INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study participants
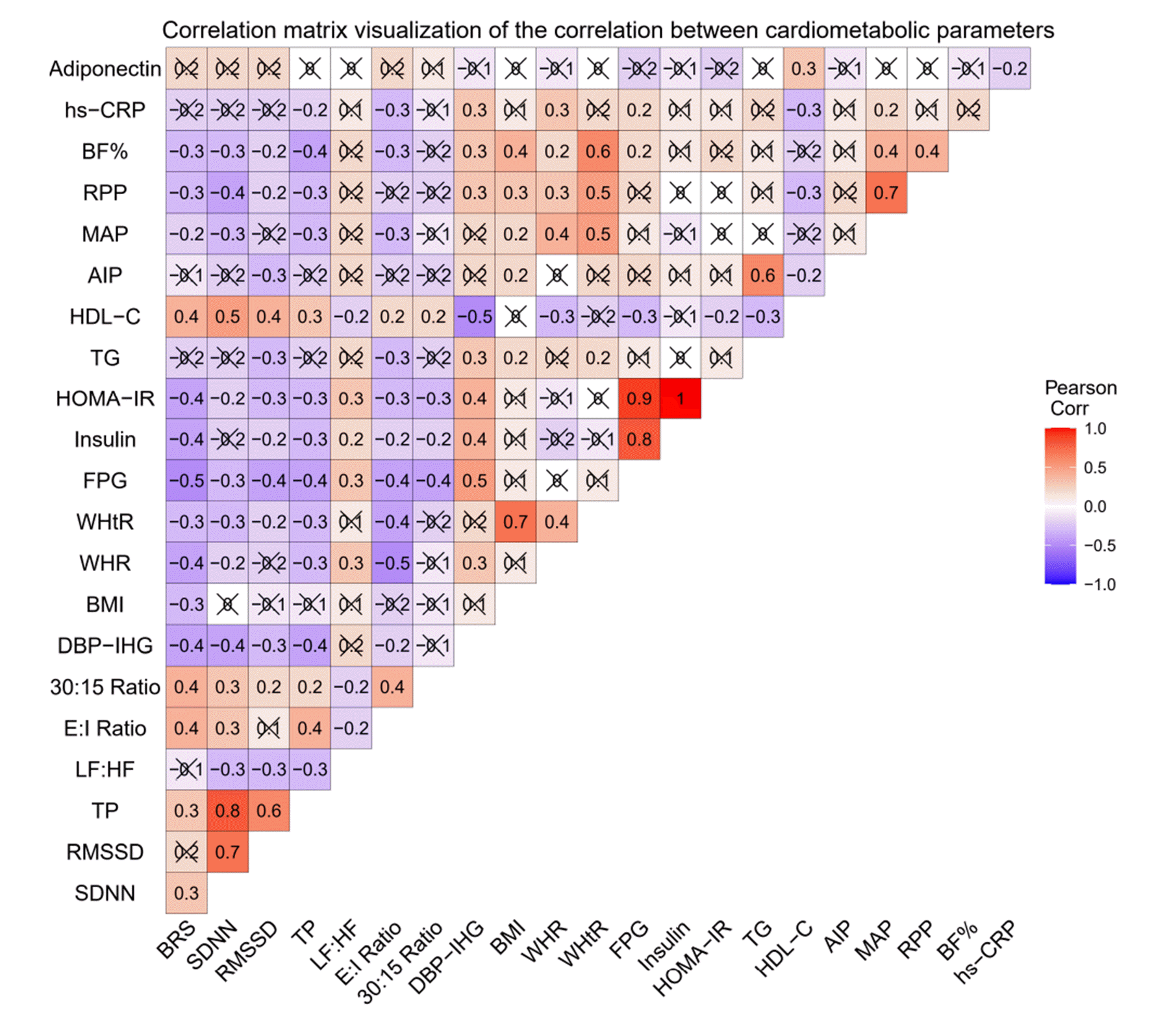
Demographic, anthropometric, clinical, and biochemical data collection
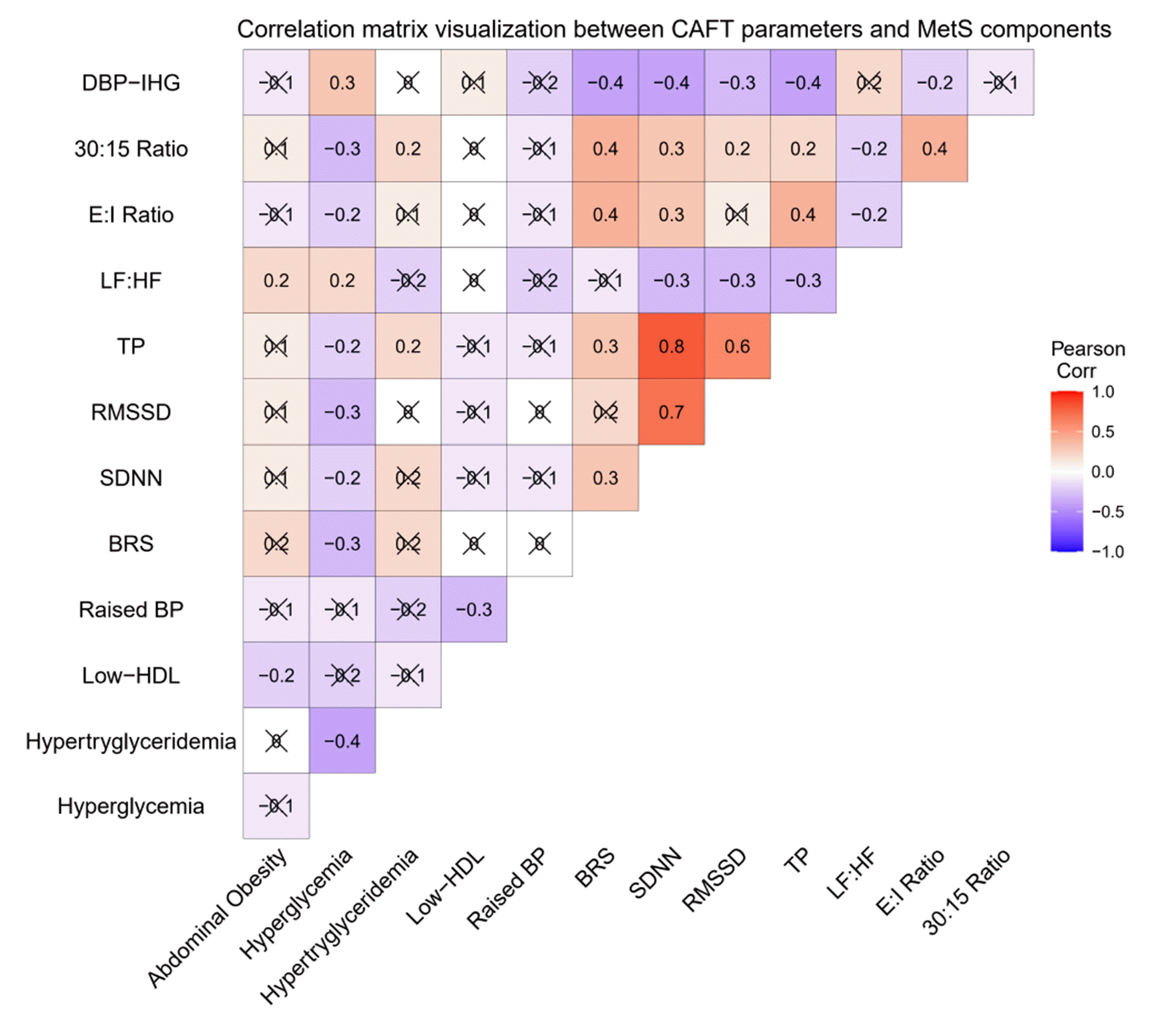
Measures of cardiac autonomic modulation
Short-term HRV
BRS
Conventional AFTs [27,28]
HR response to deep breathing: Baseline ECG recordings were taken in the supine position for 30 sec. Subjects were instructed to breathe slowly and deeply at six breaths per minute, with 5 sec of inspiratory and expiratory cycles. The E:I ratio is the measure of response calculated as a ratio of the longest RR interval during expiration (E) to the shortest RR interval during inspiration (I).
Lying to standing test: This test aimed to determine the effects of orthostasis (standing) on HR and BP. The baseline ECG and BP measurements were taken while the subject was lying down, and the subject was told to stand up within 3 sec. A continuous ECG was recorded, and the BP was monitored every 40 sec by an automatic BP monitor for five minutes. The 30/15 ratio is calculated as the ratio of the longest RR intervals around the 30th beat and the shortest RR intervals around the 15th beat in response to orthostasis.
Isometric handgrip test: The subjects were instructed to press the handgrip dynamometer (Inco, Ambala, India) for two minutes at 1/3rd of their maximum strength after obtaining their baseline BP value. Recordings of BP were taken during the first and second minutes of contraction. The measure of response is the difference between baseline and maximum rise in diastolic blood pressure (ΔDBPIHG). ΔDBPIHG is considered normal at ≥ 16 and abnormal at ≤ 10.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download