1. Gallo LG, Oliveira AF, Abrahao AA, et al. Ten epidemiological parameters of COVID-19: use of rapid literature review to inform predictive models during the pandemic. Front Public Health. 2020; 8:598547.
2. Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA. 2020; 323:1775–6.
4. Schwab N, Nienhold R, Henkel M, et al. COVID-19 autopsies reveal underreporting of SARS-CoV-2 infection and scarcity of co-infections. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022; 9:868954.
5. Grande E, Fedeli U, Pappagallo M, et al. Variation in cause-specific mortality rates in Italy during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic: a study based on nationwide data. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022; 19:805.
6. Sessa F, Bertozzi G, Cipolloni L, et al. Clinical-forensic autopsy findings to defeat COVID-19 disease: a literature review. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:2026.
7. Maiese A, Manetti AC, La Russa R, et al. Autopsy findings in COVID-19-related deaths: a literature review. Forensic Sci Med Pathol. 2021; 17:279–96.
8. Kim MY, Cheong H, Kim HS; Working Group for Standard Autopsy Guideline for COVID-19 from the Korean Society for Legal Medicine. Proposal of the autopsy guideline for infectious diseases: preparation for the post-COVID-19 era (abridged translation). J Korean Med Sci. 2020; 35:e310.
9. Salerno M, Sessa F, Piscopo A, et al. No autopsies on COVID-19 deaths: a missed opportunity and the lockdown of science. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:1472.
10. Filograna L, Manenti G, Grassi S, et al. Virtual autopsy in SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection: a case report. Forensic Imaging. 2022; 30:200520.
11. De-Giorgio F, Grassi VM, Bergamin E, et al. Dying “from” or “with” COVID-19 during the pandemic: medico-legal issues according to a population perspective. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18:8851.
12. Esposito M, Salerno M, Scoto E, Di Nunno N, Sessa F. The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the practice of forensic medicine: an overview. Healthcare (Basel). 2022; 10:319.
13. Filograna L, Manenti G, Arena V, et al. Claimed medical malpractice in fatal SARS-CoV-2 infections: the importance of combining ante- and post-mortem radiological data and autopsy findings for correct forensic analysis. Forensic Imaging. 2021; 25:200454.
14. Rakislova N, Marimon L, Ismail MR, et al. Minimally invasive autopsy practice in COVID-19 cases: biosafety and findings. Pathogens. 2021; 10:412.
15. Harapan H, Itoh N, Yufika A, et al. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a literature review. J Infect Public Health. 2020; 13:667–73.
16. Sah P, Fitzpatrick MC, Zimmer CF, et al. Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021; 118:e2109229118.
17. Wiersinga WJ, Rhodes A, Cheng AC, Peacock SJ, Prescott HC. Pathophysiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review. JAMA. 2020; 324:782–93.
18. Grippo F, Navarra S, Orsi C, et al. The role of COVID-19 in the death of SARS-CoV-2-positive patients: a study based on death certificates. J Clin Med. 2020; 9:3459.
19. Slater TA, Straw S, Drozd M, Kamalathasan S, Cowley A, Witte KK. Dying ‘due to’ or ‘with’ COVID-19: a cause of death analysis in hospitalised patients. Clin Med (Lond). 2020; 20:e189–90.
20. Giorgetti A, Orazietti V, Busardo FP, Pirani F, Giorgetti R. Died with or died of? Development and testing of a SARS CoV-2 significance score to assess the role of COVID-19 in the deaths of affected patients. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021; 11:190.
21. Sperhake JP. Autopsies of COVID-19 deceased? Absolutely! Leg Med (Tokyo). 2020; 47:101769.
22. Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020; 181:271–80.
23. Gupta A, Madhavan MV, Sehgal K, et al. Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19. Nat Med. 2020; 26:1017–32.
24. Abou-Ismail MY, Diamond A, Kapoor S, Arafah Y, Nayak L. The hypercoagulable state in COVID-19: Incidence, pathophysiology, and management. Thromb Res. 2020; 194:101–15.
25. Nishiga M, Wang DW, Han Y, Lewis DB, Wu JC. COVID-19 and cardiovascular disease: from basic mechanisms to clinical perspectives. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2020; 17:543–58.
26. Bohn MK, Mancini N, Loh TP, et al. IFCC interim guidelines on molecular testing of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2020; 58:1993–2000.
27. Pan Y, Li X, Yang G, et al. Serological immunochromatographic approach in diagnosis with SARS-CoV-2 infected COVID-19 patients. J Infect. 2020; 81:e28–32.
28. Brahim Belhaouari D, Fontanini A, Baudoin JP, et al. The strengths of scanning electron microscopy in deciphering SARS-CoV-2 infectious cycle. Front Microbiol. 2020; 11:2014.
29. Hanley B, Lucas SB, Youd E, Swift B, Osborn M. Autopsy in suspected COVID-19 cases. J Clin Pathol. 2020; 73:239–42.
30. Schaller T, Hirschbuhl K, Burkhardt K, et al. Postmortem examination of patients with COVID-19. JAMA. 2020; 323:2518–20.
31. Satturwar S, Fowkes M, Farver C, et al. Postmortem findings associated with SARS-CoV-2: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2021; 45:587–603.
32. Shatarat A, Alzghoul L, Al-Qattan D, Elbeltagy M. Anatomical and ultrastructural sex differences in mean diameter and thickness of myelinated axons in adult rat corpus callosum. Int J Morphol. 2020; 38:505–12.
33. Nurhayati N, Purnama TB. Funeral processes during the COVID-19 pandemic: perceptions among Islamic religious leaders in Indonesia. J Relig Health. 2021; 60:3418–33.
35. Grassi S, Arena V, Cattani P, et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral load and replication in postmortem examinations. Int J Legal Med. 2022; 136:935–9.
36. Sallam M, Dababseh D, Yaseen A, et al. COVID-19 misinformation: mere harmless delusions or much more? A knowledge and attitude cross-sectional study among the general public residing in Jordan. PLoS One. 2020; 15:e0243264.
37. Youd E, Moore L. COVID-19 autopsy in people who died in community settings: the first series. J Clin Pathol. 2020; 73:840–4.
38. Elezkurtaj S, Greuel S, Ihlow J, et al. Causes of death and comorbidities in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:4263.
39. Remmelink M, De Mendonca R, D’Haene N, et al. Unspecific postmortem findings despite multiorgan viral spread in COVID-19 patients. Crit Care. 2020; 24:495.
40. Bradley BT, Maioli H, Johnston R, et al. Histopathology and ultrastructural findings of fatal COVID-19 infections in Washington State: a case series. Lancet. 2020; 396:320–32.
41. Barton LM, Duval EJ, Stroberg E, Ghosh S, Mukhopadhyay S. COVID-19 autopsies, Oklahoma, USA. Am J Clin Pathol. 2020; 153:725–33.
42. Edler C, Schroder AS, Aepfelbacher M, et al. Dying with SARS-CoV-2 infection-an autopsy study of the first consecutive 80 cases in Hamburg, Germany. Int J Legal Med. 2020; 134:1275–84.
43. The COVID-19 Autopsy. The first COVID-19 autopsy in Spain performed during the early stages of the pandemic. Rev Esp Patol. 2020; 53:182–7.
44. Carsana L, Sonzogni A, Nasr A, et al. Pulmonary post-mortem findings in a series of COVID-19 cases from northern Italy: a two-centre descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020; 20:1135–40.
45. Ding Y, Wang H, Shen H, et al. The clinical pathology of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): a report from China. J Pathol. 2003; 200:282–9.
46. Menter T, Haslbauer JD, Nienhold R, et al. Postmortem examination of COVID-19 patients reveals diffuse alveolar damage with severe capillary congestion and variegated findings in lungs and other organs suggesting vascular dysfunction. Histopathology. 2020; 77:198–209.
47. Sadegh Beigee F, Pourabdollah Toutkaboni M, Khalili N, et al. Diffuse alveolar damage and thrombotic microangiopathy are the main histopathological findings in lung tissue biopsy samples of COVID-19 patients. Pathol Res Pract. 2020; 216:153228.
48. Caramaschi S, Kapp ME, Miller SE, et al. Histopathological findings and clinicopathologic correlation in COVID-19: a systematic review. Mod Pathol. 2021; 34:1614–33.
49. Zuin M, Engelen MM, Bilato C, et al. Prevalence of acute pulmonary embolism at autopsy in patients with COVID-19. Am J Cardiol. 2022; 171:159–64.
50. Lax SF, Skok K, Zechner P, et al. Pulmonary arterial thrombosis in COVID-19 with fatal outcome: results from a prospective, single-center, clinicopathologic case series. Ann Intern Med. 2020; 173:350–61.
51. Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Evans SJ, et al. Factors associated with deaths due to COVID-19 versus other causes: population-based cohort analysis of UK primary care data and linked national death registrations within the OpenSAFELY platform. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2021; 6:100109.
52. Niforatos JD, Melnick ER, Faust JS. Covid-19 fatality is likely overestimated. BMJ. 2020; 368:m1113.
53. Sallam M, Mahafzah A. Molecular analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genetic lineages in Jordan: tracking the introduction and spread of COVID-19 UK variant of concern at a country level. Pathogens. 2021; 10:302.
54. Geller RL, Aungst JL, Newton-Levinson A, et al. Is it COVID-19? The value of medicolegal autopsies during the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic. Forensic Sci Int. 2022; 330:111106.
55. Schoene D, Schnekenberg LG, Pallesen LP, et al. Pathophysiology of cardiac injury in COVID-19 patients with acute ischaemic stroke: what do we know so far?: a review of the current literature. Life (Basel). 2022; 12:75.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



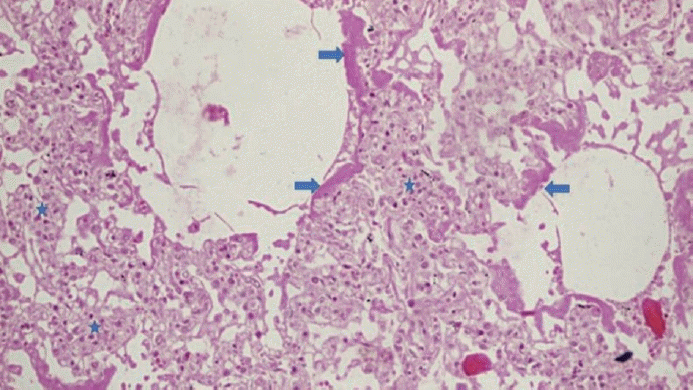
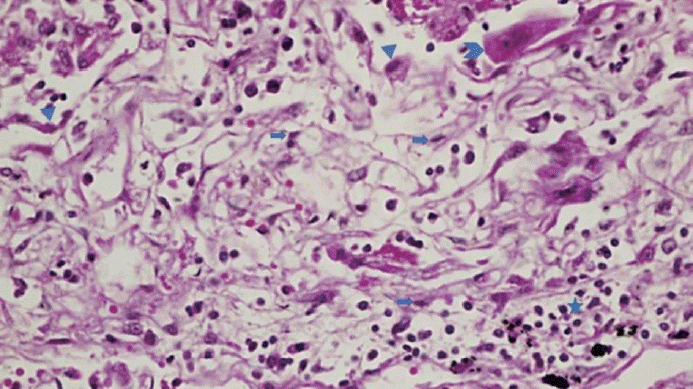
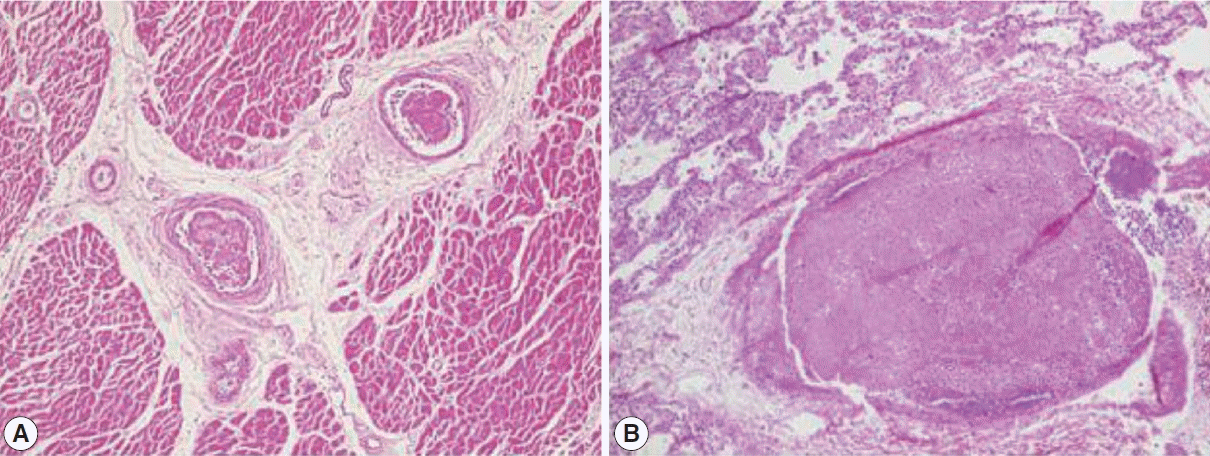
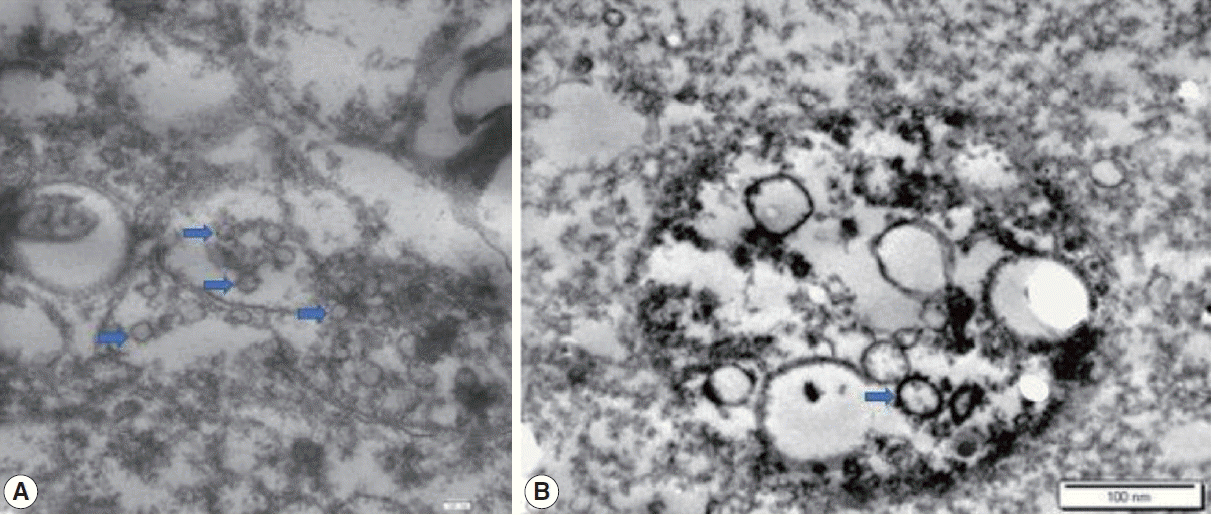
 XML Download
XML Download