1. Picanco-Castro V, Gonçalves Pereira C, Swiech K, Ribeiro Malmegrim KC, Tadeu Covas D, Silveira Porto G. 2020; Emer-ging CAR T cell therapies: clinical landscape and patent technological routes. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 16:1424–1433. DOI:
10.1080/21645515.2019.1689744. PMID:
31702480. PMCID:
PMC7482707.
5. Moll G, Ankrum JA, Kamhieh-Milz J, Bieback K, Ringdén O, Volk HD, Geissler S, Reinke P. 2019; Intravascular mesenchymal stromal/stem cell therapy product diversification: time for new clinical guidelines. Trends Mol Med. 25:149–163. DOI:
10.1016/j.molmed.2018.12.006. PMID:
30711482.
6. Golchin A, Farahany TZ. 2019; Biological products: cellular therapy and FDA approved products. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 15:166–175. DOI:
10.1007/s12015-018-9866-1. PMID:
30623359.
7. Shukla V, Seoane-Vazquez E, Fawaz S, Brown L, Rodri-guez-Monguio R. 2019; The landscape of cellular and gene therapy products: authorization, discontinuations, and cost. Hum Gene Ther Clin Dev. 30:102–113. DOI:
10.1089/humc.2018.201. PMID:
30968714.
8. Xu J, Sim JW. 2018; Characteristics of corporate R&D investment in emerging markets: evidence from manufacturing industry in China and South Korea. Sustainability. 10:3002. DOI:
10.3390/su10093002.
9. Bas TG, Oliu Castillo C. 2016; Biosimilars in developed and developing East and Southeast Asian countries: Japan, South Korea, and Malaysia-overview, evolution, and regulations assessment. Biomed Res Int. 2016:5910403. DOI:
10.1155/2016/5910403. PMID:
27213153. PMCID:
PMC4860213.
10. Mendicino M, Fan Y, Griffin D, Gunter KC, Nichols K. 2019; Current state of U.S. Food and Drug Administration regulation for cellular and gene therapy products: potential cures on the horizon. Cytotherapy. 21:699–724. DOI:
10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.04.002. PMID:
31196820.
12. Izeta A, Herrera C, Mata R, Astori G, Giordano R, Herná-ndez C, Leyva L, Arias S, Oyonarte S, Carmona G, Cuende N. 2016; Cell-based product classification procedure: what can be done differently to improve decisions on borderline products? Cytotherapy. 18:809–815. DOI:
10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.03.292. PMID:
27209278.
13. Therapeutic Goods Administration, Department of Health, Australian Government. 2018. Intended use: interpretation of homologous use Australian Regulatory Guidelines for Biologicals (ARGB). Version 1.0. Commonwealth of Australia;Woden: DOI:
10.1016/j.jcyt.2016.03.292.
14. Schmidt C. 2011; FDA approves first cell therapy for wrinkle-free visage. Nat Biotechnol. 29:674–675. DOI:
10.1038/nbt0811-674. PMID:
21822225.
16. Falanga V, Faria K, Bollenbach T. Lanza R, Langer R, Vacanti J, editors. 2014. Bioengineered skin constructs. Prin-ciples of Tissue Engineering. 4th ed. Academic Press;London: p. 1619–1643. DOI:
10.1016/B978-0-12-398358-9.00077-X.
17. Bach PB, Giralt SA, Saltz LB. 2017; FDA approval of tisagenlecleucel: promise and complexities of a $475 000 cancer drug. JAMA. 318:1861–1862. DOI:
10.1001/jama.2017.15218. PMID:
28975266.
18. Ali S, Kjeken R, Niederlaender C, Markey G, Saunders TS, Opsata M, Moltu K, Bremnes B, Grønevik E, Muusse M, Håkonsen GD, Skibeli V, Kalland ME, Wang I, Buajordet I, Urbaniak A, Johnston J, Rantell K, Kerwash E, Schuessler-Lenz M, Salmonson T, Bergh J, Gisselbrecht C, Tzogani K, Papadouli I, Pignatti F. 2020; The European Medi-cines Agency review of kymriah (Tisagenlecleucel) for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and diffuse large B-Cell lymphoma. Oncologist. 25:e321–e327. DOI:
10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0233. PMID:
32043764. PMCID:
PMC7011647.
19. Patel S, Burga RA, Powell AB, Chorvinsky EA, Hoq N, McCormack SE, Van Pelt SN, Hanley PJ, Cruz CRY. 2019; Beyond CAR T cells: other cell-based immunotherapeutic strategies against cancer. Front Oncol. 9:196. DOI:
10.3389/fonc.2019.00196. PMID:
31024832. PMCID:
PMC6467966.
20. Upadhaya S, Yu JX, Shah M, Correa D, Partridge T, Campbell J. 2021; The clinical pipeline for cancer cell therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:503–504. DOI:
10.1038/d41573-021-00100-z. PMID:
34088999.
21. Roselli E, Faramand R, Davila ML. 2021; Insight into next-generation CAR therapeutics: designing CAR T cells to improve clinical outcomes. J Clin Invest. 131:e142030. DOI:
10.1172/JCI142030. PMID:
33463538. PMCID:
PMC7810492.
23. Hou B, Tang Y, Li W, Zeng Q, Chang D. 2019; Efficiency of CAR-T therapy for treatment of solid tumor in clinical trials: a meta-analysis. Dis Markers. 2019:3425291. DOI:
10.1155/2019/3425291. PMID:
30886654. PMCID:
PMC6388318.
24. Townsend MH, Bennion K, Robison RA, O'Neill KL. 2020; Paving the way towards universal treatment with allogenic T cells. Immunol Res. 68:63–70. DOI:
10.1007/s12026-020-09119-7. PMID:
32096010.
25. Alnaggar M, Xu Y, Li J, He J, Chen J, Li M, Wu Q, Lin L, Liang Y, Wang X, Li J, Hu Y, Chen Y, Xu K, Wu Y, Yin Z. 2019; Allogenic Vγ9Vδ2 T cell as new potential immunotherapy drug for solid tumor: a case study for cholangiocarcinoma. J Immunother Cancer. 7:36. DOI:
10.1186/s40425-019-0501-8. PMID:
30736852. PMCID:
PMC6368763.
26. Deinsberger J, Reisinger D, Weber B. 2020; Global trends in clinical trials involving pluripotent stem cells: a systematic multi-database analysis. NPJ Regen Med. 5:15. DOI:
10.1038/s41536-020-00100-4. PMID:
32983575. PMCID:
PMC7486930.
27. Borlongan CV. 2019; Concise review: stem cell therapy for stroke patients: are we there yet? Stem Cells Transl Med. 8:983–988. DOI:
10.1002/sctm.19-0076. PMID:
31099181. PMCID:
PMC6708064.
29. Lalu MM, Mazzarello S, Zlepnig J, Dong YYR, Montroy J, McIntyre L, Devereaux PJ, Stewart DJ, David Mazer C, Barron CC, McIsaac DI, Fergusson DA. 2018; Safety and efficacy of adult stem cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction and ischemic heart failure (SafeCell Heart): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 7:857–866. DOI:
10.1002/sctm.18-0120. PMID:
30255989. PMCID:
PMC6265630.
30. Barker RA, Carpenter MK, Forbes S, Goldman SA, Jamieson C, Murry CE, Takahashi J, Weir G. 2018; The challenges of first-in-human stem cell clinical trials: what does this mean for ethics and institutional review boards? Stem Cell Reports. 10:1429–1431. DOI:
10.1016/j.stemcr.2018.04.010. PMID:
29742388. PMCID:
PMC5995446.
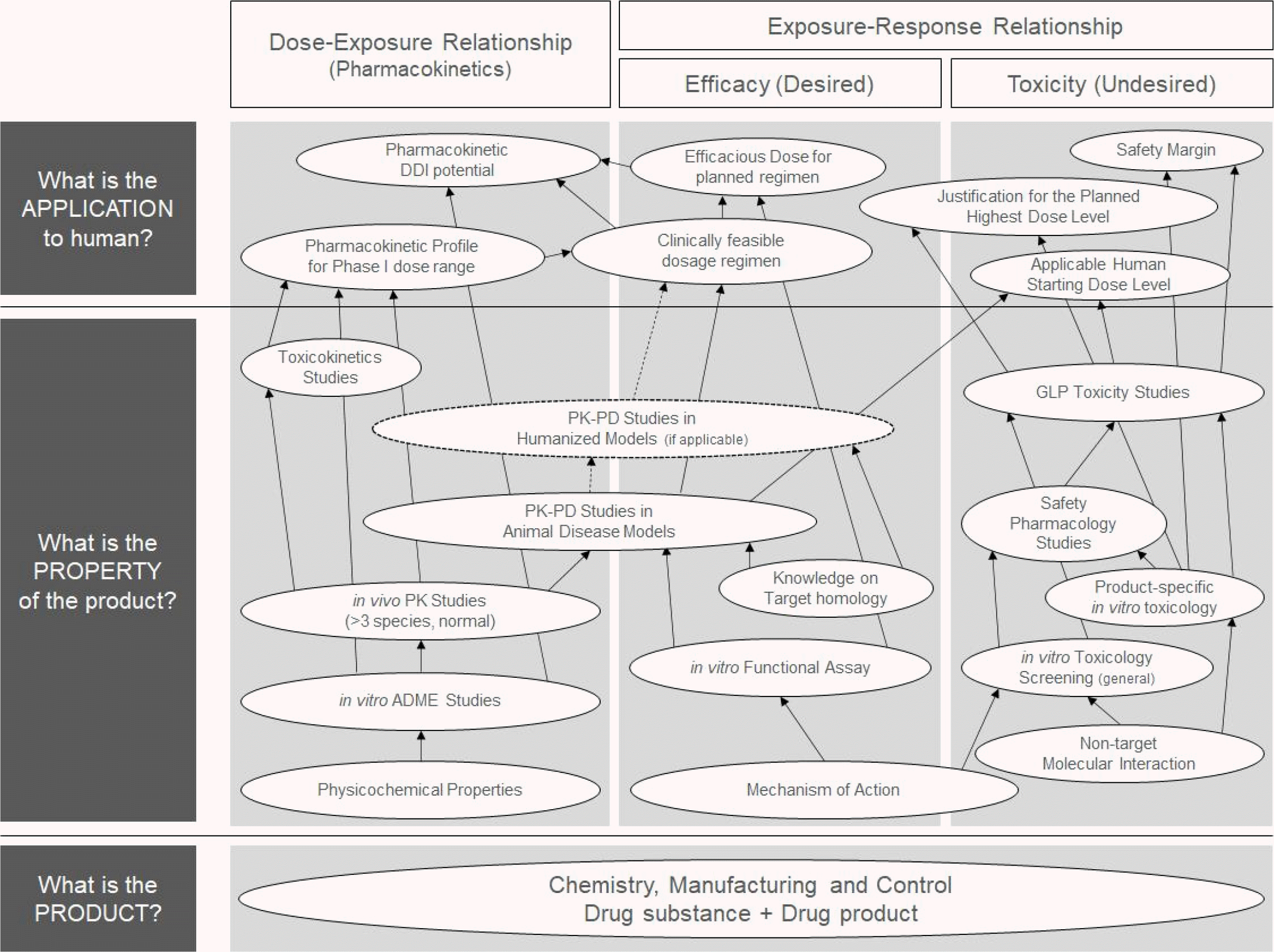
31. Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, US FDA. 2015. Considerations for the design of early-phase clinical trials of cellular and gene therapy products; guidance for industry. FDA;Silver Spring: DOI:
10.1007/s12026-020-09119-7.
32. Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, US FDA. 2015. Guidance for FDA reviewers and sponsors: content and review of chemistry, manufacturing, and control (CMC) information for human somatic cell therapy investigational new drug applications (INDs). FDA;Rockville: DOI:
10.1007/s12026-020-09119-7.
33. Geigert J. Geigert J, editor. 2019. An effective CMC strategy is possible. The challenge of CMC regulatory compliance for biopharmaceuticals. Springer;Cham: p. 53–87. DOI:
10.1007/978-3-030-13754-0_3.
34. Andrade EL, Bento AF, Cavalli J, Oliveira SK, Schwanke RC, Siqueira JM, Freitas CS, Marcon R, Calixto JB. 2016; Non-clinical studies in the process of new drug development - Part II: good laboratory practice, metabolism, pharmacokinetics, safety and dose translation to clinical studies. Braz J Med Biol Res. 49:e5646. DOI:
10.1590/1414-431x20165646. PMID:
27982281. PMCID:
PMC5188860.
36. Senderowicz AM. 2010; Information needed to conduct first-in-human oncology trials in the United States: a view from a former FDA medical reviewer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1719–1725. DOI:
10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2766. PMID:
20215544.
37. Mager DE, Woo S, Jusko WJ. 2009; Scaling pharmacodynamics from in vitro and preclinical animal studies to humans. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 24:16–24. DOI:
10.2133/dmpk.24.16. PMID:
19252333. PMCID:
PMC3727168.
38. Lee W, Cai Y, Lim TP, Teo J, Chua SC, Kwa AL. 2019; In vitro pharmacodynamics and PK/PD in animals. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1145:105–116. DOI:
10.1007/978-3-030-16373-0_8. PMID:
31364074.
39. Marx U, Akabane T, Andersson TB, Baker E, Beilmann M, Beken S, Brendler-Schwaab S, Cirit M, David R, Dehne EM, Durieux I, Ewart L, Fitzpatrick SC, Frey O, Fuchs F, Griffith LG, Hamilton GA, Hartung T, Hoeng J, Hogberg H, Hughes DJ, Ingber DE, Iskandar A, Kanamori T, Kojima H, Kuehnl J, Leist M, Li B, Loskill P, Mendrick DL, Neumann T, Pallocca G, Rusyn I, Smirnova L, Steger-Hartmann T, Tagle DA, Tonevitsky A, Tsyb S, Tra-pecar M, Van de Water B, Van den Eijnden-van Raaij J, Vulto P, Watanabe K, Wolf A, Zhou X, Roth A. 2020; Biology-inspired microphysiological systems to advance patient benefit and animal welfare in drug development. ALTEX. 37:365–394. DOI:
10.14573/altex.2001241. PMID:
32113184. PMCID:
PMC7863570.
40. Kopec AK, Yokokawa R, Khan N, Horii I, Finley JE, Bono CP, Donovan C, Roy J, Harney J, Burdick AD, Jessen B, Lu S, Collinge M, Sadeghian RB, Derzi M, Tomlinson L, Burkhardt JE. 2021; Microphysiological systems in early stage drug development: perspectives on current applications and future impact. J Toxicol Sci. 46:99–114. DOI:
10.2131/jts.46.99. PMID:
33642521.
42. Settiagounder N. 2017; Histopathology evaluation and peer review for nonclinical studies: raw data compliance to GLP quality systems. J Regul Sci. 5:45–55.
43. Food and Drug Administration. 2021. Summary basis for regulatory action for idecabtagene vicleucel. FDA;Silver Spring:
44. European Medicines Agency. 2017. Assessment report for Alofisel. European Medicines Agency;London:
45. European Medicines Agency. 2018. Assessment report for Yes-carta. European Medicines Agency;London:
46. Food and Drug Administration. 2013. Draft Guidance for Industry: Considerations for the Design of Early-Phase Clinical Trials of Cellular and Gene Therapy Products; Availability. FDA;Rockville:
47. Food and Drug Administration. 2020. Chemistry, manufacturing, and control (CMC) information for human gene therapy investigational new drug applications (INDs). FDA;Rockville:




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download