Abstract
Purpose
We provide evidence for the reclassification of the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant by presenting the clinicopathological characteristics, clinical outcomes, and family history of breast or ovarian cancer in 17 patients with this variant.
Methods
This study included breast or ovarian cancer patients tested for BRCA1/2 genes between January 2008 and June 2020 at 10 medical centers in Korea. We retrospectively reviewed 17 probands from 15 families who had the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant according to the electronic medical records.
Results
We present 10 breast cancer patients and 7 ovarian cancer patients from 15 families identified as having BRCA1:c.5017_5019del and a total of 19 cases of breast cancer and 14 cases of ovarian cancer in these families. The ratio of breast-to-ovarian cancer was 1.3:1. Breast cancer patients with this variant showed a rich family history of breast or ovarian cancer, 8 patients (80.0%). The mean age at diagnosis was 45.4 years and 6 patients (60.0%) were categorized into hormone-receptor–negative breast cancer. Also, the ovarian cancer patients with this variant showed strong family histories of breast and/or ovarian cancer in 4 patients (57.1%).
Conclusion
We presented clinical evidence for the reclassification of BRCA1:c.5017_5019del as a likely pathogenic variant (LPV). Reclassification as LPV could result in the prophylactic treatment and medical surveillance of probands, family testing recommendations, and appropriate genetic counseling of their families.
Go to : 
It is widely known that cancer is a disease in which abnormal cells proliferate uncontrolled due to changes in DNA. The causative genes for specific cancers have been identified, and the survival rate has risen due to advances in cancer screening, treatment, and prevention. BRCA1 and BRCA2 discovered in the 1990s normally belong to the DNA repair genes, which assume a regulatory function in the cell cycle [1]. These genes intrinsic to all human beings are mutated in some individuals and are representative of the causative genes of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC) [2].
The germline pathogenic variant (PV)/likely pathogenic variant (LPV) in BRCA1/2 has become one of the most important keys in treatment, surveillance, whether patients choose risk-reducing surgery, and the counseling of the HBOC family members [34]. Because poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP)-inhibitors and prophylactic treatments, such as risk-reducing agents, risk-reducing bilateral mastectomy, and risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy, are widely known to be effective in BRCA1/2-positive patients, the BRCA1/2 test is considered essential for high-risk breast cancer patients and ovarian cancer patients [567].
From this point of view, the need for genetic tests, especially for BRCA1/2 genes, has increased. In addition, with advances in genetic testing methods such as next generation sequencing (NGS), more tests can be performed. Along with the increased number of tests, new deleterious genetic mutations have been discovered and the numbers of variants of uncertain significance (VUSs) have also increased [8]. Although previous studies showed that the frequency of VUS in BRCA1/2 differed depending upon the study population [9], generally a frequency of 5%–10% VUSs has been reported [1011]. Some VUSs were reclassified as LPVs or likely benign variants based on accumulated evidence [1213]. The BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant was classified as a VUS but recently, was reclassified as an LPV [14]. Here, we present the clinicopathological characteristics of patients with BRCA1:c.5017_5019del and basic information for the interpretation of this variant.
Go to : 
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Samsung Medical Center (No. 2021-08-130). Since this study was retrospective in nature, patient consent was not required.
This study included breast or ovarian cancer patients tested for BRCA1/2 genes between January 2008 and June 2020 at 9 medical centers (Samsung Medical Center, Asan Medical Center, Ewha Womans University Mokdong Hospital, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul National University Hospital, Ajou University Hospital, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Jeonbuk National University Hospital, and Daerim St. Mary’s Hospital) in Korea. We retrospectively reviewed the clinicopathological characteristics, clinical outcomes, and family history of breast or ovarian cancer in patients who had the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant according to the electronic medical records. Since 3 of these patients diagnosed at other hospitals were confirmed to be related, we reported 17 probands from 15 families.
We reviewed the following clinicopathological characteristics of age, sex, menopausal status, site of breast cancer, estrogen-receptor (ER) status, progesterone-receptor (PR) status, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) status, and pathologic stage according to the seventh American Joint Committee on Cancer classification, history of contralateral breast cancer, and the occurrence of ovarian cancer, and clinical outcomes. We also assessed the family history of breast, ovarian, and other cancers by genetic counseling records and electric medical record review.
BRCA1/2 genetic testing was recommended according to the Korean Clinical Practice Guidelines for Breast Cancer [15] and was finally done only if the patient wanted. All genetic tests were prescribed at every 10 hospitals in the indicated patients and performed either directly at the hospital or by sending them to an outside facility. All coding exons and surrounding introns were included in Sanger sequencing and the NGS methods. All detected variants were interpreted based on the 2015 American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology (ACMG and AMP) guidelines [16] and some evidence from the Clinical Genome (ClinGen) Resource recommendations was added [171819].
Go to : 
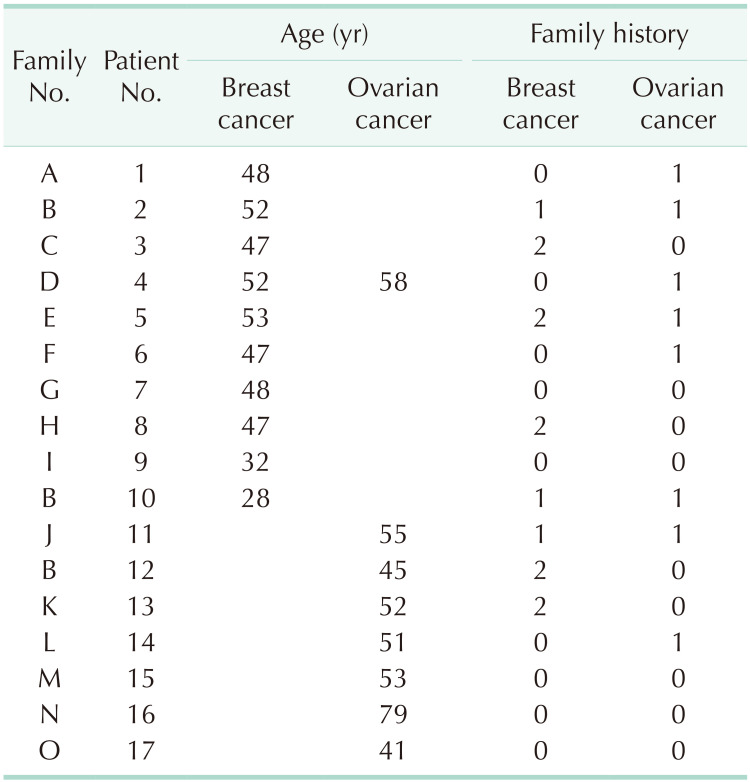
The characteristics of the patients with BRCA1: c.5017_5019del are summarized in Table 1. Seventeen patients from 15 families were identified as having the BRCA1: c.5017_5019del variant. All of the patients were female. At the time of the genetic testing, 10 patients (58.8%) had breast cancer and 7 patients (41.2%) had ovarian cancer. Of the 10 breast cancer patients, 1 patient (5.9%) was newly diagnosed with ovarian cancer 6 years after the diagnosis of breast cancer. Ten breast cancers and 8 ovarian cancers from 17 probands were reported. There were 10 unrelated families (66.7%) with a family history of breast cancer or ovarian cancer in second-degree relatives. As shown, a total of 19 breast carcinomas and 14 ovarian cancers were reported in these families.
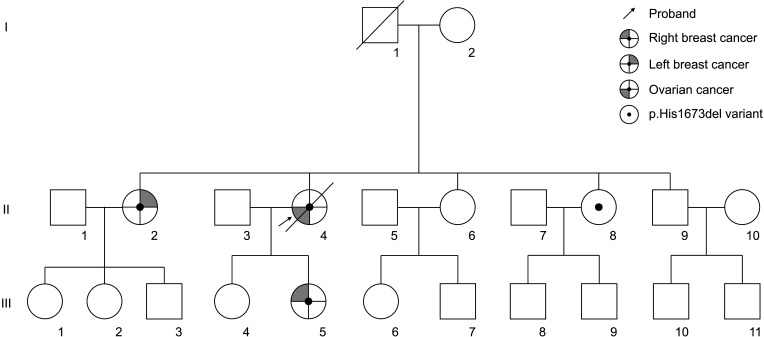
Patients 2, 10, and 12 were confirmed to be related. Since patient 12 was first identified as having BRCA1:c.5017_5019del, patients 10 and 12 were tested because they had a family history of ovarian cancer and were diagnosed with BRCA1:c.5017_5019del. The pedigree of this family is shown in Fig. 1. An additional member of this family was confirmed to have the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant and is under regular follow-up without a history of cancer.
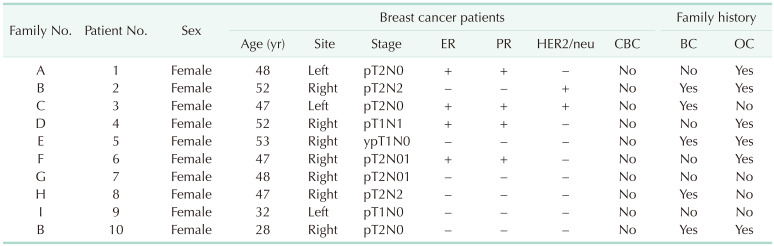
The clinicopathological characteristics of 10 breast cancer patients with the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant are summarized in Table 2. The mean age at diagnosis was 45.4 years. Seven patients (70.0%) were diagnosed before the age of 50 years and all 10 patients (100%) were diagnosed before the age of 55 years. Six patients (60.0%) had both ER- and PR-negative breast cancer and 5 patients (50.0%) had TNBC. There were 8 breast cancer patients (80.0%) with a family history of breast cancer or ovarian cancer in second-degree relatives. Furthermore, 6 patients (75.0%) had more than 2 family members with breast or ovarian cancer. However, considering that one of the indications for the BRCA1/2 gene tests is a family history of breast/ovarian cancers, there may be bias. All breast cancer patients are undergoing regular follow-ups and visited the hospital within the last year, and there has been no recurrence or death.
The mean age at diagnosis of 8 patients diagnosed with ovarian cancer was 54.3 years. There were 5 ovarian cancer patients (62.5%) with a family history of breast cancer or ovarian cancer in second-degree relatives. Three of the ovarian cancer patients died due to the progression of ovarian cancer, and 5 patients are undergoing regular follow-ups.
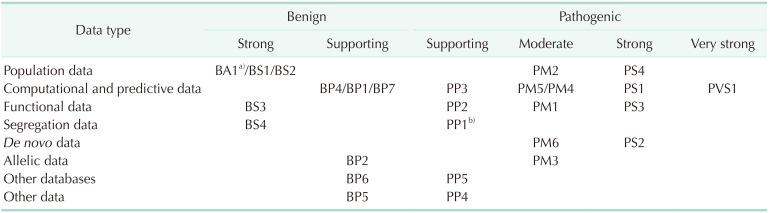
The BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant was detected in 17 probands (Fig. 2). The variant, a heterozygous 3-base-pair deletion, is expected to manifest as single amino acid deletion (p.His1673del). The evidences were that there was no reported allele frequency on the population database (PM2 of 2015 ACMG evidences), and protein length chance (PM4) (Table 3). However, several patients with breast and ovarian cancer were suspected of having HBOC (MIM 113705). After research on the patients, we could accumulate more evidence for the variant identified in other affected unrelated individuals (PS4). Finally, there was 1 piece of strong evidence for pathogenicity and 2 pieces of moderate evidence for pathogenicity, which could be interpreted as LPV.
Go to : 
BRCA1/2 gene tests have been performed more frequently with the development of testing methods and the importance of treating HBOC. Accordingly, more novel variants have been discovered and the detection of VUSs is also increasing. Since the BRCA1/2 test is essential for not only the diagnosis but also the treatment of HBOC, the misinterpretation of VUSs can cause significant damage to the carriers, requiring continuous efforts to reclassify VUSs [2021]. When a VUS is reclassified as a PV/LPV, genetic counseling or appropriate management including prophylactic strategies and treatment should be discussed with the patients and their relatives. Olaparib, a PARP inhibitor, has been approved for the treatment of patients with BRCA1/2 mutated advanced ovarian cancer [22]. Recently, it was proven to be effective as adjuvant therapy after the completion of local treatment and chemotherapy for patients with HER2-negative early breast cancer and BRCA1/2 PV or LPVs [23]. Here, we report the characteristics of patients with a specific BRCA1 gene variant (c.5017_5019del) from multiple centers in Korea.
The frequencies of VUSs in BRCA1/2 have been reported to be 5%–10% on average, but Myriad Genetics Inc. (Salt Lake City, UT, USA) reported that this decreased to 2.1% using accumulated data [24]. Therefore, studies for the reclassification of VUSs in BRCA1/2 have been conducted in Korea. In early studies by Park et al. [25] and Korean Hereditary Breast Cancer (KOHBRA) study [26], which included breast cancer patients, the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant was still reported as a VUS. However, So et al. [12] reclassified this variant into an LPV, which included both breast and ovarian cancer patients, and this result could be understood as consistent with a study by Zuntini et al. [14]. That study reported 14 families including 20 cases of breast cancer and 23 cases of ovarian cancer in Italy. Here, we present 17 patients from 15 families identified as having the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant and a total of 19 cases of breast cancer and 14 cases of ovarian cancer in these families. This was the largest number of cases for a specific variant depending on the multicenter study of breast cancer patients in Korea. Ten breast cancer patients (58.8%) with this variant showed similar clinical characteristics to those with BRCA1 mutation-related breast cancer, including 8 patients (80.0%) with a rich family history of breast or ovarian cancer, 7 patients (70.0%) with a cancer diagnosis prior to 50 years of age, and 5 patients (50.0%) categorized into the TNBC subgroup. Seven patients (41.2%) were diagnosed with ovarian cancer, and the ratio of breast-to-ovarian cancer was 1.3:1. Also, ovarian cancer patients with this variant showed strong family histories of breast and/or ovarian cancer.
After the 2015 AMP-ACMG guidelines were published, genetic interpretation became more systematic. Even when deleterious variants are highly suspected, all variants should be interpreted based on the guidelines, and familial analysis and functional studies like messenger RNA studies should be performed if needed. ClinGen Sequence Variant Interpretation Workgroup refined the AMP-ACMG guidelines and pathogenic criteria (PVS1) were suggested based on the available evidence for each variant type [27]. According to the PVS1 strength level [27], these criteria were divided into PVS1, PVS1_Strong, PVS1_Moderate, and PVS1_Supporting. An in-frame deletion, especially a single amino acid deletion should be applied carefully not to be an overestimation. Here, the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant was an amino acid deletion variant and we could only add the evidence for protein length (PM4) added to PM2 evidence for population frequency. However, detection in patients with the same phenotypes should be accessed for other evidences. PS4 can be used for typical case-control studies when the relative risk or odds ratio is >5.0, and the confidence interval (CI) does not include 1.0 and has been calculated to assess whether a variant is likely to be associated with a particular phenotype. Table 4 shows evidence codes according to the 2015 ACMP and AMP guidelines [16]. Also, PP4, which represents patient phenotypes or family history for highly specific phenotypes, can be considered as other evidence. Another consideration in genetic interpretation is the interpretation of in-frame deletions, especially, single amino acid deletion variants. There were 4 kinds of single amino acid deletion variants in BRCA1/2 genes, besides BRCA1:c.5017_5019del, which were found in Korean patients during this period. Those were 1 variant in the BRCA1 gene, c.3327_3329del (p.Lys1110del) and 3 variants in the BRCA2 gene, c.644_646del (p.Glu215del), c.7981_7983del (p.Asp2661del), and c.8437_8439del (p.Gly2813del). All those 4 variants were reported as VUS based on the 2015 AMP-ACMG guidelines. We applied the evidence for allele frequencies and protein length change to these deletions. We plan to continuously compare and analyze the clinical data to clarify the clinical significance of each variant in the future. In addition, we will continue to consider the genetic domain and functional studies of the variants.
Currently, germline testing for the BRCA1/2 genes is performed in only indicated patients such as those with a family history, certain age, etc. The optimal management for patients and carriers who have germline variants depends upon accurate risk estimation and surveillance. There are well-known overall risks for breast and ovarian cancers until the age of 80 years. Moreover, the annual incidence and cumulative risk of breast, ovarian and contralateral breast cancer has also been reported [28].
One limitation of the study was the lack of family studies of BRCA1/2 tests and few familial history updates due to the limitations of the retrospective study. In the same context, there was a lack of information on ovarian cancer patients, since the study was conducted in multicenter breast cancer departments. Since several studies that previously suggested the reclassification of this variant into a PV/LPV included gynecological cancer patients [121429] and this study had a large proportion of ovarian cancer patients, a multicenter study including gynecological cancer patients should be conducted. An interesting point was the location of the variant in what is known as the breast cancer cluster region (BCCR), but it was detected more often in ovarian cancer patients. A few points should be considered to understand the study results. First, there was a very small number of patients from which to draw statistical judgments on breast and ovarian cancer patients. Moreover, regions such as the BCCR and ovarian cancer cluster region were defined based on the ratio of breast-to-ovarian cancer incidence and there were exceptions even within the same cluster. The broad region that includes this variant (c.5017_5019del) was defined as the BCCR, but the specific region, which was defined as bin (c.4946_5123), showed a hazard ratio of 1.07 (breast-to-ovarian) (95% CI, 0.83–1.39) [30]. Another thing to consider is that this variant was previously reported as a VUS and excluded to define these regions. Therefore, we expect that additional studies will be conducted and the clinical information of the patients with this variant will be accumulated.
Another limitation is that we could not perform functional studies to make up the evidence based on the 2015 AMP-ACMG guideline for the corresponding variant. There are 8 categories including population data, computational/predictive data, functional data, segregation data, de novo data, allelic data, other databases, and other data. Public data such as population data and computational/predictive data could be used in interpreting variants; however, functional data is not easy to be used. Moreover, in this study, we described only a variant and we did not analyze other VUSs. In the future, as the BRCA1/2 analysis continues, the authors expect and make efforts so that the interpretation of the variants could be in-depth, including a functional study, with the patients’ clinical conditions.
In conclusion, we present clinical evidence for the reclassification of BRCA1:c.5017_5019del as an LPV according to ACMG standards and guidelines. Because the BRCA1:c.5017_5019del variant has been classified as a VUS, probands have not been given the option of prophylactic treatment and family testing has not been recommended. However, when reclassified as an LPV, prophylactic treatment and medical surveillance may be provided to the probands, family testing recommended, and appropriate genetic counseling provided to the family.
Go to : 
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors’ efforts for the work described herein were supported by a kind donation from Mr. Yong Seop Lee and Ms. Sun Hee Kang. We also thank all Korean Hereditary Breast Cancer (KOHBRA) study investigators.
Go to : 
Notes
Fund/Grant Support: This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government’s Ministory of Education (NRF 2021R1A2C94010, Seoul, Korea).
Author Contribution:
Conceptualization: YJB, JMR, SWK.
Formal Analysis: YJB, WKK, JMR.
Investigation: YJB, JWK, JEL, BYJ, MK, JK, JA, SPJ, HKK, ZK, HJY.
Methodology: YJB, WKK, JMR, SWK.
Project Administration: JMR, SWK.
Funding Acquisition: JEL, JMR.
Writing – Original Draft: YJB, WKK.
Writing – Review & Editing: All authors.
Go to : 
References
1. Tutt A, Ashworth A. The relationship between the roles of BRCA genes in DNA repair and cancer predisposition. Trends Mol Med. 2002; 8:571–576. PMID: 12470990.
2. Varol U, Kucukzeybek Y, Alacacioglu A, Somali I, Altun Z, Aktas S, et al. BRCA genes: BRCA 1 and BRCA 2. J BUON. 2018; 23:862–866. PMID: 30358186.
3. Rebbeck TR, Friebel TM, Friedman E, Hamann U, Huo D, Kwong A, et al. Mutational spectrum in a worldwide study of 29,700 families with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations. Hum Mutat. 2018; 39:593–620. PMID: 29446198.
4. Samadder NJ, Riegert-Johnson D, Boardman L, Rhodes D, Wick M, Okuno S, et al. Comparison of universal genetic testing vs guideline-directed targeted testing for patients with hereditary cancer syndrome. JAMA Oncol. 2021; 7:230–237. PMID: 33126242.
5. Daly MB, Pal T, Berry MP, Buys SS, Dickson P, Domchek SM, et al. Genetic/familial high-risk assessment: breast, ovarian, and pancreatic, version 2.2021, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021; 19:77–102. PMID: 33406487.
6. Warner E, Plewes DB, Hill KA, Causer PA, Zubovits JT, Jong RA, et al. Surveillance of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers with magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, mammography, and clinical breast examination. JAMA. 2004; 292:1317–1325. PMID: 15367553.
7. Brekelmans CT, Seynaeve C, Bartels CC, Tilanus-Linthorst MM, Meijers-Heijboer EJ, Crepin CM, et al. Effectiveness of breast cancer surveillance in BRCA1/2 gene mutation carriers and women with high familial risk. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19:924–930. PMID: 11181654.
8. Caputo SM, Golmard L, Léone M, Damiola F, Guillaud-Bataille M, Revillion F, et al. Classification of 101 BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants of uncertain significance by cosegregation study: a powerful approach. Am J Hum Genet. 2021; 108:1907–1923. PMID: 34597585.
9. Kurian AW. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations across race and ethnicity: distribution and clinical implications. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol. 2010; 22:72–78. PMID: 19841585.
10. Hall MJ, Reid JE, Burbidge LA, Pruss D, Deffenbaugh AM, Frye C, et al. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in women of different ethnicities undergoing testing for hereditary breast-ovarian cancer. Cancer. 2009; 115:2222–2233. PMID: 19241424.
11. Murray ML, Cerrato F, Bennett RL, Jarvik GP. Follow-up of carriers of BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants of unknown significance: variant reclassification and surgical decisions. Genet Med. 2011; 13:998–1005. PMID: 21811163.
12. So MK, Jeong TD, Lim W, Moon BI, Paik NS, Kim SC, et al. Reinterpretation of BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants of uncertain significance in patients with hereditary breast/ovarian cancer using the ACMG/AMP 2015 guidelines. Breast Cancer. 2019; 26:510–519. PMID: 30725392.
13. Augusto BM, Lake P, Scherr CL, Couch FJ, Lindor NM, Vadaparampil ST. From the laboratory to the clinic: sharing BRCA VUS reclassification tools with practicing genetics professionals. J Community Genet. 2018; 9:209–215. PMID: 29124491.
14. Zuntini R, Cortesi L, Calistri D, Pippucci T, Martelli PL, Casadio R, et al. BRCA1 p.His1673del is a pathogenic mutation associated with a predominant ovarian cancer phenotype. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:22640–22648. PMID: 28186987.
15. Lee EH, Park B, Kim NS, Seo HJ, Ko KL, Min JW, et al. The Korean guideline for breast cancer screening. J Korean Med Assoc. 2015; 58:408–419.
16. Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015; 17:405–424. PMID: 25741868.
17. Rivera-Muñoz EA, Milko LV, Harrison SM, Azzariti DR, Kurtz CL, Lee K, et al. ClinGen Variant Curation Expert Panel experiences and standardized processes for disease and gene-level specification of the ACMG/AMP guidelines for sequence variant interpretation. Hum Mutat. 2018; 39:1614–1622. PMID: 30311389.
18. Harrison SM, Biesecker LG, Rehm HL. Overview of specifications to the ACMG/AMP variant interpretation guidelines. Curr Protoc Hum Genet. 2019; 103:e93. PMID: 31479589.
19. Maxwell KN, Hart SN, Vijai J, Schrader KA, Slavin TP, Thomas T, et al. Evaluation of ACMG-guideline-based var iant classification of cancer susceptibility and non-cancer-associated genes in families affected by breast cancer. Am J Hum Genet. 2016; 98:801–817. PMID: 27153395.
20. Krontiras H, Farmer M, Whatley J. Breast cancer genetics and indications for prophylactic mastectomy. Surg Clin North Am. 2018; 98:677–685. PMID: 30005767.
21. Practice Bulletin No 182: hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 2017; 130:e110–e126. PMID: 28832484.
22. Friedlander M, Moore KN, Colombo N, Scambia G, Kim BG, Oaknin A, et al. Patient-centred outcomes and effect of disease progression on health status in patients with newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer and a BRCA mutation receiving maintenance olaparib or placebo (SOLO1): a randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021; 22:632–642. PMID: 33862001.
23. Tutt AN, Garber JE, Kaufman B, Viale G, Fumagalli D, Rastogi P, et al. Adjuvant olaparib for patients with BRCA1- or BRCA2-mutated breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384:2394–2405. PMID: 34081848.
24. Eggington JM, Bowles KR, Moyes K, Manley S, Esterling L, Sizemore S, et al. A comprehensive laboratory-based program for classification of variants of uncertain significance in hereditary cancer genes. Clin Genet. 2014; 86:229–237. PMID: 24304220.
25. Park KS, Cho EY, Nam SJ, Ki CS, Kim JW. Comparative analysis of BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants of uncertain significance in patients with breast cancer: a multifactorial probability-based model versus ACMG standards and guidelines for interpreting sequence variants. Genet Med. 2016; 18:1250–1257. PMID: 27124784.
26. Kim JH, Park S, Park HS, Park JS, Lee ST, Kim SW, et al. Analysis of BRCA1/2 variants of unknown significance in the prospective Korean Hereditary Breast Cancer study. Sci Rep. 2021; 11:8485. PMID: 33875706.
27. Abou Tayoun AN, Pesaran T, DiStefano MT, Oza A, Rehm HL, Biesecker LG, et al. Recommendations for interpreting the loss of function PVS1 ACMG/AMP variant criterion. Hum Mutat. 2018; 39:1517–1524. PMID: 30192042.
28. Kuchenbaecker KB, Hopper JL, Barnes DR, Phillips KA, Mooij TM, Roos-Blom MJ, et al. Risks of breast, ovarian, and contralateral breast cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. JAMA. 2017; 317:2402–2416. PMID: 28632866.
29. Ha HI, Ryu JS, Shim H, Kong SY, Lim MC. Reclassification of BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants found in ovarian epithelial, fallopian tube, and primary peritoneal cancers. J Gynecol Oncol. 2020; 31:e83. PMID: 33078592.
30. Rebbeck TR, Mitra N, Wan F, Sinilnikova OM, Healey S, McGuffog L, et al. Association of type and location of BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations with risk of breast and ovarian cancer. JAMA. 2015; 313:1347–1361. PMID: 25849179.
Go to : 




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print





 XML Download
XML Download