INTRODUCTION
TARGET BLOOD PRESSURE IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETES MELLITUS ACCORDING TO CURRENT GUIDELINES
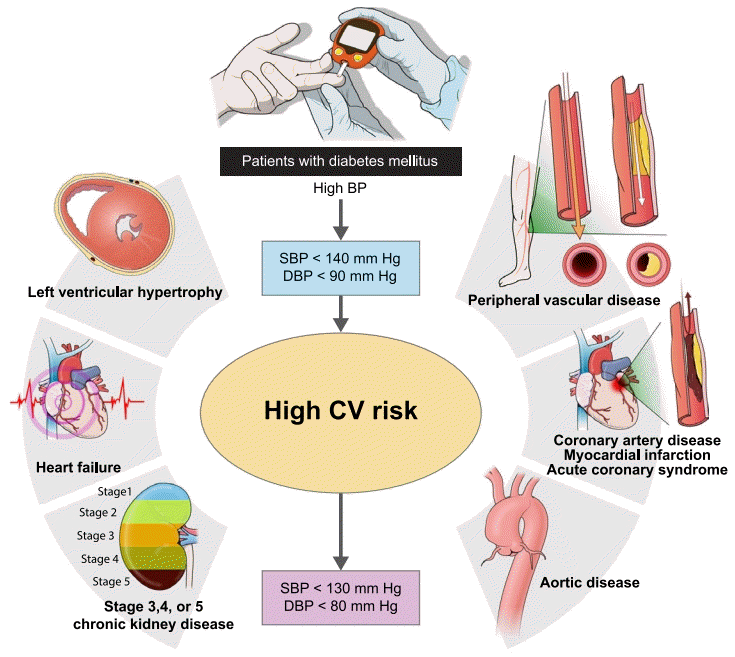 | Fig. 1.Optimal target blood pressure (BP) for general and high-risk clinical features in patients with diabetes mellitus. Considering these guidelines and studies, it is important to apply individualized target BP for patients with diabetes mellitus. SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; CV, cardiovascular. |
Table 1.
| Guidelines identifier | Year | Target populations | BP thresholds, mm Hg | BP target, mm Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JNC 8 | 2014 | General | Office ≥140/90 | Office <140/90 |
| JNC 8 | 2014 | Diabetes | Office ≥140/90 | Office <140/90 |
| ACC/AHA | 2017 | General | Office ≥130/80 | Office <130/80 |
| ACC/AHA | 2017 | Diabetes | Office ≥130/80 | Office <130/80 |
| ESC/ESH | 2018 | General | Office ≥140/90 | Office <140/90a |
| ESC/ESH | 2018 | Diabetes | Office ≥140/90 | 120/70≤ Office ≤130/80 |
| KSH | 2018 | General | Office >140/90 | Office <140/90 |
| KSH | 2018 | Diabetes | Office >140/90 | Office <140/85 |
| KSH | 2018 | Diabetes with CVDb | Office >140/90 | Office <130/80 |
| NICE | 2019 | General | Office BP ≥140/90 | Office <140/90 |
| NICE | 2019 | Diabetes | Office BP ≥140/90 | Office <140/90 |
| ESC/EASD | 2019 | Diabetes | Office ≥140/90 | 120/70≤ Office ≤130/80 |
| KDA | 2021 | Diabetes | - | Office <140/85 |
| KDA | 2021 | Diabetes with CVD | - | Office <130/80 |
| ADA | 2022 | Diabetes | Office ≥140/90 | Office <140/90 |
| ADA | 2022 | Diabetes with higher CV riskc | Office ≥140/90 | Office <130/80 |
BP, blood pressure; JNC, Joint National Committee; ACC, American College of Cardiology; AHA, American Heart Association; ESC, European Society of Cardiology; ESH, European Society of Hypertension; KSH, Korean Society of Hypertension; CVD, cardiovascular disease; NICE, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; EASD, European Association for the Study of Diabetes; KDA, Korean Diabetes Association; ADA, American Diabetes Association.
a BP target for all patients; if the treatment is well tolerated, the treated BP target should be office ≤130/80,
THE EVIDENCE BEHIND THE OPTIMAL BLOOD PRESSURE TARGET FROM RANDOMIZED CONTROL TRIALS
Table 2.
| Clinical trial | Population | Follow-up | Initial BP, mm Hg | Achieved BP active, mm Hg | Achieved BP control, mm Hg | Clinical outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UKPDS 38, 1998 [5] | 1,148 Hypertensive participants with T2DM aged with 25–65 yr | Median 8.4 yr | Active: 159/94 | 144/82 (target: <150/85) | 154/87 (target: <180/105) | Reduced risk for diabetes related any end points risk by 24% with active control |
| Control: 160/94 | Deaths related to diabetes risk by 32%, stroke risk by 44%, and heart failure risk by 56% | |||||
| Microvascular end points risk by 37% | ||||||
| No benefit in all-cause mortality | ||||||
| HOT, 1998 [24] | 18,790 Hypertensive participants including 1,501 with T2DM | Mean 3.8 yr | 170/105 | DBP: 81.1 in target DBP ≤80 | DBP: 85.2 in target DBP ≤90 | No benefit in CV event in overall participants |
| DBP: 83.2 in target DBP ≤85 | In participants with diabetes, increased major CV event risk by 2.06-fold in target DBP ≤90 compared with ≤80; Increased CV mortality risk by 3.0-fold in target DBP ≤90 compared with ≤80 | |||||
| ADVANCE, 2007 [25] | 11,140 With T2DM aged with 55 yr and older with prior CVD or CV risk factors | Mean 4.3 yr | Active: 145/81 | 136/73 | 140/73 | Reduced risk of major macrovascular or microvascular event by 9%, death from CV disease by 18%, death from any cause by 14% |
| Control: 145/81 | ||||||
| Subgroup analysis of INVEST, 2010 [26] | 6,400 Participants of the 22,576 participants in INVEST aged at least 50 yr with T2DM and CAD | 16,893 Patient-yr | Active: 144/85 | Active SBP: 121.5 (SBP category <130) | Uncontrolled: SBP 146.1 (SBP category ≥140) | No benefit in adverse CV outcome including all-cause death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke in active control of SBP compared with usual control |
| Usual: 149/85 | Usual SBP 131.2 (SBP category 130–140) | Increased risk of adverse CV outcome in uncontrolled SBP group compared with usual control by 1.46-fold | ||||
| Uncontrolled: 159/86 | Increased risk of all-cause mortality in active control compared with usual control by 1.15-fold when extended follow-up | |||||
| ACCORD-BP, 2010 [20] | 4,733 Participants with T2DM aged 40–79 yr with prior CVD or 55–79 yr with CV risk factors | Mean 4.7 yr | Active: 139.0/75.9 | 119.3/64.4 (target SBP: <120) | 135/70.5 (target SBP: 130–140) | No benefit in primary composite outcome including nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, and CV death |
| Control: 139.4/76.0 | Reduced risk of stroke by 41% with active control | |||||
| SAEs more common in intensive group, particularly hypotension, elevated serum creatinine and electrolyte imbalance | ||||||
| SPRINT-eligible ACCORD-BP, 2017 [23] | SPRINT-eligible 1,284 participants of the 4,733 participants in ACCORD-BP aged at least 75 yr with T2DM or clinical CVD or subclnical CVD or high CV risk | - | Active: 139.8 | SBP: 120.1 (target SBP: <120) | SBP: 133.5 (target SBP: <140) | Reduced risk of composite of CV death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, any revascularization, and HF by 21% |
| Control: 140.8 | Reduced risk of CV death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke by 31% | |||||
| More frequent treatment-related adverse events in active control |
BP, blood pressure; UKPDS, UK Prospective Diabetes Study; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; HOT, Hypertension Optimal Treatment trial; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; CV, cardiovascular; ADVANCE, Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: preterAx and diamicroN-MR Controlled Evaluation trial; CVD, cardiovascular disease; INVEST, International Verapamil SR-Trandolapril Study; CAD, coronary artery disease; SBP, systolic blood pressure; ACCORD-BP, Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Blood Pressure Trial; MI, myocardial infarction; SAE, serious adverse event; SPRINT, Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial; HF, heart failure.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download