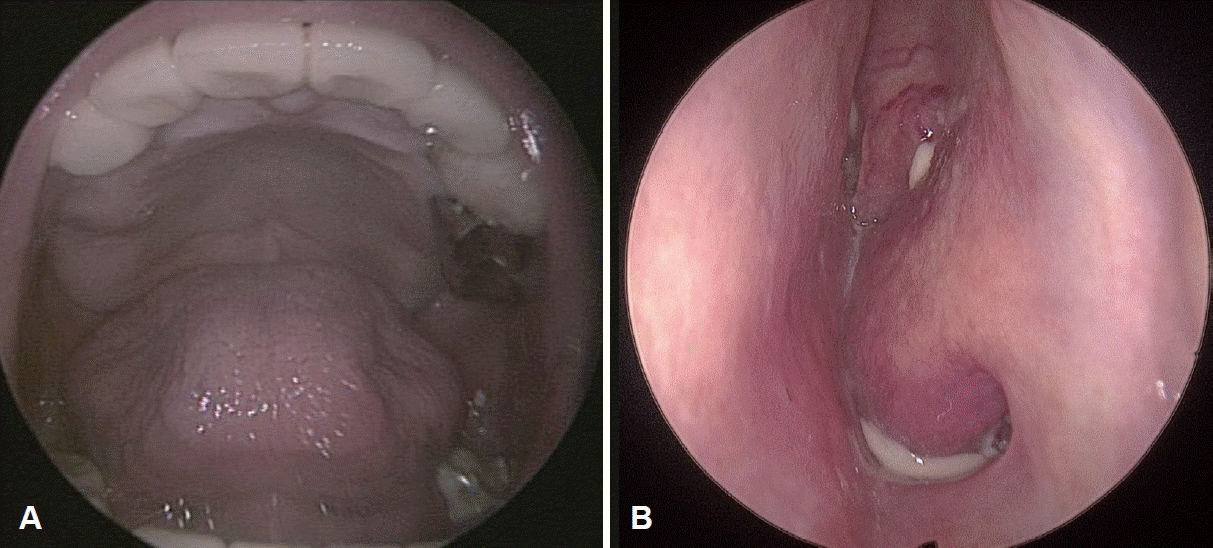
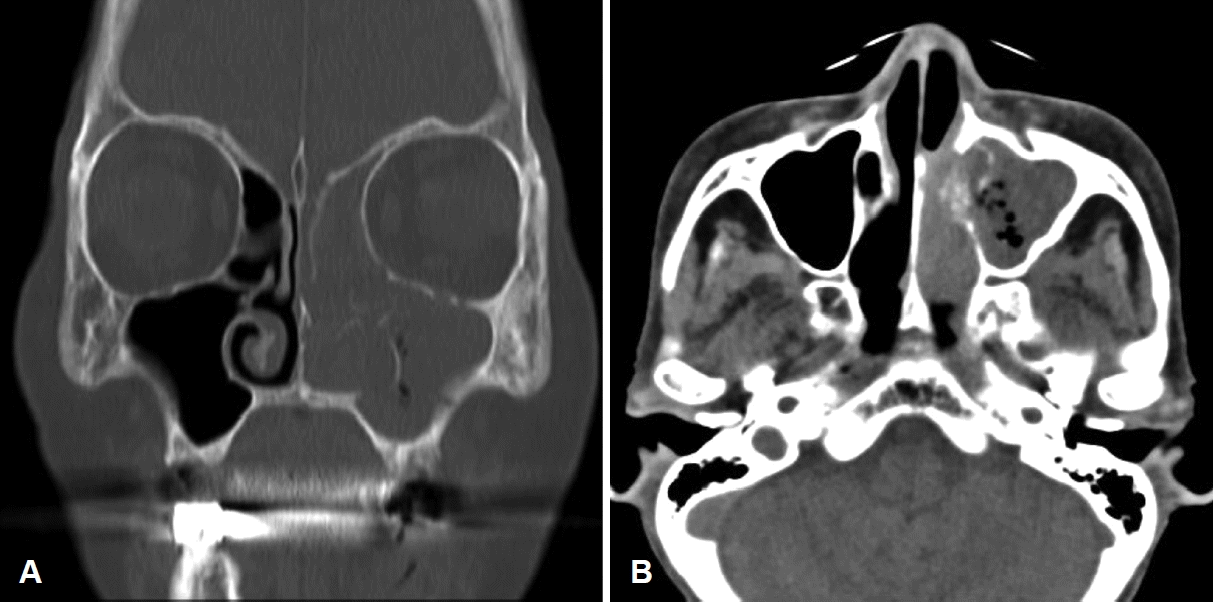
만성 신부전, 빈혈, 만성 C형 간염 과거력을 갖는 77세의 여자 환자가 골다공증에 대해 2년 전부터 denosumab 주사 치료를 6개월마다 피하주사로 투여 받던 중, 본원 내원 8개월 전 개인의원에서 임플란트를 위해 상악 좌측 제1, 제2 대구치, 하악 좌측 제1, 제2 소구치, 제1, 제2 대구치를 발거한 후 좌측 하악의 점막 치유 지연 및 하악의 치조골 노출이 8주 이상 지속되어 이에 대해 약물성 턱뼈괴사 진단하에 denosumab 중단 후 구강악안면외과에서 좌측 하악 약물성 턱뼈괴사에 대해 정주 항생제와 부골절제술(sequestrectomy)을 시행하였다. 이후 구강 내 병변은 호전되었으나 2개월 전부터 좌측 농성 비루가 발생하여 좌측 상악동 부비동염에 대한 치료를 위해 본원 이비인후과로 전원되었다. 좌측 농성 비루 외에 동반되는 코 증상은 없었고 이학적 검사상 좌측 안면부에 압통이나 열감은 없었다. 구강 점막이나 치아는 정상이었고 내시경 소견에서 좌측 비강 외측의 부종과 중비도에서 농성 비루가 관찰되었다(Fig. 1). 부비동 전산화단층촬영에서 좌측 범부비동염 소견과 좌측 하비갑개의 골파괴가 확인되었다(Fig. 2). 치과에서 amoxicillin/clavulanate 항생제 복용 중인 상태로, 추가 항생제 처방 없이 부비동 내시경수술을 계획하였다.
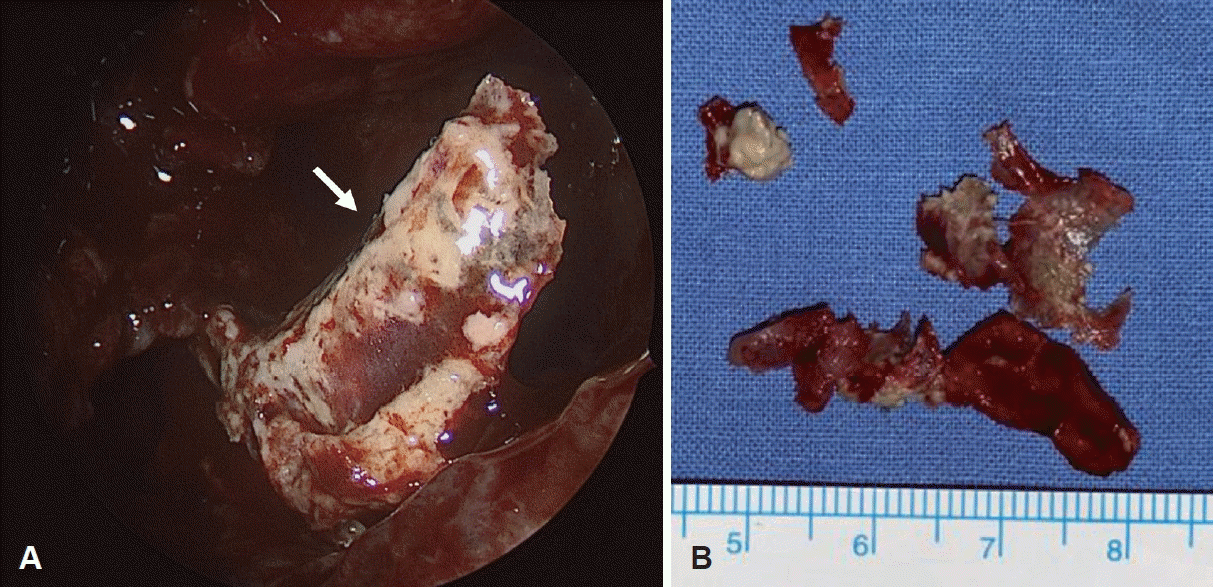
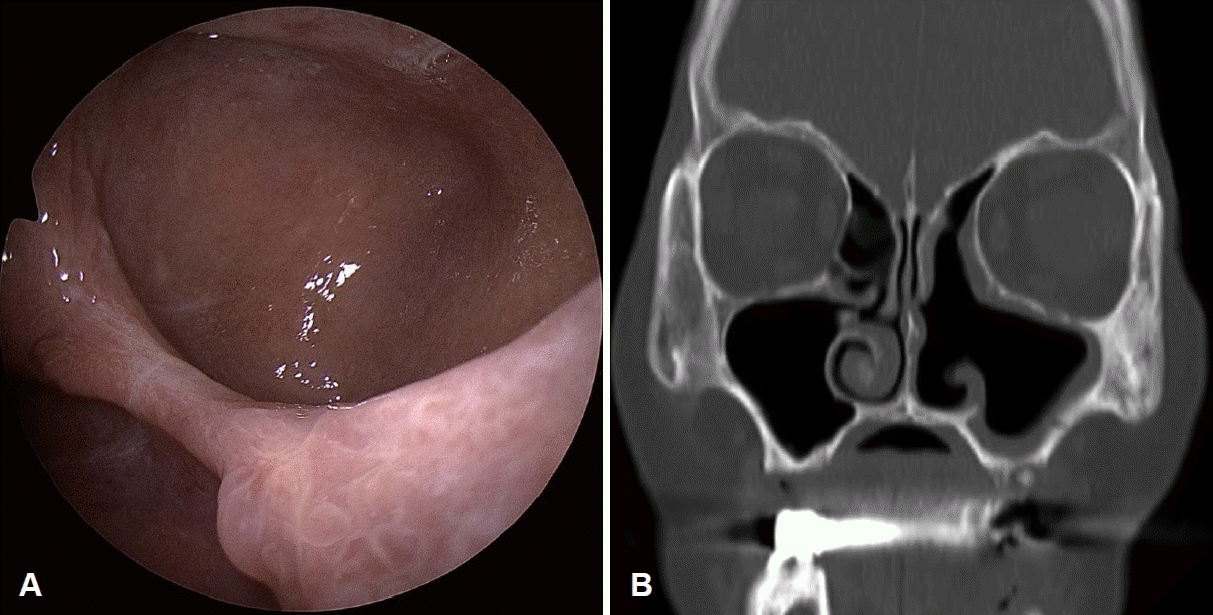
부비동 내시경수술을 시행하였고 중비도 개창술을 통해 좌측 상악동의 농을 배출하였다. 농을 다량 배액한 이후 좌측 하비갑개의 괴사된 골조직이 확인되어 해당 병변과 주변 점막을 포함하여 부분 하비갑개 절제술을 시행하였다(Fig. 3). 부비동염에 대해서는 상악동 자연공을 넓히고 내부점막은 보존한 후 생리식염수를 이용하여 좌측 상악동 세척을 하였다. 수술장 소견상 상악동에 노출된 상악 뼈병변은 없었다. 수술 후 다음날 특별한 합병증 없이 퇴원하였다. 수술 후 농성 비루는 호전되었으며 수술 2개월째 시행한 부비동 전산화단층촬영과 내시경 소견에서 하비갑개 및 상악동의 병변은 호전되었다(Fig. 4).
Go to : 
미국 구강악안면외과학회에 따르면 약물성 턱뼈괴사를 진단하기 위해서는 현재 혹은 과거에 골흡수 억제제 단독 혹은 면역 조절제(immune modulator), 혈관형성 억제제(antiangiogenic medication)와 함께 투여한 병력과, 8주 이상 지속된 구강악안면영역의 뼈 노출 또는 구강 외, 구강 내 누공이 있어야 하며 악골에 방사선 조사 병력이나 전이의 소견이 없어야한다[6].
미국 구강악안면외과학회에서는 약물성 턱뼈괴사에 대해 0에서 3기까지 병기를 나누고 있다. 0기는 골괴사의 임상적 증거는 없지만 비특이적인 증상이나 영상소견을 보일 때, 1기는 골노출이나 골괴사는 있으나 무증상이며 감염, 염증을 보이지 않는 경우, 2기는 골노출이나 골괴사와 함께 증상, 감염, 염증을 보일 때, 3기는 2기 소견에 더해서 병변이 치조골을 넘거나 병적 골절이 있는 경우이다[7].
하비갑개 괴사는 코카인 남용 환자에서 코카인의 혈관 수축작용, 점막 자극, 독성으로 인해 발생하는 경우, 비출혈에 대해 접형구개동맥 결찰 후 혈액공급의 감소로 발생하는 경우, 고주파 절제술 후 발생하는 경우가 보고된바 있으나 본 증례와 같이 골흡수 억제제로 인한 하비갑개 골괴사는 보고된 바가 없다[8-10]. 본 증례의 하비갑개 골괴사는 병력상 약물성 턱뼈괴사에서 뼈의 괴사가 일어나는 것과 같은 기전으로 발생된 것으로 추정되며, 약물성 턱뼈괴사 발생에 대한 명확한 기전은 아직 밝혀지지 않았지만 몇 가지 가설이 제기되고 있다. 골흡수 억제제가 파골세포의 형성이나 분화 및 기능을 저하시켜 골 재생성(bone remodeling)을 억제한다는 것이 약물성 턱뼈괴사에 주된 가설이다. Bisphosphonate를 복용한 환자의 괴사한 뼈를 대상으로 시행된 연구에서 기능하지 않는 파골세포 양의 증가가 관찰되어 앞의 가설을 지지하고 있다[11]. 또한 혈관신생성의 억제도 하나의 기전으로 제기되고 있다. Bisphosphonate 복용 시 약물성 턱뼈괴사 병변 주변으로 혈관분포가 저하되어 있고 뼈의 회복 단계에서도 미세혈관의 양의 감소가 있었다는 동물 연구가 이를 뒷받침하고 있다[12]. 그 외에도 면역기능 장애나 유전적 요인도 연관이 있다고 알려져 있다.
스테로이드 복용, 흡연, 빈혈, 암환자인 경우, 치조골 수술, 발치, 치주질환 같은 국소적인 요인이 있는 경우 약물성 턱뼈 괴사 위험도를 높인다고 알려져 있다[7]. 본 증례에서는 빈혈과 발치가 위험인자였다고 할 수 있겠다.
코카인 남용, 접형구개동맥 결찰, 고주파 절제술 후 발생하는 하비갑개 괴사의 경우 유발 약제의 중단, 필요 시 괴사부위의 제거가 필요하다[8-10]. 본 증례의 경우 약물성 턱뼈괴사와 같은 기전으로 발생했다고 보이며, 미국 구강악안면외과악회의 2022년도 가이드라인에 따르면 약물성 턱뼈괴사의 치료방법은 병기에 따라 나누어 제시하고 있다. 모든 병기에 있어 비수술적 치료 혹은 수술적 치료 둘 다 고려할 수 있고 2기 이상부터 항생제를 사용하도록 권고된다. 수술적 치료 시 괴사된 골조직을 잘 제거해야 치료 성공률이 높다고 알려져 있고, 1기에서는 치조골절제술, 2기부터는 상악골 하부구조 부분절제술을 통해 명확히 괴사된 뼈의 경계를 넘어 정상적인 출혈을 보이는 건강한 뼈가 확인되는 지점까지 절제하라고 권고하고 있다[7]. 본 증례에서는 상악골에서의 병변은 확인되지 않아 구강을 통한 상악골 절제 없이 비강을 통해 괴사되어 노출된 하비갑개 뼈만 완전히 제거해서 성공적으로 치료할 수 있었다. 약물성 턱뼈괴사의 비수술적 치료는 클로르헥시딘 가글, 통증 조절, 부골제거술을 포함하며, 그 외에 고압 산소 치료나 비타민 E, 펜톡시필린도 보조적인 치료로 연구된바 있으나 이에 대한 효과는 명확히 증명되지는 못한 상태이다[13,14].
약물성 턱뼈괴사에서 부비동염이 동반되는 원인은 골파괴와 이차 감염 때문으로 여겨지며 부비동염이 동반된 약물성 턱뼈괴사에서 부비동 내시경수술에 대한 효과나 치료 방법에 대한 가이드라인은 정립되지 않은 상태이다. 2021년 시행된 연구에 따르면 상악동 부비동염이 동반된 3기 약물성 턱뼈괴사 환자에서 부비동 내시경수술과 치과 수술을 동시에 시행한 군과 치과 수술만 단독으로 시행한 군을 치료 4개월 뒤 비교하였을 때 각각 84.2%, 37.5%의 호전율을 보이며 통계적으로 유의미한 차이를 보였다[15].
약물성 턱뼈괴사는 구강악안면외과, 내분비내과에서 최근 많은 연구와 보고가 되며, 부비동 합병증도 발생할 수 있는데도 불구하고 이비인후과에서는 보고된 바가 적고 생소한 질환이다. 부비동염이 약물로 인한 턱뼈괴사의 합병증 혹은 본 증례처럼 약물로 인해 발생한 하비갑개 골괴사가 원인일 수 있지만, 주의하지 않으면 단순 부비동염이나 치성 부비동염으로 간과될 수 있어 이비인후과 의사들도 반드시 인지해야 한다. 본 증례와 같이 골흡수 억제제 복용 후 하비갑개에서도 단독 병변으로 나타날 수 있어, 비강 및 부비동에서 뼈괴사가 의심되는 경우 골흡수 억제제 복용 여부의 확인이 필요하다. 이를 인지하지 못하고 수술 시 하비도 개창술이나 견치와 접근법을 사용하여 상악골 처치를 하는 경우 오히려 골괴사를 유발할 수 있어 주의하여야 한다.
Go to : 
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (NRF- 2022R1F1A1076118).
Go to : 
Notes
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: Il-Ho Park, Yongmin Cho. Data curation: Dongha Kim. Methodology: Il-Ho Park. Supervision: Il-Ho Park, Jae-Min Shin. Validation: Il-Ho Park. Writing—original draft: Yongmin Cho. Writing—review & editing: Il-Ho Park.
Go to : 
REFERENCES
1. Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR, Siris ES, Eastell R, Reid IR, et al. Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361(8):756–65.
2. Papapoulos S, Chapurlat R, Libanati C, Brandi ML, Brown JP, Czerwiński E, et al. Five years of denosumab exposure in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: Results from the first two years of the FREEDOM extension. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27(3):694–701.
3. Mast G, Otto S, Mücke T, Schreyer C, Bissinger O, Kolk A, et al. Incidence of maxillary sinusitis and oro-antral fistulae in bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012; 40(7):568–71.
4. Jung SD, Son HR, Chung YJ, Mo JH. A case of sinusitis due to bisphosphonate related osteonecrosis of jaw. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2012; 55(9):590–4.
5. Kim S. A case of medication related osteonecrosis of the jaw which presented with the chief complaint of nasal stuffiness. J Clin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021; 32(3):286–90.
6. Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Fantasia J, Goodday R, Aghaloo T, Mehrotra B, et al. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw--2014 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 72(10):1938–56.
7. Ruggiero SL, Dodson TB, Aghaloo T, Carlson ER, Ward BB, Kademani D. American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons’ position paper on medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaws-2022 update. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022; 80(5):920–43.
8. Kuriloff DB, Kimmelman CP. Osteocartilaginous necrosis of the sinonasal tract following cocaine abuse. Laryngoscope. 1989; 99(9):918–24.
9. Moorthy R, Anand R, Prior M, Scott PM. Inferior turbinate necrosis following endoscopic sphenopalatine artery ligation. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003; 129(1):159–60.
10. Deenadayal DS, Kumar MN, Sudhakshin P, Hameed S. Radiofrequency reduction of inferior turbinates in allergic and non allergic rhinitis. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014; 66(Suppl 1):231–6.
11. Wehrhan F, Gross C, Creutzburg K, Amann K, Ries J, Kesting M, et al. Osteoclastic expression of higher-level regulators NFATc1 and BCL6 in medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw secondary to bisphosphonate therapy: A comparison with osteoradionecrosis and osteomyelitis. J Transl Med. 2019; 17(1):69.
12. Gao SY, Lin RB, Huang SH, Liang YJ, Li X, Zhang SE, et al. PDGFBB exhibited therapeutic effects on rat model of bisphosphonaterelated osteonecrosis of the jaw by enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Bone. 2021; 144:115117.
13. Freiberger JJ, Padilla-Burgos R, McGraw T, Suliman HB, Kraft KH, Stolp BW, et al. What is the role of hyperbaric oxygen in the management of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A randomized controlled trial of hyperbaric oxygen as an adjunct to surgery and antibiotics. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70(7):1573–83.
14. Epstein MS, Wicknick FW, Epstein JB, Berenson JR, Gorsky M. Management of bisphosphonate-associated osteonecrosis: Pentoxifylline and tocopherol in addition to antimicrobial therapy. An initial case series. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2010; 110(5):593–6.
15. Park JH, Alfafara AM, Park YL, Bae JH, Kim SJ. Medicationrelated osteonecrosis of the maxilla: Prognosis of oral surgery combined with endoscopic sinus surgery. Oral Dis. 2021; 27(4):962–9.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download