INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study design
Assessment of sleep habit
Study outcome
Measurements of covariates
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Table 1.
| Characteristic | ≤5-hr/night (n=881) | >5 to 7-hr/night (n=4,060) | >7-hr/night (n=2,466) | P valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 52.4±9b | 50.7±8.4 | 52.6±9.0c | <0.001 |
| Male sex | 349 (39.6)b,d | 1,928 (47.5) | 1,189 (48.2) | <0.001 |
| WC, cm | 81.8±9.2 | 81.7±8.7 | 82.6±8.5c | <0.001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.6±3.2 | 24.5±3.1 | 24.4±3.0 | 0.174 |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 120.4±19.0 | 119.4±17.7 | 121.6±18.0c | <0.001 |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 79.7±11.9d | 79.3±11.3 | 80.8±11.3c | <0.001 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 82.5±8.4 | 82.7±8.5 | 82.8±8.6 | 0.692 |
| Glycated hemoglobin, % | 5.6±0.3 | 5.5±0.3 | 5.5±0.3 | 0.059 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 190.2±35.2 | 189.4±34.3 | 190±33.4 | 0.713 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 132.2 (100–188) | 126.8 (94.6–178) | 136 (100–187)c | <0.001 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 45.2±10.7d | 45.1±10.1 | 44.6±9.9 | 0.096 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 113.5±33 | 114.2±31.8 | 114±31.4 | 0.841 |
| HOMA-IR | 1.4 (1–1.9) | 1.4 (1–1.9) | 1.4 (1–2) | 0.387 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.6±0.2b | 0.6±0.2 | 0.6±0.2 | 0.002 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 110.2 ±11.6 | 110.9±12.2 | 110±12.6c | 0.012 |
| Current drinker | 366 (41.5)b,d | 1,975 (48.7) | 1,188 (48.2) | 0.001 |
| Current smoker | 182 (20.7)d | 960 (23.7) | 673 (27.3)c | <0.001 |
| Regular exercise | 243 (27.6)d | 995 (24.5) | 381 (15.5)c | <0.001 |
| Antihypertensive drug | 88 (10) | 339 (8.4) | 248 (10.1)c | 0.042 |
| Antihyperlipidemic drug | 2 (0.2) | 19 (0.5) | 6 (0.2) | 0.265 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 16 (1.8) | 79 (2) | 58 (2.4) | 0.459 |
| Habitual snoring | 121 (13.7) | 561 (13.8) | 331 (13.4) | 0.902 |
| Sleep apnea | 99 (11.3) | 524 (13) | 305 (12.5) | 0.364 |
Values are expressed as mean±standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range).
WC, waist circumference; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
Table 2.
| Sleep duration, hr/day | Incident diabetes |
Multivariate adjusted HR (95% CI) |
P for interactiona | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | ||||
| Total (n=7,407) | |||||
| ≤5 (n=881) | 272 (30.87) | 1.19 (1.04–1.36) | 1.17 (1.02–1.33) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=4,060) | 1,096 (27) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=2,466) | 656 (26.6) | 1.01 (0.91–1.11) | 1.03 (0.93–1.14) | ||
| Women (n=3,941) | 0.174 | ||||
| ≤5 (n=532) | 149 (28.01) | 1.14 (0.95–1.37) | 1.12 (0.94–1.35) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=2,132) | 536 (25.14) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=1,277) | 342 (26.78) | 1.12 (0.97–1.29) | 1.1 (0.96–1.27) | ||
| Men (n=3,466) | |||||
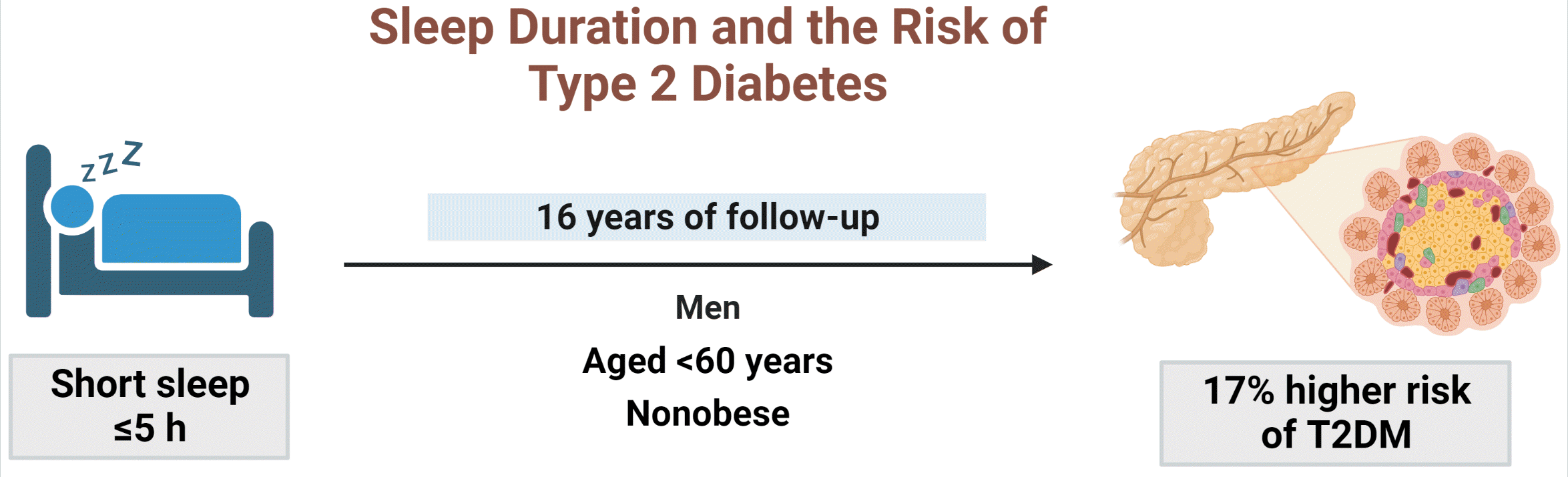
| ≤5 (n=349) | 123 (35.24) | 1.25 (1.03–1.53) | 1.22 (1–1.49) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=1,928) | 560 (29.05) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=1,189) | 314 (26.41) | 0.91 (0.79–1.05) | 0.97 (0.84–1.11) | ||
| Age <60 (n=5,645) | 0.130 | ||||
| ≤5 (n=630) | 185 (29.37) | 1.21 (1.03–1.42) | 1.18 (1.01–1.39) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=3,257) | 855 (26.25) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=1,758) | 467 (26.56) | 1.06 (0.95–1.19) | 1.09 (0.97–1.22) | ||
| Age ≥60 (n=1,762) | |||||
| ≤5 (n=251) | 87 (34.66) | 1.19 (0.93–1.53) | 1.2 (0.94–1.54) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=803) | 241 (30.01) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=708) | 189 (26.69) | 0.9 (0.75–1.1) | 0.92 (0.76–1.12) | ||
| BMI <25 kg/m2 (n=4,377) | 0.002 | ||||
| ≤5 (n=499) | 144 (28.86) | 1.34 (1.11–1.61) | 1.34 (1.11–1.61) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=2,384) | 519 (21.77) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=1,494) | 300 (20.08) | 0.9 (0.78–1.04) | 0.91 (0.79–1.06) | ||
| BMI ≥25 kg/m2 (n=3,030) | |||||
| ≤5 (n=382) | 128 (33.51) | 1.06 (0.88–1.29) | 1.03 (0.85–1.25) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=1,676) | 577 (34.43) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=972) | 356 (36.63) | 1.12 (0.98–1.28) | 1.13 (1.01–1.33) | ||
Values are expressed as number (%). Model 1 was adjusted for age, sex, study site, body mass index, alcohol consumption, smoking, regular exercise, and fasting glucose levels; Model 2 was adjusted for age, sex, study site, body mass index, alcohol consumption, smoking, regular exercise, homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance, presence of hypertension or cardiovascular disease, use of antihyperlipidemic drugs, presence of habitual snoring, and sleep apnea.
HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index.
Table 3.
| Sleep duration, hr/day | Incident diabetes |
Multivariate adjusted HR (95% CI) |
P for interactiona | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | ||||
| Total (n=1,772) | |||||
| ≤5 (n=224) | 77 (34.48) | 1.37 (1.06–1.76) | 1.32 (1.02–1.7) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=1,305) | 361 (27.66) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=243) | 65 (26.75) | 0.97 (0.74–1.26) | 1.07 (0.82–1.4) | ||
| BMI <25 kg/m2 (n=1,048) | 0.161 | ||||
| ≤5 (n=127) | 42 (33.07) | 1.64 (1.16–2.32) | 1.64 (1.16–2.32) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=771) | 168 (21.79) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=150) | 38 (25.33) | 1.15 (0.8–1.65) | 1.26 (0.88–1.81) | ||
| BMI ≥25 kg/m2 (n=724) | |||||
| ≤5 (n=97) | 35 (36.08) | 1.1 (0.76–1.6) | 1.13 (0.78–1.64) | ||
| >5 to 7 (n=534) | 193 (36.14) | 1 (Ref) | 1 (Ref) | ||
| >7 (n=93) | 27 (29.03) | 0.77 (0.51–1.15) | 0.86 (0.57–1.29) | ||
Values are expressed as number (%). Model 1 was adjusted for age, sex, study site, body mass index, alcohol consumption, smoking, regular exercise, and fasting glucose levels; Model 2 was adjusted for age, sex, study site, body mass index, alcohol consumption, smoking, regular exercise, homeostasis model assessment-estimated insulin resistance, presence of hypertension or cardiovascular disease, use of antihyperlipidemic drugs, presence of habitual snoring, and sleep apnea.
HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download