Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Conclusion
References
Figure 1.
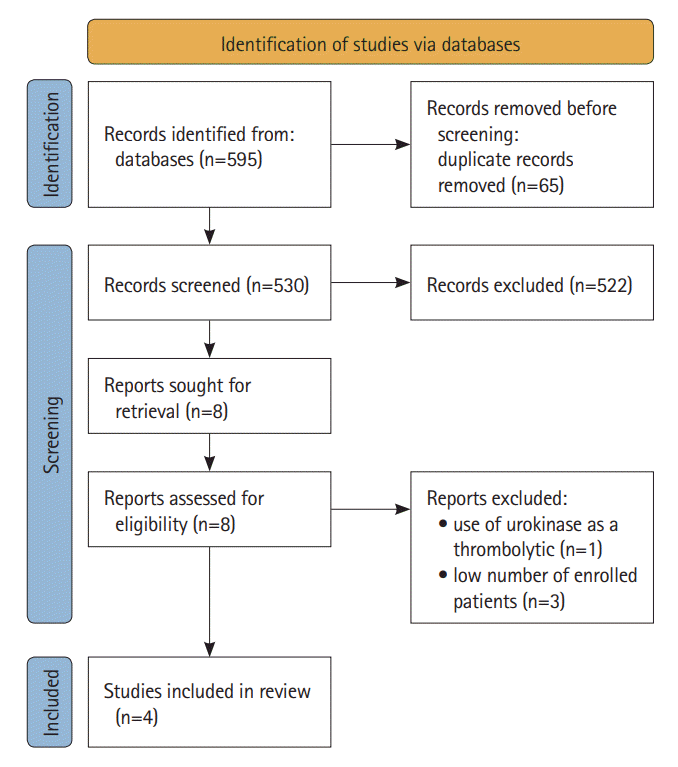
Figure 2.
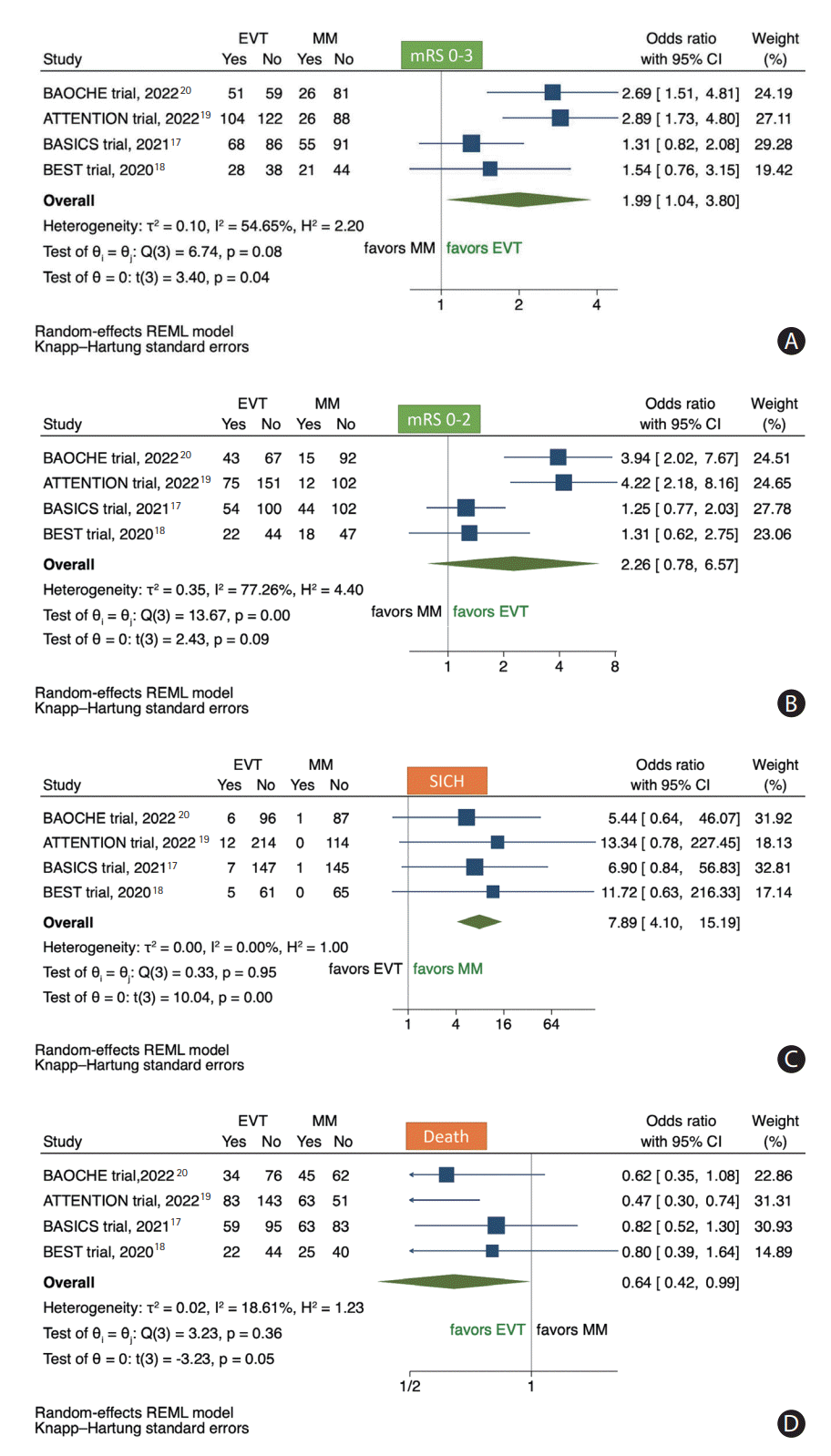
Figure 3.
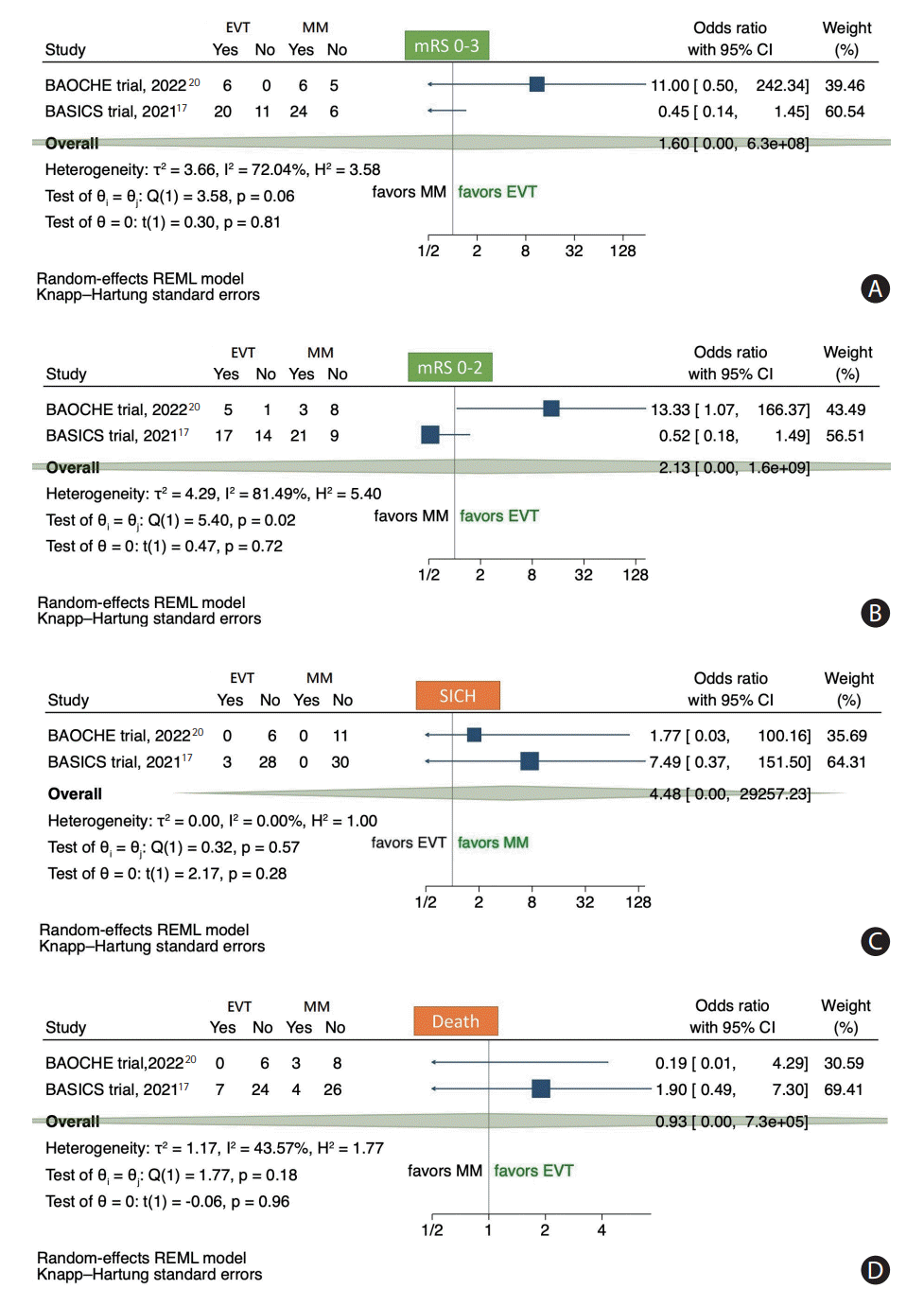
Table 1.
| BEST [18] | BASICS [17] | ATTENTION [19] | BAOCHE [20] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trial summary | |||||
| Publication year | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2022 | |
| Years trial conducted | 2015–2017 | 2011–2019 | 2021–2022 | 2016–2021 | |
| Screened patients | 288 | 424 | 507 | 537 | |
| No. of patients enrolled/target sample size | 131/344 (66 EVT, 65 MM) | 300/300 (154 EVT, 146 MM) | 342/342 (228 EVT, 114 MM) | 217/318 (110 EVT, 107 MM) | |
| Countries | China | 7 Countries | China | China | |
| Estimated symptom onset to randomization (hr) | 0–8 | 0–6 | 0–12 | 6–24* | |
| Age inclusion criteria, years (yr) | ≥18 | Initially18–85 (extended later to ≥18) | ≥18 | 18–80 | |
| NIHSS inclusion criteria | Not specified | Initially ≥10 (extended later to include NIHSS <10) | ≥10 | Initially ≥10 (extended to include NIHSS ≥6 | |
| Pre-stroke mRS inclusion criteria | 0–2 | 0–2 | ≤80 years: 0–2 | ≤1 | |
| >80 years: 0 | |||||
| Imaging selection criteria | No evidence of intracranial hemorrhage, significant cerebellar mass effect, acute hydrocephalus, or extensive bilateral brainstem ischemia on CT or MRI | No evidence of intracranial hemorrhage, extensive bilateral brainstem infarction on CT, cerebellar mass effect, or acute hydrocephalus on neuroimaging | NCCT/CTA-SI/DWI | pc-ASPECTS ≥6 or Pons-midbrain-index of ≤2 | |
| pc-ASPECTS | |||||
| ≤80 years: ≥6 | |||||
| >80 years: ≥8 | |||||
| Endovascular treatment modality | At the discretion of treating physician | At the discretion of treating physician | At the discretion of treating physician | Solitaire stent retriever | |
| Crossover | |||||
| EVT to MM | 3/66, 5% | 3/154, 1.9% | 3/226, 1.3% | 1/110, 0.9% | |
| MM to EVT | 14/65, 22% | 7/146, 4.8% | 3/114, 2.6% | 4/107, 3.7% | |
| Trial demographics | |||||
| Age (yr) | |||||
| EVT | 62 (50–74) | 66.8±13.1 | 66.0±11.1 | 64.2±9.6 | |
| MM | 68 (57–74) | 67.2±11.9 | 67.3±10.2 | 63.7±9.8 | |
| Male sex | |||||
| EVT (%) | 73 | 64.9 | 66 | 73 | |
| MM (%) | 80 | 65.8 | 72 | 74 | |
| Baseline NIHSS | |||||
| EVT | 32 (18–38) | 21 | 24 (15–35) | 20 (15–29) | |
| MM | 26 (13–37) | 22 | 24 (14–35) | 19 (12–30) | |
| Baseline pc-ASPECTS | |||||
| EVT | 8 (7–9) | 10 (8–10) | 9 (8–10) | 8 (7–10) | |
| MM | 8 (7–9) | 10 (8–10) | 10 (8–10) | 8 (7–10) | |
| IVT | |||||
| EVT | 18 (27) | 121 (78.6) | 69 (31) | 15 (13.6) | |
| MM | 21 (32) | 116 (79.5) | 39 (34) | 23 (21.5) | |
| ICAD† | |||||
| EVT | 37 (56) | 53/146 (36.3) | 90/226 (40) | N/A | |
| MM | 32 (49) | 43/132 (32.6) | 33/114 (29) | N/A | |
Demographic data are median (IQR), n (%), or mean±SD unless otherwise indicated.
BEST, Basilar Artery Occlusion Endovascular Intervention versus Standard Medical Treatment; BASICS, Basilar Artery International Cooperation Study; ATTENTION, Endovascular Treatment for Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion: A Multicentre Randomised Clinical Trial; BAOCHE, Basilar Artery Occlusion Chinese Endovascular Trial; EVT, endovascular thrombectomy; MM, medical management; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; CT, computed tomography; MRI, magnetic resonance imaging; NCCT, non-contrast CT; CTA, computed tomography angiography; SI, source images; DWI, diffusion-weighted imaging; pc-ASPECTS, posterior circulation Acute Stroke Prognosis Early CT Score; IVT, intravenous thrombolysis; ICAD, intracranial atherosclerotic disease; N/A, not available; IQR, interquartile range.
† The percentage of patients with intracranial atherosclerotic disease was not reported in BAOCHE publication. Noting that 41/110 (37.3%) underwent intracranial stenting in the endovascular group. Large artery atherosclerosis was reported as the cause of stroke in 75/110 (68.2%) in the EVT group and in 69/107 (64.5%) in the control group in the BAOCHE study.
Table 2.
| BEST [18] | BASICS [17] | ATTENTION [19] | BAOCHE [20] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary outcome: mRS 0–3 at 90 days | ||||
| EVT | 28/66 (42%) | 68/154 (44%) | 104/226 (46%) | 51/110 (46.4%) |
| MM | 21/65 (32%) | 55/146 (38%) | 26/114 (23%) | 26/107 (24.3%) |
| aOR: 1.74 (0.81–3.74) | RR: 1.18 (0.92–1.50) | RR: 2.06 (1.46–2.91) | aRR: 1.81 (1.26–2.60) | |
| P=0.23 | P=0.19 | P<0.001 | P<0.001 | |
| mRS 0–2 at 90 days | ||||
| EVT | 22 (33%) | 54 (35.1%) | 75 (33%) | 43 (39.1%) |
| MM | 18 (28%) | 44 (30.1%) | 12 (10.5%) | 15 (14%) |
| aOR: 1.40 (0.64–3.10) | RR: 1.17 (0.87–1.57) | RR: 3.17 (1.84–5.46) | RR: 2.75 (1.65–4.56) | |
| P=0.48 | ||||
| Artery patency at 24 to 72 hours | ||||
| EVT | 45/63 (71.4%) (TICI ≥2b) | 93/110 (84.5%) (CTA patency 24 h) | 147/161 (91.3%) (artery patency) | 89/101 (88.1%) (TICI ≥2b) |
| MM | 9/14 (64.2%) (TICI ≥2b) | 54/96 (56.3%) (CTA patency 24 h) | 26/69 (37.7%) (artery patency) | N/A |
| sICH* | ||||
| EVT | 5/66 (7.6%) | 7/154 (4.5%) | 12 (5.3%) | 6/102 (5.9%) |
| MM | 0/65 (0%) | 1/146 (0.7%) | 0% | 1/88 (1.1%) |
| OR: N/A | RR: 6.9 (0.9–53.0) | RR: 5.18 (0.64–42.18) | ||
| P=0.06 | P=0.06 | P=0.125 | ||
| Mortality | ||||
| EVT | 22/66 (33%) | 59/154 (38.3%) | 83/226 (36.7%) | 34/110 (30.9%) |
| MM | 25/65 (38%) | 63/146 (43.2%) | 63/114 (55.3%) | 45/107 (42.1%) |
| OR: 0.80 (0.37–1.64) | RR: 0.87 (0.68–1.12) | RR: 0.66 (0.52–0.82) | RR: 0.75 (0.54–1.04) | |
| P=0.54 | P=0.29 | |||
BEST, Basilar Artery Occlusion Endovascular Intervention versus Standard Medical Treatment; BASICS, Basilar Artery International Cooperation Study; ATTENTION, Endovascular Treatment for Acute Basilar Artery Occlusion: A Multicentre Randomised Clinical Trial; BAOCHE, Basilar Artery Occlusion Chinese Endovascular Trial; mRS, modified Rankin Scale; EVT, endovascular treatment; MM, medical management; aOR, adjusted odds ratio; RR, risk ratio; TICI, thrombolysis in cerebral infarction; CTA, computed tomography angiography; N/A, not available; sICH, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage; OR, odds ratio; NIHSS, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale; SITS-MOST, The Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Monitoring Study.
* sICH definitions: BEST, defined as evidence of intracranial hemorrhage on imaging and an increase of 4 or more points on the NIHSS within 24 h after randomization; BASICS, Heidelberg bleeding classification; ATTENTION, SITS-MOST criteria; BAOCHE, SITS-MOST criteria (deterioration in NIHSS score of >4 points within 24 h from treatment and evidence of intraparenchymal hemorrhage type 2 in the 22–36 h follow-up imaging scans). BAOCHE also included sICH according to ECASS II criteria.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download