1. Congdon NG, Friedman DS, Lietman T. Important causes of visual impairment in the world today. JAMA. 2003; 290:2057–60.

2. Fong DS, Aiello LP, Ferris FL 3rd, Klein R. Diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27:2540–53.

3. Thomas RL, Halim S, Gurudas S, Sivaprasad S, Owens DR. IDF Diabetes Atlas: a review of studies utilising retinal photography on the global prevalence of diabetes related retinopathy between 2015 and 2018. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 157:107840.

4. Zhang X, Saaddine JB, Chou CF, Cotch MF, Cheng YJ, Geiss LS, et al. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in the United States, 2005-2008. JAMA. 2010; 304:649–56.

5. Chung YR, Ha KH, Lee K, Kim DJ. Diabetic retinopathy and related clinical practice for people with diabetes in Korea: a 10-year trend analysis. Diabetes Metab J. 2020; 44:928–32.

6. Lima VC, Cavalieri GC, Lima MC, Nazario NO, Lima GC. Risk factors for diabetic retinopathy: a case-control study. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2016; 2:21.

7. Rema M, Deepa R, Mohan V. Prevalence of retinopathy at diagnosis among type 2 diabetic patients attending a diabetic centre in South India. Br J Ophthalmol. 2000; 84:1058–60.

8. Lee KM, Sum WM. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in patients with recently diagnosed diabetes mellitus. Clin Exp Optom. 2011; 94:371–5.

9. Harris MI, Klein R, Welborn TA, Knuiman MW. Onset of NIDDM occurs at least 4-7 yr before clinical diagnosis. Diabetes Care. 1992; 15:815–9.

10. American Diabetes Association. 11. Microvascular complications and foot care: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44(Suppl 1):S151–67.
11. Shi Q, Zhao Y, Fonseca V, Krousel-Wood M, Shi L. Racial disparity of eye examinations among the U.S. working-age population with diabetes: 2002-2009. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1321–8.

12. Jones S, Edwards RT. Diabetic retinopathy screening: a systematic review of the economic evidence. Diabet Med. 2010; 27:249–56.

13. Lee YH, Armstrong EJ, Kim G, Oh J, Kang SM, Lee BW, et al. Undiagnosed diabetes is prevalent in younger adults and associated with a higher risk cardiometabolic profile compared to diagnosed diabetes. Am Heart J. 2015; 170:760–9.

14. Klein R, Sharrett AR, Klein BE, Moss SE, Folsom AR, Wong TY, et al. The association of atherosclerosis, vascular risk factors, and retinopathy in adults with diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Ophthalmology. 2002; 109:1225–34.

15. Niazi MK, Akram A, Naz MA, Awan S. Duration of diabetes as a significant factor for retinopathy. Pak J Ophthalmol. 2010; 26:182–6.
16. Ponto KA, Koenig J, Peto T, Lamparter J, Raum P, Wild PS, et al. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in screening-detected diabetes mellitus: results from the Gutenberg Health Study (GHS). Diabetologia. 2016; 59:1913–9.

17. Kim Y. The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES): current status and challenges. Epidemiol Health. 2014; 36:e2014002.

18. Korean Ophthalmological Society. Standardization for eye survey in Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Seoul: Korean Ophthalmological Society;2018.
19. Lee WJ, Sobrin L, Lee MJ, Kang MH, Seong M, Cho H. The relationship between diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy in a population-based study in Korea (KNHANES V-2, 3). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014; 55:6547–53.

20. Seo MH, Lee WY, Kim SS, Kang JH, Kang JH, Kim KK, et al. 2018 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guideline for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr. 2019; 28:40–5.

21. Hill L, Makaroff LE. Early detection and timely treatment can prevent or delay diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2016; 120:241–3.

22. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. Brussels: International diabetes Federation;2019.
23. Jung CH, Son JW, Kang S, Kim WJ, Kim HS, Kim HS, et al. Diabetes fact sheets in Korea, 2020: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J. 2021; 45:1–10.

24. Claypool KT, Chung MK, Deonarine A, Gregg EW, Patel CJ. Characteristics of undiagnosed diabetes in men and women under the age of 50 years in the Indian subcontinent: the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4)/Demographic Health Survey 2015-2016. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020; 8:e000965.

25. Wong A, Wouterse B, Slobbe LC, Boshuizen HC, Polder JJ. Medical innovation and age-specific trends in health care utilization: findings and implications. Soc Sci Med. 2012; 74:263–72.

26. Koo BK, Roh E, Yang YS, Moon MK. Difference between old and young adults in contribution of β-cell function and sarcopenia in developing diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig. 2016; 7:233–40.

27. Barrett T, Jalaludin MY, Turan S, Hafez M, Shehadeh N; Novo Nordisk Pediatric Type 2 Diabetes Global Expert Panel. Rapid progression of type 2 diabetes and related complications in children and young people: a literature review. Pediatr Diabetes. 2020; 21:158–72.

28. Carter JS, Gilliland SS, Perez GE, Skipper B, Gilliland FD. Public health and clinical implications of high hemoglobin A1c levels and weight in younger adult Native American people with diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 2000; 160:3471–6.

29. El-Kebbi IM, Cook CB, Ziemer DC, Miller CD, Gallina DL, Phillips LS. Association of younger age with poor glycemic control and obesity in urban African Americans with type 2 diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 2003; 163:69–75.

30. Toh MP, Wu CX, Leong HS. Association of younger age with poor glycemic and cholesterol control in Asians with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Singapore. J Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 1:27–37.

31. Dall TM, Yang W, Halder P, Pang B, Massoudi M, Wintfeld N, et al. The economic burden of elevated blood glucose levels in 2012: diagnosed and undiagnosed diabetes, gestational diabetes mellitus, and prediabetes. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:3172–9.

32. Karachaliou F, Simatos G, Simatou A. The challenges in the development of diabetes prevention and care models in low-income settings. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020; 11:518.

33. Le C, Jun D, Zhankun S, Yichun L, Jie T. Socioeconomic differences in diabetes prevalence, awareness, and treatment in rural southwest China. Trop Med Int Health. 2011; 16:1070–6.

34. Fong DS, Aiello L, Gardner TW, King GL, Blankenship G, Cavallerano JD, et al. Retinopathy in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2004; 27 Suppl 1:S84–7.

35. Duh EJ, Sun JK, Stitt AW. Diabetic retinopathy: current understanding, mechanisms, and treatment strategies. JCI Insight. 2017; 2:e93751.

36. ACCORD Study Group; ACCORD Eye Study Group, Chew EY, Ambrosius WT, Davis MD, Danis RP, et al. Effects of medical therapies on retinopathy progression in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:233–44.

37. Writing Team for the DCCT/EDIC Research Group, GubitosiKlug RA, Sun W, Cleary PA, Braffett BH, Aiello LP, et al. Effects of prior intensive insulin therapy and risk factors on patient-reported visual function outcomes in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) cohort. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016; 134:137–45.

38. Zou W, Ni L, Lu Q, Zou C, Zhao M, Xu X, et al. Diabetes onset at 31-45 years of age is associated with an increased risk of diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep. 2016; 6:38113.

39. Middleton TL, Constantino MI, Molyneaux L, D’Souza M, Twigg SM, Wu T, et al. Young-onset type 2 diabetes and younger current age: increased susceptibility to retinopathy in contrast to other complications. Diabet Med. 2020; 37:991–9.

40. Zhang Y, Moran AE. Trends in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among young adults in the United States, 1999 to 2014. Hypertension. 2017; 70:736–42.

41. Kalra R, Parcha V, Patel N, Bhargava A, Booker KS, Arora G, et al. Increased awareness, inadequate treatment, and poor control of cardiovascular risk factors in American young adults: 2005-2016. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2021; 28:304–12.

42. Heng LZ, Comyn O, Peto T, Tadros C, Ng E, Sivaprasad S, et al. Diabetic retinopathy: pathogenesis, clinical grading, management and future developments. Diabet Med. 2013; 30:640–50.

43. Bermea KC, Rodriguez-Garcia A, Tsin A, Barrera-Saldana HA. Somatolactogens and diabetic retinopathy. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2018; 41:42–7.

44. Prescott G, Sharp P, Goatman K, Scotland G, Fleming A, Philip S, et al. Improving the cost-effectiveness of photographic screening for diabetic macular oedema: a prospective, multicentre, UK study. Br J Ophthalmol. 2014; 98:1042–9.

45. Shi L, Wu H, Dong J, Jiang K, Lu X, Shi J. Telemedicine for detecting diabetic retinopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol. 2015; 99:823–31.

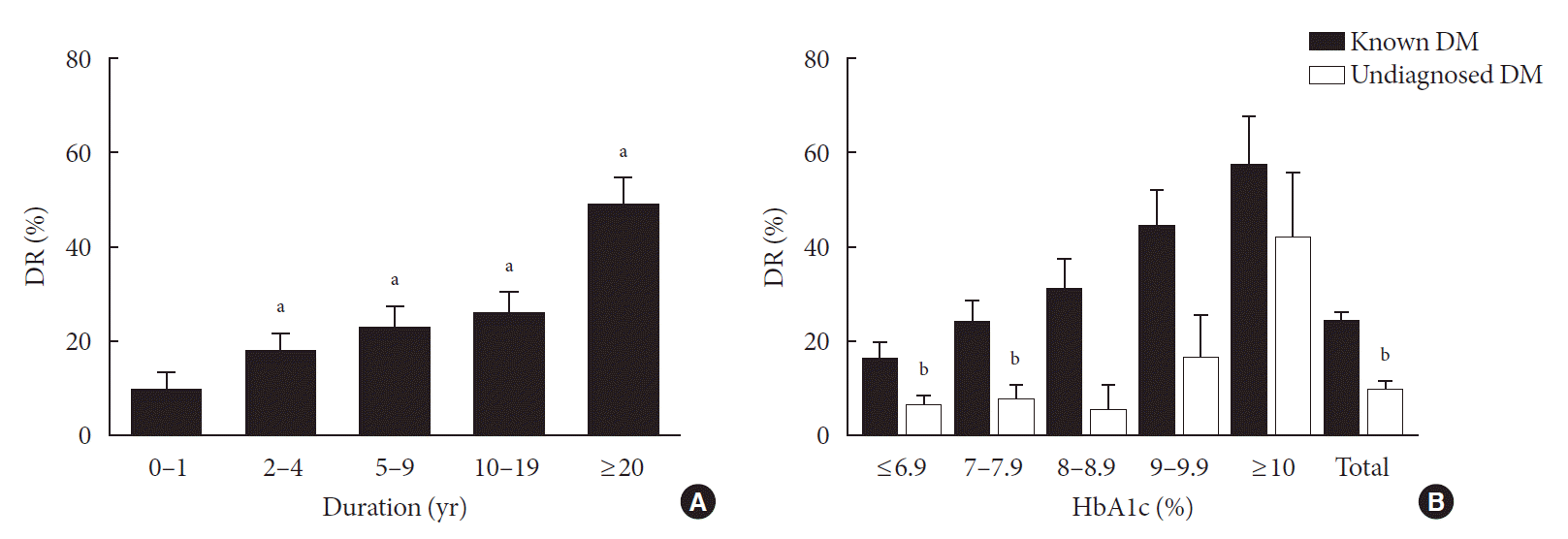
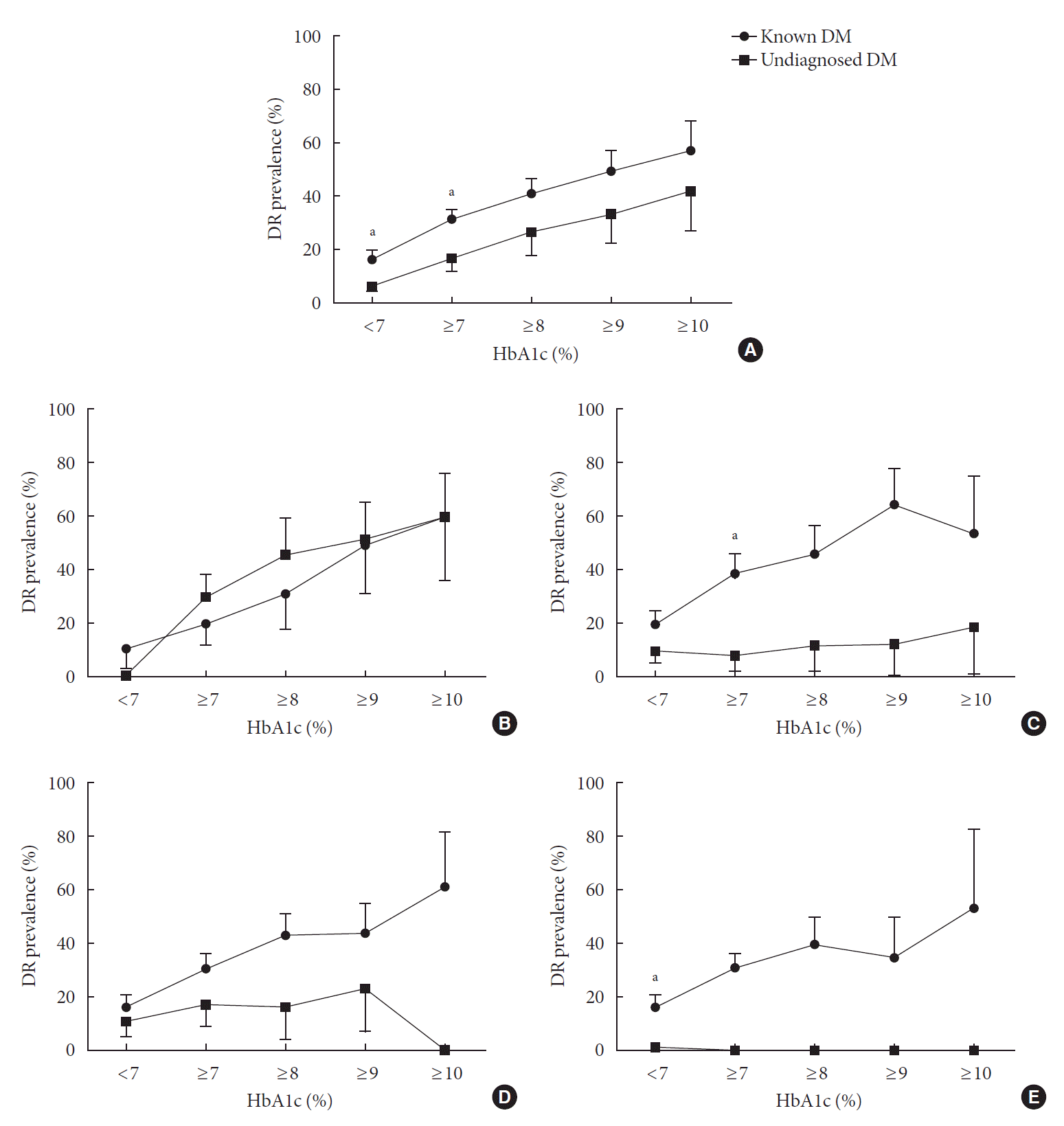




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download