1. Rosen MJ, Dhawan A, Saeed SA. Inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents. JAMA Pediatr. 2015; 169(11):1053–1060. PMID:
26414706.

2. Jang HJ, Suh HR, Choi S, Hong SJ, Cho SM, Choi KH, et al. Severe disease activity based on the Paris classification is associated with the development of extraintestinal manifestations in Korean children and adolescents with ulcerative colitis. J Korean Med Sci. 2021; 36(44):e278. PMID:
34783212.

3. Kang B, Choe YH. Early biologic treatment in pediatric Crohn’s disease: catching the therapeutic window of opportunity in early disease by treat-to-target. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2018; 21(1):1–11. PMID:
29383299.

4. Kang B, Choi SY, Kim HS, Kim K, Lee YM, Choe YH. Mucosal healing in paediatric patients with moderate-to-severe luminal Crohn’s disease under combined immunosuppression: escalation versus early treatment. J Crohns Colitis. 2016; 10(11):1279–1286. PMID:
27095752.

5. Choi MG, Ye BD, Yang SK, Shim TS, Jo KW, Park SH. The risk of tuberculosis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with vedolizumab or ustekinumab in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2022; 37(14):e107. PMID:
35411727.

6. Barberio B, Savarino EV, Card T, Canova C, Baldisser F, Gubbiotti A, et al. Incidence comparison of adverse events in patients with inflammatory bowel disease receiving different biologic agents: retrospective long-term evaluation. Intest Res. 2022; 20(1):114–123. PMID:
34333908.

7. Song HY, Seo GS. Treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases: focusing on biologic agents and new therapies. J Korean Med Assoc. 2021; 64(9):605–613.

8. Sandborn WJ, Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Hanauer S, Colombel JF, Sands BE, et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369(8):711–721. PMID:
23964933.

9. Feagan BG, Rutgeerts P, Sands BE, Hanauer S, Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med. 2013; 369(8):699–710. PMID:
23964932.

10. van Rheenen PF, Aloi M, Assa A, Bronsky J, Escher JC, Fagerberg UL, et al. The Medical Management of Paediatric Crohn’s Disease: an ECCO-ESPGHAN Guideline Update. J Crohns Colitis. Forthcoming. 2020; DOI:
10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa161.

11. Turner D, Ruemmele FM, Orlanski-Meyer E, Griffiths AM, de Carpi JM, Bronsky J, et al. Management of paediatric ulcerative colitis, Part 1: Ambulatory care-an evidence-based guideline from European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization and European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018; 67(2):257–291. PMID:
30044357.

12. Choi S, Choi BS, Choe BH, Kang B. Successful treatment with vedolizumab in an adolescent with Crohn disease who had developed active pulmonary tuberculosis while receiving infliximab. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2021; 38(3):251–257. PMID:
33601494.

13. Conrad MA, Stein RE, Maxwell EC, Albenberg L, Baldassano RN, Dawany N, et al. Vedolizumab therapy in severe pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016; 22(10):2425–2431. PMID:
27598742.

14. Ledder O, Assa A, Levine A, Escher JC, de Ridder L, Ruemmele F, et al. Vedolizumab in paediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a retrospective multi-centre experience from the Paediatric IBD Porto Group of ESPGHAN. J Crohns Colitis. 2017; 11(10):1230–1237. PMID:
28605483.

15. Singh N, Rabizadeh S, Jossen J, Pittman N, Check M, Hashemi G, et al. Multi-center experience of vedolizumab effectiveness in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2016; 22(9):2121–2126. PMID:
27542130.

16. Fabiszewska S, Derda E, Szymanska E, Osiecki M, Kierkus J. Safety and effectiveness of vedolizumab for the treatment of pediatric patients with very early onset inflammatory bowel diseases. J Clin Med. 2021; 10(13):2997. PMID:
34279480.

17. Wu JF. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Biologics for Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: How, When, and for Whom? Gut Liver. 2022; 16(4):515–524. PMID:
34670875.

18. Shmidt E, Kochhar G, Hartke J, Chilukuri P, Meserve J, Chaudrey K, et al. Predictors and Management of Loss of Response to Vedolizumab in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018; 24(11):2461–2467. PMID:
29788240.

19. Billiet T, Papamichael K, de Bruyn M, Verstockt B, Cleynen I, Princen F, et al. A matrix-based model predicts primary response to infliximab in Crohn’s disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2015; 9(12):1120–1126. PMID:
26351386.

20. Ding NS, Hart A, De Cruz P. Systematic review: predicting and optimising response to anti-TNF therapy in Crohn’s disease - algorithm for practical management. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016; 43(1):30–51. PMID:
26515897.

21. Barber GE, Yajnik V, Khalili H, Giallourakis C, Garber J, Xavier R, et al. Genetic markers predict primary non-response and durable response to anti-TNF biologic therapies in Crohn’s disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016; 111(12):1816–1822. PMID:
27596696.

22. Kopylov U, Ron Y, Avni-Biron I, Koslowsky B, Waterman M, Daher S, et al. Efficacy and safety of vedolizumab for induction of remission in inflammatory bowel disease-the Israeli real-world experience. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017; 23(3):404–408. PMID:
28178003.

23. Lenti MV, Levison S, Eliadou E, Willert R, Kemp K, Carter A, et al. A real-world, long-term experience on effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease: the Cross Pennine study. Dig Liver Dis. 2018; 50(12):1299–1304. PMID:
30077465.

24. Chaparro M, Garre A, Ricart E, Iborra M, Mesonero F, Vera I, et al. Short and long-term effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease: results from the ENEIDA registry. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 48(8):839–851. PMID:
30281832.

25. Dulai PS, Singh S, Jiang X, Peerani F, Narula N, Chaudrey K, et al. The real-world effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab for moderate-severe Crohn’s disease: results from the US VICTORY Consortium. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016; 111(8):1147–1155. PMID:
27296941.

26. Shelton E, Allegretti JR, Stevens B, Lucci M, Khalili H, Nguyen DD, et al. Efficacy of vedolizumab as induction therapy in refractory IBD patients: a multicenter cohort. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015; 21(12):2879–2885. PMID:
26288002.

27. Amiot A, Grimaud JC, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Filippi J, Pariente B, Roblin X, et al. Effectiveness and safety of vedolizumab induction therapy for patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 14(11):1593–1601.e2. PMID:
26917043.
28. Baumgart DC, Bokemeyer B, Drabik A, Stallmach A, Schreiber S. Vedolizumab Germany Consortium. Vedolizumab induction therapy for inflammatory bowel disease in clinical practice--a nationwide consecutive German cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2016; 43(10):1090–1102. PMID:
27038247.

29. Dulai PS, Boland BS, Singh S, Chaudrey K, Koliani-Pace JL, Kochhar G, et al. Development and validation of a scoring system to predict outcomes of vedolizumab treatment in patients with Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. 2018; 155(3):687–695.e10. PMID:
29857091.

30. Singh S, George J, Boland BS, Vande Casteele N, Sandborn WJ. Primary non-response to tumor necrosis factor antagonists is associated with inferior response to second-line biologics in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Crohns Colitis. 2018; 12(6):635–643. PMID:
29370397.

31. Wang Y, Wang J, Pekow J, Dalal S, Cohen RD, Ollech J, et al. Outcome of elective switching to vedolizumab in inflammatory bowel disease patients under tumor necrosis factor antagonist-maintained clinical remission. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 34(12):2090–2095. PMID:
31169926.

32. Feagan BG, Rubin DT, Danese S, Vermeire S, Abhyankar B, Sankoh S, et al. Efficacy of vedolizumab induction and maintenance therapy in patients with ulcerative colitis, regardless of prior exposure to tumor necrosis factor antagonists. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 15(2):229–239.e5. PMID:
27639327.

33. Sands BE, Sandborn WJ, Van Assche G, Lukas M, Xu J, James A, et al. Vedolizumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease in patients Naïve to or who have failed tumor necrosis factor antagonist therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017; 23(1):97–106. PMID:
27930408.

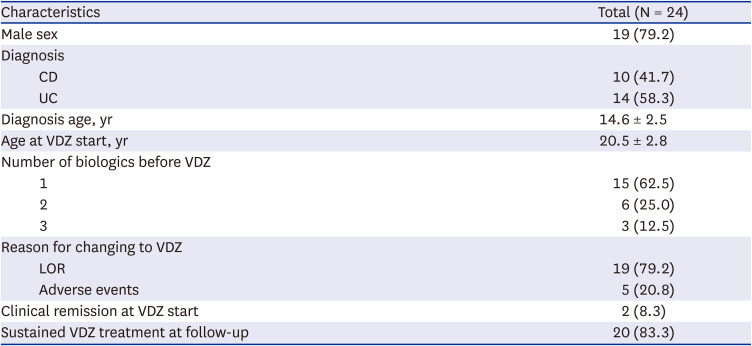
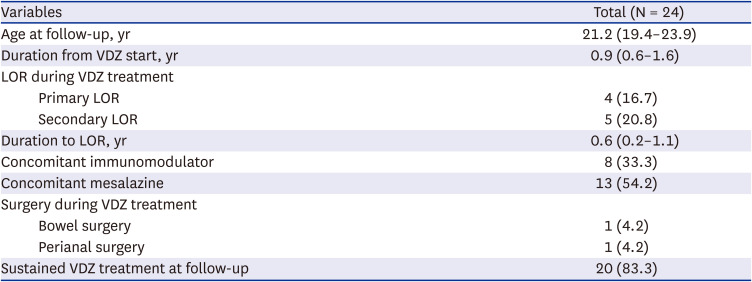
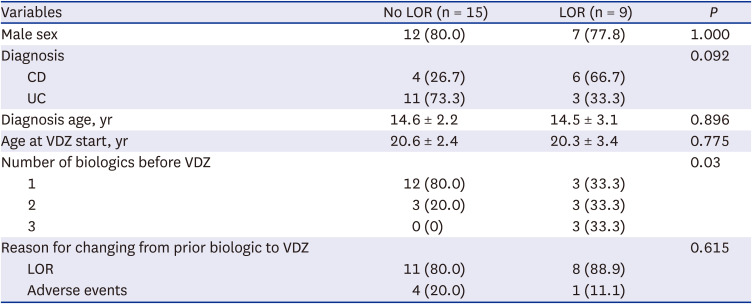
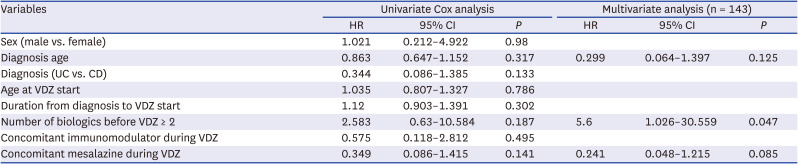




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download