INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Eligibility criteria
Population (P) – Patients with impacted teeth
Intervention (I) – Orthodontic traction
Comparison (C) – Teeth with normal eruption (contralateral)
Outcomes (O): Periodontal parameters (gingival recession, probing depth, plaque index, gingival index, and width of keratinized mucosa)
Study design (S): Randomized clinical studies, pseudo-randomized or non-randomized, cross-sectional observational studies, and cohort or case-control
Inclusion criteria
a) Gingival recession: distance between the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) and the gingival margin, where the gingival margin found apically at the CEJ is positive, and the gingival margin coronally at the CEJ is negative.
b) Probing depth: periodontal pockets were measured from the level of the free gingival margin to the bottom of the pocket.
c) Periodontal attachment level: measurement of the probing depth and the distance between the gingival margin and the CEJ. In cases where the gingival recession was present, the clinical attachment level was calculated as follows: clinical attachment level = depth of periodontal probing + gingival recession.
d) Plaque index: the tooth surfaces were classified with a score between 0 and 3, according to the method described by Silness and Löe.22
e) Gingival index: the tooth surfaces were classified with a score between 0 and 3, similar to the plaque index.22
f) Gingival bleeding index: the presence or absence of bleeding was checked after periodontal probing using the method described by Carter and Barnes.23
g) Width of keratinized mucosa: measurement of the distance between the gingival margin and mucogingival junction.
Exclusion criteria
Studies on animals or patients with associated syndromes.
Studies in which tractioned tooth or a tooth with normal eruption underwent surgical periodontal treatment.
Studies in which at least one of the periodontal parameters stated above was not evaluated.
Reviews, letters, conference abstracts, expert opinions, case reports, and case series.
Information sources and search strategy
Selection process
Data collection process
Data items
Assessment of risk of bias
Effect measurement
Synthesis method
Reporting bias assessment
Certainty of evidence
RESULTS
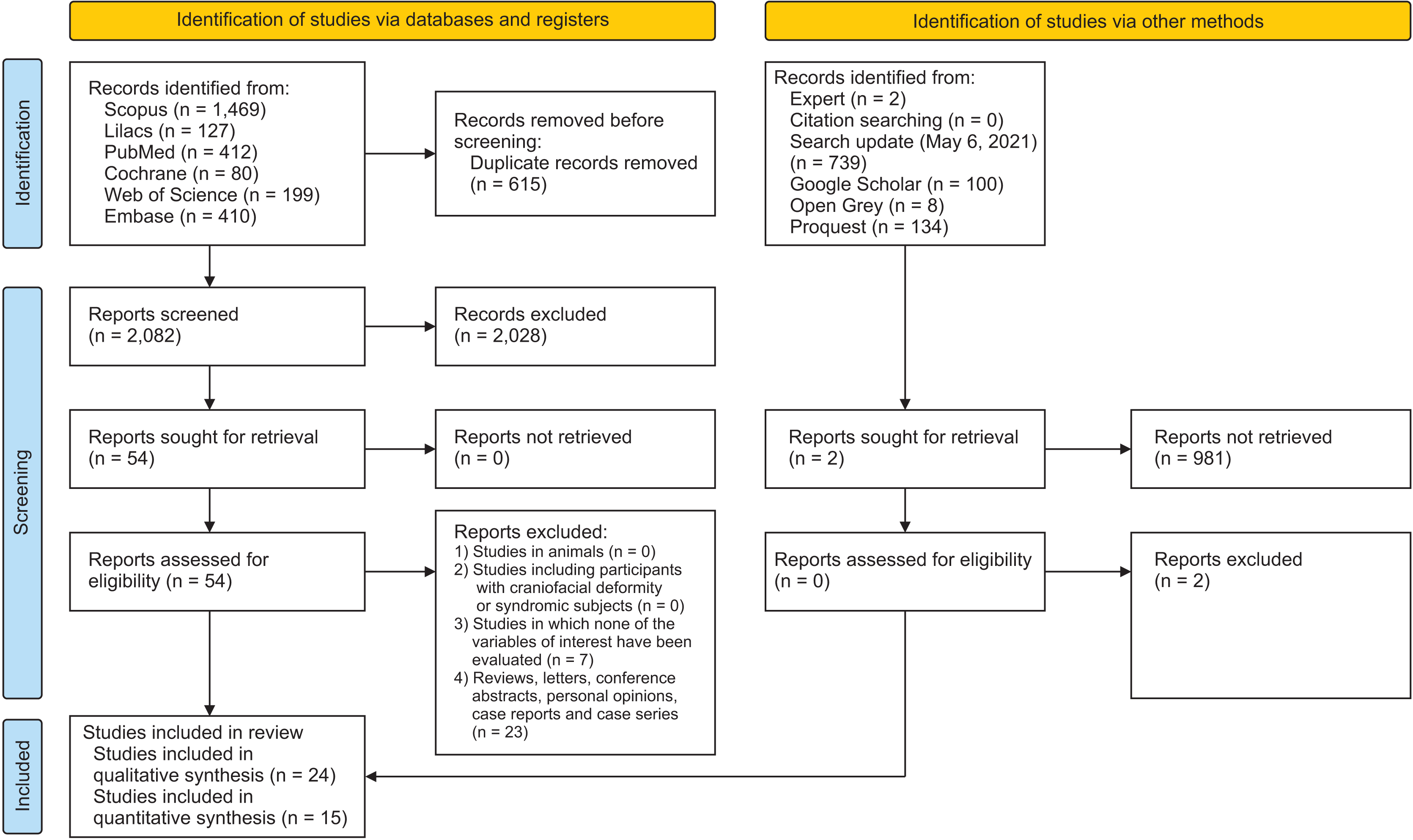
Study selection
Study characteristics
Risk of bias
Results of individual studies
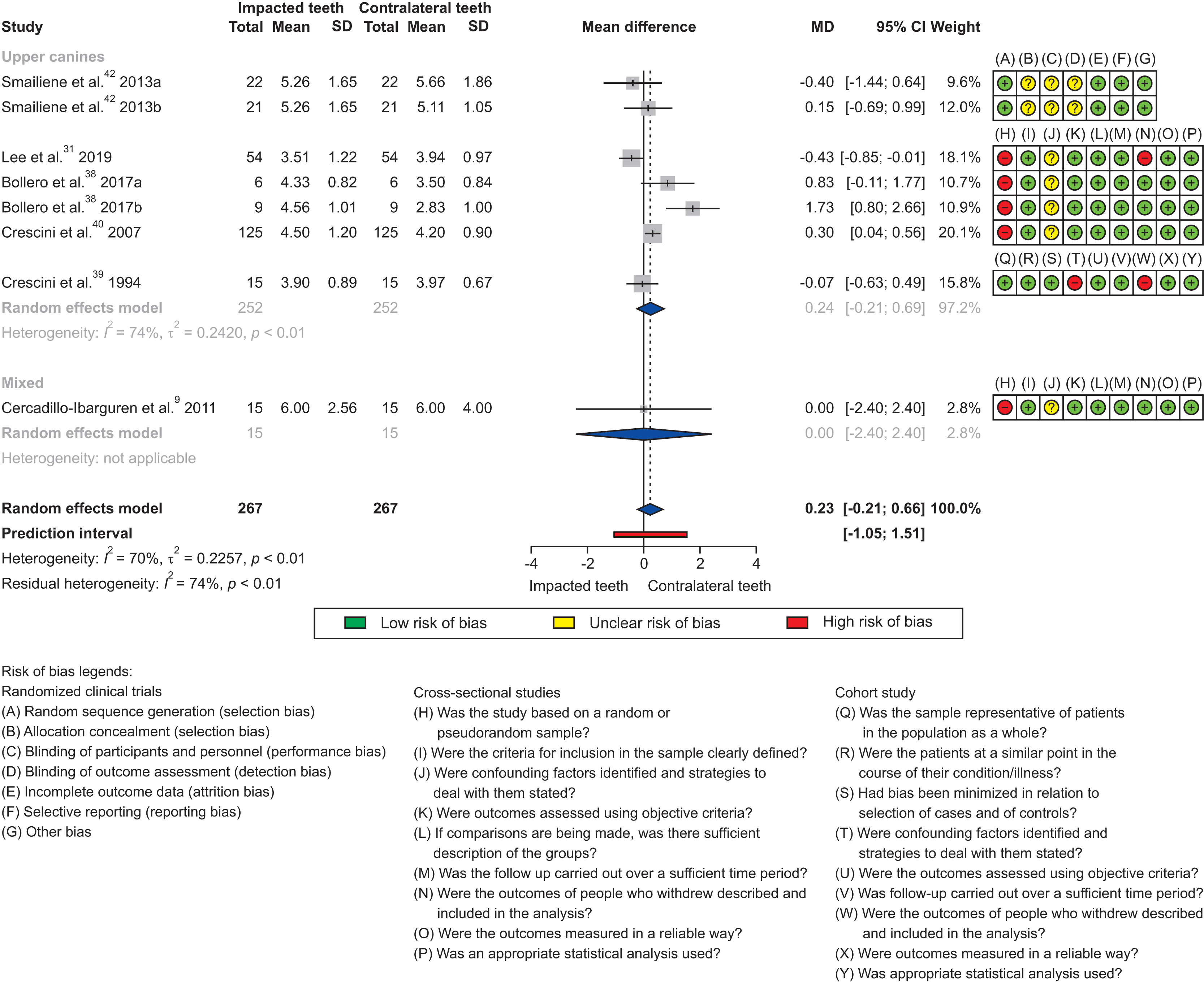
Synthesis of results
Figure 2

Figure 3
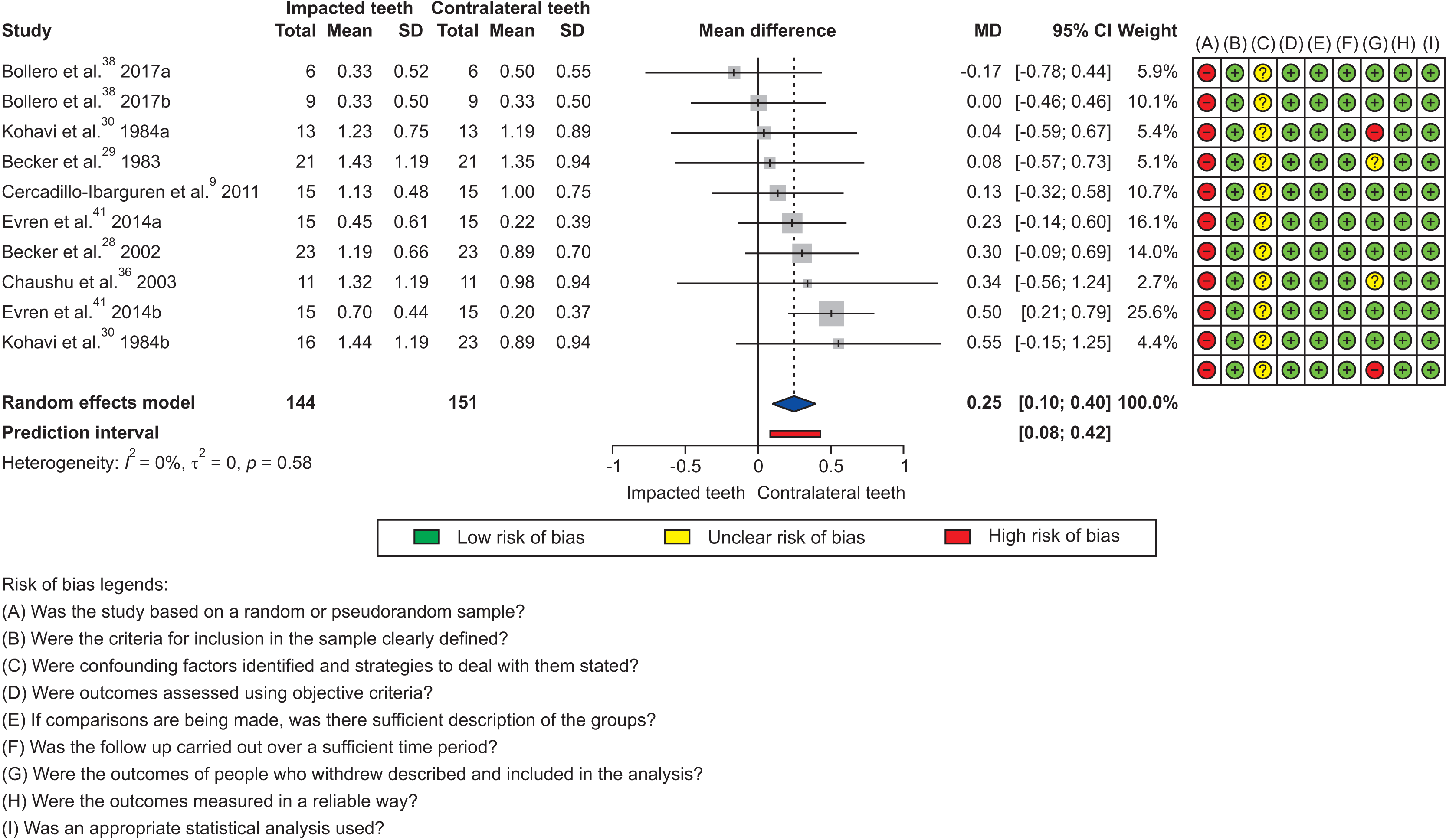
Figure 4

Figure 5




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download