Abstract
Supplementary Materials
Notes
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Hyung-Ju Cho, Chang-Hoon Kim. Data curation: Jong Gyun Ha. Formal analysis: Jong Gyun Ha. Funding acquisition: Chang-Hoon Kim. Methodology: Hyung-Ju Cho, Jong Gyun Ha. Project administration: Chang-Hoon Kim. Writing—original draft: Hyung-Ju Cho. Writing—review & editing: Chang-Hoon Kim.
Funding Statement
This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2016M3A- 9D5A01952414). This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIP) (No. 2016R1A5A2008630). This study was supported by the “Team Science Award” of Yonsei University College of Medicine (6-2021-0005).
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
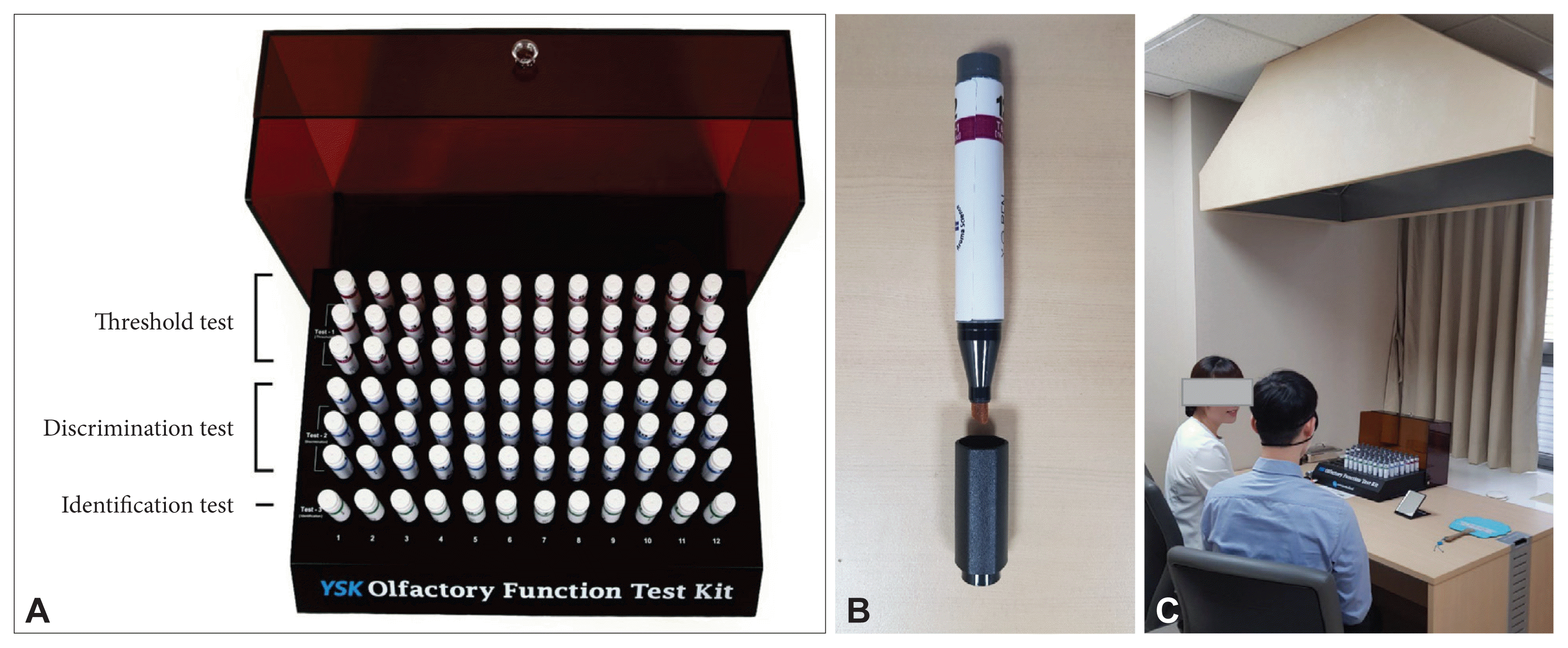
Fig. 2
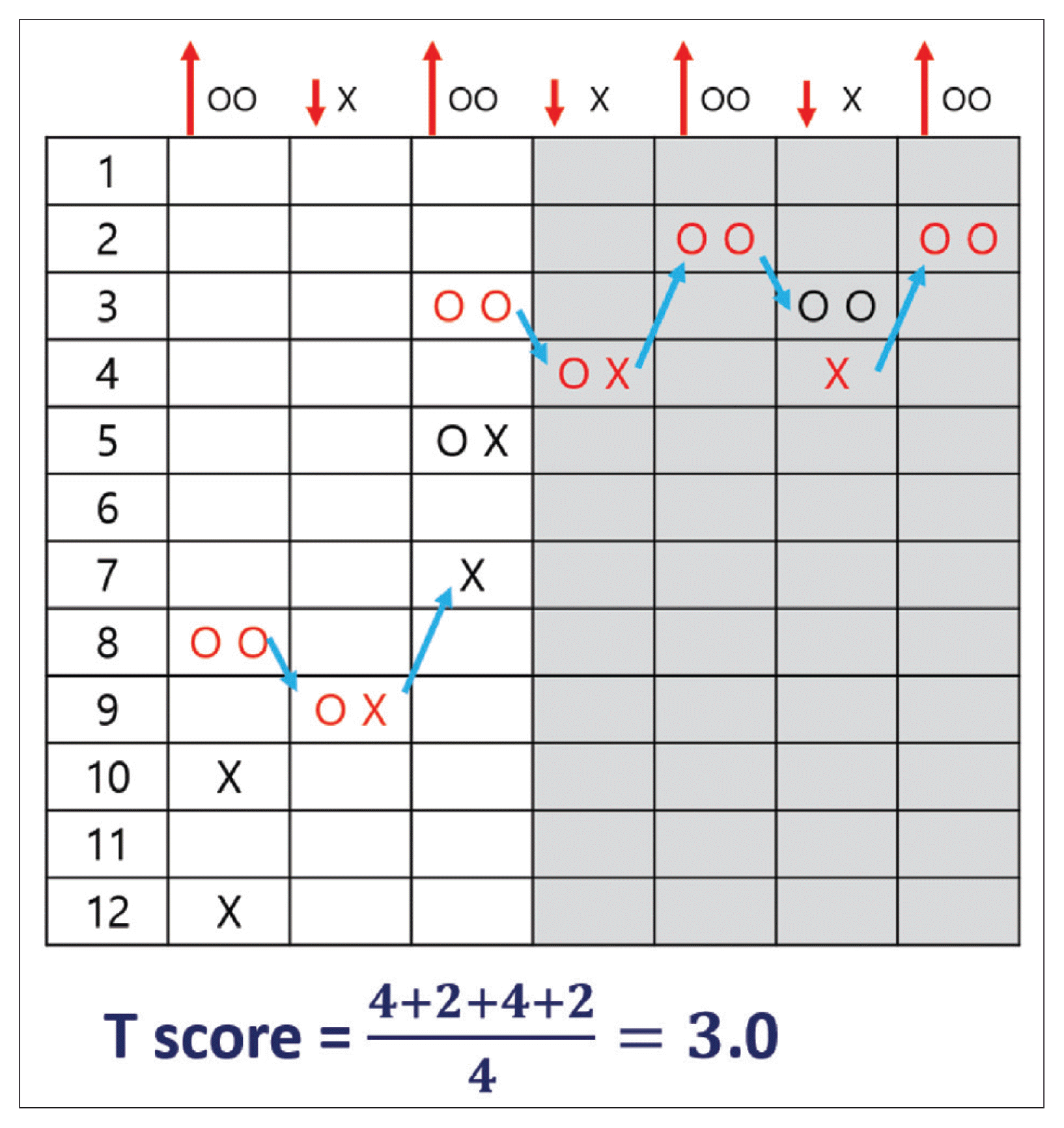
Fig. 3
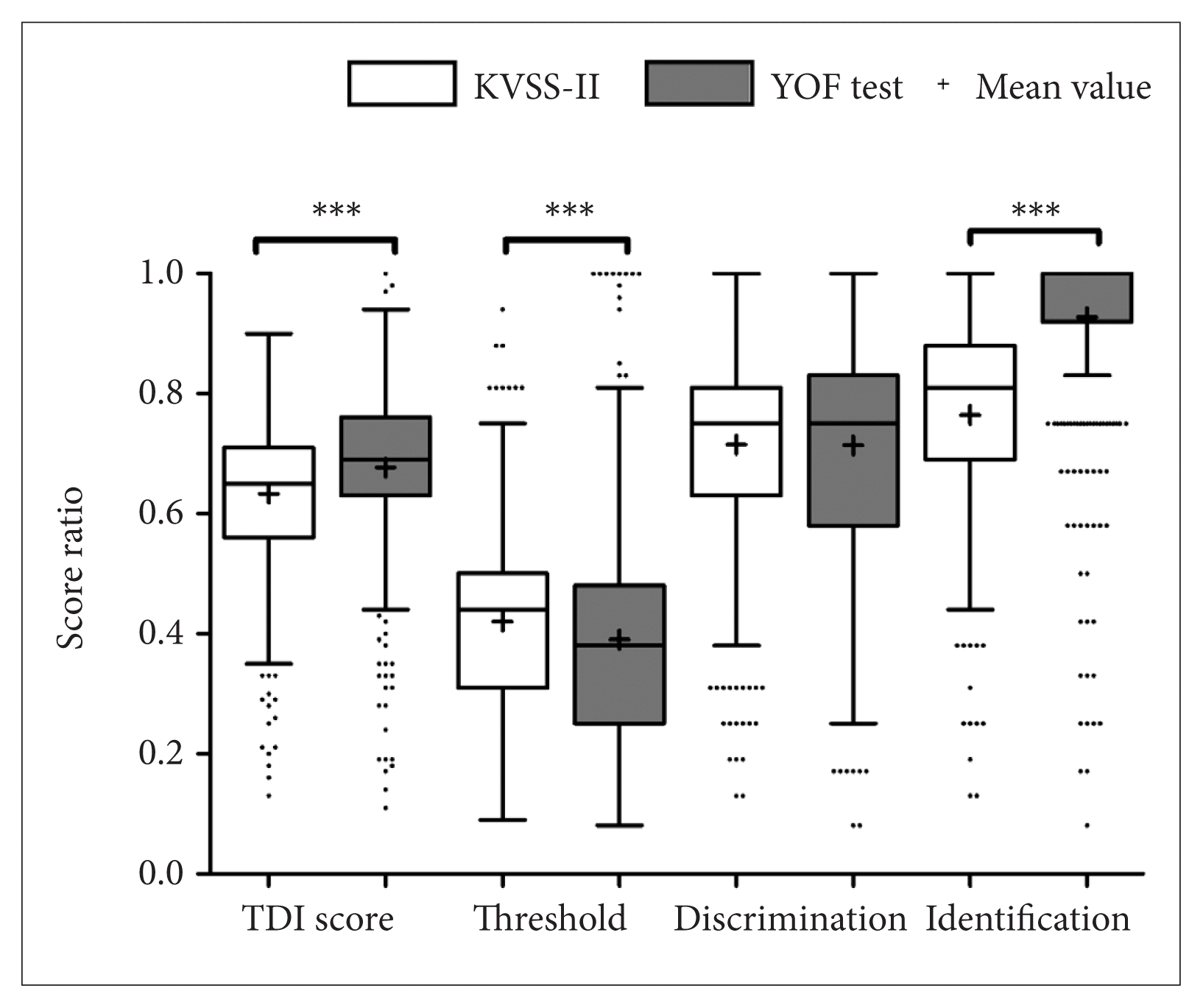
Table 1
YOF, YSK olfactory function. Adapted from Ha et al. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 2020;13(3):274–84 [9].
Table 2
YOF, YSK olfactory function. Adapted from Ha et al. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 2020;13(3):274–84 [9].
Table 3
| Number | Odorants and distractors | Correct (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baby powder* | Apple | Curry | Chocolate | 96.3 |
| 2 | Strawberry | Rose | Cinnamon* | Lemon | 80.7 |
| 3 | Ginseng | Watermelon | Peach* | Peanut | 90.8 |
| 4 | Prune | Melon | Scorched rice* | Acacia flowers | 97.2 |
| 5 | Spearmint* | Apple | Orange | Tree | 93.6 |
| 6 | Chocolate* | Mugwort | Garlic | Grape | 96.3 |
| 7 | Strawberry | Grape | Oriental medicine* | Kimchi | 98.6 |
| 8 | Medicated patch* | Cherry | Chocolate | Rose | 96.3 |
| 9 | Cotton candy | Honey | Korean red ginseng* | Kimchi | 94.0 |
| 10 | Grapefruit | Naphthalene* | Coffee | Rose | 87.2 |
| 11 | Corn | Lemon | Marinated grilled beef* | Soap | 95.0 |
| 12 | Melon | Ginger | Banana | Ashes* | 97.2 |
YOF, YSK olfactory function. Adapted from Ha et al. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 2020;13(3):274–84 [9].
Table 4
| Variable | Normosmia (n=542) | Hyposmia (n=472) | Anosmia (n=113) | p-value | Post hoc test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | <0.001* | ||||
| Male | 335 | 245 | 54 | ||
| Female | 207 | 227 | 59 | ||
| Age (yr) | 47.0±16.9 | 49.6±16.3 | 52.9±14.1 | <0.001† | P1=0.031, P2<0.001, P3=0.131 |
| YOF test | |||||
| TDI score | 24.2±4.5 | 19.5±6.4 | 11.8±5.6 | <0.001† | P1<0.001, P2<0.001, P3<0.001 |
| Threshold | 4.6±2.3 | 3.3±2.2 | 1.7±1.2 | <0.001 † | P1<0.001, P2<0.001, P3<0.001 |
| Discrimination | 8.6±2.1 | 7.1±2.5 | 5.1±2.5 | <0.001 † | P1<0.001, P2<0.001, P3<0.001 |
| Identification | 11.1±1.7 | 9.2±3.1 | 5.0±3.2 | <0.001 † | P1<0.001, P2<0.001, P3<0.001 |
| KVSS-II test | |||||
| TDI score | 30.4±5.9 | 24.3±8.2 | 14.6±6.7 | <0.001† | P1<0.001, P2<0.001, P3<0.001 |
| Threshold | 6.8±2.6 | 5.0±2.8 | 2.5±1.9 | <0.001† | P1<0.001, P2<0.001, P3<0.001 |
| Discrimination | 11.5±2.7 | 9.4±3.1 | 6.2±2.9 | <0.001† | P1<0.001, P2<0.001, P3<0.001 |
| Identification | 12.1±2.3 | 10.0±3.7 | 5.7±3.1 | <0.001† | P1<0.001, P2<0.001, P3<0.001 |
Continuous variables are presented as the means±standard deviation. The KVSS-II score for each TDI subtest is shown.
KVSS, Korean version of Sniffin’ Stick; P1, the difference between normosmia group and hyposmia group; P2, the difference between normosmia group and anosmia group; P3, the difference between hyposmia group and anosmia group; YOF, YSK olfactory function; TDI, Threshold Discrimination Identification. Adapted from Ha et al. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 2020;13(3):274–84 [9].




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download