I. Introduction
II. Materials and Methods
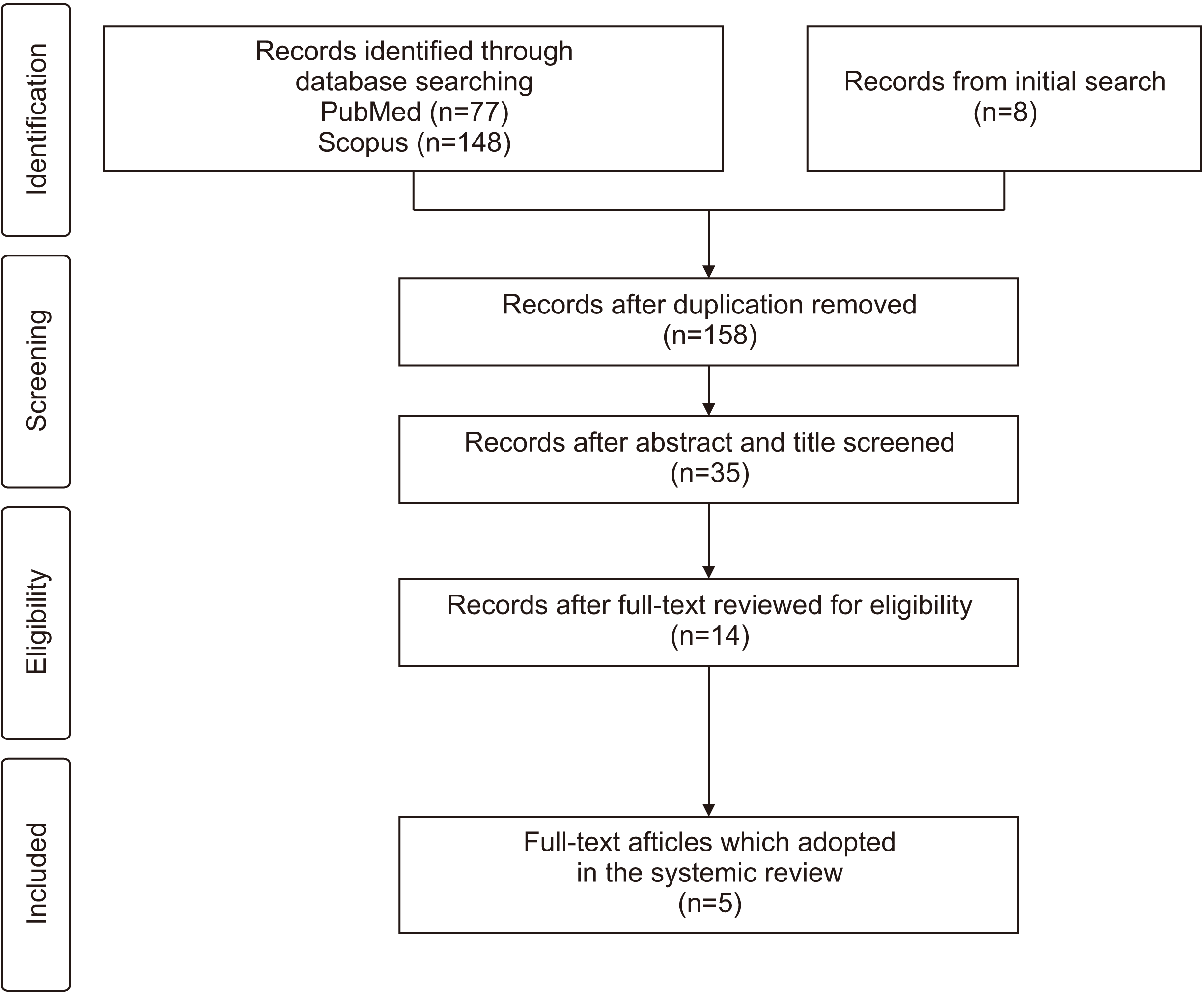
1. Study design and registration
2. Eligibility criteria
3. Search strategies
Table 1
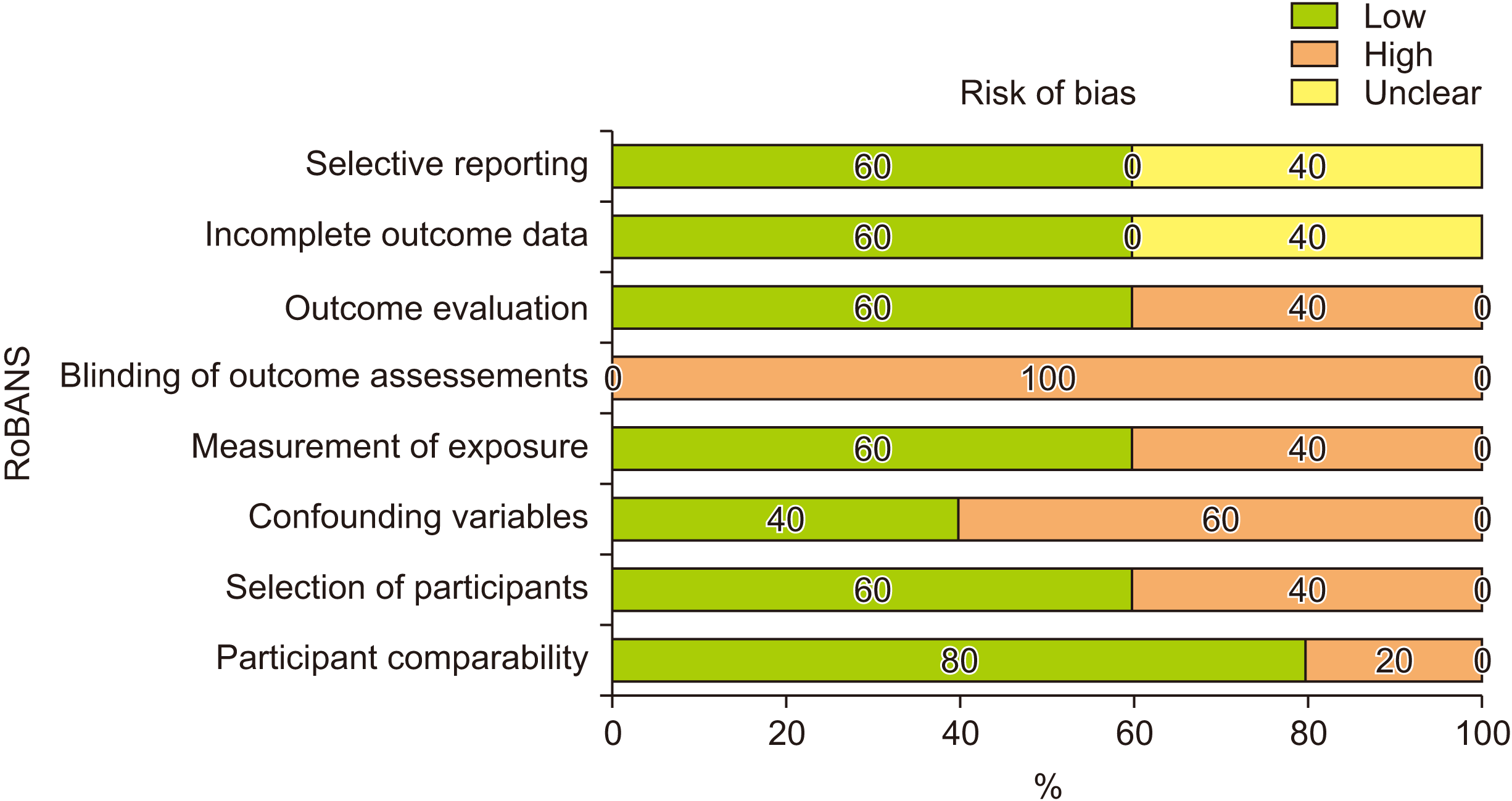
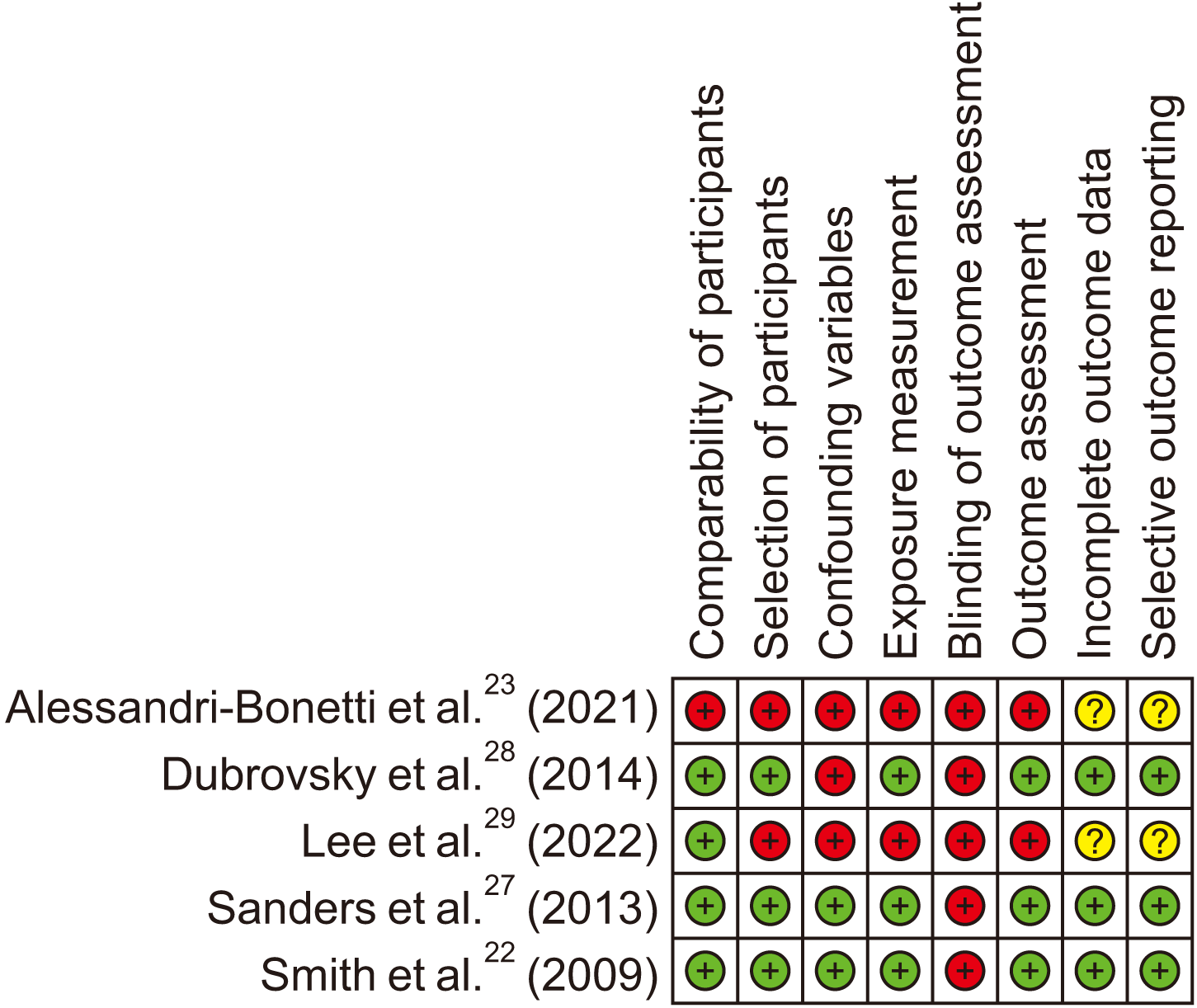
4. Risk of bias assessment
III. Results
1. Literature selection and characteristics of the selective studies
Table 2
| Study | Study design | Cases | Controls | Diagnostic criterial for painful TMD | Evaluation of sleep apnea and sleep quality | Major study findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alessandri-Bonetti et al.23 (2021) | Cross-sectional | 41 consecutive patients with OSA | 41 healthy controls | DC/TMD | PSG, site of obstruction observed by DISE | • 51% of consecutive OSA patients presented TMD signs and/or symptoms and 32% of controls showed TMD signs and/or symptoms. |
| Dubrovsky et al.28 (2014) | Case-control | 124 females with myofascial TMD | 46 females without myofascial TMD | RDC/TMD criteria | PSG, ESS |
• TMD cases demonstrated higher levels of respiratory events and arousal. • TMD cases with chronic myofascial TMD presented mild sleep disturbance and mild increase in upper airway resistance. • The degree of sleep disturbance and upper airway resistance were associated with acute myofascial pain levels. |
| Lee et al.29 (2022) | Cross-sectional | 503 chronic TMD patients | 180 healthy controls | DC/TMD axis I | PSQI, STOP-BANG, ESS |
• PSQI scores were higher in patients compared to controls and poor sleep was more prevalent in TMD patients. • Patients with chronic TMD had a higher likelihood of OSA and showed higher daytime sleepiness. |
| Sanders et al.27 (2013) |
Prospective cohort Case-control |
2,604 participants in cohort study 1,614 participants in the case-control study |
Random sample of 102 controls with low likelihood of OSA | RDC/TMD criteria | PSQI, 4-itmes STOP screening questionnaire |
• Prospective cohort study: 1st onset TMD was two times higher in the 60% participants with high likelihood of OSA. • Case control study: chronic TMD cases had 3-fold higher odd ratios of high likelihood of OSA. |
| Smith et al.22 (2009) | Cross-sectional | 53 patients with myofascial TMD | - | RDC/TMD axis I | ISI, PSG, PSQI, ESS |
• 89% of participants with myofascial TMD met the criteria for at least one sleep disorder and 43.4% of participants with myofascial TMD were diagnosed with more than 2 sleep disorders. • Prevalence of primary insomnia and sleep apnea was high in myofascial TMD patients. • The primary insomnia bay play a role in hyperalgesia in myofascial TMD patients. |
(OSA: obstructive sleep apnea, DC/TMD: Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders, PSG: polysomnography, DISE: drug induced sleep endoscopy, TMD: temporomandibular disorder, RDC/TMD: Research Diagnostic Criteria for TMD, ESS: excessive daytime sleepiness, PSQI: Pittsburg Sleep Quality Index, ISI: Insomnia Severity Index)




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download