Introduction
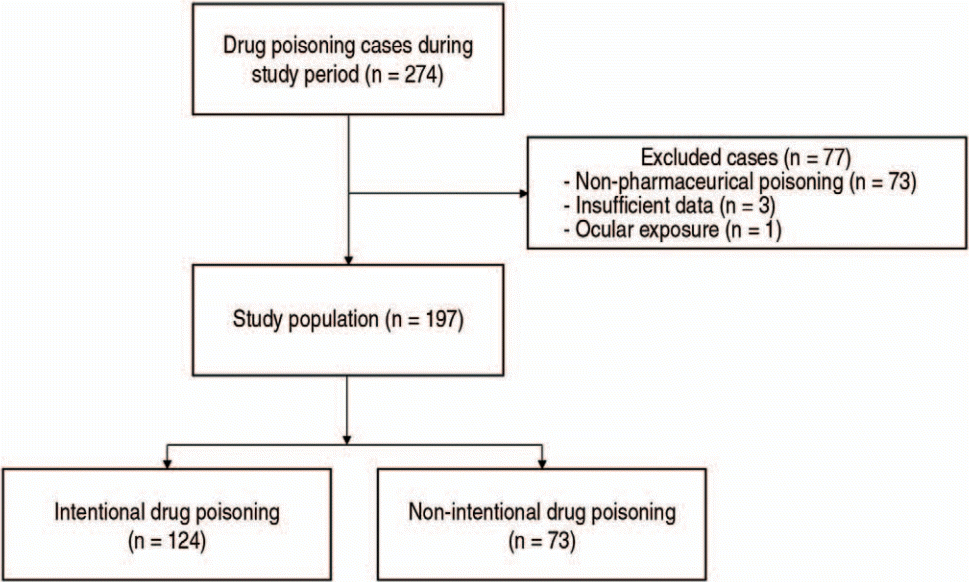
Methods
Results
Table 1.
| Variable | Intentional (N = 124) | Non-intentional (N = 73) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 15.5 (14.2-16.3) | 2.1 (1.5-2.9) | < 0.001 |
| Girls | 95 (76.6) | 33 (45.2) | < 0.001 |
| Time ingestion-visit, h | 3.1 (1.4-8.2) | 0.9 (0.5-1.7) | < 0.001 |
| Drug category | |||
| Antipyretics/analgesics | 53 (42.7)* | 5 (6.8) | < 0.001 |
| Psychotropic drugs | 54 (43.5)* | 13 (17.8) | < 0.001 |
| Antihistamines/cold preparations | 12 (9.7)* | 14 (19.2) | 0.057 |
| Miscellaneous | 5 (4.0)* | 41 (56.2) | < 0.001 |
| Initial manifestations † | |||
| Asymptomatic | 32 (25.8) | 65 (89.0) | < 0.001 |
| Gastrointestinal | 75 (60.5) | 2 (2.7) | < 0.001 |
| Neurologic | 45 (36.3) | 3 (4.1) | < 0.001 |
| Cardiopulmonary | 14 (11.3) | 2 (2.7) | 0.034 |
| Anticholinergic toxidrome | 2 (1.6) | 1 (1.4) | > 0.999 |
| Psychiatric comorbidity‡ | 102 (82.3) | 1 (1.4) | < 0.001 |
| Multiple drug ingestion | 53 (42.7) | 3 (4.1) | < 0.001 |
| Suicide attempt | 67 (54.0) | 0 (0) | < 0.001 |
| Decontamination | 16 (12.9) | 2 (2.7) | 0.017 |
| Antidote | 27 (21.8) | 1 (1.4) | < 0.001 |
| History of poisoning | 36 (29.0) | 0 (0) | < 0.001 |
| Hospitalization, overall | 28 (22.6) | 5 (6.8) | 0.004 |
| Length of stay, d | 3.0 (2.0-4.0) | 3.0 (2.0-4.0) | 0.948 |
| Intensive care unit§ | 2 (1.6) | 1 (1.4) | > 0.999 |
| In-hospital mortality | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NA |
‡ Major depressive disorder (n = 49), bipolar disorder (n = 12), obsessive-compulsive disorder (n = 5), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (n = 5), unspecified depressive disorder (n = 4), anxiety disorder (n = 3), adjustment disorders (n = 3), panic disorder (n = 3), and autistic disorder (n = 2).
Table 2.
| Variable | Acetaminophen (N = 54) | Psychotropic drugs (N = 67) | Antihistamines/cold preparations (N = 26) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, y | 15.0 (14.0-16.2) | 15.0 (13.2-16.2) | 9.0 (2.4-16.2) | 0.075 |
| Girls | 44 (81.5) | 50 (74.6) | 12 (46.2) | 0.004 |
| Time ingestion-visit, h | 4.7 (1.9-11.7) | 2.1 (1.0-5.2) | 1.5 (0.6-2.1) | < 0.001 |
| Initial manifestations* | ||||
| Asymptomatic | 8 (14.8) | 35 (52.2) | 15 (57.7) | < 0.001 |
| Gastrointestinal† | 45 (83.3) | 17 (25.4) | 9 (34.6) | < 0.001 |
| Neurologic‡ | 17 (31.5) | 22 (32.8) | 4 (15.4) | 0.227 |
| Cardiopulmonary§ | 8 (14.8) | 6 (9.0) | 1 (3.8) | 0.285 |
| Anticholinergic toxidrome∥ | 0 (0) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (3.8) | 0.377 |
| Laboratory abnormalities¶ | ||||
| Rhabdomyolysis | 0 (0) | 4 (6.0) | 0 (0) | 0.086 |
| Acidosis | 0 (0) | 1 (1.5) | 1 (3.8) | 0.377 |
| Hepatocellular injury | 2 (3.7) | 0 (0) | 0 (0)1 | 0.169 |
| Electrocardiographic abnormalities** | 10 (18.5) | 17 (25.4) | 6 (23.1) | 0.666 |
| Psychiatric comorbidity | 37 (68.5) | 53 (79.1) | 9 (34.6) | < 0.001 |
| Multiple drug ingestion | 18 (33.3) | 32 (47.8) | 4 (15.4) | 0.012 |
| Suicide attempt | 31 (57.4) | 29 (43.3) | 3 (11.5) | 0.001 |
| Decontamination | 3 (5.6) | 12 (17.9) | 2 (7.7) | 0.085 |
| Antidote | 27 (50.0) | 1 (1.5) | 0 (0)1 | < 0.001 |
| Time ingestion-therapy, h | 7.3 (4.1-10.9) | 15.2 (15.2-15.2) | NA | NA |
| Hospitalization, overall | 21 (38.9) | 1 7 (10.4) | 1 (3.8) | < 0.001 |
| Length of stay, d | 3.0 (2.0-3.0) | 4.0 (2.5-4.0) | 5.0 (5.0-5.0) | 0.420 |
| Intensive care unit | 1 (1.9) | 2 (3.0) | 0 (0) | 0.654 |
‡ In common, headache, dizziness, confusion or loss of consciousness; in psychotropic drugs, plus tremor, dystonia, drooling or hiccups; and in antihistamines/cold preparations, plus seizure.
§ In acetaminophen and psychotropic drugs, chest pain, dyspnea or palpitation; in antihistamines/cold preparations, only palpitation.
¶ Rhabdomyolysis was defined as creatine kinase > 5 times the upper normal limit; acidosis, pH < 7.30; and hepatocellular injury, alanine aminotransferase > 2 times the upper normal limit.
** In acetaminophen, sinus tachycardia or bradycardia (n = 4), nonspecific T wave abnormality (n = 3), and QTc prolongation (> 470 msec) (n = 3); in psychotropic drugs, QTc prolongation (> 470 msec) (n = 10), sinus tachycardia or bradycardia (n = 4), and nonspecific T wave abnormality (n = 3); in antihistamines/cold preparations, sinus tachycardia or bradycardia (n = 3) and nonspecific T wave abnormality (n = 3).
Table 3.
| Psychotropic drugs (N = 67)* | Antihistamines/cold preparations (N = 26)‡ | Miscellaneous (N = 46) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| BZDs, 37 (55.2) | First generation antihistamines, 14 (53.8) | Antihypertensive medications, 13 (28.3) | |
| SSRIs, 35 (52.2) | Nasal decongestants, 8 (30.8) | Montelukast, 4 (8.7) | |
| Atypical antipsychotics, 26 (38.8) | Second generation antihistamines, 7 (26.9) | Finasteride, 4 (8.7) | |
| Anti-epileptic drugs, 13 (19.4) | Mucolytics, 3 (11.5) | Synthyroid, 3 (6.5) | |
| Anti-anxiety drugs other than BZDs, 5 (7.5) | Bronchodilators, 2 (7.7) | Antibiotics, 3 (6.5) | |
| Atypical antidepressants, 4 (6.0) | Herbal cold medications, 2 (7.7) | Dyslipidemia medication, 3 (6.5) | |
| Stimulants, 3 (4.5) | Diabetes medication, 2 (4.3) | ||
| SNRIs, 2 (3.0) | Antiplatelet drugs, 2 (4.3) | ||
| Tricyclic antidepressants, 1 (1.5) | Vitamins, 2 (4.3) | ||
| Others, 5 (7.5)† | Others, 11 (23.9)§ |
* The combinations of generic names or subcategories in the order of frequencies were as follows: SSRI + BZD (n = 8), SSRI + BZD + atypical antipsychotics (n = 5), and SSRI + atypical antipsychotics (n = 4); escitalopram (n = 17), alprazolam (n = 17), clonazepam (n = 14), quetiapine (n = 11), fluoxetine (n = 10), aripiprazole (n = 10), lorazepam (n = 9), divalproex (n = 6), risperidone (n = 5), and lamotrigine (n = 4).




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download