INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study design and population
Data assessment
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
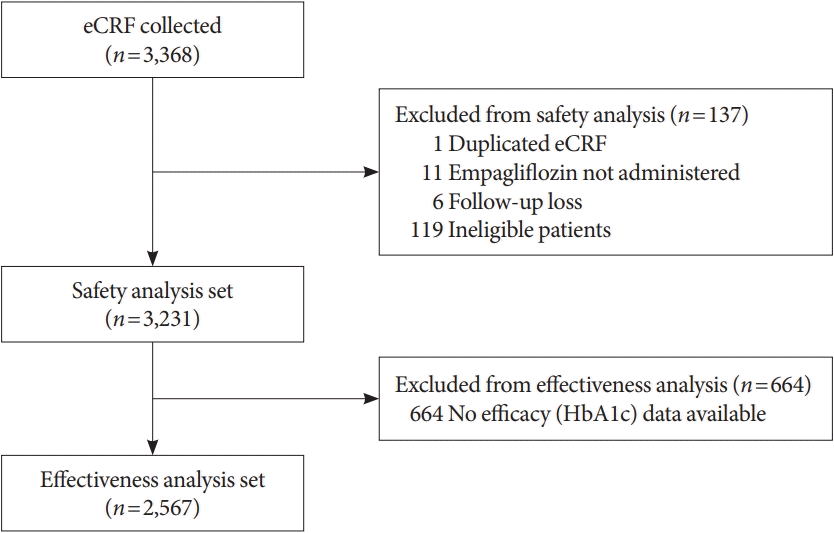
Study population characteristics
Fig. 1.
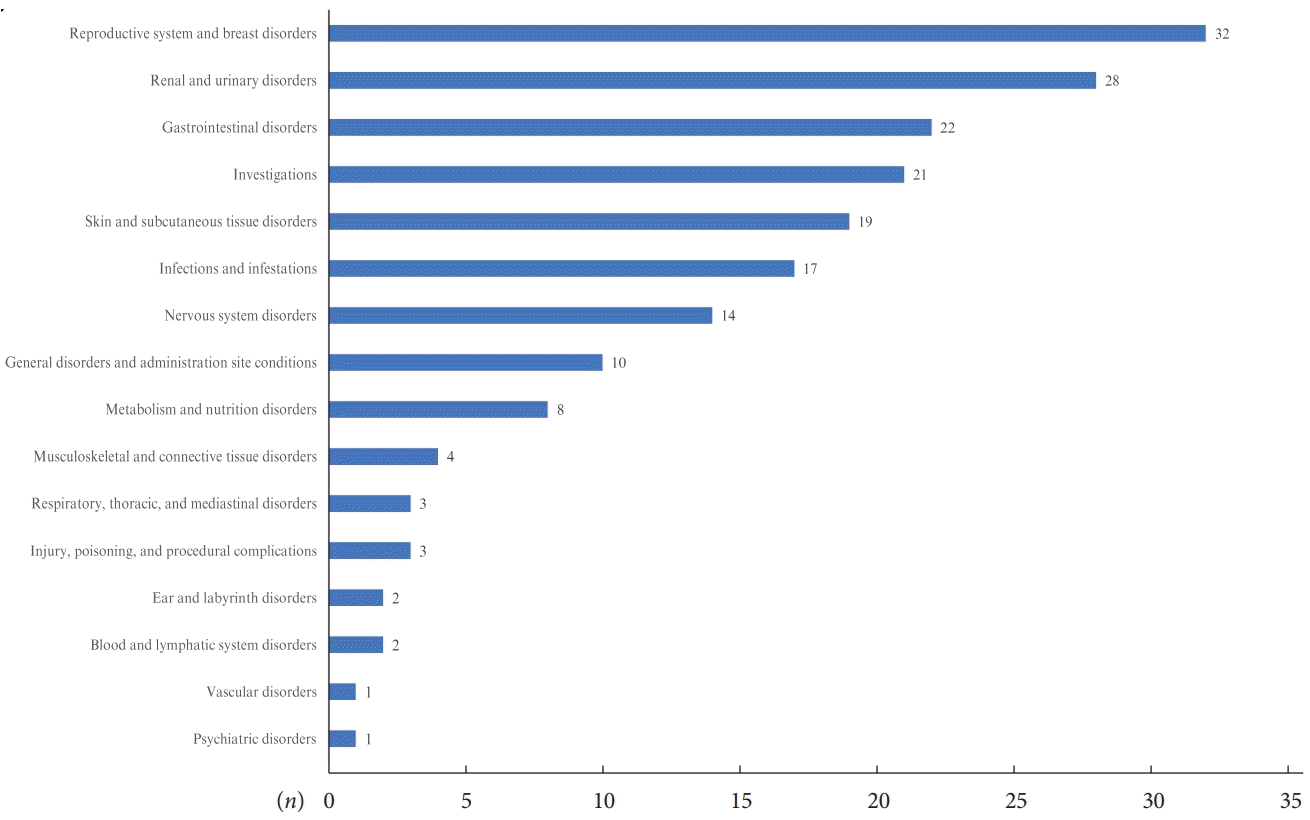
Safety of empagliflozin
Table 1.
| Variable | No. of events in the safety analysis set (n=3,231) (%) |
|---|---|
| Total no. of AE | 606 |
| Patients with an AE | 450 (13.93) |
| Total no. of ADR | 193 |
| Patients with an ADR | 166 (5.14) |
| Ten most frequent types of ADRsa | |
| Pollakiuria | 19 (0.59) |
| Vulvovaginal pruritusb | 18 (0.56) |
| Weight decreased | 17 (0.53) |
| Pruritusc | 15 (0.46) |
| Pruritus genitald | 9 (0.28) |
| Constipation | 7 (0.22) |
| Dizziness | 7 (0.22) |
| Thirst | 6 (0.19) |
| Vulvovaginitis | 5 (0.15) |
| Vaginal infection | 4 (0.12) |
Table 2.
| Variable |
Safety analysis set (n=3,231) |
|
|---|---|---|
| No. of patients (%) | No. of events | |
| Total AE of special interest | 47 (1.45) | 48 |
| Total ADR of special interest | 38 (1.18) | 38 |
| Genital infectionb | 13 (0.40) | 13 |
| Increased urination | 22 (0.68) | 22 |
| Urinary tract infection | 3 (0.09) | 3 |
| Volume depletion | 0 | 0 |
| Diabetic ketoacidosis | 0 | 0 |
| Decreased renal functionc | 0 | 0 |
| Hepatic injury defined by the following alterations of liver parametersd,e | 0 | 0 |
| Lower limb amputationf,g | 0 | 0 |
c Creatinine value shows a >2-fold increase from baseline and is above the upper limit of normal (ULN),
d An elevation of aspartate transaminase (AST) and/or alanine transferase (ALT) >3-fold ULN combined with an elevation of total bilirubin >2-fold ULN measured in the same blood draw sample,
e An isolated elevation of AST and/or ALT >5-fold ULN (without an elevation of total bilirubin >2-fold ULN),
f Amputation (i.e., resection of a limb through a bone), disarticulation (i.e., resection of a limb through a joint), auto-amputations (i.e., spontaneous separation of non-viable portion of the lower limb),
g Not included in this definition are debridement (removal of callus or dead tissue), procedures on a stump (such as stump revision, drainage of an abscess, wound revision), and other procedures (e.g., nail resection or removal) without a concomitant resection of a limb (amputation or disarticulation).
Effectiveness of empagliflozin
Table 3.
| Variable | No. of patients | Baseline visit | Last visit | Differencea | P valueb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c, % | 2,567 | 7.98±1.38 | 7.30±1.16 | –0.68±1.39 | <0.0001 |
| Final HbA1c <7.0 | 1,132 (44.10) | ||||
| More than 0.5% reduction | 1,315 (51.23) | ||||
| FPG, mg/dL | 2,160 | 164.49±54.50 | 138.90±42.99 | –25.59±59.84 | <0.0001 |
| Weight, kg | 2,097 | 74.70±14.06 | 72.79±13.72 | –1.91±3.37 | <0.0001 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 2,355 | 129.78±15.07 | 125.83±14.33 | –3.95±15.44 | <0.0001 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 2,354 | 77.84±10.58 | 76.04±10.52 | –1.80±10.82 | <0.0001 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 433 | 94.11±21.48 | 92.89±21.55 | –1.22±15.57 | 0.0365 |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | 432 | 0.81±0.18 | 0.82±0.19 | 0.01±0.12 | 0.2561 |
| Urine ACR, mg/g | 24 | 28.84±28.55 | 25.99±24.44 | –2.85±17.74 | 0.4297 |
Clinical factors associated with the effectiveness of empagliflozin
Table 4.
| Variable |
∆ HbA1c, %a |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| βb | 95% CI | P value | |
| Age, yr | 0.00 | 0.00 to 0.01 | 0.804 |
| Sex | –0.06 | –0.16 to 0.03 | 0.1935 |
| Smoking status (current/other) | –0.09 | –0.22 to 0.03 | 0.1535 |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 0.05 | 0.04 to 0.05 | <0.0001 |
| Other diseasec | 0.10 | –0.11 to 0.31 | 0.3366 |
| Hypertension | 0.04 | –0.07 to 0.14 | 0.4652 |
| Dyslipidemia | 0.11 | 0.01 to 0.22 | 0.0355 |
| Coronary artery disease | 0.01 | –0.10 to 0.11 | 0.916 |
| Baseline HbA1c, % | –0.68 | –0.72 to –0.65 | <0.0001 |
| Baseline BMI, kg/m2 | 0.00 | –0.01 to 0.02 | 0.4717 |
| Baseline FPG, mg/dL | 0.00 | 0.00 to 0.00 | 0.5869 |
| Baseline eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 0.00 | 0.00 to 0.00 | 0.6641 |
Sex (standardized by ‘female’ from male/female), smoking status (standardized by ‘others’ from current/others), other disease (standardized by the nonexperience from experience/nonexperience of any comorbidities such as stroke, liver disease, renal failure, allergy, and nephropathy within 6 months), hypertension, dyslipidemia, and coronary artery disease (standardized by ‘nonexperience’ from experience/nonexperience) were included as categorical variables. Age, duration of diabetes, HbA1c, BMI, FPG, and eGFR were included as continuous variables.
HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; β, regression coefficient; CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download