Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Notes
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Chae JH contributed to study conception and design; Chae JH, Kim SY, Lee JS, and Ko JM were involved in clinical evaluation; Kim MJ interpreted the results; Kim MJ and Kim SY drafted the manuscript; and Chae JH and Seong MW supervised the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
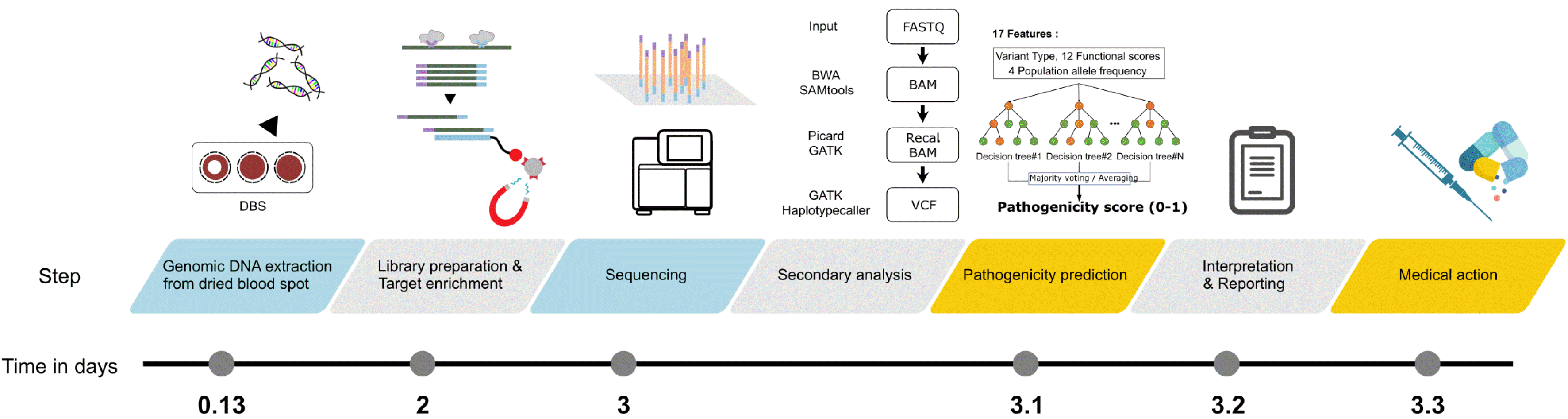
Fig. 2
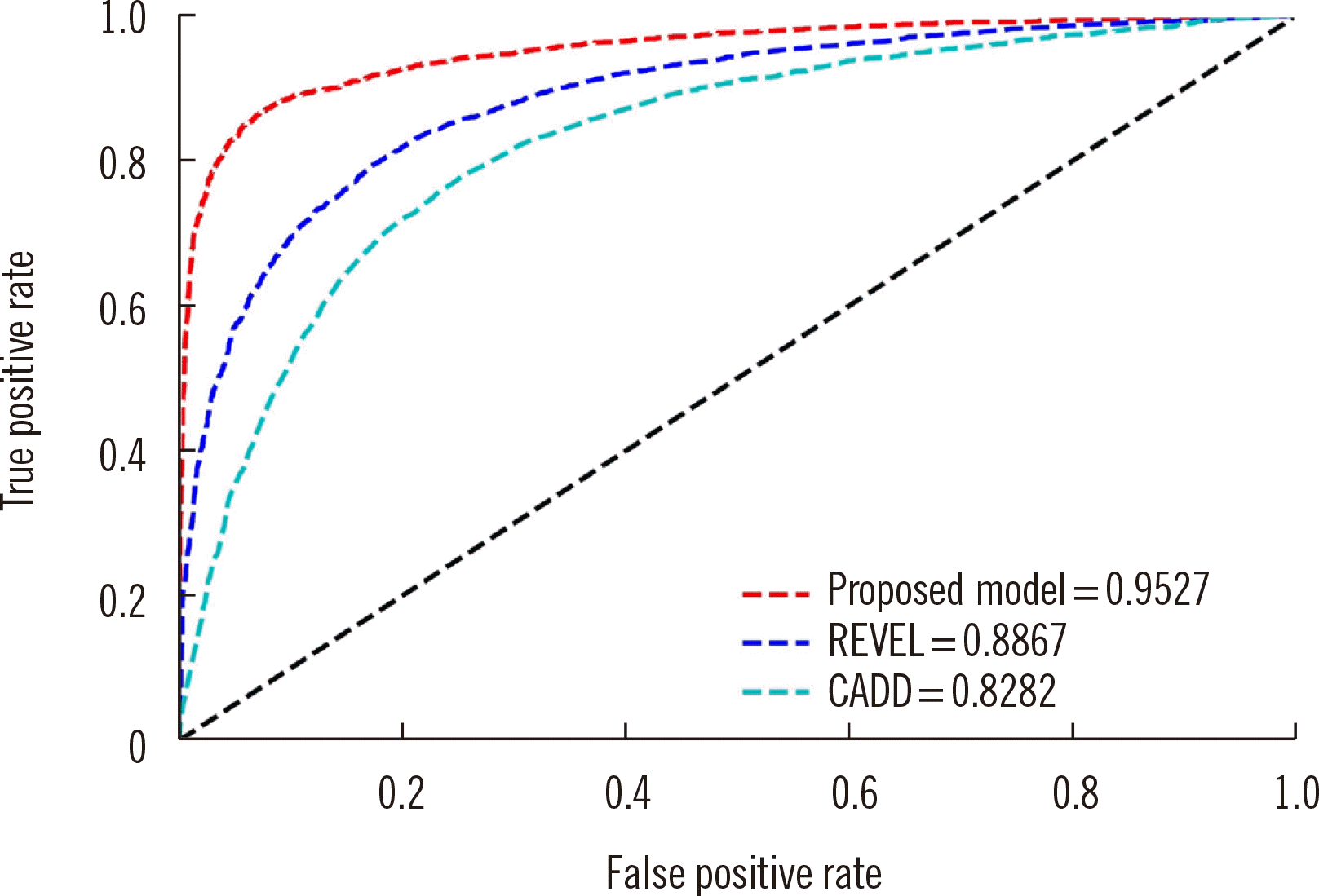
Table 1
Table 2
Table 3
| Case No. | Gene symbol | Transcript | Nucleotide change | Amino acid change | Zygosity | Variant classification by MedyPatho | Segregation | Clinical validation | Final classification | ACMG evidences* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2 | GALNS | NM_000512.4 | c.319G >A | p.Ala107Thr | Het | LP | Trans | Serum galactose-6-sulfatase 0.37 nmol/17 hr/mg protein (ref, 18.6–61.8) | LP | PM2, PM3, PP3, PP5 |
| GALNS | NM_000512.4 | c.451C >A | p.Pro151Thr | Het | LP | LP | PM1, PM2, PM5, PP3, PP5 | |||
| P5 | ACADS | NM_000017.2 | c.1031A >G | p.Glu344Gly | Het | LP | Not done | Serum C4 1.995 μmol/L (cut off, 0.41) | LP | PM1, PM2, PP3, PP5 |
| ACADS | NM_000017.2 | c.164C >T | p.Pro55Leu | Het | LP | LP | PS3, PM2, PP5 | |||
| P6 | PCCA | NM_000282.3 | c.1846-2A >G | p? | Het | LP | Trans | Urine propionylglycine 80.0 (ref, not detected) | LP | PVS1, PM2 |
| PCCA | NM_000282.3 | c.938G >C | p.Arg313Pro | Het | VUS† | LP† | PM2, PM3, PM5, PP3 | |||
| P10 | PAH | NM_000277.1 | c.975C >G | p.Tyr325* | Het | P | Not done | Serum phenylalanine 163 μmol/L (ref, 13–91) | P | PVS1, PM2, PP5 |
| PAH | NM_000277.1 | c.158G >A | p.Arg53His | Het | VUS | VUS | BS2, PM5 | |||
| P14 | SLC25A13 | NM_014252.3 | c.852_855delTATG | p.Met285Profs*2 | Het | P | Not done | Serum citrulline 378 μmol/L (ref, 8–36) | P | PVS1, PM2, PP5 |
| SLC25A13 | NM_014252.3 | c.1177+1G >A | p? | Het | P | P | PVS1, PM2, PP5 | |||
| P25 | ACADM | NM_000016.4 | c.1189T >A | p.Try397Asn | Het | LP | Trans | Serum C6 0.145 μmol/L (cut off < 0.1), C8 0.26 μmol/L (cut off < 0.18), C10:1 0.16 μmol/L (cut off < 0.13) | LP | PM2, PM5, PP2, PP3, PP4, PP5 |
| ACADM | NM_000016.4 | c.1231G >T | p.Val411Leu | Het | VUS† | LP† | PM2, PM3, PP2, PP4 | |||
| P36 | ACADM | NM_000016.4 | c.1189T >A | p.Tyr397Asn | Het | LP | Not done | Serum C6 0.64 μmol/L (cut off < 0.1), C8 1.59 μmol/L (cut off < 0.12), C10:1 0.45 μmol/L (cut off < 0.08) | LP | PM2, PM5, PP2, PP3, PP4, PP5 |
| ACADM | NM_000016.4 | c.91C >T | p.Arg31Cys | Het | VUS† | LP† | PM2, PM5, PP2, PP4, PP5 | |||
| P40 | MCCC2 | NM_022132.4 | c.838G >T | p.Asp280Tyr | Het | LP | Not done | Urine 3-hydroxyisovaleric acid 1,731.1 mmol/mol Cr (ref, < 18) | LP | PM2, PP2, PP3, PP4, PP5 |
| MCCC2 | NM_022132.4 | c.1342G >A | p.Gly448Arg | Het | VUS† | LP† | PM2, PP2, PP3, PP4, PP5 | |||
| P41 | PREPL | NM_006036.4 | c.1979_1980del | p.Leu660Glnfs*9 | Het | LP† | Trans | Repetitive nerve stimulation test, insignificant | P† | PVS1, PM2, PM3 |
| PREPL | NM_006036.4 | c.1747-9_1747del | p? | Het | LP† | P† | PVS1, PM2, PM3 | |||
| P45‡ | HBA2 | NM_000517.4 | c.427T >C | p.*143Qext*31 | Hem | LP | Not done | Not done | LP | PM2, PM3, PM4 |
| P46 | PHKA2 | NM_000292.2 | c.1246-2A >G | p? | Hem | LP | Not done | GOT/GPT 59/49 IU/L (ref, 1–40/1–40) | LP | PVS1, PM2 |
| P72 | ACADS | NM_000017.2 | c.164C >T | c.Pro55Leu | Hom | LP | Not done | Serum C4 0.805 μmol/L (ref, < 0.41) | LP | PS3, PM2, PP5 |
| P74 | ACADS | NM_000017.2 | c.1031A >G | p.Glu344Gly | Het | LP | Not done | Serum C4 0.905 μmol/L (ref, < 0.41) | LP | PM1, PM2, PP3, PP5 |
| ACADS | NM_000017.2 | c.1130C >T | p.Pro377Leu | Het | LP | LP | PM1, PM2, PP3, PP5 | |||
| P83 | ACADS | NM_000017.2 | c.1031A >G | p.Glu344Gly | Hom | LP | Not done | Serum C4 1.965 μmol/L (ref, < 0.41) | LP | PM1, PM2, PP3, PP5 |
| P111 | PAH | NM_000277.1 | c.1068C >G | p.Tyr356* | Het | P | Not done | Serum phenylalanine 173 μmol/L (ref, 25–74) | P | PVS1, PM2, PP5 |
| PAH | NM_000277.1 | c.158G >A | p.Arg53His | Het | VUS | VUS | BS2, PM5 |
*All variants were assessed based on the ACMG or Association for Molecular Pathology guidelines [17]; †Initial classification using MedyPatho was changed at final classification; ‡Given the high homology between HBA1 and HBA2 and that common deletions account for 85% of pathogenic variants in alpha thalassemia, Sanger sequencing and multiplex ligation probe amplification were performed to confirm the variant. This patient had a heterozygous common–SEA deletion; thus, the zygosity of the c.427T>C variant was determined to be hemizygous.
Table 4
| Case No. | Age at symptom onset (months) | Major complaint | Final diagnosis | Time to result reporting (days) | Time to medical decision (days) | Treatment plan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2 | 40 | Joint pain | Mucopolysaccharidosis IVA | 5 | 12 | Enzyme replacement therapy |
| P5 | 0 | NST abnormality | SCAD deficiency | 3 | 18 | Avoid fasting, frequent meals |
| P6 | 8 | Seizure | Propionic acidemia | 3 | NA† | L-carnitine, low-isoleucine/valine diet |
| P10 | 0 | NST abnormality | Hyperphenylalaninemia | 3 | 11 | Avoid unnecessary treatment, further testing |
| P14 | 0 | NST abnormality | Citrullinemia, type II | 2 | NA† | Low-carbohydrate and high-protein diet |
| P25 | 149 | LFT abnormality | MCAD deficiency | 2 | 68 | Low-fat diet, avoid fasting |
| P36 | 0 | NST abnormality | MCAD deficiency | 5 | 19 | Low-fat diet, avoid fasting |
| P40 | 0 | NST abnormality | 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase 2 deficiency | 2 | NA† | L-carnitine, avoid fasting |
| P41 | 1 | Neonatal hypotonia | Congenital myasthenic syndrome | 2 | 2 | Acetylcholine esterase inhibitor, salbutamol |
| P45 | 0 | NST abnormality (incidental finding*) | Alpha thalassemia | 10 | 22 | Waiting for stem cell transplantation |
| P46 | 21 | Abdominal distension | Glycogen storage disease IXa1 | 10 | 22 | Corn starch, low-fat diet, avoid fasting |
| P72 | 0 | NST abnormality | SCAD deficiency | 4 | 28 | Avoid fasting, frequent meals |
| P74 | 0 | NST abnormality | SCAD deficiency | 9 | 17 | Avoid fasting, frequent meals |
| P83 | 0 | NST abnormality | SCAD deficiency | 4 | 24 | Avoid fasting, frequent meals |
| P111 | 0 | NST abnormality | Hyperphenylalaninemia | 1 | 8 | Avoid unnecessary treatment |
*The patient was enrolled because of NST abnormality (elevated C18, C20–C24) and was diagnosed as having alpha thalassemia, unrelated to the initial NST findings. We concluded that the initial NST finding and diagnosis were incidental; †Medical action was started before the genetic diagnosis in P6, P14, and P40 based on their symptoms or NST findings.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download