INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Cell culture and treatment
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction
Real-time PCR
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Western blot
Immunofluorescence staining
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
The presence of GHSR1a in HNEpCs
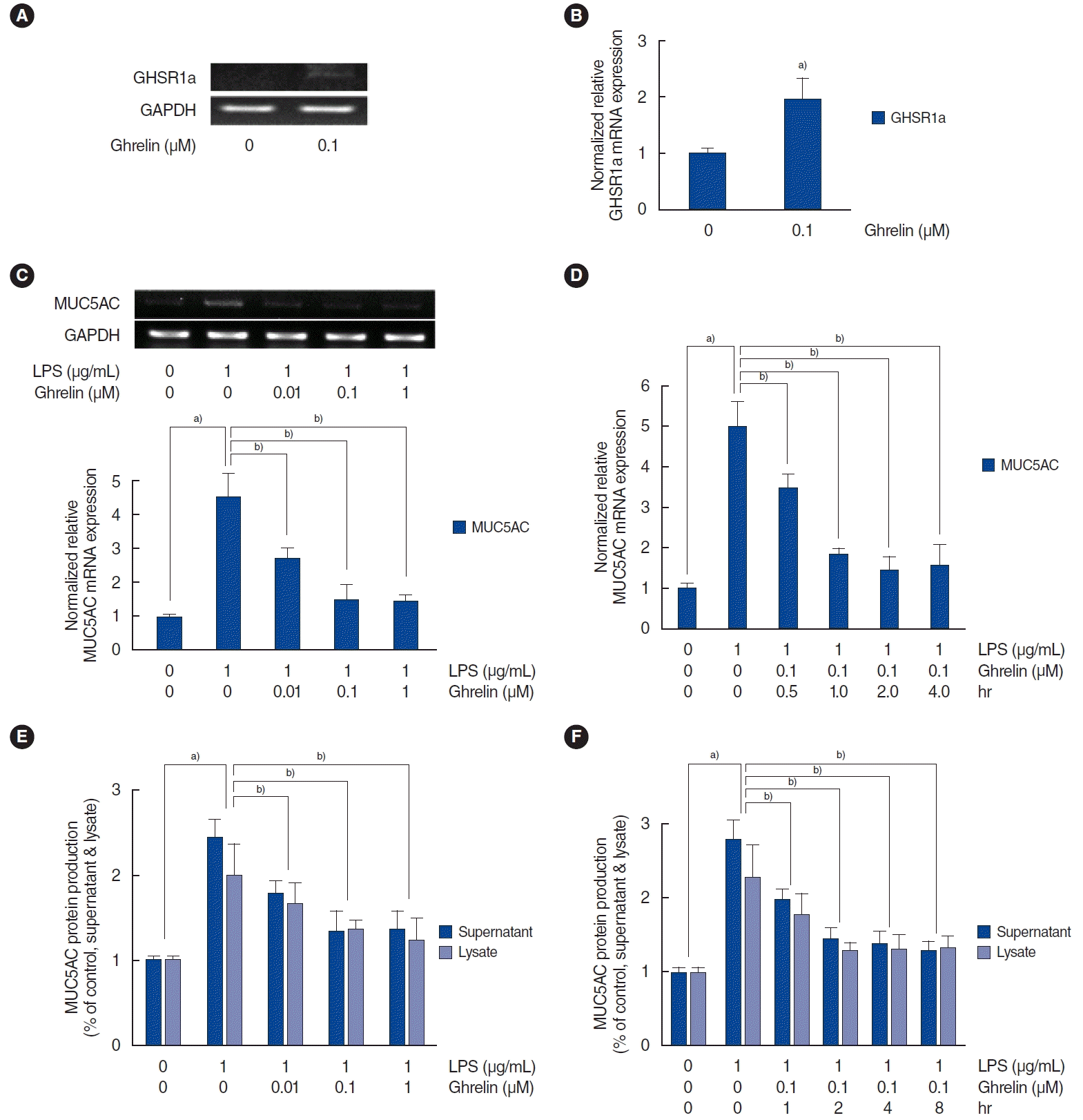 | Fig. 1.Effect of ghrelin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced MUC5AC expression in human nasal epithelial cells. (A, B) The results of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real-time PCR show that ghrelin significantly induced GHSR1a messenger RNA (mRNA) expression. (C) The results of RT-PCR and real-time PCR show that ghrelin significantly inhibited LPS-induced MUC5AC mRNA expression. LPS-induced MUC5AC expression started to be maximally suppressed at ta ghrelin concentration of 0.1 μM. (D) The results of real-time PCR show that the maximal inhibition of LPS-induced MUC5AC mRNA expression by ghrelin (0.1 μM) occurred after 2 hours. (E, F) The results of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay also show that ghrelin significantly inhibited LPS-induced MUC5AC protein production. The images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate. The bars indicate the mean±standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. GHSR1a, growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. a)P<0.05 compared to the baseline value. b)P<0.05 is compared with samples treated with LPS (1 μg/mL) alone. |
The dose- and time-dependent effects of ghrelin on LPS-induced
The inhibitory mechanism of ghrelin on LPS-induced MUC5AC in HNEpCs
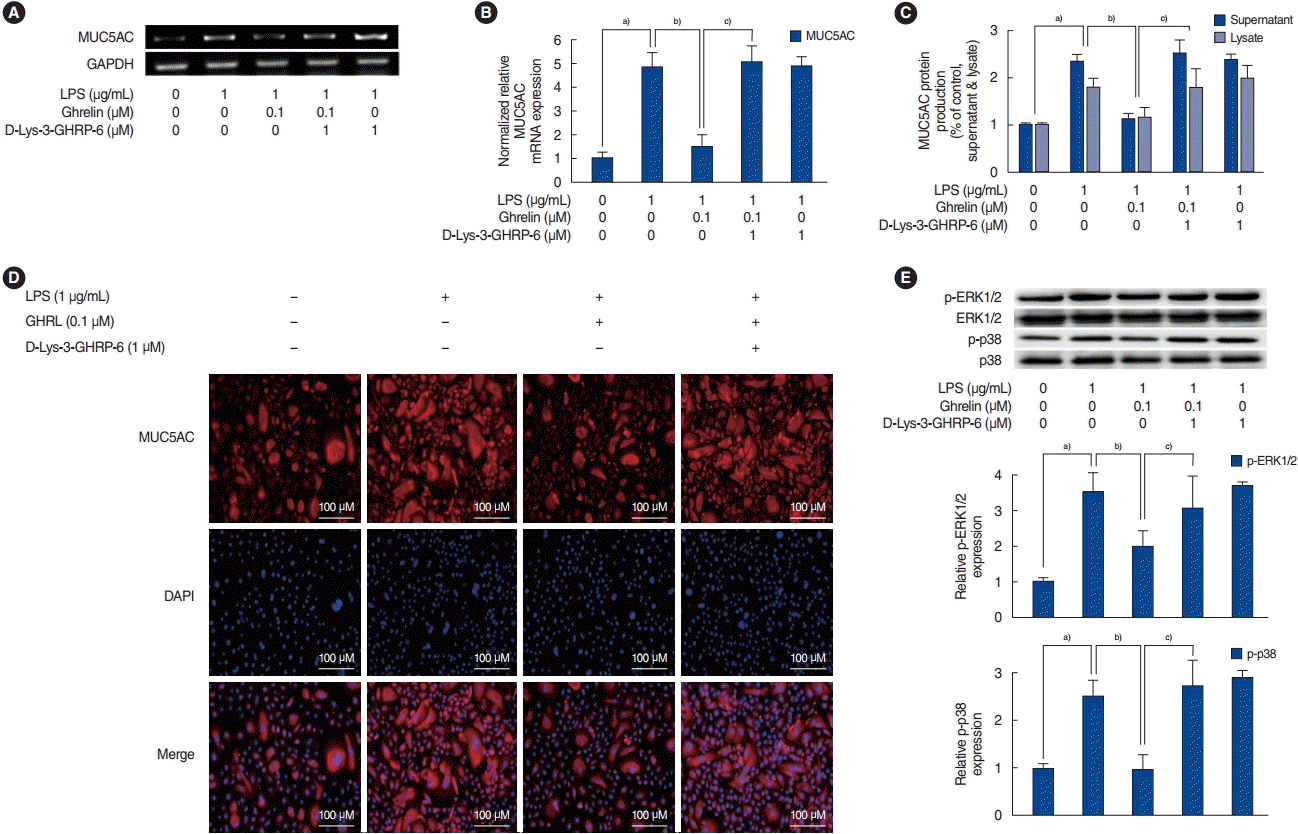 | Fig. 2.The regulatory mechanism of ghrelin on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced MUC5AC expression in human nasal epithelial cells. (A, B) The results of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real-time PCR show that ghrelin inhibited LPS-induced MUC5AC expression, and this inhibition was abolished by D-Lys-3-growth hormone-releasing peptide 6 (D-Lys-3-GHRP-6). (C, D) The results of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunofluorescence staining also show that ghrelin significantly inhibited LPS-induced MUC5AC protein production, while the inhibitory effect of LPS-induced MUC5AC protein production was abolished by D-Lys-3-GHRP-6. (E) Western blot results show that ghrelin significantly inhibited LPS-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). These ghrelin-mediated changes in MAPK activation were also abolished by D-Lys-3-GHRP-6. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI, 4´,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; p-ERK1/2, phosphorylated ERK 1/2; p-p38, phosphorylated p38. a)P<0.05 compared to the baseline value. b)P<0.05 compared with samples treated with LPS (1 μg/mL) alone. c)P<0.05 compared to samples treated with LPS (1 μg/mL) and ghrelin (0.1 μM). |
The effect of ghrelin on leptin-induced MUC5AC in HNEpCs
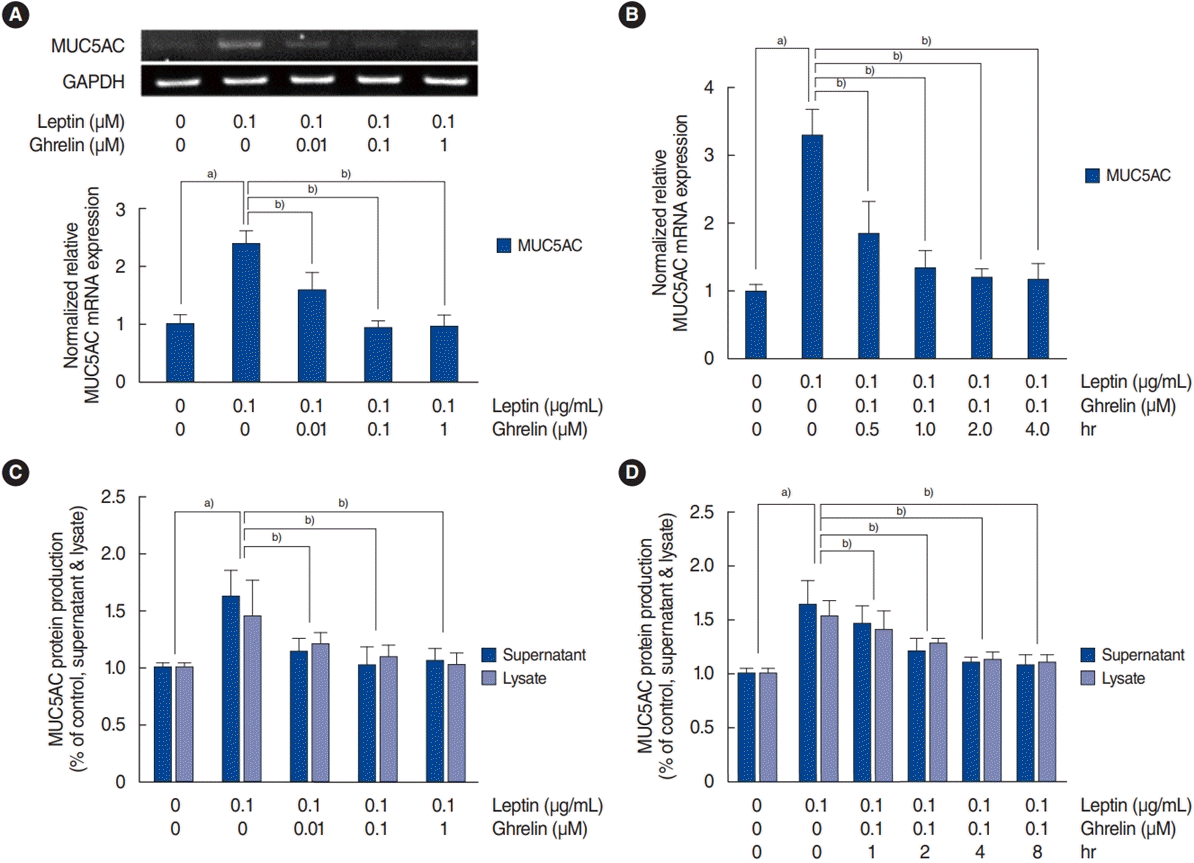 | Fig. 3.Effect of ghrelin on leptin-induced MUC5AC expression in human nasal epithelial cells. (A) The results of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real-time PCR show that ghrelin significantly inhibited leptin-induced MUC5AC mRNA expression. Leptin-induced MUC5AC expression started to be maximally suppressed at a ghrelin concentration of 0.1 μM. (B) Real-time PCR results show that the maximal inhibition of leptin-induced MUC5AC mRNA expression by ghrelin (0.1 μM) occurred after 2 hours. (C, D) The results of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay also showed that ghrelin significantly inhibited leptin-induced MUC5AC protein production. The images are representative of three separate experiments performed in triplicate. The bars indicate the mean±standard deviation of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. a)P<0.05 compared to the baseline value. b)P<0.05 compared with samples treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 1 μg/mL) alone. |
The inhibitory mechanism of ghrelin in leptin-induced MUC5AC in HNEpCs
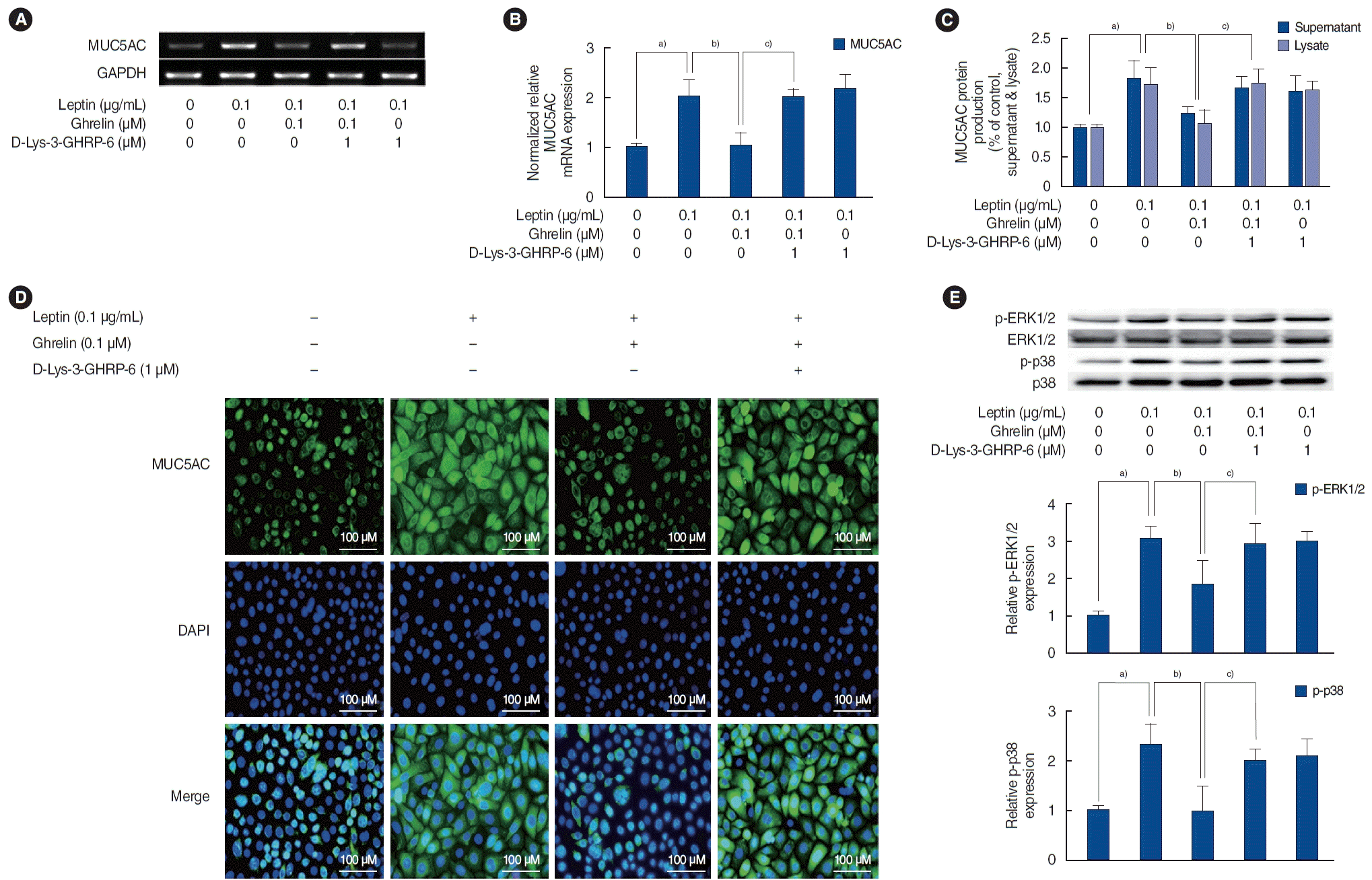 | Fig. 4.The regulatory mechanism of ghrelin in leptin-induced MUC5AC in human nasal epithelial cells. (A, B) The results of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real-time PCR show that ghrelin inhibited leptin-induced MUC5AC expression, and this inhibition was abolished by D-Lys-3-growth hormone-releasing peptide 6 (D-Lys-3-GHRP-6). (C, D) The results of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunofluorescence staining also show that ghrelin significantly inhibited leptin-induced MUC5AC protein production, while the inhibitory effect of leptin-induced MUC5AC protein production was abolished by D-Lys-3-GHRP-6. (E) Western blot results show that ghrelin significantly inhibited leptin-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs). These ghrelin-mediated changes in MAPK activation were also abolished by D-Lys-3-GHRP-6. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; DAPI, 4´,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; p-ERK1/2, phosphorylated ERK 1/2; p-p38, phosphorylated p38. a)P<0.05 compared to the baseline value. b)P<0.05 compared to samples treated with leptin (0.1 μg/mL) alone. c)P<0.05 compared to samples treated with leptin (0.1 μg/mL) and ghrelin (0.1 μM). |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download