Abstract
Notes
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: Joo Yeon Kim. Data curation: Young Seok Han, Jun Sang Cha. Formal analysis: Min Jung Jung, Joo Yeon Kim. Investigation: Young Seok Han. Methodology: Joo Yeon Kim. Resources: Min Jung Jung. Supervision: Joo Yeon Kim. Visualization: Young Seok Han. Writing—original draft: Young Seok Han. Writing—review & editing: Joo Yeon Kim.
REFERENCES
Fig. 1.
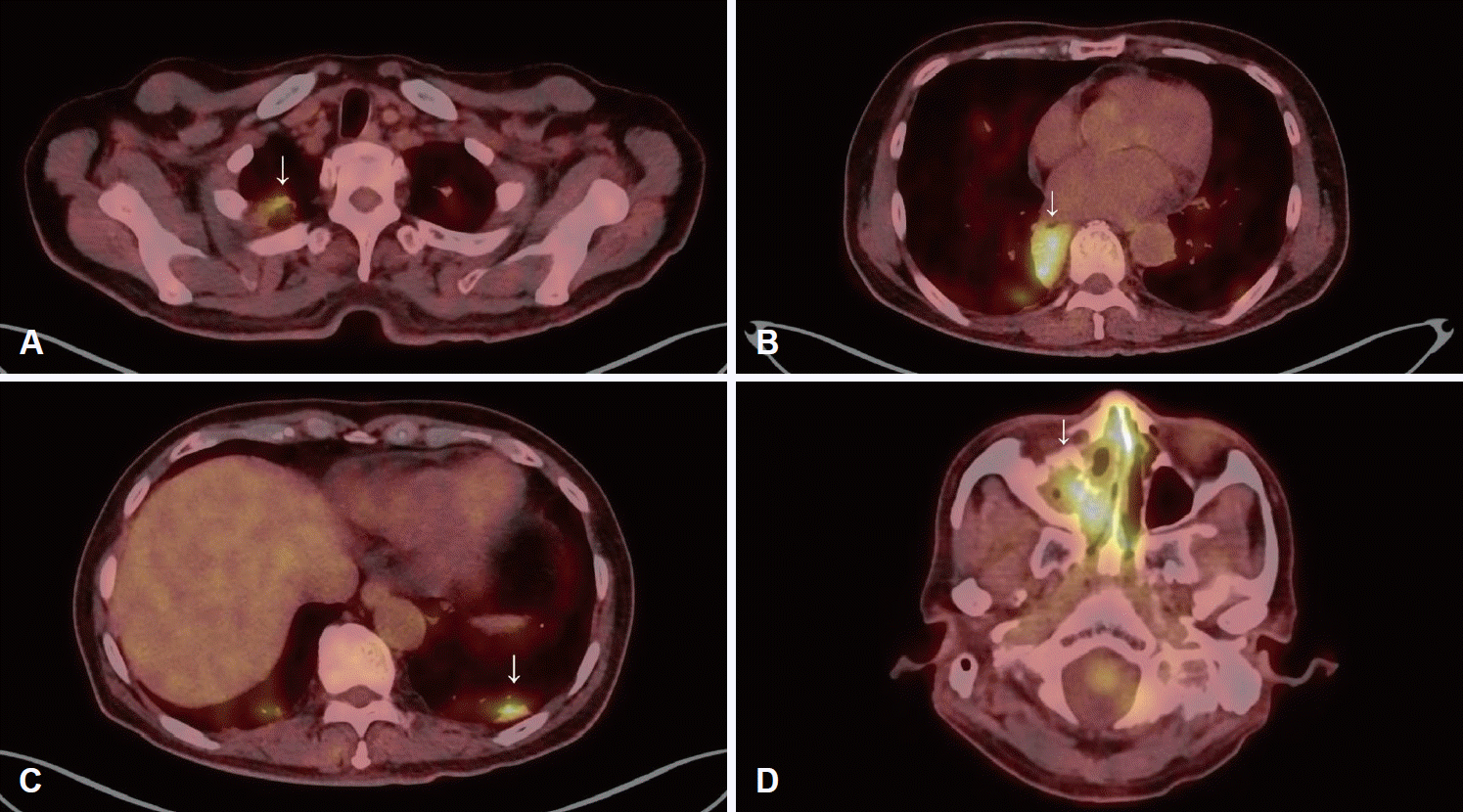
Fig. 2.
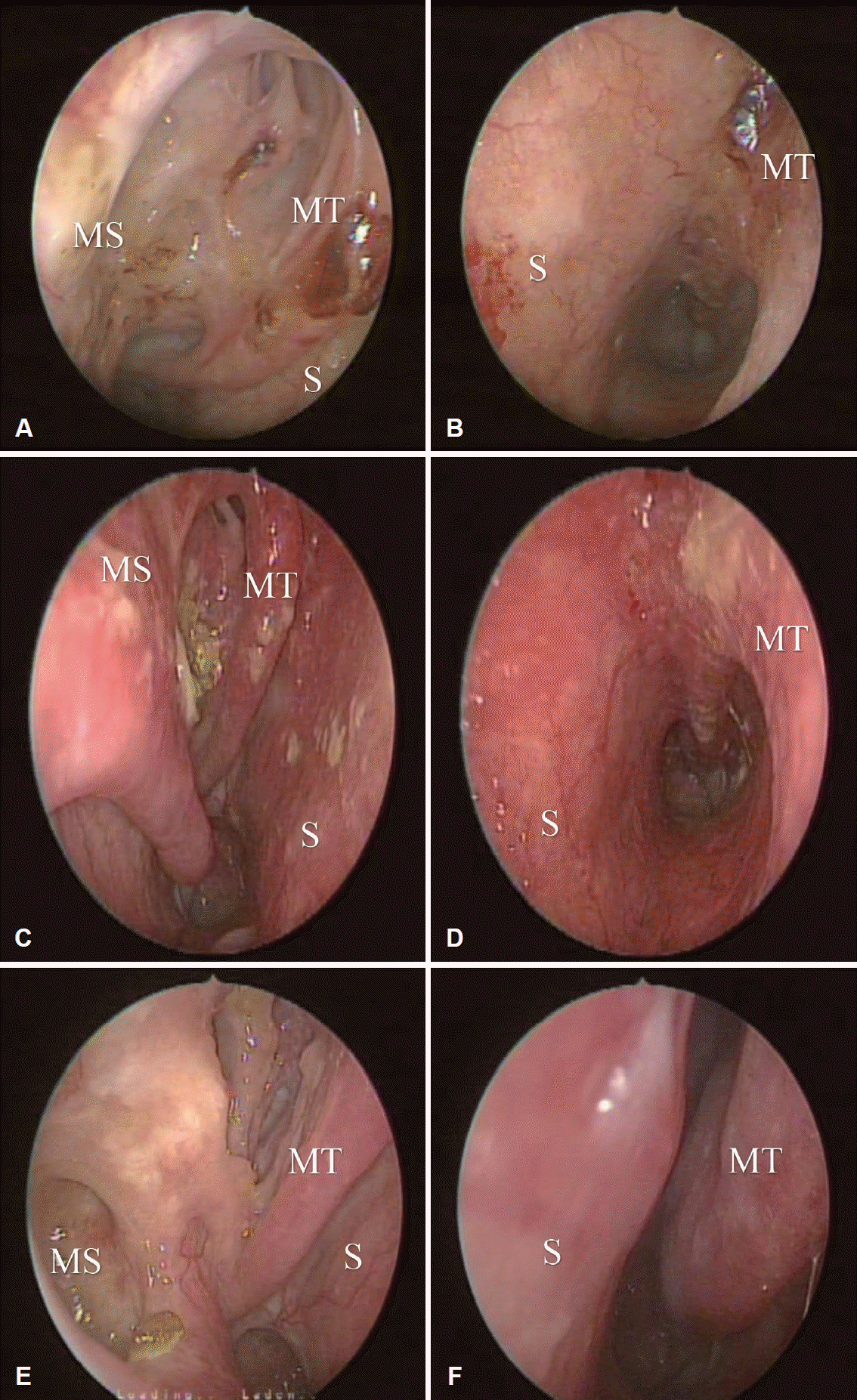
Fig. 3.
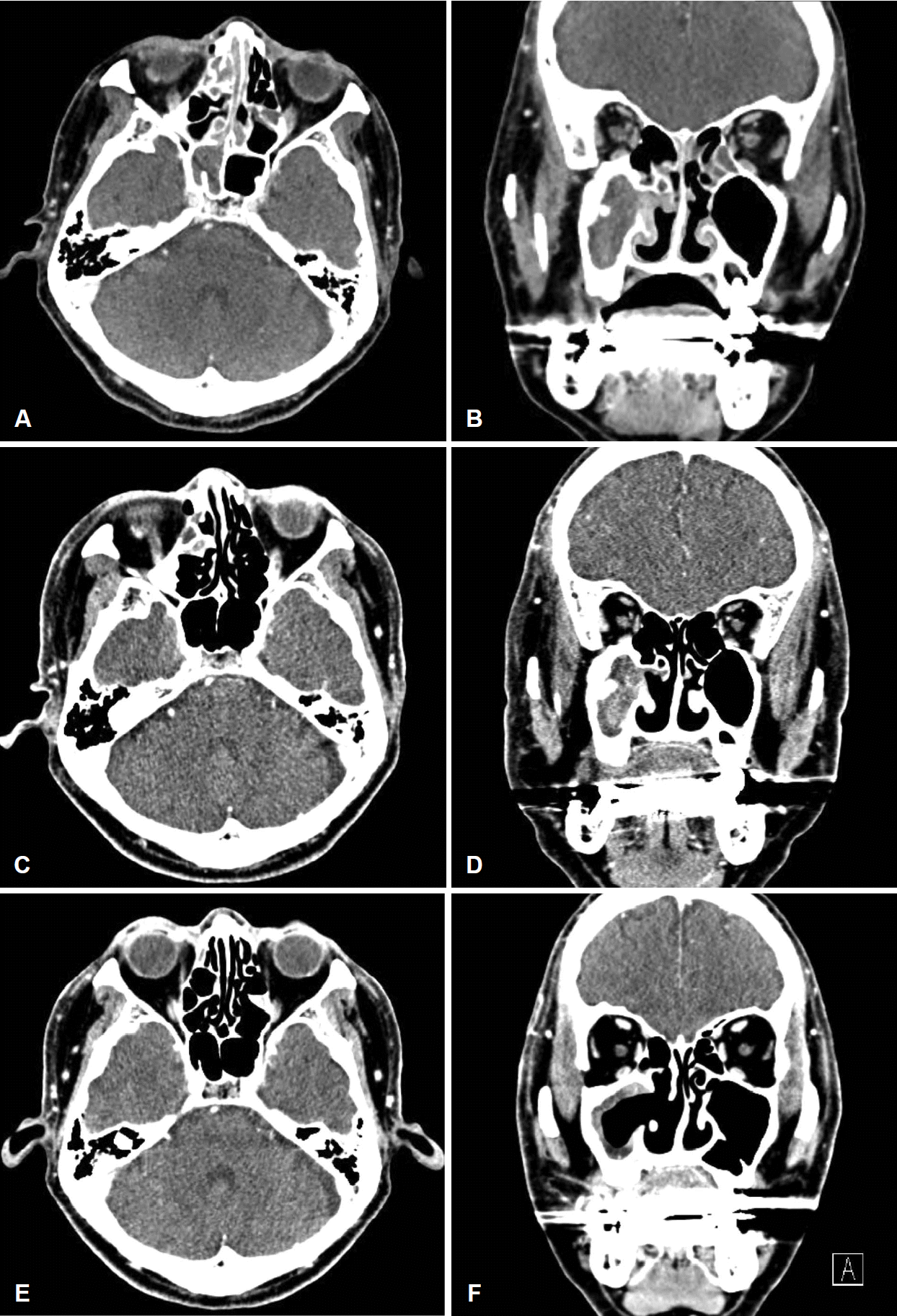
Fig. 4.
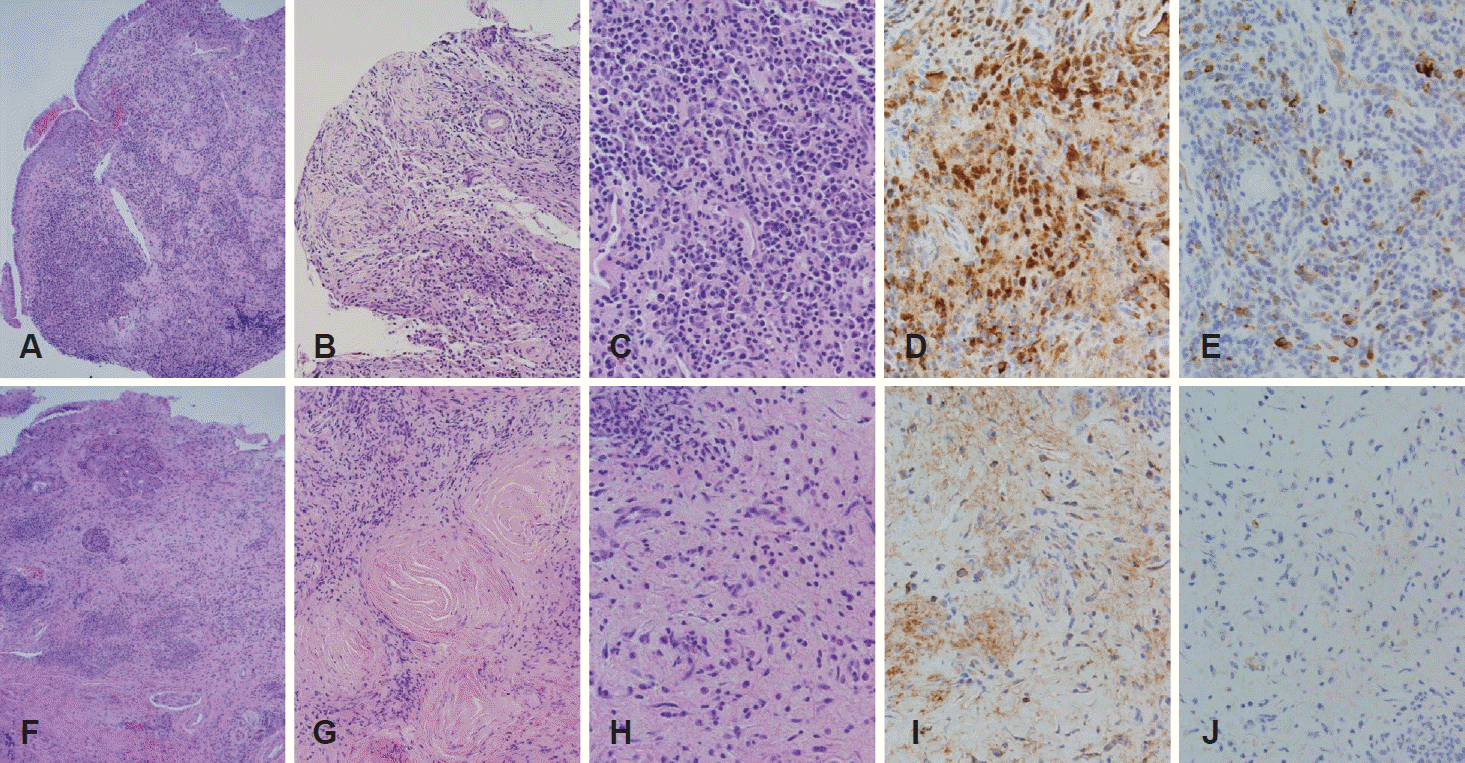
Table 1.
| Case | Age | Sex | Underlying diseases | Presenting symptoms |
Involvement sites |
Diagnostic findings |
Treatment | Progress | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intranasal | Extranasa | Serum IgG4 (reference range; 30-2010 mg/L) | Pathology | |||||||
| Lee, et al. [5] | 54 | F | None | NO, Rt | IT, Rt | Pituitary gland | 550 mg/L | IgG4(+) plasma cells (>106/HPF) | - Diagnostic endoscopic IT mass excision, Rt | - Recurred 10 months after surgery, prednisolone 60 mg/day for 3 weeks and then tapering for 10 months |
| R, Rt | - Endoscopic TSA for pituitary lesion | - No symptoms or recurrence for 4 years from then on | ||||||||
| Lee, et al. [5] | 26 | F | None | NO, both | Septum | None | Unknown | IgG4(+) plasma cells (>30/HPF) | - Methylprednisolone 32 mg/day for 4 weeks and taper | - No symptoms or recurrence for 2 months after treatment and follow-up loss |
| R, both | Cribriform plate | Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor | ||||||||
| PND | ||||||||||
| Sneezing | ||||||||||
| Lee, et al. [5] | 20 | M | None | NO, both | MS, both | None | 530 mg/L | Infiltration of lymphoplasma cells and fibrosis | - Diagnostic ESS, both | - No symptoms or recurrence for 2 months after treatment and follow-up loss |
| ES, both | - Postoperative methylprednisolone 16 mg/day for 6 weeks | |||||||||
| FS, Lt | IgG4(+) plasma cells | |||||||||
| Chung and Lee [6] | 43 | F | None | Facial pain, Lt | MS, Lt | None | 3000 mg/L | Infiltration of lymphoplasma cells and fibrosclerosis | - Diagnostic ESS, Lt | - No symptoms or recurrence for 6 months after treatment |
| NO, Lt | ES, Lt | - Postoperative prednisolone 0.6 mg/kg for 4 weeks and 10 mg/day for 2 months in sequence | ||||||||
| Headache | FS, Lt | IgG4(+) plasma cells (>60/HPF) | ||||||||
| LP, Lt | ||||||||||
| Ko, et al. [7] | 40 | F | Unknown | Saddle nose | MS, Lt | None | 37.5 mg/L | Infiltration of lymphoplasma cells and fibrosclerosis | - Prednisolone 60 mg/day for 5 weeks | - Still no improvement, stopping MTX and changing to AZA 100 mg/day, showing response |
| Epistaxis | LNW, Lt | IgG4(+) plasma cells (>35/HPF) | - Steroid only therapy showed no improvement and changed to combined therapy with MTX 7.5 mg/day for 4 weeks | |||||||
| Crust | Septum | IgG4/IgG ratio 40% | - No symptoms or recurrence for 2 months after low-dose steroid and AZA combination therapy | |||||||
| UP, both | ||||||||||
| Mun, et al. [8] | 69 | F | HTN | Epistaxis | MS, both | None | 1028 mg/L | Infiltration of lymphoplasma cells | - Diagnostic ESS, both | - Symptoms and endoscopic findings improved for 6 months after treatment |
| CKD | Mucopurulent | ES, both | IgG4(+) plasma cells (>90/HPF) | - Postoperative prednisolone 40 mg/day for 1 week, 20 mg/day for 2 weeks and, 10 mg/day for 6 months in sequence | - Intermittent use of steroids as needed | |||||
| Pulmonary Tb | R, both | Septum | IgG4/IgG ratio 70% | - Acute cerebral infarction in the left pons 3 months after ESS | ||||||
| Corneal ulcer | IT, both | - Expired from complications of cerebral infarction one year later of its onset | ||||||||
| Our case | 70 | M | HTN | NO, both | MS, Rt | Lung, both | 4960 mg/L | Infiltration of lymphoplasma cells and storiform fibrosis | - Prednisolone 40 mg/day for 4 weeks, tapering for 6 months | - No symptoms or recurrence for 6 months after treatment |
| CRS | PND | ES, Rt | ||||||||
| Dry nose | SS, Rt | IgG4(+) plasma cells (>100/HPF) | - Curative ESS, both | - Prednisolone 5 mg/day maintenance therapy for residual lung lesions | ||||||
| Crust | ||||||||||
| Hyposmia | IgG4/IgG ratio 30% | |||||||||
HTN, hypertension; CKD, chronic kidney disease; Tb, tuberculosis; CRS, chronic rhinosinusitis; NO, nasal obstruction; R, rhinorrhea; PND, postnasal drip; Rt, right; Lt, left; IT, inferior turbinate; MS, maxillary sinus; ES, ethmoid sinus; FS, frontal sinus; LP, lamina papyracea; LNW, lateral nasal wall; UP, uncinate process; SS, sphenoid sinus; TSA, transsphenoidal approach; ESS, endoscopic sinus surgery; MTX, methotrexate; AZA, azathioprine




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download