1. Senior PA, Pettus JH. Stem cell therapies for type 1 diabetes: current status and proposed road map to guide successful clinical trials. Diabet Med. 2019; 36:297–307.

2. Cryer PE. Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369:362–72.

3. Bellin MD, Dunn TB. Transplant strategies for type 1 diabetes: whole pancreas, islet and porcine beta cell therapies. Diabetologia. 2020; 63:2049–56.

4. Ellis C, Lyon JG, Korbutt GS. Optimization and scale-up isolation and culture of neonatal porcine islets: potential for clinical application. Cell Transplant. 2016; 25:539–47.

5. Elliott RB, Escobar L, Tan PL, Muzina M, Zwain S, Buchanan C. Live encapsulated porcine islets from a type 1 diabetic patient 9.5 yr after xenotransplantation. Xenotransplantation. 2007; 14:157–61.
6. Korbutt GS, Elliott JF, Ao Z, Smith DK, Warnock GL, Rajotte RV. Large scale isolation, growth, and function of porcine neonatal islet cells. J Clin Invest. 1996; 97:2119–29.

7. Dufrane D, Gianello P. Pig islets for clinical islet xenotransplantation. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009; 18:495–500.

8. Kuppan P, Seeberger K, Kelly S, Rosko M, Adesida A, Pepper AR, et al. Co-transplantation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with neonatal porcine islets within a prevascularized subcutaneous space augments the xenograft function. Xenotransplantation. 2020; 27:e12581.

9. Hayward JA, Ellis CE, Seeberger K, Lee T, Salama B, Mulet-Sierra A, et al. Cotransplantation of mesenchymal stem cells with neonatal porcine islets improve graft function in diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2017; 66:1312–21.

10. Hassouna T, Seeberger KL, Salama B, Korbutt GS. Functional maturation and in vitro differentiation of neonatal porcine islet grafts. Transplantation. 2018; 102:e413–23.

11. van der Windt DJ, Bottino R, Kumar G, Wijkstrom M, Hara H, Ezzelarab M, et al. Clinical islet xenotransplantation: how close are we? Diabetes. 2012; 61:3046–55.
12. Zhang N, Su D, Qu S, Tse T, Bottino R, Balamurugan AN, et al. Sirolimus is associated with reduced islet engraftment and impaired beta-cell function. Diabetes. 2006; 55:2429–36.
13. Sun CL, Ham DS, Park HS, Kim JW, Cho JH, Song KH, et al. Rapamycin suppresses the expansion and differentiation of porcine neonatal pancreas cell clusters. Transplantation. 2010; 90:717–24.

14. Yang HK, Ham DS, Park HS, Rhee M, You YH, Kim MJ, et al. Long-term efficacy and biocompatibility of encapsulated islet transplantation with chitosan-coated alginate capsules in mice and canine models of diabetes. Transplantation. 2016; 100:334–43.

15. Yoon KH, Quickel RR, Tatarkiewicz K, Ulrich TR, HollisterLock J, Trivedi N, et al. Differentiation and expansion of beta cell mass in porcine neonatal pancreatic cell clusters transplanted into nude mice. Cell Transplant. 1999; 8:673–89.

16. Park HS, Ham DS, You YH, Shin J, Kim JW, Jo JH, et al. Successful xenogenic islet transplantation with Ba2+-alginate encapsulation. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2010; 7:523–30.
17. Nagaya M, Hayashi A, Nakano K, Honda M, Hasegawa K, Okamoto K, et al. Distributions of endocrine cell clusters during porcine pancreatic development. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0216254.

18. Kim S, Whitener RL, Peiris H, Gu X, Chang CA, Lam JY, et al. Molecular and genetic regulation of pig pancreatic islet cell development. Development. 2020; 147:dev186213.

19. Trivedi N, Hollister-Lock J, Lopez-Avalos MD, O’Neil JJ, Keegan M, Bonner-Weir S, et al. Increase in beta-cell mass in transplanted porcine neonatal pancreatic cell clusters is due to proliferation of beta-cells and differentiation of duct cells. Endocrinology. 2001; 142:2115–22.
20. Lopez-Avalos MD, Tatarkiewicz K, Sharma A, Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC. Enhanced maturation of porcine neonatal pancreatic cell clusters with growth factors fails to improve transplantation outcome. Transplantation. 2001; 71:1154–62.

21. Luca G, Nastruzzi C, Calvitti M, Becchetti E, Baroni T, Neri LM, et al. Accelerated functional maturation of isolated neonatal porcine cell clusters: in vitro and in vivo results in NOD mice. Cell Transplant. 2005; 14:249–61.

22. Lau H, Corrales N, Alexander M, Mohammadi MR, Li S, Smink AM, et al. Necrostatin-1 supplementation enhances young porcine islet maturation and in vitro function. Xenotransplantation. 2020; 27:e12555.

23. Blum B, Roose AN, Barrandon O, Maehr R, Arvanites AC, Davidow LS, et al. Reversal of β cell de-differentiation by a small molecule inhibitor of the TGFβ pathway. Elife. 2014; 3:e02809.

24. Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Zavacki AM, Marinelarena A, HollisterLock J, El Khattabi I, Marsili A, et al. Thyroid hormone promotes postnatal rat pancreatic β-cell development and glucoseresponsive insulin secretion through MAFA. Diabetes. 2013; 62:1569–80.
25. Rezania A, Bruin JE, Arora P, Rubin A, Batushansky I, Asadi A, et al. Reversal of diabetes with insulin-producing cells derived in vitro from human pluripotent stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2014; 32:1121–33.

26. Pagliuca FW, Millman JR, Gurtler M, Segel M, Van Dervort A, Ryu JH, et al. Generation of functional human pancreatic β cells in vitro. Cell. 2014; 159:428–39.

27. Xu G, Stoffers DA, Habener JF, Bonner-Weir S. Exendin-4 stimulates both beta-cell replication and neogenesis, resulting in increased beta-cell mass and improved glucose tolerance in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1999; 48:2270–6.

28. Buteau J, Foisy S, Joly E, Prentki M. Glucagon-like peptide 1 induces pancreatic beta-cell proliferation via transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Diabetes. 2003; 52:124–32.
29. Lau H, Corrales N, Lee S, Heng J, Zhang K, Alexander M, et al. Exendin-4 improves yield and function of isolated pre-weaned porcine islets. J Endocrinol Diabetes. 2018; 5:1–7.
30. Zhang J, Liu F. The de-, re-, and trans-differentiation of β-cells: regulation and function. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2020; 103:68–75.

31. Montanari E, Szabo L, Balaphas A, Meyer J, Perriraz-Mayer N, Pimenta J, et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells derived from porcine exocrine pancreas improve insulin secretion from juvenile porcine islet cell clusters. Xenotransplantation. 2021; 28:e12666.

32. Miyagawa S. Xenotransplantation: comprehensive study. London: IntechOpen;2020. Chapter 3, Porcine islet cell xenotransplantation [cited 2021 Dec 5]. Available from:
https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/70850.
33. Gazda LS, Vinerean HV, Laramore MA, Diehl CH, Hall RD, Rubin AL, et al. Encapsulation of porcine islets permits extended culture time and insulin independence in spontaneously diabetic BB rats. Cell Transplant. 2007; 16:609–20.

34. Omer A, Duvivier-Kali VF, Trivedi N, Wilmot K, Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC. Survival and maturation of microencapsulated porcine neonatal pancreatic cell clusters transplanted into immunocompetent diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2003; 52:69–75.

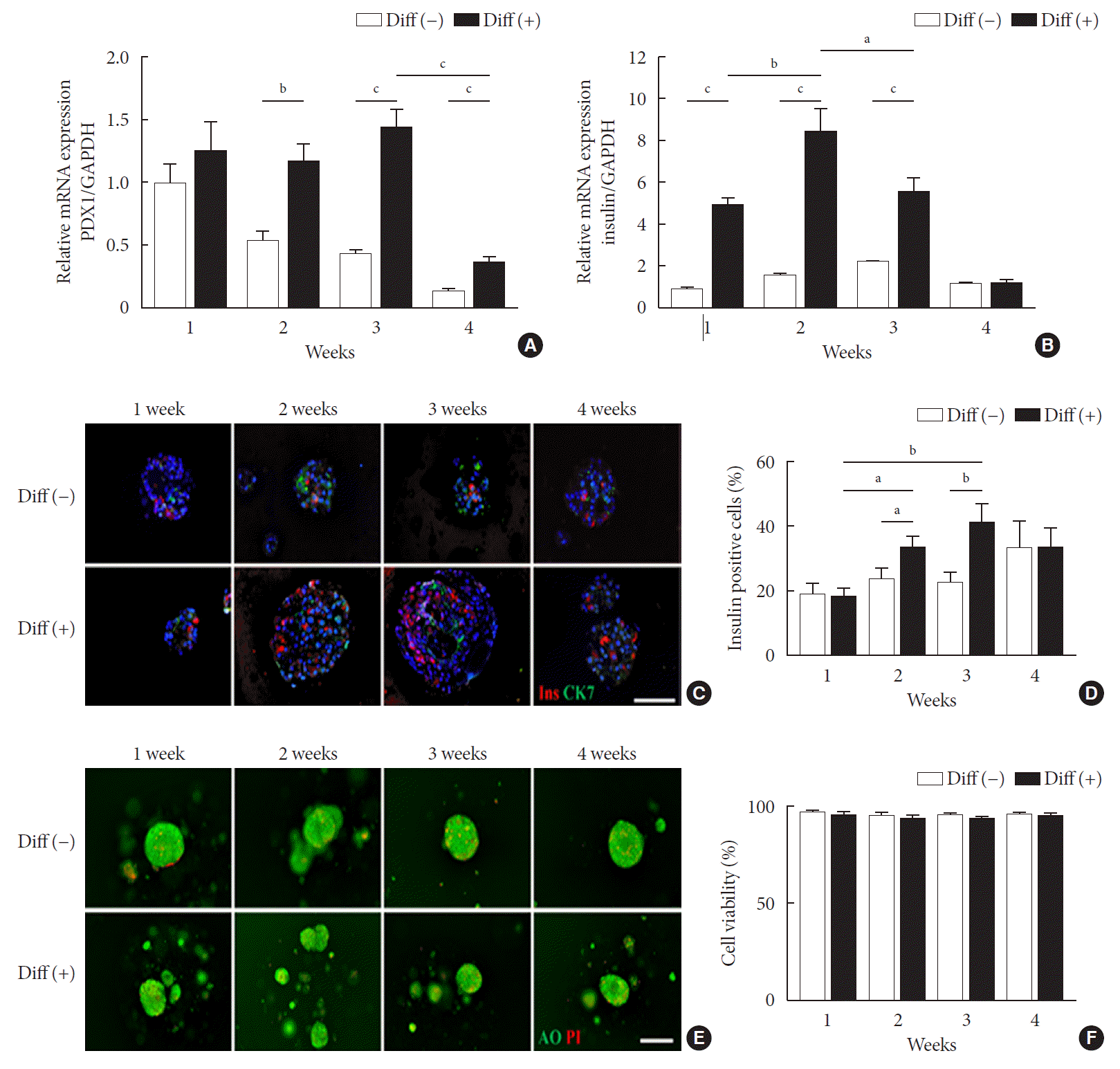
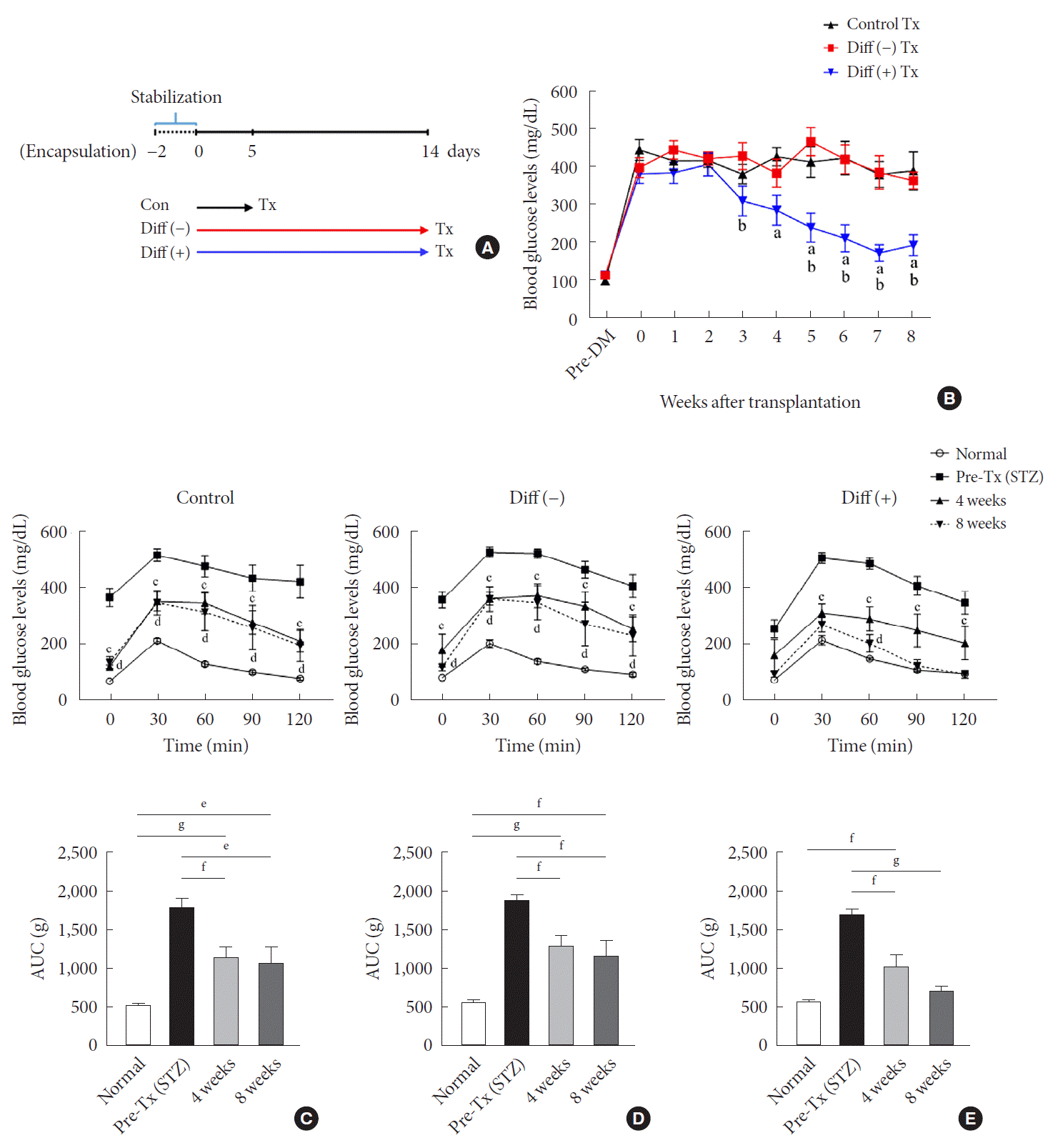
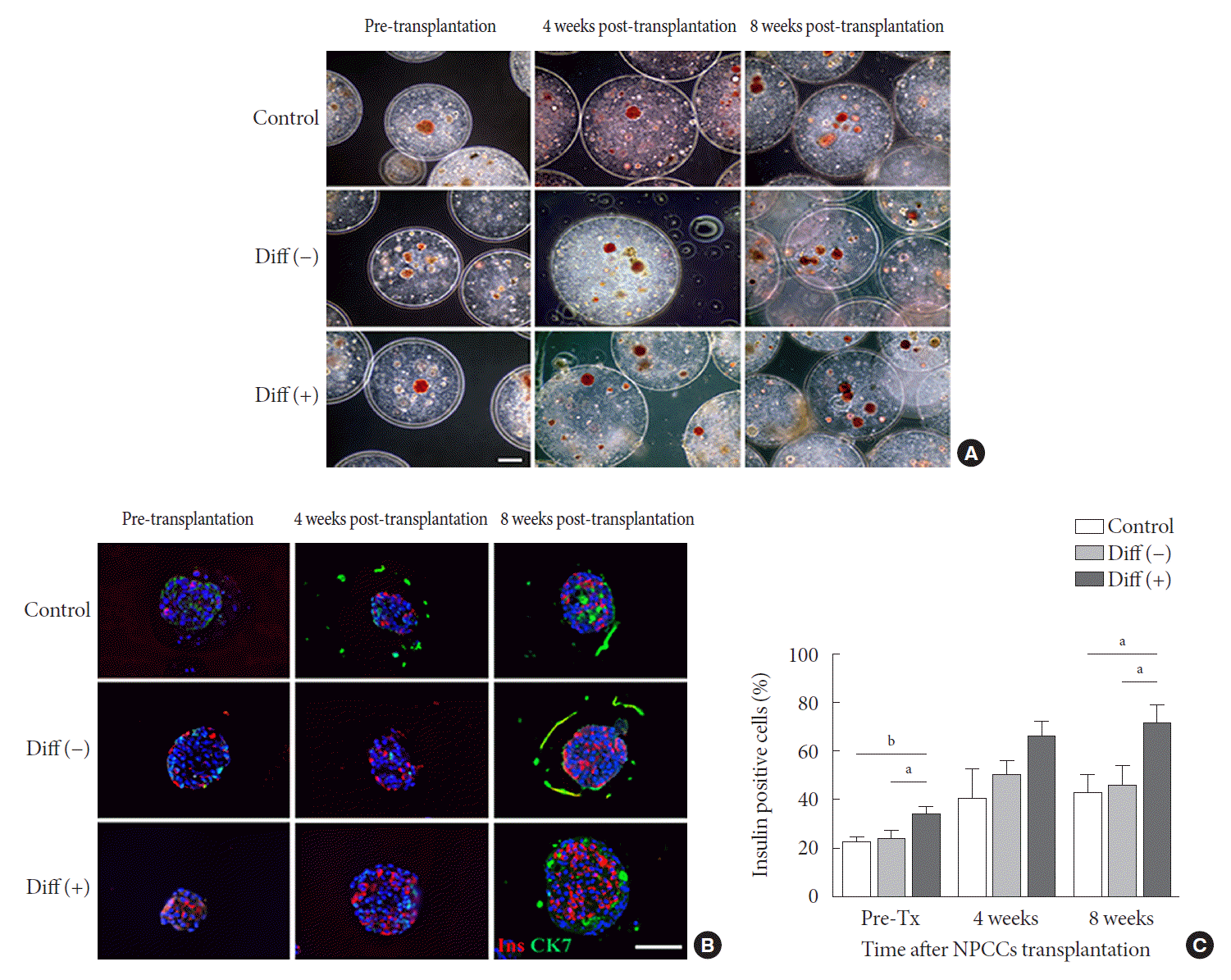
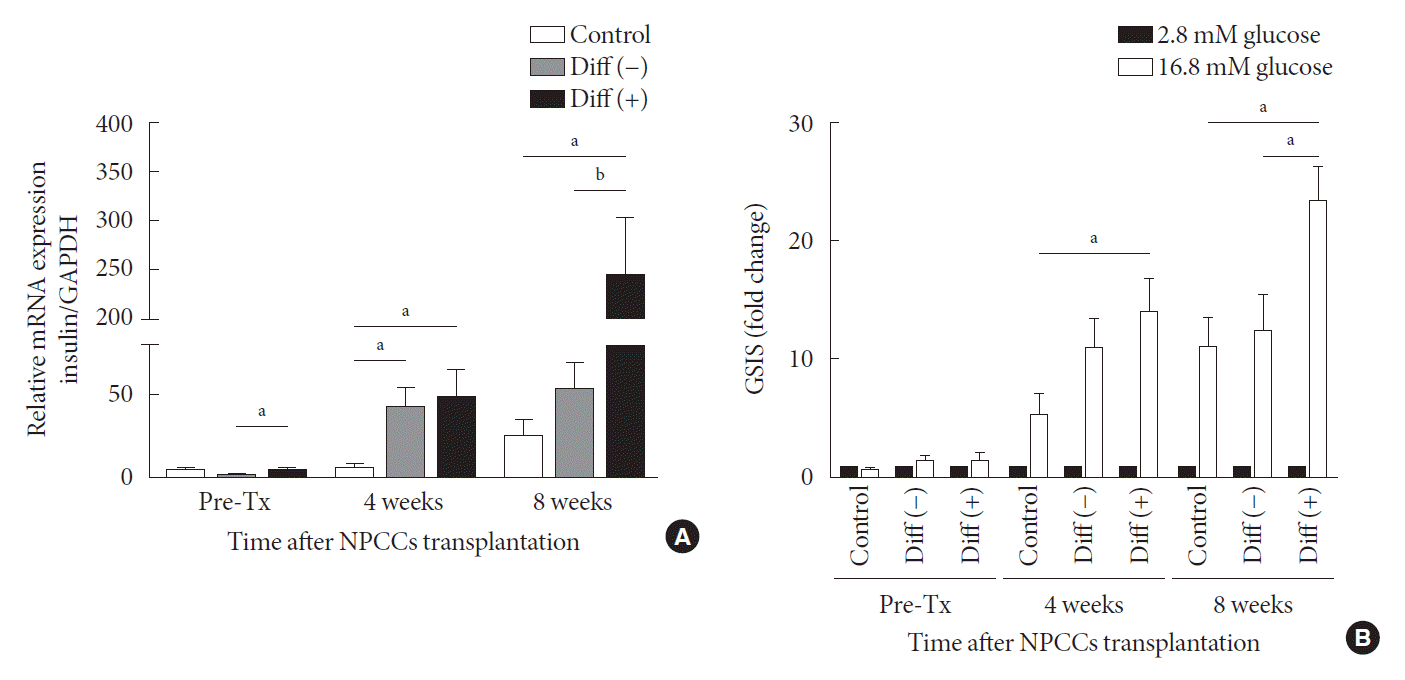




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download