1. Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:394–424.
2. Miyazaki J, Nishiyama H. Epidemiology of urothelial carcinoma. Int J Urol. 2017; 24:730–4.
3. Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, et al. Bladder cancer. Lancet. 2016; 388:2796–810.
4. Chang SS, Boorjian SA, Chou R, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: AUA/SUO guideline. J Urol. 2016; 196:1021–9.
5. Mathieu R, Lucca I, Klatte T, Babjuk M, Shariat SF. Trimodal therapy for invasive bladder cancer: is it really equal to radical cystectomy? Curr Opin Urol. 2015; 25:476–82.
6. Ceylan C, Doluoglu OG, Keles I, et al. Importance of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in muscle-invasive and non-muscle invasive bladder tumors. Urologia. 2014; 81:120–4.
7. Abdou Hassan W, Shalaby E, Abo-Hashesh M, Ibrahim Ali R. Evaluation of the expression of HER2 and c-KIT proteins as prognostic markers in superficial bladder urothelial carcinoma. Res Rep Urol. 2021; 13:197–206.
8. Lobo N, Mount C, Omar K, Nair R, Thurairaja R, Khan MS. Landmarks in the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2017; 14:565–74.
9. Gakis G, Todenhofer T, Stenzl A. The prognostic value of hematological and systemic inflammatory disorders in invasive bladder cancer. Curr Opin Urol. 2011; 21:428–33.
10. Schepisi G, Santoni M, Massari F, et al. Urothelial cancer: inflammatory mediators and implications for immunotherapy. BioDrugs. 2016; 30:263–73.
11. Cavallo F, De Giovanni C, Nanni P, Forni G, Lollini PL. 2011: the immune hallmarks of cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011; 60:319–26.
12. Amulic B, Cazalet C, Hayes GL, Metzler KD, Zychlinsky A. Neutrophil function: from mechanisms to disease. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012; 30:459–89.
13. Mano R, Baniel J, Shoshany O, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts progression and recurrence of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 2015; 33:67.
14. Gondo T, Nakashima J, Ohno Y, et al. Prognostic value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and establishment of novel preoperative risk stratification model in bladder cancer patients treated with radical cystectomy. Urology. 2012; 79:1085–91.
15. Ho WY, Yee C, Greenberg PD. Adoptive therapy with CD8(+) T cells: it may get by with a little help from its friends. J Clin Invest. 2002; 110:1415–7.
16. Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, et al. Intraepithelial CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8+/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102:18538–43.
17. Sheu BC, Hsu SM, Ho HN, Lin RH, Torng PL, Huang SC. Reversed CD4/CD8 ratios of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are correlated with the progression of human cervical carcinoma. Cancer. 1999; 86:1537–43.
18. Sharma MD, Hou DY, Liu Y, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase controls conversion of Foxp3+ Tregs to TH17-like cells in tumor-draining lymph nodes. Blood. 2009; 113:6102–11.
19. Comperat EM, Burger M, Gontero P, et al. Grading of urothelial carcinoma and the new “World Health Organisation classification of tumours of the urinary system and male genital organs 2016”. Eur Urol Focus. 2019; 5:457–66.
20. Uribe-Querol E, Rosales C. Neutrophils in cancer: two sides of the same coin. J Immunol Res. 2015; 2015:983698.
21. Liu K, Zhao K, Wang L, Sun E. The prognostic values of tumor-infiltrating neutrophils, lymphocytes and neutrophil/lymphocyte rates in bladder urothelial cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 2018; 214:1074–80.
22. Jensen HK, Donskov F, Marcussen N, Nordsmark M, Lundbeck F, von der Maase H. Presence of intratumoral neutrophils is an independent prognostic factor in localized renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:4709–17.
23. Trellakis S, Bruderek K, Dumitru CA, et al. Polymorphonuclear granulocytes in human head and neck cancer: enhanced inflammatory activity, modulation by cancer cells and expansion in advanced disease. Int J Cancer. 2011; 129:2183–93.
24. Naso JR, Topham JT, Karasinska JM, et al. Tumor infiltrating neutrophils and gland formation predict overall survival and molecular subgroups in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 2021; 10:1155–65.
25. Lin C, Lin W, Yeh S, Li L, Chang C. Infiltrating neutrophils increase bladder cancer cell invasion via modulation of androgen receptor (AR)/MMP13 signals. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:43081–9.
26. Joseph M, Enting D. Immune responses in bladder cancer-role of immune cell populations, prognostic factors and therapeutic implications. Front Oncol. 2019; 9:1270.
27. Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. 2011; 331:1565–70.
28. Kim HS, Ku JH. Prognostic impact of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in bladder urothelial carcinoma. Transl Androl Urol. 2019; 8(Suppl 3):S291–2.
29. Rouanne M, Betari R, Radulescu C, et al. Stromal lymphocyte infiltration is associated with tumour invasion depth but is not prognostic in high-grade T1 bladder cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2019; 108:111–9.
30. Pichler R, Fritz J, Zavadil C, Schafer G, Culig Z, Brunner A. Tumor-infiltrating immune cell subpopulations influence the oncologic outcome after intravesical bacillus Calmette-Guerin therapy in bladder cancer. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:39916–30.
31. Masson-Lecomte A, Maille P, Pineda S, et al. CD8+ cytotoxic immune infiltrate in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a standardized methodology to study association with clinico-pathological features and prognosis. Bladder Cancer. 2019; 5:159–69.
32. Li F, Li C, Cai X, et al. The association between CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and the clinical outcome of cancer immunotherapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. EClinicalMedicine. 2021; 41:101134.
33. Faraj SF, Munari E, Guner G, et al. Assessment of tumoral PD-L1 expression and intratumoral CD8+ T cells in urothelial carcinoma. Urology. 2015; 85:703.
34. Hulsen S, Lippolis E, Ferrazzi F, et al. High stroma T-cell infiltration is associated with better survival in stage pT1 bladder cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21:8407.
35. Zhang Q, Hao C, Cheng G, et al. High CD4(+) T cell density is associated with poor prognosis in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8:11510–6.
36. Yu A, Mansure JJ, Solanki S, et al. Presence of lymphocytic infiltrate cytotoxic T lymphocyte CD3+, CD8+, and immunoscore as prognostic marker in patients after radical cystectomy. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0205746.
37. Shi MJ, Meng XY, Wu QJ, Zhou XH. High CD3D/CD4 ratio predicts better survival in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2019; 11:2987–95.
38. Favilla V, Castelli T, Urzi D, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, a biomarker in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: a single-institutional longitudinal study. Int Braz J Urol. 2016; 42:685–93.
39. Kawahara T, Furuya K, Nakamura M, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic marker in bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy. BMC Cancer. 2016; 16:185.
40. Tazeh NN, Canter DJ, Damodaran S, et al. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) at the time of transurethral eesection of bladder tumor: a large retrospective study and analysis of racial differences. Bladder Cancer. 2017; 3:89–94.
41. Mandelli GE, Missale F, Bresciani D, et al. Tumor infiltrating neutrophils are enriched in basal-type urothelial bladder cancer. Cells. 2020; 9:291.
42. Nukui A, Kamai T, Arai K, et al. Association of cancer progression with elevated expression of programmed cell death protein 1 ligand 1 by upper tract urothelial carcinoma and increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020; 69:689–702.
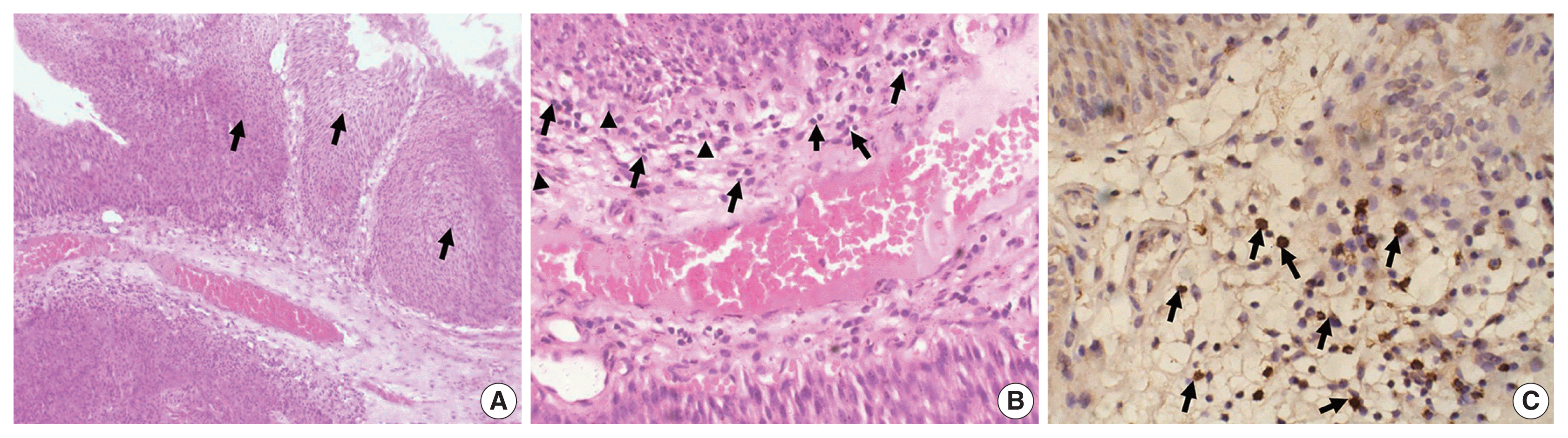
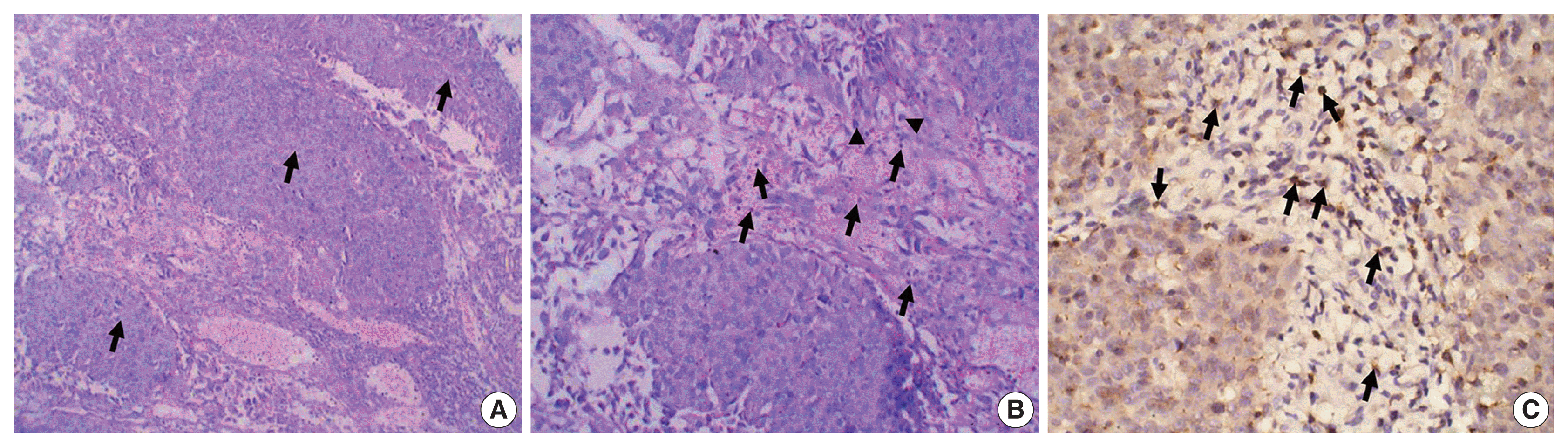
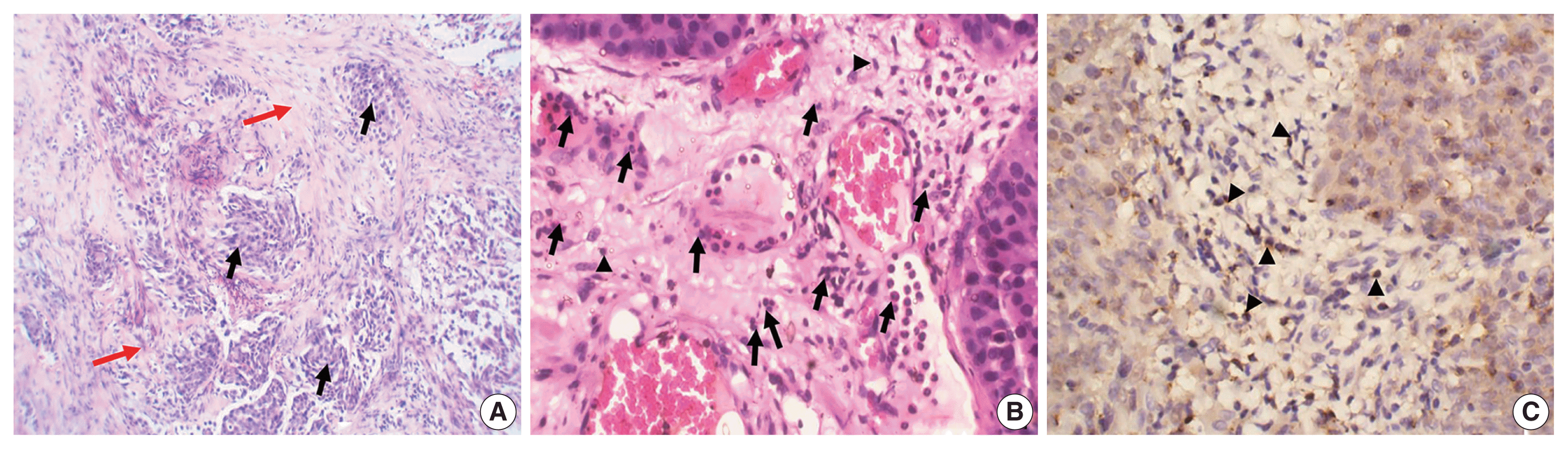




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download