INTRODUCTION
METHODS
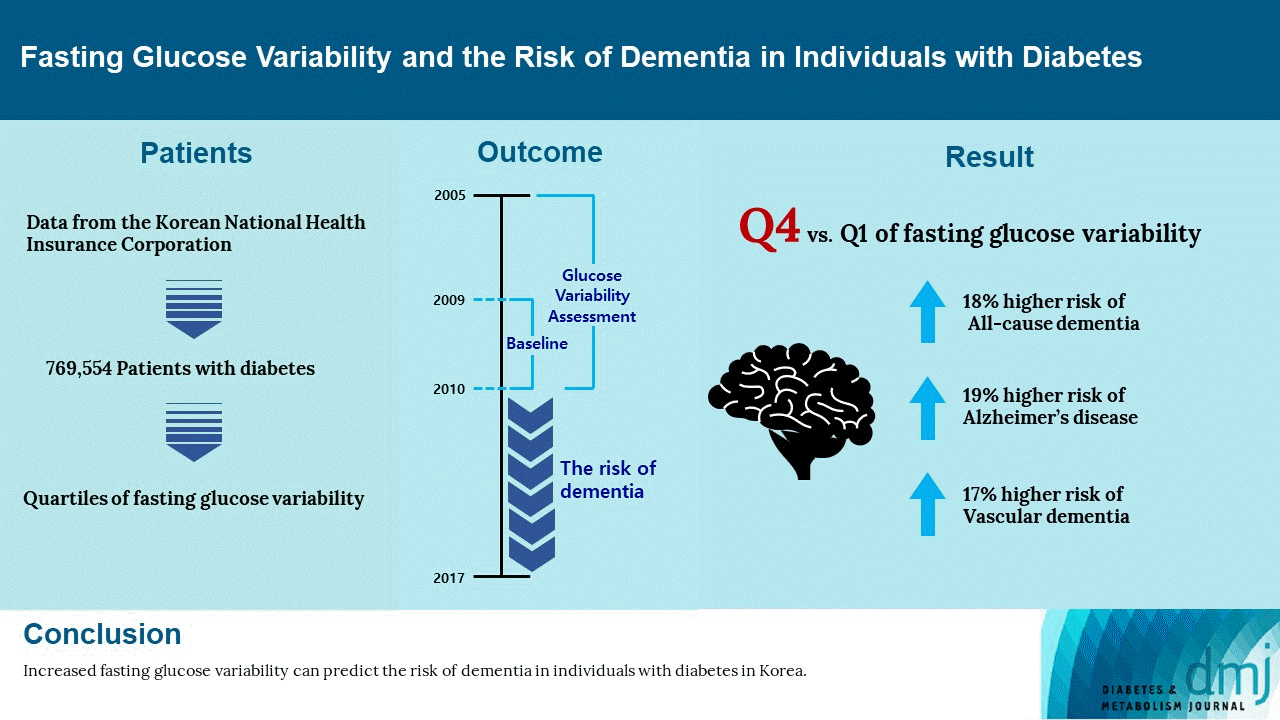
Study design
Study participants
Definition of dementia
Definition of GV
Measurements of covariates
Operational definition of comorbidities
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Table 1.
| Characteristic | VIM Q1 (n=192,387) | VIM Q2 (n=192,390) | VIM Q3 (n=192,389) | VIM Q4 (n=192,388) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 61.1±9.8 | 60.1±9.9 | 59.6±10.1 | 59.2±10.4 | <0.001 | |
| Male sex | 108,883 (56.6) | 115,446 (60) | 119,618 (62.2) | 124,812 (64.9) | <0.001 | |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 24.8±3.0 | 24.9±3.1 | 24.9±3.1 | 24.8±3.2 | <0.001 | |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 128.3±15.2 | 128.7±15.2 | 128.8±15.3 | 128.5±15.3 | <0.001 | |
| FG, mg/dL | 125.1±34.0 | 130.2±35.5 | 135.8±39.0 | 146±53.4 | <0.001 | |
| TC, mg/dL | 193.6±39.1 | 194.9±39.9 | 195.6±40.7 | 194.4±41.5 | <0.001 | |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 132.9 (132.6–133.2) | 138.51 (138.2–138.9) | 143.1 (142.7–143.5) | 146.4 (146.1–146.8) | <0.001 | |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 52.6±22.7 | 52.3±21.6 | 52±21.8 | 51.5±21.2 | <0.001 | |
| FG_VIM, % | 8.2±3.0 | 16.6±2.3 | 25.5±3.0 | 43.6±11.1 | <0.001 | |
| FG_SD, mg/dL | 8.1±5.3 | 16.8±8.5 | 26.7±13.1 | 49±25.2 | <0.001 | |
| FG_CV, % | 6.2±2.6 | 12.8±2.8 | 19.9±4.3 | 35±11.2 | <0.001 | |
| FG_ARV, mg/dL | 10±7.2 | 20.3±11.9 | 31.7±18.3 | 56.5±34.3 | <0.001 | |
| Current smoker | 31,515 (16.4) | 36,711 (19.1) | 42,474 (22.1) | 49,993 (26.0) | <0.001 | |
| Heavy drinking | 12,345 (6.4) | 13,803 (7.2) | 14,628 (7.6) | 14,245 (7.4) | <0.001 | |
| Regular exercise | 49,632 (25.8) | 48,136 (25) | 46,054 (23.9) | 43,129 (22.4) | <0.001 | |
| Comorbidities | ||||||
| Hypertension | 118,250 (61.5) | 116,410 (60.5) | 114,378 (59.5) | 111,527 (58.0) | <0.001 | |
| Dyslipidemia | 101,550 (52.8) | 97,619 (50.7) | 94,080 (48.9) | 89,773 (46.7) | <0.001 | |
| CKDb | 22,748 (11.8) | 22,675 (11.8) | 23,351 (12.1) | 25,858 (13.4) | <0.001 | |
| IHD | 28,227 (14.7) | 26,090 (13.6) | 24,489 (12.7) | 23,436 (12.2) | <0.001 | |
| Stroke | 10,356 (5.4) | 9,681 (5.0) | 9,347 (4.9) | 9,239 (4.8) | <0.001 | |
| Depressive disorder | 13,266 (6.9) | 12,147 (6.3) | 11,513 (6.0) | 10,802 (5.6) | <0.001 | |
| Income (lower 20%) | 34,619 (18.0) | 36,476 (19.0) | 38,776 (20.2) | 43,129 (22.4) | <0.001 | |
| Oral GLM | ||||||
| Metformin | 71,746 (37.3) | 74,741 (38.9) | 78,666 (40.9) | 84,539 (43.9) | <0.001 | |
| Sulfonylurea | 69,720 (36.2) | 76,044 (39.5) | 83,883 (43.6) | 91,683 (47.7) | <0.001 | |
| Meglitinide | 3,926 (2.0) | 4,258 (2.2) | 4,767 (2.5) | 5,895 (3.1) | <0.001 | |
| Thiazolidinedione | 11,549 (6.0) | 12,336 (6.4) | 13,279 (6.9) | 14,556 (7.6) | <0.001 | |
| DPP-4 inhibitor | 7,517 (3.9) | 7,775 (4.0) | 8,205 (4.3) | 8,425 (4.4) | <0.001 | |
| α-Glucosidase inhibitor | 18,679 (9.7) | 20,872 (10.9) | 23,989 (12.5) | 28,594 (14.9) | <0.001 | |
| Number of oral GLM | <0.001 | |||||
| 0 | 96,069 (49.9) | 92,826 (48.3) | 88,128 (45.8) | 82,178 (42.7) | ||
| 1 | 34,001 (17.7) | 31,634 (16.4) | 29,259 (15.2) | 26,576 (13.8) | ||
| 2 | 41,699 (21.7) | 44,149 (23.0) | 47,255 (24. 6) | 50,910 (26.5) | ||
| 3 | 17,080 (8.9) | 19,466 (10.12) | 22,559 (11.7) | 26,347 (13.7) | ||
| ≥4 | 3,538 (1.8) | 4,315 (2.24) | 5,188 (2.7) | 6,377 (3.3) | ||
| Insulin | 8,029 (4.2) | 9,406 (4.9) | 11,803 (6.1) | 19,440 (10.1) | <0.001 | |
| Duration of diabetes (≥5 years) | 56,320 (29.3) | 58,809 (30.6) | 62,606 (32.5) | 67,659 (35.2) | <0.001 | |
| E10 | 2,921 (1.52) | 3,325 (1.73) | 4,079 (2.1) | 6,139 (3.2) | <0.001 | |
| Number of exams | <0.001 | |||||
| 3 | 165,083 (85.8) | 150,451 (78.2) | 144,273 (75.0) | 140,434 (73.0) | ||
| 4 | 13,841 (7.2) | 19,425 (10.1) | 22,308 (11.6) | 24,602 (12.8) | ||
| 5 | 13,463 (7.0) | 22,514 (11.7) | 25,808 (13.4) | 27,352 (14.2) | ||
| Time interval between adjacent exams, yr | 1.9 (1.3–2.1) | 1.8 (1.11–2.1) | 1.76 (1.1–2.1) | 1.7 (1–2.1) | <0.001 | |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation, number (%), or median (interquartile range). One-way analysis of variance and the chi-square test were used to compare the characteristics of the study participants at baseline. Post hoc multiple comparison analysis was performed using Bonferroni correction, and triglyceride levels were log-transformed for analysis.
VIM, variability independent of mean; BP, blood pressure; FG, fasting glucose; TC, total cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; SD, standard deviation; CV, coefficient of variation; ARV, average real variability; CKD, chronic kidney disease; IHD, ischemic heart disease; GLM, glucose-lowering medication; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase 4.
Table 2.
Model 1 was adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, alcohol consumption, smoking, regular exercise, presence of hypertension, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease, lower 20% income, and hemoglobin levels. Model 2 is the same as model 1, with additional adjustment for the duration of diabetes for at least 5 years, the prescription number of glucose-lowering medications, prescription history of insulin, mean fasting glucose, and presence of depressive disorder.
Table 3.
Adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, alcohol consumption, smoking, regular exercise, presence of hypertension, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease, lower 20% income, hemoglobin levels, duration of diabetes for at least 5 years, prescription number of glucose-lowering medications, prescription history of insulin, mean fasting glucose, and presence of depressive disorder.
IR, incidence rate; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; CKD, chronic kidney disease.
Table 4.
Adjusted for age, sex, body mass index, alcohol consumption, smoking, regular exercise, presence of hypertension, dyslipidemia, chronic kidney disease, lower 20% income, hemoglobin levels, duration of diabetes for at least 5 years, prescription number of glucose-lowering medications, prescription history of insulin, mean fasting glucose, and presence of depressive disorder.
IR, incidence rate; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase 4.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download