INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study population
Measurements of clinical and laboratory indices
Definition of incident chronic kidney disease
Short insulin tolerance test
Assessment of NAFLD and definition of advanced liver fibrosis
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics of the study population according to the presence of NAFLD
Table 1
| Characteristic | Non-NAFLD (n=1,459) | NAFLD without advanced fibrosis (n=1,639) | NAFLD with advanced liver fibrosis (n=90) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 57.6±10.2 | 55.4±9.9a | 64.8±7.2a,b | 0.039c |
| Male sex | 685 (46.9) | 863 (52.7) | 49 (54.4) | 0.005c |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 8.4±7.4 | 6.4±6.0a | 8.1±7.3 | <0.001c |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.0±2.8 | 25.6±2.9a | 26.3±2.7a,b | <0.001c |
| WC, cm | 79.5±7.9 | 86.9±7.6a | 89.9±7.0a,b | <0.001c |
| SBP, mm Hg | 132.8±18.3 | 135.8±16.9a | 142.3±18.4a,b | <0.001c |
| DBP, mm Hg | 90.9±275.7 | 87.0±11.0 | 86.3±12.3 | 0.565 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 158.6±61.5 | 161.0±55.1 | 161.1±56.5 | 0.263 |
| HbA1c, % | 8.3±2.1 | 8.4±1.8 | 8.1±1.7 | 0.606 |
| KITT, %/min | 2.3±1.0 | 1.9±0.8a | 1.7±0.8a | <0.001c |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 189.4±37.8 | 201.9±41.8a | 194.0±37.6 | <0.001c |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 114.9±68.8 | 175.1±132.6a | 158.1±90.8a | <0.001c |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 54.3±14.8 | 48.7±12.0a | 48.8±13.2a | <0.001c |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 112.6±32.6 | 119.2±37.3a | 114.6±34.4 | <0.001c |
| AST, IU/L | 25.8±13.0 | 28.5±12.2a | 56.1±46.9a,b | <0.001c |
| ALT, IU/L | 24.7±17.5 | 34.0±25.6a | 52.4±69.5a,b | <0.001c |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 90.9±15.7 | 91.8±15.4 | 86.3±14.3 | 0.924 |
| Hs-CRP, mg/dL | 0.6 (0.3–1.1) | 1.0 (0.5–2.0)a | 1.0 (0.6–2.2)a | <0.001c |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 4.2 ±1.3 | 4.6±1.4a | 4.6±1.3a | <0.001c |
| Hypertension | 358 (24.5) | 493 (30.1)a | 34 (37.8)a | <0.001c |
| Insulin | 204 (14.0) | 131 (8.0)a | 13 (14.4) | <0.001c |
| Metformin | 541 (37.1) | 815 (49.7)a | 26 (28.9) | <0.001c |
| Sulfonylurea | 739 (50.7) | 875 (53.4) | 51 (56.7)a,b | 0.218 |
| Thiazolidinedione | 160 (11.0) | 125 (7.6)a | 10 (11.1)b | 0.005c |
| ARB/ACE inhibitors | 60 (4.1) | 106 (6.5)a,b | 10 (11.1)a,b | 0.001c |
| Statin | 177 (12.1) | 320 (19.5)a | 8 (8.9)b | <0.001c |
| Incident CKD | 220 (15.1) | 231 (14.1) | 28 (31.1)a,b | <0.001c |
NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; KITT, rate constant for plasma glucose disappearance; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; Hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blockers; ACE, angiotensin converting enzyme; CKD, chronic kidney disease.
Baseline characteristics of the study population according to the severity of NAFLD
Risk of incident CKD according to the severity of NAFLD
Fig. 1
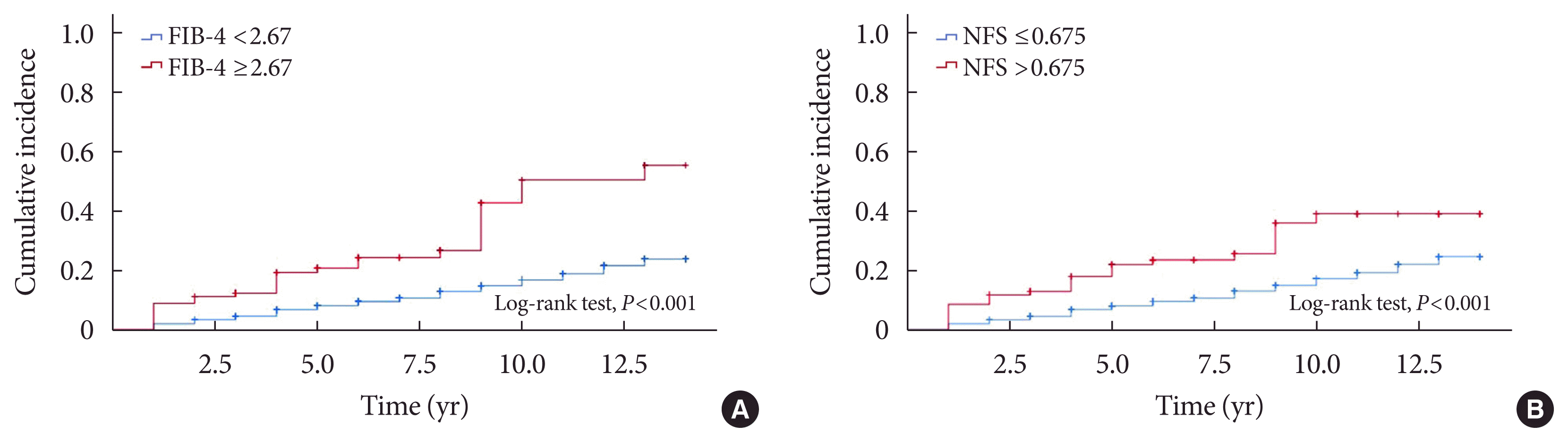
Table 2
| Characteristic | No CKD (n=2,716) | Incident CKD (n=472) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 55.5±10.1 | 63.4±7.6 | <0.001a |
| Male sex | 1,426 (52.5) | 170 (36.0) | <0.001a |
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 6.9±6.5 | 10.2±7.5 | <0.001a |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.4±3.2 | 24.6±3.0 | 0.175 |
| WC, cm | 83.6±8.8 | 84.0±7.6 | 0.300 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 133.2±17.2 | 142.8±18.2 | <0.001a |
| DBP, mm Hg | 85.4±11.0 | 108.4±48.3 | 0.303 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 159.5±57.9 | 162.0±59.2 | 0.395 |
| HbA1c, % | 8.3±1.9 | 8.6±1.9 | 0.003a |
| KITT, %/min | 2.1±1.0 | 1.9±0.9 | <0.001a |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 195.7±40.1 | 197.1±41.7 | 0.473 |
| Triglyceride, mg/dL | 145.5±110.0 | 156.1±116.3 | 0.055 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 51.4±13.6 | 50.5±13.8 | 0.187 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 116.0±34.9 | 116.0±37.4 | 0.993 |
| AST, IU/L | 28.0±15.8 | 28.3±13.4 | 0.683 |
| ALT, IU/L | 30.5±25.9 | 28.8±22.2 | 0.130 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 92.9±15.1 | 81.3±14.2 | <0.001a |
| Hs-CRP, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.4–1.6) | 0.9 (0.5–2.2) | <0.001a |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 4.4±1.3 | 4.7±1.5 | <0.001a |
| Hypertension | 690 (25.4) | 195 (41.3) | <0.001a |
| Insulin | 257 (9.5) | 91 (19.3) | <0.001a |
| Metformin | 1,158 (42.6) | 224 (47.5) | 0.057 |
| Sulfonylurea | 1,365 (50.3) | 300 (63.6) | <0.001a |
| Thiazolidinedione | 251 (9.2) | 44 (9.3) | 1.000 |
| ARB/ACE inhibitors | 149 (5.5) | 27 (5.7) | 0.924 |
| Statin | 400 (14.7) | 105 (22.2) | <0.001a |
| NAFLD (+) | 1,476 (54.4) | 252 (53.4) | 0.732 |
CKD, chronic kidney disease; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; KITT, rate constant for plasma glucose disappearance; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; Hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; ARB, angiotensin II receptor blocker; ACE, angiotensin converting enzyme; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Table 3
| HR | 95% CI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crude hazard ratio | 0.98 | 0.82–1.18 | 0.849 |
| Model 1 | 1.09 | 0.91–1.30 | 0.368 |
| Model 2 | 1.13 | 0.94–1.36 | 0.194 |
| Model 3 | 1.13 | 0.93–1.36 | 0.212 |
| Model 4 | 1.08 | 0.89–1.32 | 0.435 |
Model 1: adjustment for age (age was applied as a categorical variable with median age of 58 years), sex, and body mass index; Model 2: Model 1+adjustment for duration of diabetes, systolic blood pressure, hypertension, glycosylated hemoglobin level, total cholesterol level, and estimated glomerular filtration rate; Model 3: Model 2+adjustments for use of sulfonylurea, insulin, statin, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blockers; and Model 4: Model 3+adjustments for log high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level and rate constant for plasma glucose disappearance (KITT) value.
Table 4
| By FIB-4 | By NFS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|||||
| HR | 95% CI | P value | HR | 95% CI | P value | |
| Crude hazard ratio | 2.86 | 1.93–4.23 | <0.001a | 2.32 | 1.55–3.48 | <0.001a |
|
|
||||||
| Model 1 | 1.96 | 1.32–2.92 | 0.001a | 1.52 | 1.01–2.29 | 0.046a |
|
|
||||||
| Model 2 | 1.88 | 1.26–2.81 | 0.002a | 1.50 | 1.00–2.27 | 0.056 |
|
|
||||||
| Model 3 | 1.84 | 1.23–2.75 | 0.003a | 1.49 | 0.98–2.27 | 0.063 |
|
|
||||||
| Model 4 | 1.75 | 1.15–2.66 | 0.009a | 1.58 | 1.03–2.41 | 0.035a |
Model 1: adjustment for age (age was applied as a categorical variable with median age of 58 years), sex, and body mass index; Model 2: Model 1+adjustment for duration of diabetes, systolic blood pressure, hypertension, glycosylated hemoglobin level, total cholesterol level, and estimated glomerular filtration rate; Model 3: Model 2+adjustments for use of sulfonylurea, insulin, statin, and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blockers; and Model 4: Model 3+adjustments for log high-sensitivity C-reactive protein level and rate constant for plasma glucose disappearance (KITT) value.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download