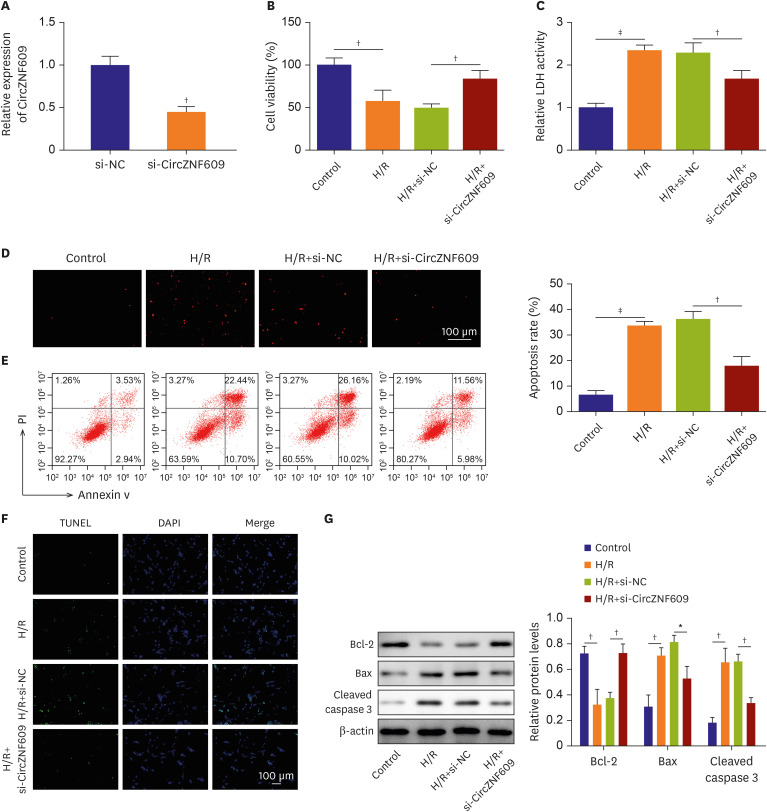
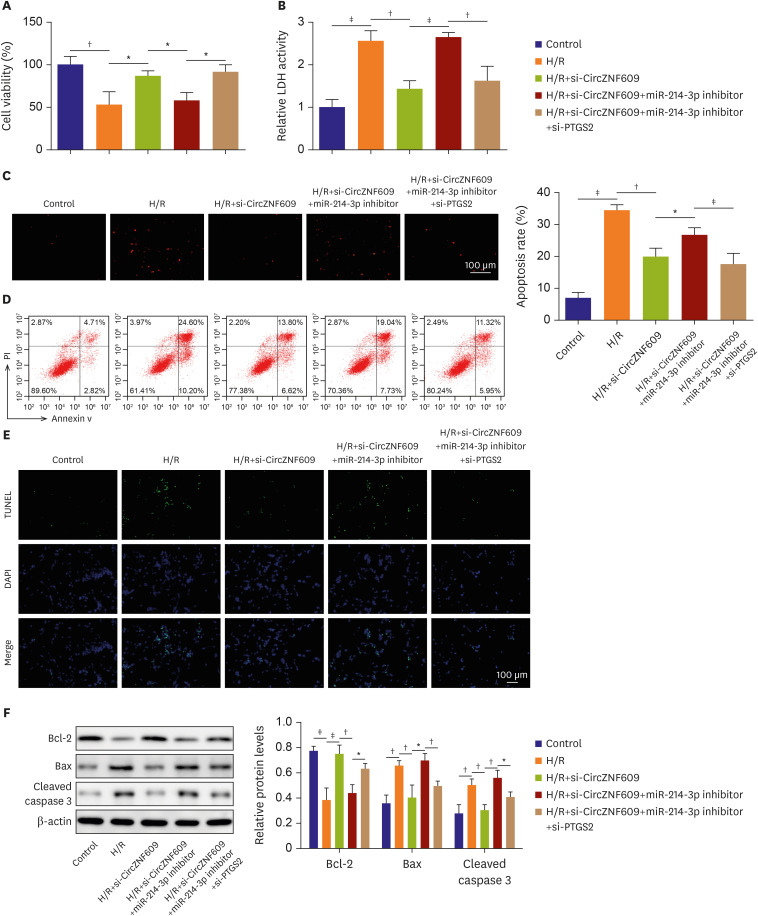
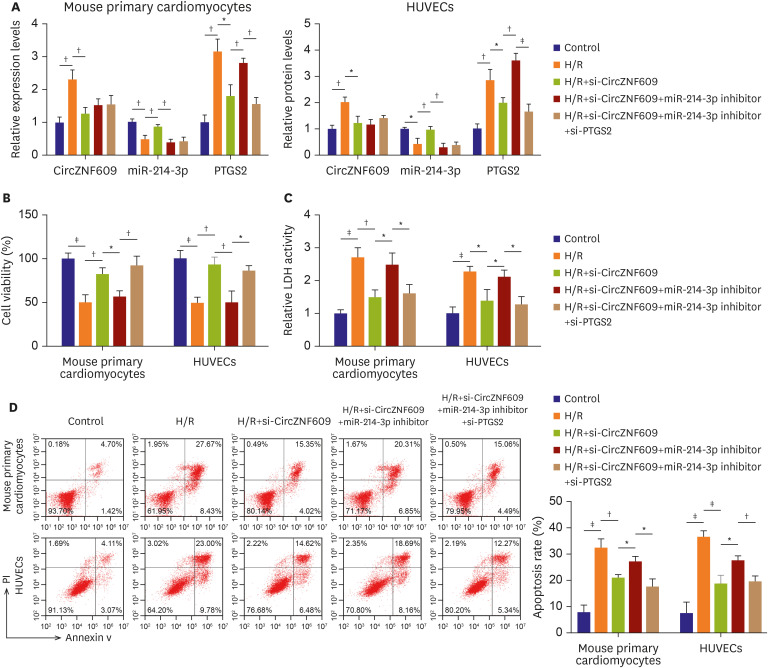
Based on previous experimental data, we further validated our main findings in H/R induced mouse cardiomyocytes and HUVECs. In brief, mouse myocardial cells and HUVECs were following divided into five group: control, H/R, H/R+si-CircZNF609, H/R+si-CircZNF609+miR-214-3p inhibitor, H/R+si-CircZNF609+miR-214-3p inhibitor+si-PTGS2. The corresponding transfection efficiency were showed in
Figure 6A, the expressions of CircZNF609 (cardiomyocytes, 1.00±0.17 vs. 2.31±0.29, p=0.003; HUVECs, 1.00±0.15 vs. 2.02±0.20, p=0.002) and PTGS2 (cardiomyocytes, 1.00±0.22 vs. 3.15±0.39, p=0.001; HUVECs, 1.00±0.19 vs. 2.85±0.41, p=0.002) were obviously increased while miR-214-3p (cardiomyocytes, 1.00±0.10 vs. 0.48±0.12, p=0.005; HUVECs, 1.00±0.06 vs. 0.43±0.22, p=0.011) was downregulated in mouse cardiomyocytes and HUVECs after H/R stimulation. After si-CircZNF609 transfection, CircZNF609 (cardiomyocytes, 2.31±0.29 vs. 1.27±0.18, p=0.006; HUVECs, 2.02±0.20 vs. 1.22±0.26, p=0.014) and PTGS2 (3.15±0.39 vs. 1.80±0.34, p=0.011; 2.85±0.41 vs. 2.00±0.41, p=0.031) were following greatly reduced while miR-214-3p (cardiomyocytes, 0.48±0.12 vs. 0.86±0.07, p=0.003; HUVECs, 0.43±0.22 vs. 0.97±0.12, p=0.020) was elevated, however, co-transfection with miR-214-3p inhibitor remarkably inhibited miR-214-3p level (cardiomyocytes, 0.86±0.07 vs. 0.39±0.10, p=0.003; HUVECs, 0.97±0.12 vs. 0.30±0.16, p=0.004), but restored PTGS2 level (cardiomyocytes, 1.80±0.34 vs. 2.80±0.15, p=0.009; HUVECs, 2.00±0.41 vs. 3.60±0.27, p=0.001) (
Figure 6A). Importantly, si-PTGS2 transfection decreased PTGS2 expression again (cardiomyocytes, 2.80±0.15 vs. 1.55±0.21, p=0.001; HUVECs, 3.60±0.27 vs. 1.64±0.30, p=0.001) (
Figure 6A). All of that indicated the corresponding RNAs were successfully transfected. By CCK-8 and LDH detections, we observed that knockdown of CircZNF609 greatly enhanced cell viability (cardiomyocytes, 50.12±8.76% vs. 82.51±7.39%, p=0.008; HUVECs, 49.40±6.61% vs. 93.18±8.60%, p=0.002) and suppressed LDH generation (cardiomyocytes, 2.70±0.30 vs. 1.49±0.23, p=0.005; HUVECs, 2.28±0.16 vs. 1.39±0.34, p=0.016), but miR-214-3p co-silence partly reduced cell viability (cardiomyocytes, 82.51±7.39% vs. 56.97±6.48%, p=0.011; HUVECs, 93.18±8.60% vs. 50.07±13.18%, p=0.001) and promoted LDH generation (cardiomyocytes, 1.49±0.23 vs. 2.48±0.36, p=0.017; HUVECs, 1.39±0.34 vs. 2.11±0.21, p=0.037) on these basis, partly diminished the biological effects of CircZNF609 downregulation. Moreover, inhibition of PTGS2 strikingly abolished the inhibitory roles of miR-214-3p inhibitor, and further rescued the protective roles of CircZNF609 silence in H/R-triggered damage in cardiomyocytes (cell viability 56.97±6.48% vs. 92.13±10.77%, p=0.008; LDH 2.48±0.36 vs. 1.60±0.28, p=0.030) and HUVECs (cell viability 50.07±13.18% vs. 86.05±5.84%, p=0.013; LDH 2.11±0.21 vs. 1.28±0.24, p=0.011) (
Figure 6B and C). Similarly, apoptotic assay suggested that knockdown of CircZNF609 greatly reduced H/R-induced cell apoptotic rate (cardiomyocytes, 32.24±3.45% vs. 20.88±1.33%, p=0.006; HUVECs, 36.44±2.35% vs. 18.68±3.17%, p=0.001), and miR-214-3p co-silencing further increased cell apoptosis (cardiomyocytes, 20.88±1.33% vs. 27.06±1.98%, p=0.011; HUVECs, 18.68±3.17% vs. 27.47±1.79%, p=0.014), however, these effects of miR-214-3p inhibitor were reversed by PTGS2 downregulation (cardiomyocytes, 27.06±1.98% vs. 17.43±3.06%, p=0.010; HUVECs, 27.47±1.79% vs. 19.44±2.17%, p=0.008) (
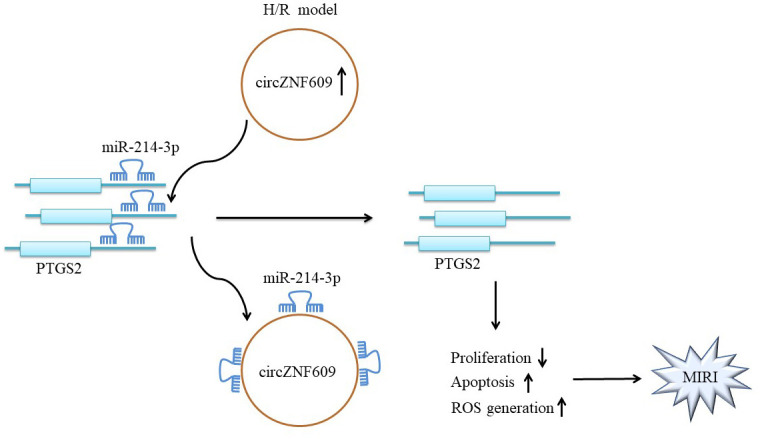
Figure 6D). Overall, these results further confirmed that protective mechanism of CircZNF609 in H/R-induced myocardial injury by regulating miR-214-3p/PTGS2 signaling.







 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download