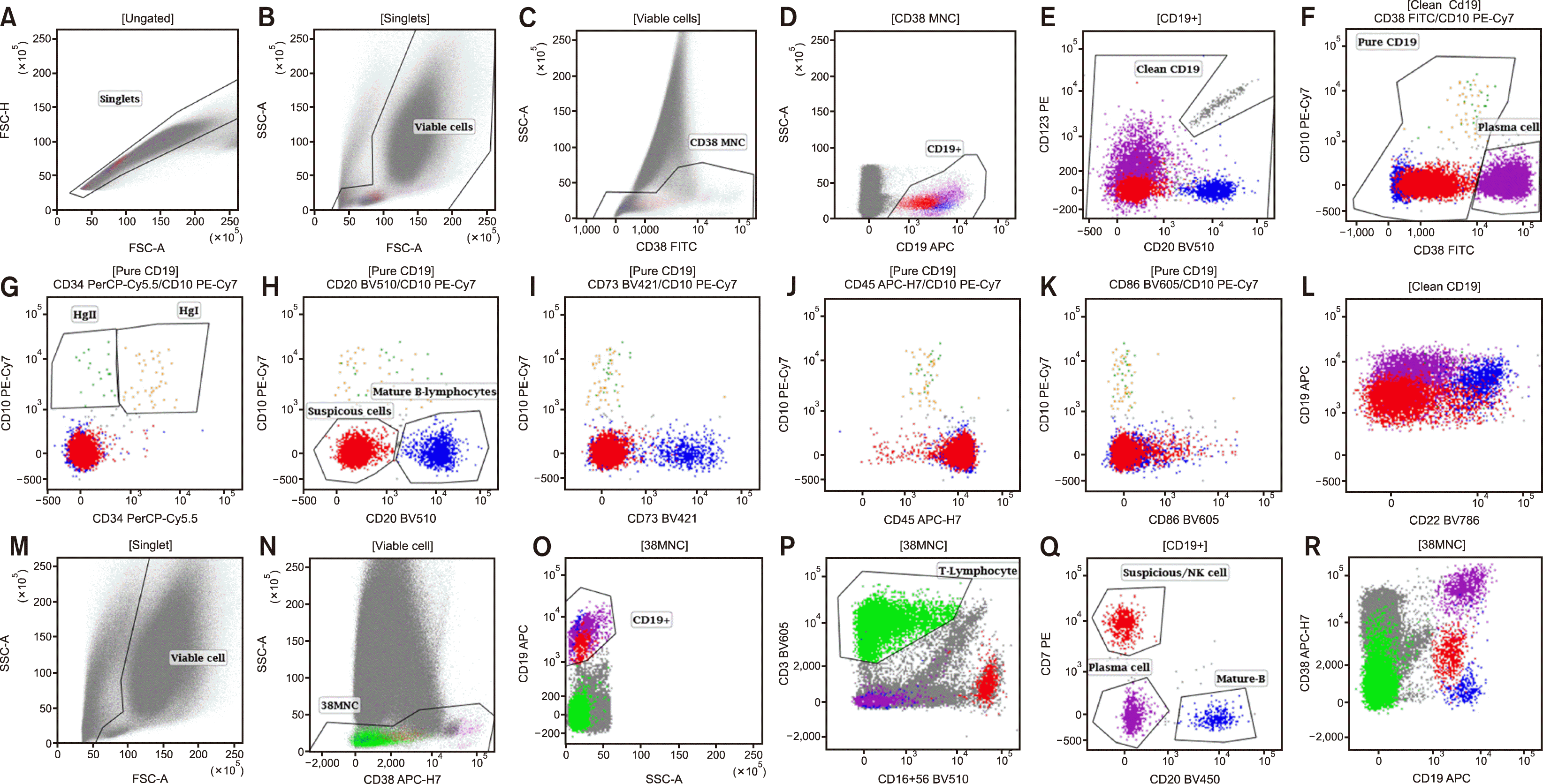
A 10-year-old male patient with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) came in for a post-induction measurable residual disease (MRD) assessment. The diagnostic immunophenotype was CD19+/CD10+/CD34heterogeneous+/cCD79a+/CD22+/CD20heterogeneous+/CD38Dim+/CD73bright+/CD45-/CD123-/CD86-/CD304-. The bone marrow aspirate sample was processed via a bulk lyse-stain-wash technique using a 10-color antibody panel and 3.3 million events were observed on the BD FACS Lyric flow cytometer. Using the Kaluza software, a suspicious population was identified with an unusual CD19+/CD45bright+/CD38heterogeneous+/CD34-/CD10-/CD20-/CD73-/CD123-/CD22-/ CD86-immunophenotype (A–L). There was no therapeutic history of rituximab use. The presence of a single B-lineage marker, CD19, coupled with the absence of CD10 and CD22 made this population unlikely to be associated with MRD. Considering the bright expression of CD45, a custom tube was processed and the population was found to be CD7+, CD16/CD56+, and sCD3-(M–R); they also showed a CD19 expression, similar to the prior observation. Finally, an MRD negative report was issued; the MRD mimicking cells were attributed to trogocytosis of the CD19 antigen by the NK cells. Diagnostic immunophenotyping revealed a significant clue in this case. NK-cell trogocytosis of the CD19 receptor, the initial gating marker for B-ALL MRD evaluation, though rare, can mimic MRD and should be considered as a differential.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download