Introduction
Materials and Methods
Identification and marking the related bony structures on the base of the skulls
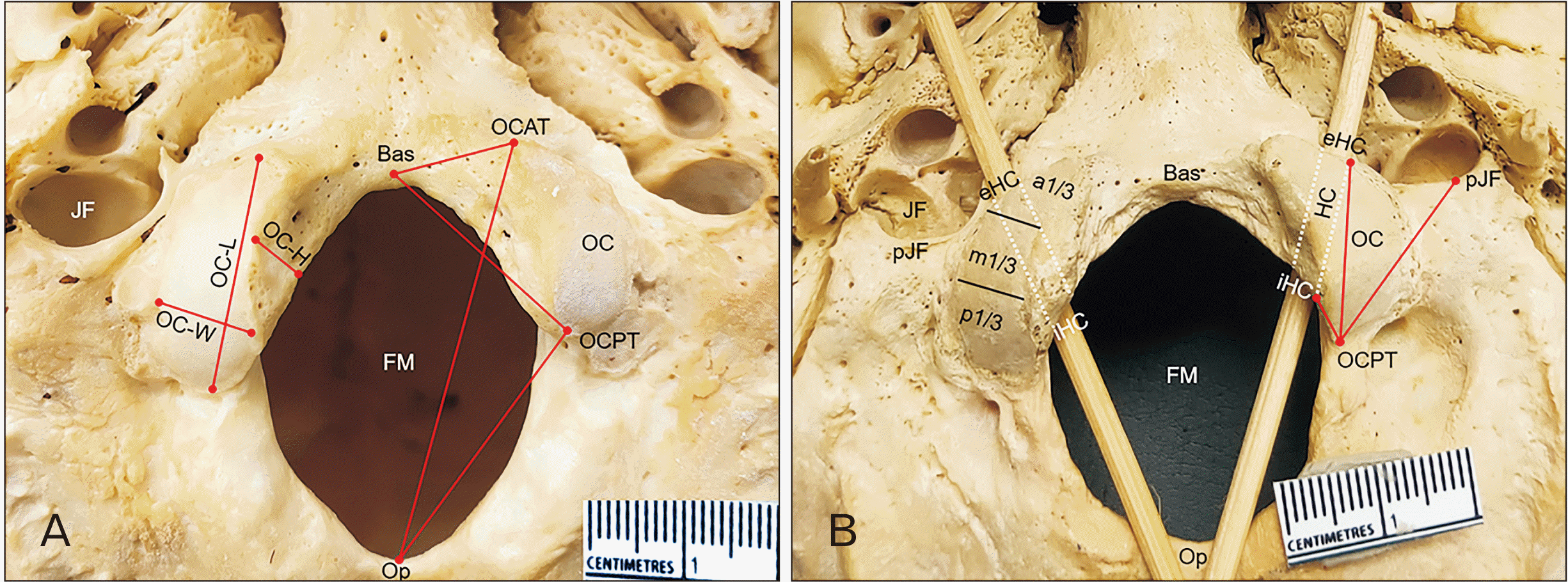 | Fig. 1Inferior view of the skull base. (A) Right occipital condyle showing occipital condyle width (OC-W), occipital condyle length (OC-L), and occipital condyle height (OC-H). Left occipital condyle showing the distances from anterior and posterior tips of occipital condyle (OCAT and OCPT) to basion (Bas) and opisthion (Op). (B) Right occipital condyle showing the relationship of jugular foramen (JF) and occipital condyle, the location of extracranial orifice and intracranial orifice of hypoglossal canal (L-eHC, L-iHC) related to occipital condyle. Left occipital condyle showing the distances from posterior tip of occipital condyle (OCPT) to iHC, eHC and posterior most end of jugular foramen (pJF). FM, foramen magnum; HC, hypoglossal canal; a1/3, anterior one third; m1/3, middle one third; p1/3, posterior one third. |
Morphological analysis of the shape of OC, location of iHC and eHc, JF-OC relationship
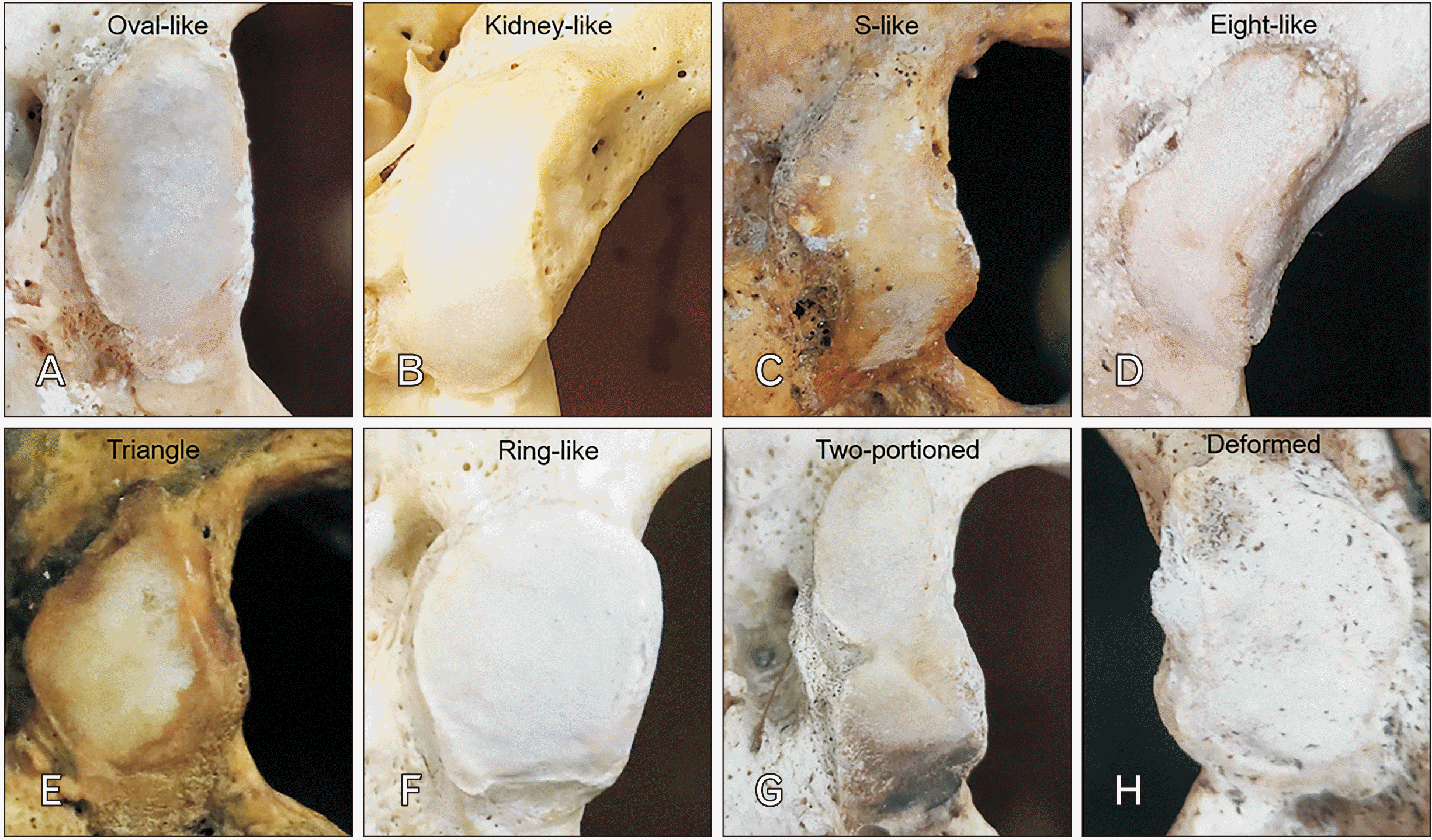 | Fig. 2Photographs showing eight shapes of occipital condyle. (A) Type I, oval-like condyle. (B) Type II, kidney-like condyle. (C) Type III, S-like condyle. (D) Type IV, eight-like condyle. (E) Type V, triangle condyle. (F) Type VI, ring-like condyle. (G) Type VII, two-portioned condyle, and (H) Type VIII, deformed condyle. |
Morphometric evaluations of the OC dimensions, distance from iHC and eHC to OCPT, distance from OCAT to Op and Bas, distance from OCPT to Op and Bas, and distance of OCPT to pJF
Statistical analysis
Results
Shapes and dimension of the OC
Table 1
| Types | Number of occipital condyles | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males (n=100) | Females (n=100) | Both sexes (n=200) | ||||||||||
| Left | Right | Total | P-value | Left | Right | Total | P-value | Total | P-value | |||
| I | 14 (14.0) | 11 (11.0) | 25 (25.0) | 0.886 | 23 (23.0) | 18 (18.0) | 41 (41.0) | 0.757 | 66 (33.0) | 0.037a | ||
| II | 4 (4.0) | 7 (7.0) | 11 (11.0) | 9 (9.0) | 7 (7.0) | 16 (16.0) | 27 (13.5) | |||||
| III | 13 (13.0) | 13 (13.0) | 26 (26.0) | 6 (6.0) | 8 (8.0) | 14 (14.0) | 40 (20.0) | |||||
| IV | 6 (6.0) | 4 (4.0) | 10 (10.0) | 1 (1.0) | 3 (3.0) | 4 (4.0) | 14 (7.0) | |||||
| V | 7 (7.0) | 8 (8.0) | 15 (15.0) | 9 (9.0) | 10 (10.0) | 19 (19.0) | 34 (17.0) | |||||
| VI | - | 1 (1.0) | 1 (1.0) | - | 1 (1.0) | 1 (1.0) | 2 (1.0) | |||||
| VII | 3 (3.0) | 2 (2.0) | 5 (5.0) | - | 1 (1.0) | 1 (1.0) | 6 (3.0) | |||||
| VIII | 3 (3.0) | 4 (4.0) | 7 (7.0) | 2 (2.0) | 2 (2.0) | 4 (4.0) | 11 (5.5) | |||||
| Total | 50 (50.0) | 50 (50.0) | 100 (100.0) | 50 (50.0) | 50 (50.0) | 100 (100.0) | 200 (100.0) | |||||
Values are presented as number (%). OC, occipital condyle; Type I, oval-like condyle; type II, kidney-like condyle; type III, S-like condyle; type IV, eight-like condyle; type V, triangle condyle; type VI, ring-like condyle; type VII, two-portioned condyle; type VIII, deformed condyle. aStatistically significant difference between group.
Table 2
| Parameters | Both sexes | P-value | Males | P-value | Females | P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left (n=50 sides) | Right (n=50 sides) | Total (n=100 sides) | Left (n=50 sides) | Right (n=50 sides) | Total (n=100 sides) | |||||
| (n=200 sides) | ||||||||||
| OC-L (mm) |
21.3±2.4 (16.0–28.8) |
<0.001a |
22.1±2.5 (18.2–28.8) |
22.2±2.6 (18.2–28.3) |
22.1±2.5 (18.2–28.8) |
0.745 |
20.3±2.0 (16.0–24.8) |
20.7±2.2 (16.4–26.0) |
20.5±2.1 (16.0–26.0) |
0.220 |
| OC-W (mm) |
10.5±1.4 (7.4–15.1) |
0.294 |
10.3±1.4 (7.4–15.1) |
10.5±1.6 (7.7–14.6) |
10.4±1.5 (7.4–15.1) |
0.394 |
10.6±1.2 (7.4–13.6) |
10.7±1.5 (8.2–13.7) |
10.6±1.3 (7.4–13.7) |
0.766 |
| OC-H (mm) |
7.4±1.1 (4.5–10.8) |
0.484 |
7.3±1.1 (5.2–10.3) |
7.6±1.2 (5.5–10.8) |
7.5±1.1 (5.2–10.8) |
0.024a |
7.1±1.2 (4.5–9.5) |
7.5±1.1 (5.3–9.7) |
7.3±1.1 (4.5–9.7) |
0.003a |
| OCAT-Bas (mm) |
11.5±1.4 (8.3–15.9) |
0.961 |
11.7±1.6 (8.3–15.9) |
11.3±1.4 (8.6–14.8) |
11.5±1.5 (8.3–15.9) |
0.137 |
11.6±1.3 (8.8–14.3) |
11.4±1.4 (8.6–14.3) |
11.5±1.4 (8.6–14.3) |
0.271 |
| OCAT-Op (mm) |
39.1±3.3 (24.5–47.5) |
<0.001a |
40.3±2.9 (34.7–47.5) |
39.9±2.8 (33.8–46.3) |
40.1±2.8 (33.8–47.5) |
0.091 |
38.2±3.5 (24.5–44.1) |
38.1±3.3 (28.1–44.3) |
38.1±3.4 (24.5–44.3) |
0.658 |
| OCPT-Bas (mm) |
25.2±2.2 (19.9–32.3) |
0.047a |
25.3±2.3 (20.4–31.2) |
25.7±2.2 (21.7–31.6) |
25.5±2.3 (20.4–31.6) |
0.090 |
24.6±2.1 (19.9–29.5) |
25.2±2.1 (20.2–32.3) |
24.9±2.1 (19.9–32.3) |
0.029a |
| OCPT-Op (mm) |
27.4±2.7 (21.2–35.5) |
0.680 |
27.5±3.0 (21.5–35.5) |
27.5±2.8 (21.5–34.4) |
27.5±2.9 (21.5–35.5) |
0.976 |
27.1±2.4 (23.1–32.1) |
27.5±2.6 (21.2–32.0) |
27.3±2.5 (21.2–32.6) |
0.310 |
| OCPT-iHC (mm) |
9.0±1.6 (4.4–12.4) |
0.138 |
9.1±1.4 (6.2–12.2) |
9.3±1.7 (5.5–12.0) |
9.2±1.6 (5.5–12.2) |
0.332 |
8.6±1.7 (4.4–12.1) |
9.0±1.6 (6.2–12.4) |
8.8±1.6 (4.4–12.4) |
0.023a |
| OCPT-eHC (mm) |
13.7±2.2 (7.0–18.7) |
0.011a |
14.2±2.0 (9.4–18.4) |
14.0±2.0 (8.7–17.2) |
14.1±2.0 (8.7–18.4) |
0.604 |
13.1±2.2 (7.0–18.7) |
13.5±2.6 (8.4–18.0) |
13.3±2.4 (7.0–18.7) |
0.189 |
| OCPT-pJF (mm) |
16.2±2.4 (9.3–21.6) |
0.164 |
16.7±2.4 (12.0–21.6) |
16.1±2.2 (10.3–20.1) |
16.4±2.3 (10.3–21.6) |
0.091 |
16.1±1.8 (12.3–20.7) |
15.8±2.9 (9.3–21.5) |
15.9±2.4 (9.3–21.5) |
0.485 |
Values are presented as mean±SD (range). OC, occipital condyle; iHC, intracranial orifice of hypoglossal canal; eHC, extracranial orifice of hypoglossal canal; JF, jugular foramen; OC-L, occipital condyle length; OC-W, occipital condyle width; OC-H, occipital condyle height; OCAT-Bas, distance from the anterior tip of occipital condyle to basion; OCAT-Op, distance from the anterior tip of occipital condyle to opisthion; OCPT-Bas, distance from the posterior tip of occipital condyle to basion; OCPT-Op, distance from the posterior tip of occipital condyle to opisthion; OCPT-iHC, distances from posterior tip of occipital condyle to intracranial orifice of hypoglossal canal; OCPT-eHC, distances from posterior tip of occipital condyle to extracranial orifice of hypoglossal canal; OCPT-pJF, distance from the posterior tip of occipital condyle to the posterior most end of jugular foramen. aStatistically significant difference between group.
Table 3
| Types | Classification of occipital condyle according to its length | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males (n=100 condyles) | Females (n=100 condyles) | Both sexes (n=200 condyles) | P-value | ||||||
| Left | Right | Total | Left | Right | Total | ||||
| Short | 12 (12.0) | 13 (13.0) | 25 (25.0) | 21 (21.0) | 20 (20.0) | 41 (41.0) | 66 (33.0) | 0.001a | |
| Moderate | 34 (34.0) | 32 (32.0) | 66 (66.0) | 29 (29.0) | 30 (30.0) | 59 (59.0) | 125 (62.5) | ||
| Long | 4 (4.0) | 5 (5.0) | 9 (9.0) | - | - | - | 9 (4.5) | ||
| Total | 50 (50.0) | 50 (50.0) | 100 (100.0) | 50 (50.0) | 50 (50.0) | 100 (100.0) | 200 (100.0) | ||
Locations of HC and its distance to OC
Table 4
| Locations | iHC | eHC | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Males (N=100 canals) | Females (N=100 canals) | Males (N=100 canals) | Females (N=100 canals) | ||||||||||||||||
| Left | Right | Total | P-value | Left | Right | Total | P-value | Left | Right | Total | P-value | Left | Right | Total | P-value | ||||
| 1 |
3 (3.0) |
4 (4.0) |
7 (7.0) |
<0.001a |
3 (3.0) |
3 (3.0) |
6 (6.0) |
0.292 |
43 (43.0) |
33 (33.0) |
76 (76.0) |
0.058 |
38 (38.0) |
34 (34.0) |
72 (72.0) |
0.585 | |||
| 2 |
9 (9.0) |
28 (28.0) |
37 (37.0) |
13 (13.0) |
22 (22.0) |
35 (35.0) |
6 (6.0) |
13 (13.0) |
19 (19.0) |
10 (10.0) |
12 (12.0) |
22 (22.0) |
|||||||
| 3 |
29 (29.0) |
17 (17.0) |
46 (46.0) |
25 (25.0) |
19 (19.0) |
44 (44.0) |
1 (1.0) |
4 (4.0) |
5 (5.0) |
2 (2.0) |
4 (4.0) |
6 (6.0) |
|||||||
| 4 |
9 (9.0) |
1 (1.0) |
10 (10.0) |
9 (9.0) |
6 (6.0) |
15 (15.0) |
- | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 5 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| Total |
50 (50.0) |
50 (50.0) |
100 (100.0) |
50 (50.0) |
50 (50.0) |
100 (100.0) |
50 (50.0) |
50 (50.0) |
100 (100.0) |
50 (50.0) |
50 (50.0) |
100 (100.0) |
|||||||
Values are presented as number (%). iHC, intracranial orifice of hypoglossal canal; eHC, extracranial orifice of hypoglossal canal; OC, occipital condyle; location 1, anterior 1/3 of OC; location 2, junction between anterior and middle 1/3 of OC; location 3, middle 1/3 of OC; location 4, junction between middle and posterior 1/3 of OC, location 5, posterior 1/3 of OC; –, none. aStatistically significant difference between groups.
The relation and distance between OC and JF
Table 5
| JF in relation to OC | Males (n=100 foramens) | Females (n=100 foramens) | Both sexes (n=200 foramens) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left | Right | Total | P-value | Left | Right | Total | P-value | |||
| a1/3 | 15 (15.0) | 2 (2.0) | 17 (17.0) | 0.001a | 6 (6.0) | 2 (2.0) | 8 (8.0) | 0.165 | 25 (12.5) | |
| a2/3 | 35 (35.0) | 45 (45.0) | 80 (80.0) | 41 (41.0) | 41 (41.0) | 82 (82.0) | 162 (81.0) | |||
| Entire OC length | - | 3 (3.0) | 3 (3.0) | 3 (3.0) | 7 (7.0) | 10 (10.0) | 13 (6.5) | |||
| Total | 50 (50.0) | 50 (50.0) | 100 (100.0) | 50 (50.0) | 50 (50.0) | 100 (100.0) | 200 (100.0) | |||




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download