INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Data source
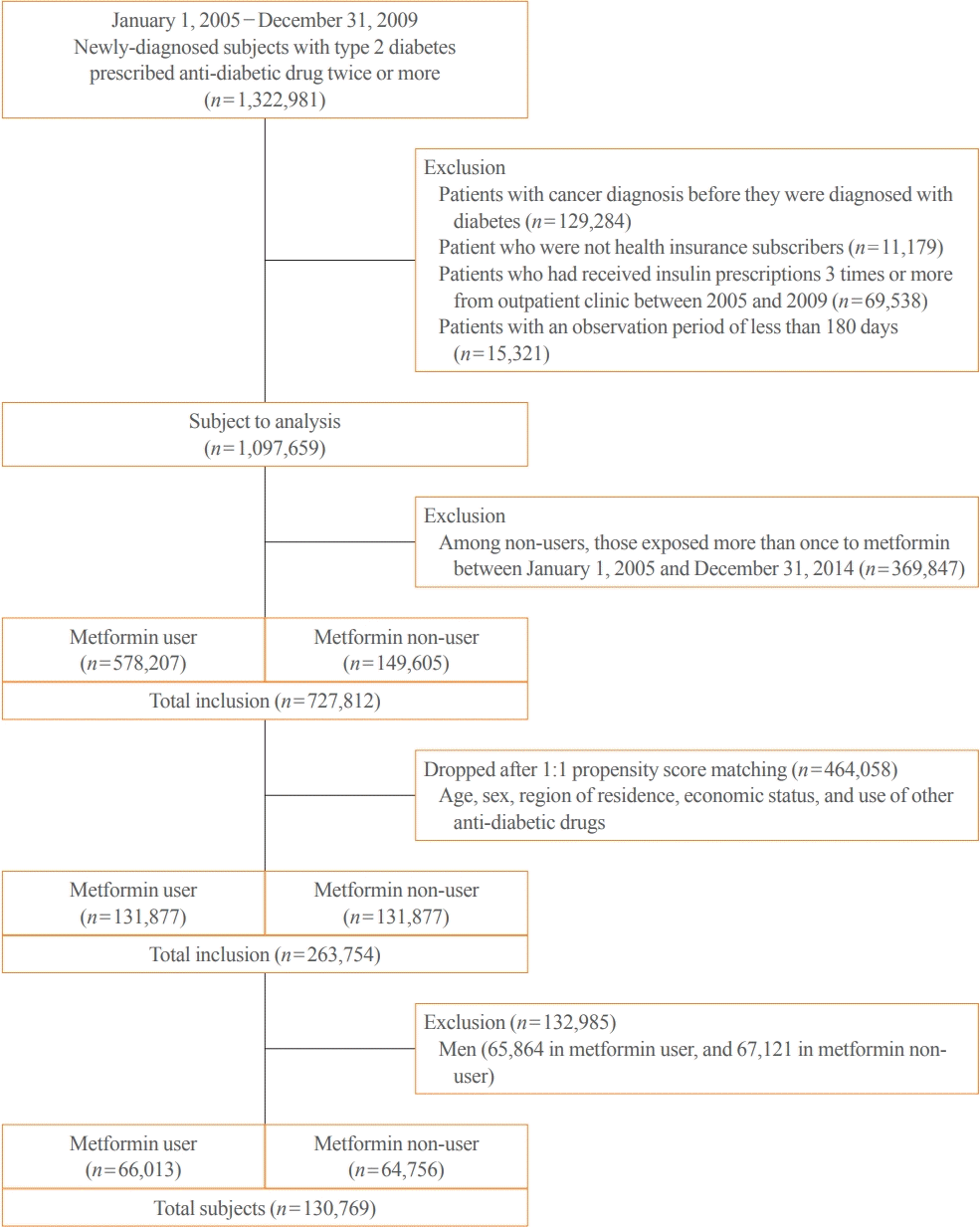
Study population
Definition of metformin exposure
Definitions and covariates
Statistical analyses
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Metformin non-users (n=64,756) | Metformin users (n=66,013) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, yra | 63.9±16.4 | 64.2±13.7 |
| 0–14 | 269 (0.4) | 212 (0.3) |
| 15–20 | 163 (0.3) | 226 (0.3) |
| 20–24 | 333 (0.5) | 295 (0.4) |
| 25–29 | 1,145 (1.8) | 422 (0.6) |
| 30–34 | 1,711 (2.6) | 571 (0.9) |
| 35–39 | 1,593 (2.5) | 1,205 (1.8) |
| 40–44 | 2,274 (3.5) | 2,050 (3.1) |
| 45–49 | 3,543 (5.5) | 3,633 (5.5) |
| 50–54 | 4,890 (7.6) | 5,203 (7.9) |
| 55–59 | 5,792 (8.9) | 5,534 (8.4) |
| 60–64 | 7,540 (11.6) | 9,967 (15.1) |
| 65–69 | 9,960 (15.4) | 11,399 (17.3) |
| 70–74 | 8,784 (13.6) | 11,979 (18.1) |
| 75–79 | 7,962 (12.3) | 8,007 (12.1) |
| ≥80 | 8,797 (13.6) | 5,310 (8.0) |
| Year of study enrollmenta | ||
| 2005 | 15,370 (23.7) | 16,125 (24.4) |
| 2006 | 14,158 (21.9) | 11,613 (17.6) |
| 2007 | 12,823 (19.8) | 12,209 (18.5) |
| 2008 | 11,863 (18.3) | 12,704 (19.2) |
| 2009 | 10,542 (16.3) | 13,362 (20.2) |
| Economic status | ||
| 1–5 (lowest) | 21,860 (33.8) | 22,175 (33.6) |
| 6–10 | 11,162 (17.2) | 11,452 (17.3) |
| 11–15 | 14,349 (22.2) | 14,346 (21.7) |
| 16–20 (highest) | 17,385 (26.8) | 18,040 (27.3) |
| Region of residenceb | ||
| Seoul (capital city) | 13,558 (20.9) | 13,510 (20.5) |
| Metropolitan cities | 15,690 (24.2) | 16,344 (24.8) |
| Rural areas | 35,508 (54.8) | 36,159 (54.8) |
| Anti-diabetic drugs | ||
| Metformin | ||
| Yes | 0 | 66,013 (100.0) |
| No | 64,756 (100.0) | 0 |
| Sulfonylureasb | ||
| Yes | 30,135 (46.5) | 30,155 (45.7) |
| No | 34,621 (53.5) | 35,858 (54.3) |
| TZD | ||
| Yes | 2,190 (3.4) | 2,204 (3.3) |
| No | 62,566 (96.6) | 63,809 (96.7) |
| DPP4i | ||
| Yes | 1,140 (1.8) | 1,138 (1.7) |
| No | 63,616 (98.2) | 64,875 (98.3) |
| AGIa | ||
| Yes | 5,812 (9.0) | 5,534 (8.4) |
| No | 58,944 (91.0) | 60,479 (91.6) |
| Meglitinide | ||
| Yes | 1,968 (3.0) | 1,939 (2.9) |
| No | 62,788 (97.0) | 64,074 (97.1) |
| Daily metformin dose, mean (range), mg | 519 (148) | |
| Cumulative metformin dose, mean (range), mg | 865,999 (547,170) | |
| None | 64,756 (100.0) | 0 |
| 0–239,999 | 0 | 9,611 (14.6) |
| 240,000–1,200,000 | 0 | 39,900 (60.4) |
| >1,200,000 | 0 | 16,502 (25.0) |
| Cumulative duration of therapy, mean (range), day | 1,666 (912) | |
| None | 64,756 (100.0) | 0 |
| 0–469 | 0 | 9,161 (13.9) |
| 470–1,999 | 0 | 30,429 (46.1) |
| ≥2,000 | 0 | 26,423 (40.0) |
| Cervical cancer cases | 274 | 219 |
Cervical cancer incidence according to metformin use
Table 2.
|
Cancer cases (%) |
Incidence of cancer, /100,000 person-years |
Hazard ratio (95% CI) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metformin non-user | Metformin user | Metformin non-user | Metformin user | Univariate | Multivariatea |
| 274 (0.42) | 219 (0.33) | 30.5 | 24.2 | 0.805 (0.674–0.961)b | 0.783 (0.655–0.936)b |
a The comparisons were made using metformin non-users as the reference group. The hazard ratio was adjusted for age, economic status, region of residence, and anti-diabetic medications (sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, and meglitinide);
Table 3.
| Variable | Hazard ratio (95% CI)a | Hazard ratio (95% CI)b |
|---|---|---|
| Cumulative duration, day | ||
| Non-users | 1.000 | - |
| 0–469 | 1.603 (1.205–2.131)d | 1.000 |
| 470–1,999 | 1.140 (0.931–1.396)c | 0.723 (0.530–0.095)d |
| ≥2,000 | 0.151 (0.093–0.243)c | 0.094 (0.055–0.161)c |
| Cumulative dose, mg | ||
| Non-users | 1.000 | - |
| 0–239,999 | 1.798 (1.376–2.349)c | 1.000 |
| 240,000–1,200,000 | 0.849 (0.692–1.042)c | 0.549 (0.356–0.642)c |
| >1,200,000 | 0.141 (0.077–0.258)c | 0.079 (0.042–0.151)c |
| Age, yr | ||
| Non-users | 1.000 | - |
| <50 | 0.763 (0.481–1.252)d | - |
| ≥50 | 0.791 (0.650–0.961)d | - |
a The comparisons were made using metformin non-users as the reference group. The hazard ratios were adjusted for age, economic status, region of residence, and anti-diabetic medications (sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, and meglitinide);
b The comparisons were made using a cumulative duration of 0–469 days or a cumulative dose of 0–239,999 mg as the reference groups. The hazard ratios were adjusted for age, economic status, region of residence, and anti-diabetic medications (sulfonylureas, thiazolidinediones, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, and meglitinide);




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download