Introduction
Subjects and Methods
Subjects
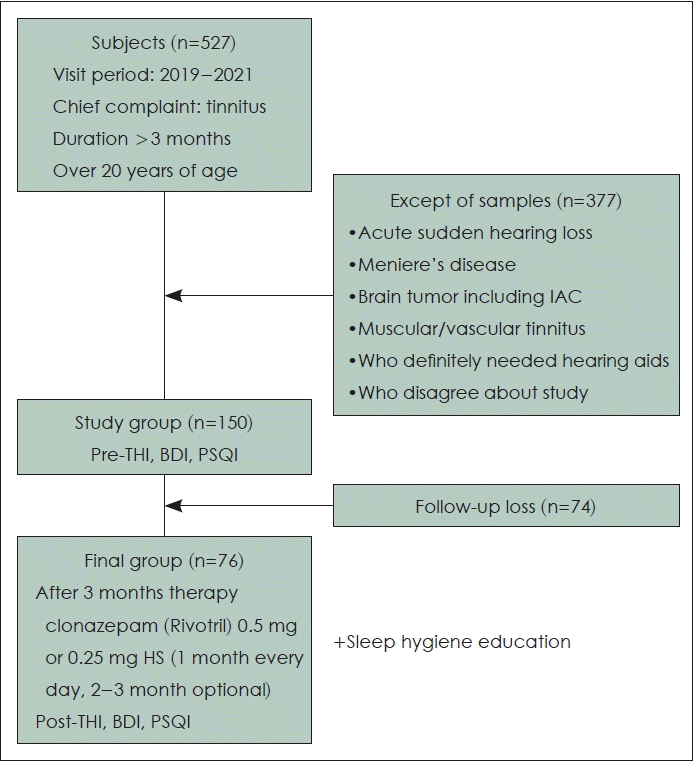 | Fig. 1.A total of 527 patients with tinnitus who visited a tertiary hospital in 2019–2021, underwent hearing and tinnitus tests, and completed a tinnitus questionnaire were considered for this study. IAC, internal auditory canal; THI, Tinnitus Handicap Inventory; BDI, Beck Depression Inventory; PSQI, Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index. |
Treatment protocol
Statistical analysis
Results
Demographics of tinnitus patients
Table 1.
| Pre-treatment | Post-treatment | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, M/F | 38 (50)/38 (50) | ||
| Age, yrs | 57.2±9.01 | 0.914 | |
| PTA (dB) | |||
| Rt | 30.4±20.67 | 0.101 | |
| Lt | 31.7±17.06 | 0.549 | |
| THI | 44.3±23.4 | 33.6±17.1 | <0.0001*** |
| BDI | 7.96±2.36 | 7.38±2.25 | 0.1231 |
| PSQI | 6.85±4.68 | 4.04±3.20 | 0.0002*** |
| Correlation | |||
| Pre: THI-BDI | 0.0027** | ||
| Pre: THI-PSQI | <0.0001*** | ||
| Pre: THI-BDI/PSQI | Pre-THI=-6.299+2.884×pre-BDI+2.832×pre-PSQI | <0.0001*** | |
| Post THI-THI, BDI, PSQI | Post-THI=0.7673+0.6947×pre-THI+0.3572×pre-PSQI | <0.0001*** | |
Data are presented as n (%) or mean±standard deviation. There were 38 males and 38 females each, and the average age was 57.2±9.01 years, the right PTA was 30.4±20.67 dB HL, and the left was 31.7±17.06 dB HL, which was almost similar. As for the score results of each questionnaire, before treatment, THI was 44.3±23.4, BDI was 7.96±2.36, PSQI was 6.85±4.68, and after treatment, THI was 33.6±17.1, BDI was 7.38±2.25, PSQI was 4.04±3.20. In general, the symptoms of tinnitus (THI) were closely related to depression (BDI) and sleep quality (PSQI). Initial THI score could be calculated as “pre-THI=-6.299+2.884 × pre-BDI+2.832 × pre-PSQI.” Also, the effect of tinnitus treatment using clonazepam could be predicted and seen as “post-THI=0.7673+0.6947× pre-THI+0.3572×pre-PSQI.”
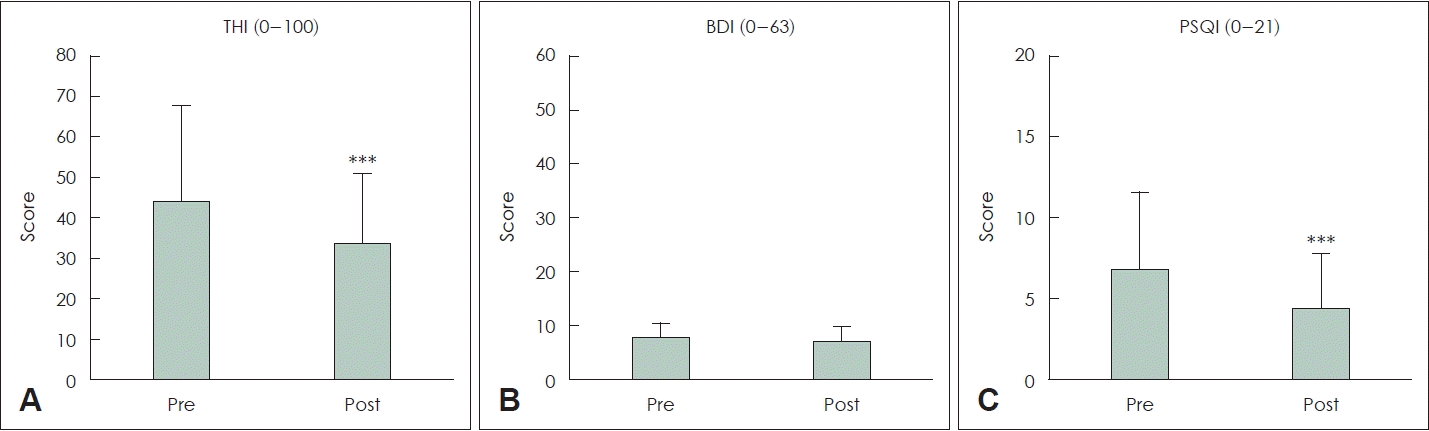 | Fig. 2.Changes in Tinnitus Handicap Inventory (THI), Beck Depression Inventory (BDI), and Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). A: Results of THI showed a statistically significant improvement from 44.3 before treatment to 33.6 after treatment (75.8%, ***p<0.001). B: Results of BDI showed no significant improvement from 7.96 before treatment to 7.38 after treatment (92.7%, p=0.1231). C: Results of PSQI showed a statistically significant improvement from 6.85 before treatment to 4.04 after treatment (58.0%, ***p<0.001). |
Discussion
Table 2.
| Study (year) | Nation | Design | Participants | Intervention, comparator | Outcome measure | Result | Side effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lectenberg and Shulman [24] (1984) | New York, USA | Prospective, randomized, single-blind comparison | 116 participants, 18-85 yrs, at least 1 month | Diazepam, oxazepam, clonazepam 0.5-3 mg | Self-rating scale | Diazepam: 1/15 improved | Sedation |
| Oxazepam: 12/23 | Drowsiness | ||||||
| Clonazepam: 18/26 | |||||||
| Johnson, et al. [25] (1993) | Poland, USA | Prospective, randomized, single-blind comparison | 40 participants, 21-65 yrs, at least 1 yr | Alprazolam 0.5-1.5 mg | Tinnitus loudness, VAS | Alprazolam: 13/17 improved | |
| Placebo: 1/19 | |||||||
| Gananca, et al. [21] (2002) | Brazil | Retrospective survey | 1020 participants, 13-87 yrs | Clonazepam 0.5-1.0 mg, 60-180 days | 32% improved | 16.9% SE | |
| Headache | |||||||
| Drowsiness | |||||||
| Nightmare | |||||||
| Bahmad, et al. [26] (2006) | Brazil | Prospective, randomized, single-blind controlled trial | 36 participants, VAS score>7, at least 6 months | Clonazepam 0.5-2 mg with gabapentin 300-900 mg or placebo | VAS | Clonazepam+placebo: decrease in tinnitus intensity & annoyance compared with placebo | Drowsiness |
| Clonazepam+gabapentin: no difference | |||||||
| Jalali, et al. [27] (2009) | Iran | Prospective, randomized, triple-blind, cross-over | 36 participants, 21-65 yrs, at least 1 yr | Alprazolam 0.5-1.5 mg, 8 weeks | Tinnitus loudness, VAS, THI | No significant improved | Sedation |
| Drowsiness | |||||||
| Han, et al. [28] (2012) | Chuncheon, Korea | Prospective, randomized, open-label, cross-over comparison | 38 participants, 16-80 yrs, at least 2 months | Clonazepam 0.5-2 mg | Tinnitus loudness, THI, VAS | Mean THI score 61%, VAS score, tinnitus loudness 74% improved | Drowsiness (36.8%) |
| Ginkgo biloba 40-160 ng, 5 weeks | Dizziness (5.3%) |
Related studies for benzodiazepine in the treatment of tinnitus. The effectiveness of alprazolam varies from study to study. Johnson, et al. [25] study showed that alprazolam improved 13 out of 17 patients with tinnitus. But the other study Jalali, et al. [27] showed alprazolam cannot improved tinnitus. Unlike alprazolam, clonazepam is known to be effective in most studies. Lectenberg and Shulman’s study [24] showed that 18 out of 26 tinnitus improved when clonazepam 0.5–3 mg was used. Gananca, et al. [21] showed that when using clonazepam 0.5–1.0 mg for 60–180 days, 32% of tinnitus patients showed improvement. Bahmad, et al. [26] showed that when using clonazepam 0.5–2 mg, VAS of tinnitus was improved. Recently, Han’s study [28] showed that 61% of mean THI score, VAS score, and 74% of tinnitus loudness was improved when using clonazepam 0.5–2 mg for 5 weeks. Although clonazepam was effective in the treatment of tinnitus, there were also side effects, and a common side effects during study was drowsiness, headache and sedation. VAS, visual analog scale; THI, Tinnitus Handicap Inventory; SE, side effect




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download