2. Puzenat E, Bronsard V, Prey S, Gourraud PA, Aractingi S, Bagot M, et al. What are the best outcome measures for assessing plaque psoriasis severity? A systematic review of the literature. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010; 24(Suppl 2):10–6.
https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03562.x.

3. Bhushan M, Burden AD, McElhone K, James R, Vanhoutte FP, Griffiths CE. Oral liarozole in the treatment of palmoplantar pustular psoriasis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Br J Dermatol. 2001; 145(4):546–53.
https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.2001.04411.x.

4. Kolios AG, French LE, Navarini AA. Detection of small changes in psoriasis intensity with PrecisePASI. Dermatology. 2015; 230(4):314–7.
https://doi.org/10.1159/000371811.

5. Youn SW, Choi CW, Kim BR, Chae JB. Reduction of inter-rater and intra-rater variability in psoriasis area and severity index assessment by photographic training. Ann Dermatol. 2015; 27(5):557–62.
https://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.5.557.

6. Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM, et al. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature. 2017; 542(7639):115–8.
https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21056.

7. Meienberger N, Anzengruber F, Amruthalingam L, Christen R, Koller T, Maul JT, et al. Observer-independent assessment of psoriasis-affected area using machine learning. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020; 34(6):1362–8.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.16002.

8. Andermatt S, Horvath A, Pezold S, Cattin P. Pathology segmentation using distributional differences to images of healthy origin. Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T, editors. Brainlesion: glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. Cham, Switzerland: Springer;2018. p. 228–38.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11723-8_23.

9. Furger F, Amruthalingam L, Navarini A, Pouly M. Applications of generative adversarial networks to dermatologic imaging. Schilling FP, Stadelmann T, editors. Artificial neural networks in pattern recognition. Cham, Switzerland: Springer;2020. p. 187–99.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58309-5_15.

10. Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells W, Frangi A, editors. Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention – MICCAI 2015. Cham, Switzerland: Springer;2015. p. 234–41.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28.

11. He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In : Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2016 Jun 26–Jul 1; Las Vegas, NV. p. 770–8.

12. Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L. ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In : Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition; 2009 Jun 20–25; Miami, FL. p. 248–55.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848.

13. Smith LN. A disciplined approach to neural network hyper-parameters: Part 1--learning rate, batch size, momentum, and weight decay [Internet]. Ithaca (NY): arXiv.org;2018. [cited at 2022 Jul 20]. Available from:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.09820.
14. Yeung M, Sala E, Schonlieb CB, Rundo L. Unified focal loss: generalising dice and cross entropy-based losses to handle class imbalanced medical image segmentation. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2022; 95:102026.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compmedimag.2021.102026.

16. Zhu W, Huang Y, Zeng L, Chen X, Liu Y, Qian Z, et al. AnatomyNet: deep learning for fast and fully automated whole-volume segmentation of head and neck anatomy. Med Phys. 2019; 46(2):576–89.
https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.13300.

17. El Jurdi R, Petitjean C, Honeine P, Cheplygina V, Abdallah F. High-level prior-based loss functions for medical image segmentation: a survey. Comput Vis Image Underst. 2021; 210:103248.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2021.103248.

18. Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, et al. PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst. 2019; 32:8024–35.
20. van Stralen KJ, Dekker FW, Zoccali C, Jager KJ. Measuring agreement, more complicated than it seems. Nephron Clin Pract. 2012; 120(3):c162–7.
https://doi.org/10.1159/000337798.

21. Schaap MJ, Cardozo NJ, Patel A, de Jong EM, van Ginneken B, Seyger MM. Image-based automated psoriasis area severity index scoring by convolutional neural networks. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2022; 36(1):68–75.
https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.17711.

22. Wu X, Yan Y, Zhao S, Kuang Y, Ge S, Wang K, et al. Automatic severity rating for improved psoriasis treatment. Medical image computing and computer assisted intervention – MICCAI 2021. Cham, Switzerland: Springer;2021. p. 185–94.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87234-2_18.

23. Pal A, Chaturvedi A, Garain U, Chandra A, Chatterjee R, Senapati S. Severity assessment of psoriatic plaques using deep CNN based ordinal classification. OR 20 Context-aware operating theaters, computer assisted robotic endoscopy, clinical image-based procedures, and skin image analysis. Cham, Switzerland: Springer;2018. p. 252–9.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01201-4_27.

24. Cazzolato MT, Ramos JS, Rodrigues LS, Scabora LC, Chino DY, Jorge AE, et al. The UTrack framework for segmenting and measuring dermatological ulcers through telemedicine. Comput Biol Med. 2021; 134:104489.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104489.

25. Zhao C, Shuai R, Ma L, Liu W, Wu M. Segmentation of dermoscopy images based on deformable 3D convolution and ResU-NeXt +. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2021; 59(9):1815–32.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02397-9.

27. Schnurle S, Pouly M, vor der Bruck T, Navarini A, Koller T. On using support vector machines for the detection and quantification of hand eczema. In : Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART); 2017 Feb 24–26; Porto, Portugal. p. 75–84.

28. Raj R, Londhe ND, Sonawane RS. Deep learning based multi-segmentation for automatic estimation of psoriasis area score. In : Proceedings of 2021, 8th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN); 2021 Aug 26–27; Noida, India. p. 1137–42.
https://doi.org/10.1109/SPIN52536.2021.9566039.

30. Finnane A, Curiel-Lewandrowski C, Wimberley G, Caffery L, Katragadda C, Halpern A, et al. Proposed technical guidelines for the acquisition of clinical images of skin-related conditions. JAMA Dermatol. 2017; 153(5):453–7.
https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.6214.

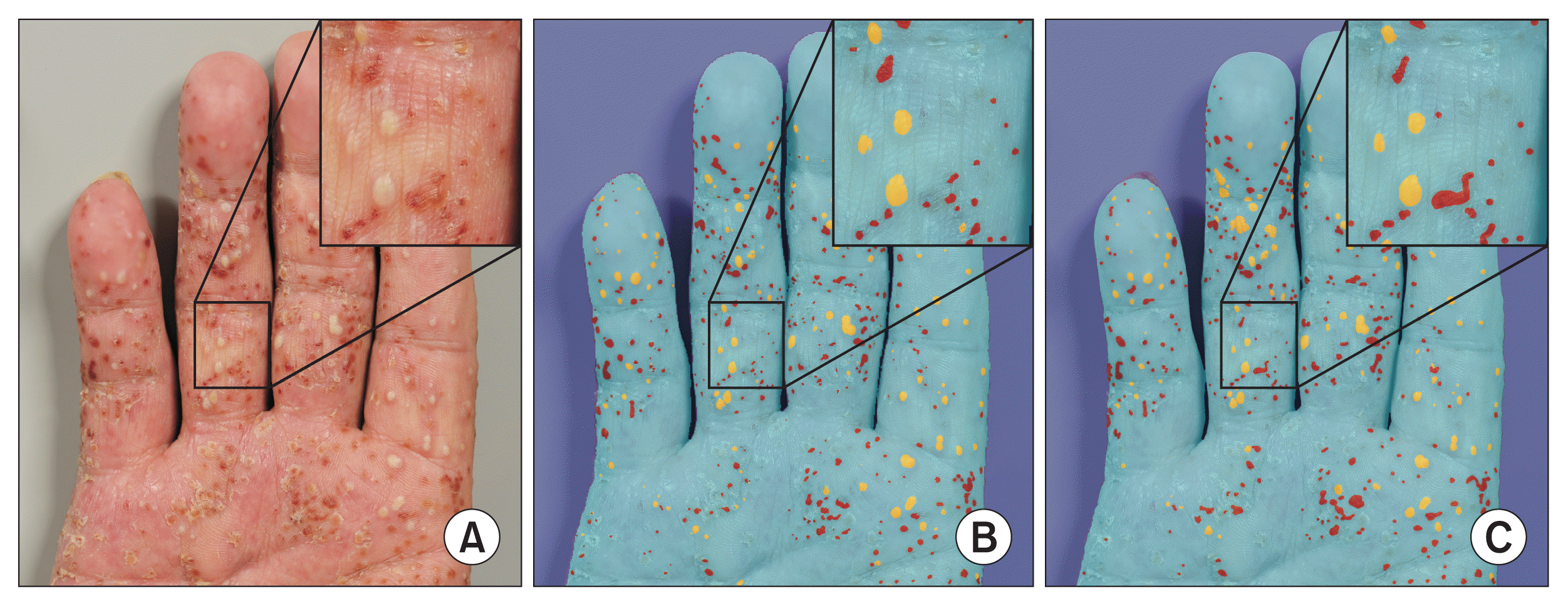
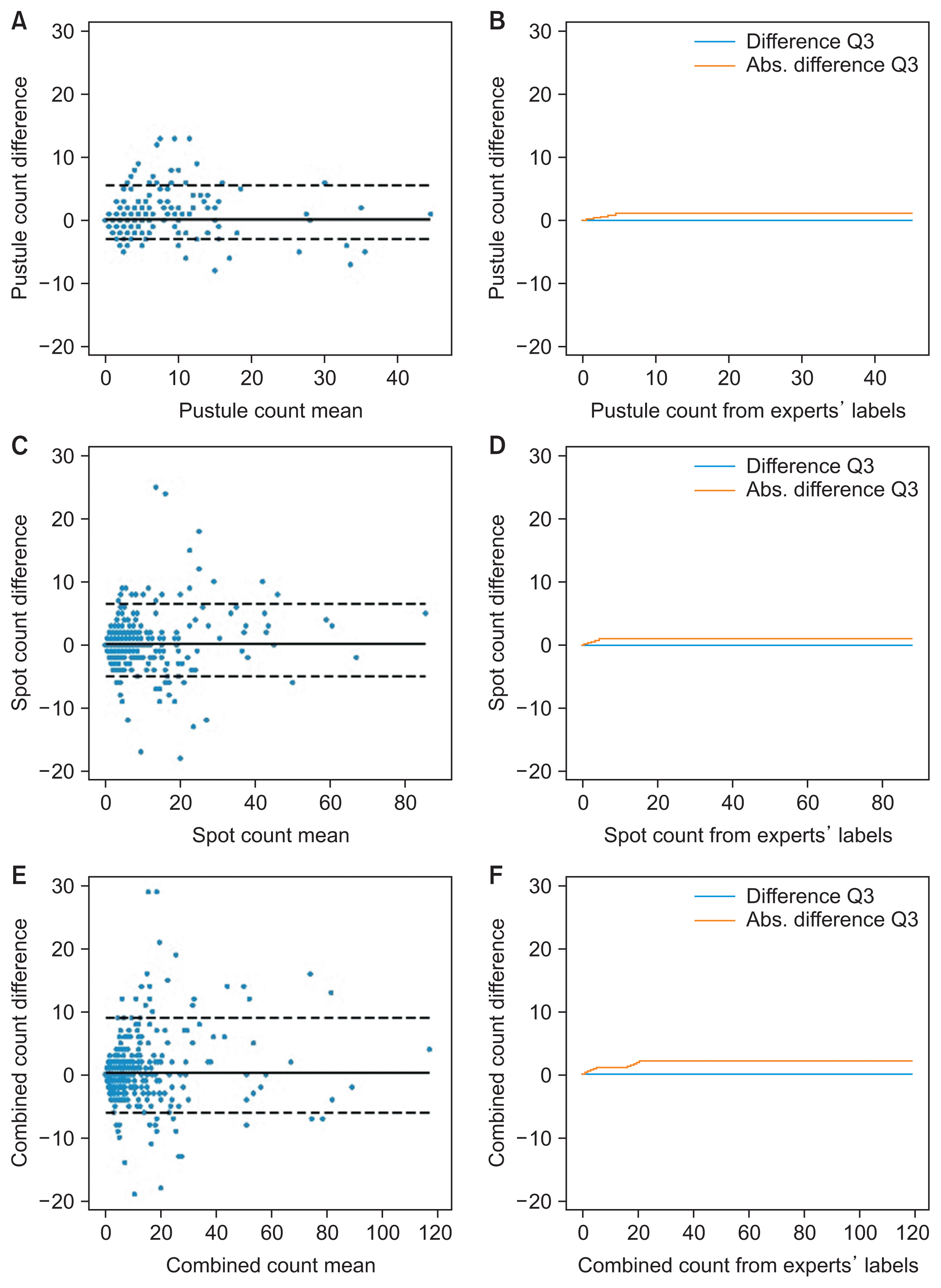
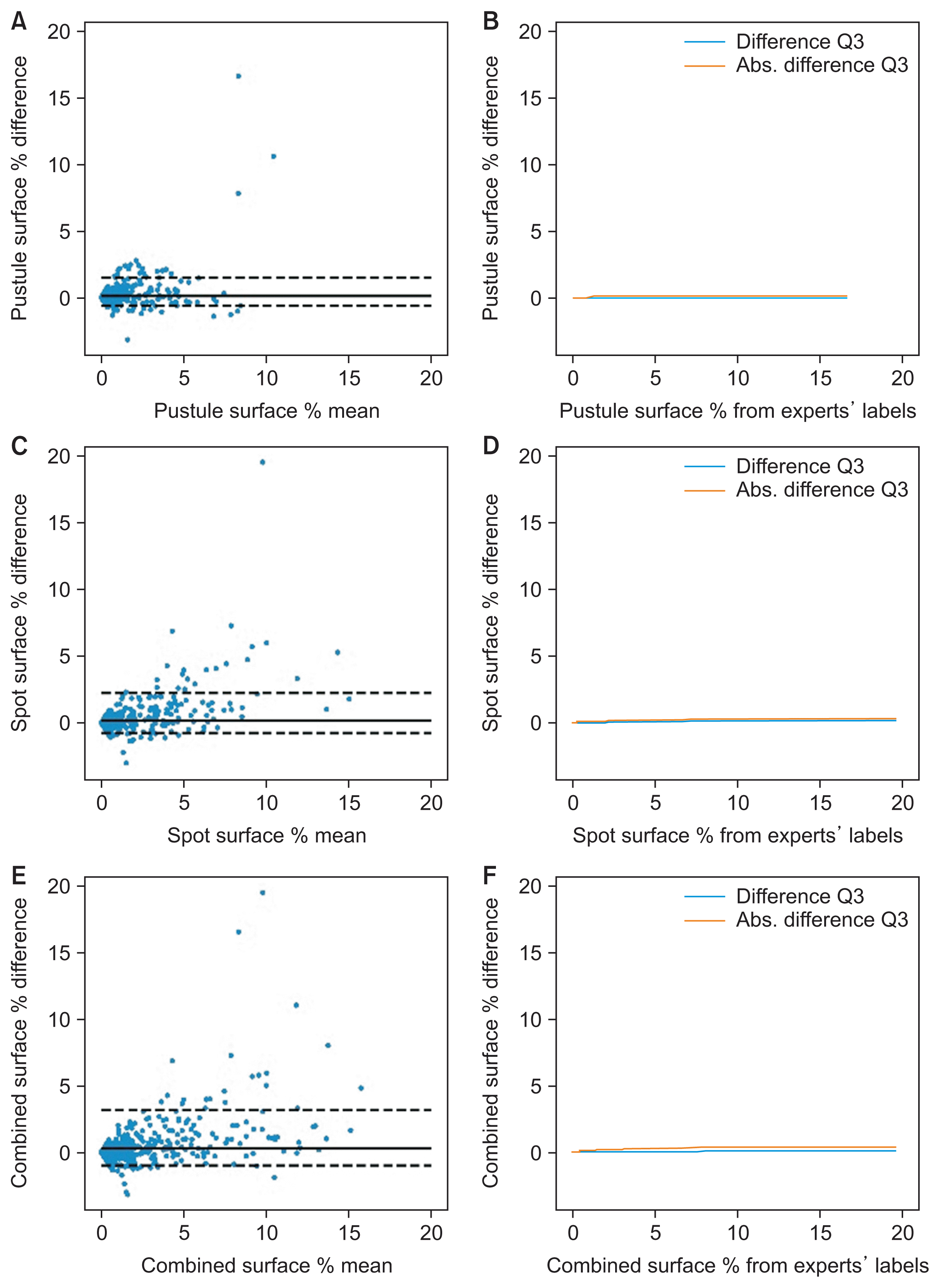




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download