Introduction
Subjects and Methods
Participants
Olfactory function testing
Neurocognitive testing
Statistical analysis
Results
Characteristics of enrolled subjects
Table 1.
Data are presented as mean± standard deviation or n (%).
NCD, neurocognitive disorder; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; MMSEK, Korean version of the Mini-Mental State Examination; CERADK, Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Packet; TDI, threshold-discrimination-identification; VAS, visual analog scale
Relationship between subjective gustatory function and olfactory function according to cognitive function
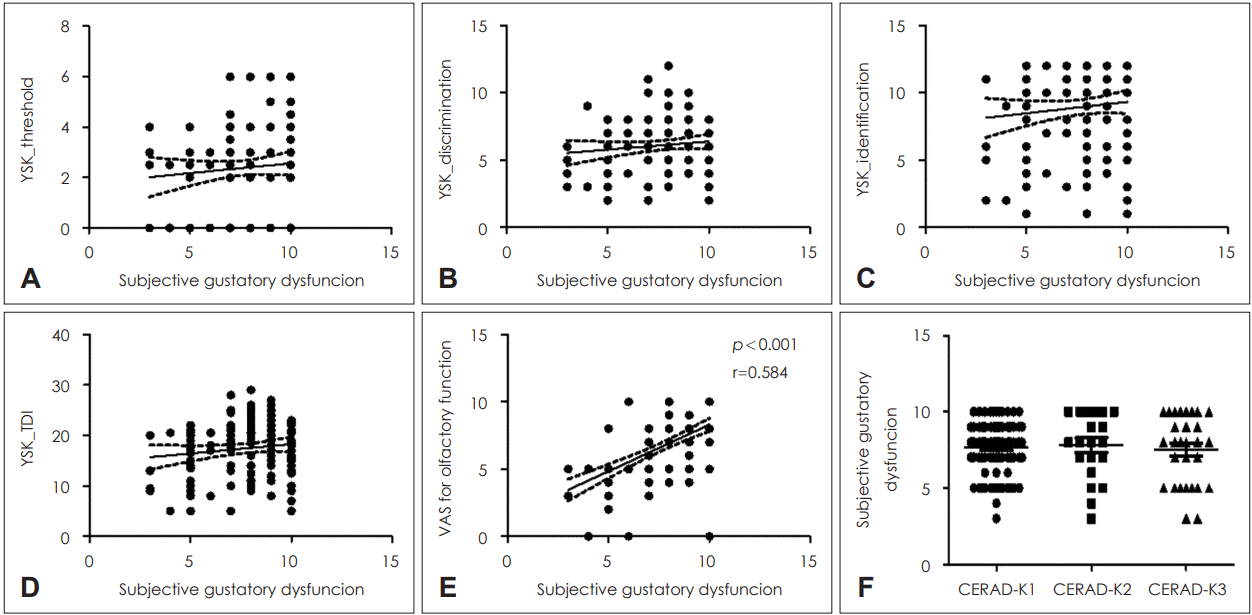 | Fig. 1.Relationship between subjective gustatory dysfunction and olfactory dysfunction. Correlation between the subjective gustatory dysfunction score and YSK olfactory function scores for threshold (A), discrimination (B), and identification (C), as well as with the summation of TDI score (D), and subjective olfactory function score (E). The subjective gustatory dysfunction score was compared with the results of CERAD-K (F). CERAD-K1: normal range; CERAD-K2: significant decline but not dementia level; and CERAD-K3: impaired performance comparable to dementia. TDI, threshold-discrimination-identification; VAS, visual analog scale; CERAD-K, Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Packet. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download