1. Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011; 6:425–56.

2. Roehlen N, Crouchet E, Baumert TF. Liver fibrosis: mechanistic concepts and therapeutic perspectives. Cells. 2020; 9:875.

3. Tsuchida T, Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 14:397–411.

4. Schuppan D, Surabattula R, Wang XY. Determinants of fibrosis progression and regression in NASH. J Hepatol. 2018; 68:238–50.

5. Bostrom P, Wu J, Jedrychowski MP, Korde A, Ye L, Lo JC, et al. A PGC1-α-dependent myokine that drives brown-fatlike development of white fat and thermogenesis. Nature. 2012; 481:463–8.

6. Huh JY, Panagiotou G, Mougios V, Brinkoetter M, Vamvini MT, Schneider BE, et al. FNDC5 and irisin in humans: I. Predictors of circulating concentrations in serum and plasma and II. mRNA expression and circulating concentrations in response to weight loss and exercise. Metabolism. 2012; 61:1725–38.

7. Korta P, Pochec E, Mazur-Bialy A. Irisin as a multifunctional protein: implications for health and certain diseases. Medicina (Kaunas). 2019; 55:485.

8. Maak S, Norheim F, Drevon CA, Erickson HP. Progress and challenges in the biology of FNDC5 and irisin. Endocr Rev. 2021; 42:436–56.

9. Peng H, Wang Q, Lou T, Qin J, Jung S, Shetty V, et al. Myokine mediated muscle-kidney crosstalk suppresses metabolic reprogramming and fibrosis in damaged kidneys. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:1493.

10. Petta S, Valenti L, Svegliati-Baroni G, Ruscica M, Pipitone RM, Dongiovanni P, et al. Fibronectin type III domain-containing protein 5 rs3480 A>G polymorphism, irisin, and liver fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017; 102:2660–9.

11. Zhou B, Ling L, Zhang F, Liu TY, Zhou H, Qi XH, et al. Fibronectin type III domain-containing 5 attenuates liver fibrosis via inhibition of hepatic stellate cell activation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018; 48:227–36.

12. Chen RR, Fan XH, Chen G, Zeng GW, Xue YG, Liu XT, et al. Irisin attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis via Nrf2 mediated inhibition of ROS/TGFβ1/Smad2/3 signaling axis. Chem Biol Interact. 2019; 302:11–21.

13. Liao Q, Qu S, Tang LX, Li LP, He DF, Zeng CY, et al. Irisin exerts a therapeutic effect against myocardial infarction via promoting angiogenesis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2019; 40:1314–21.

14. Ren Y, Zhang J, Wang M, Bi J, Wang T, Qiu M, et al. Identification of irisin as a therapeutic agent that inhibits oxidative stress and fibrosis in a murine model of chronic pancreatitis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020; 126:110101.

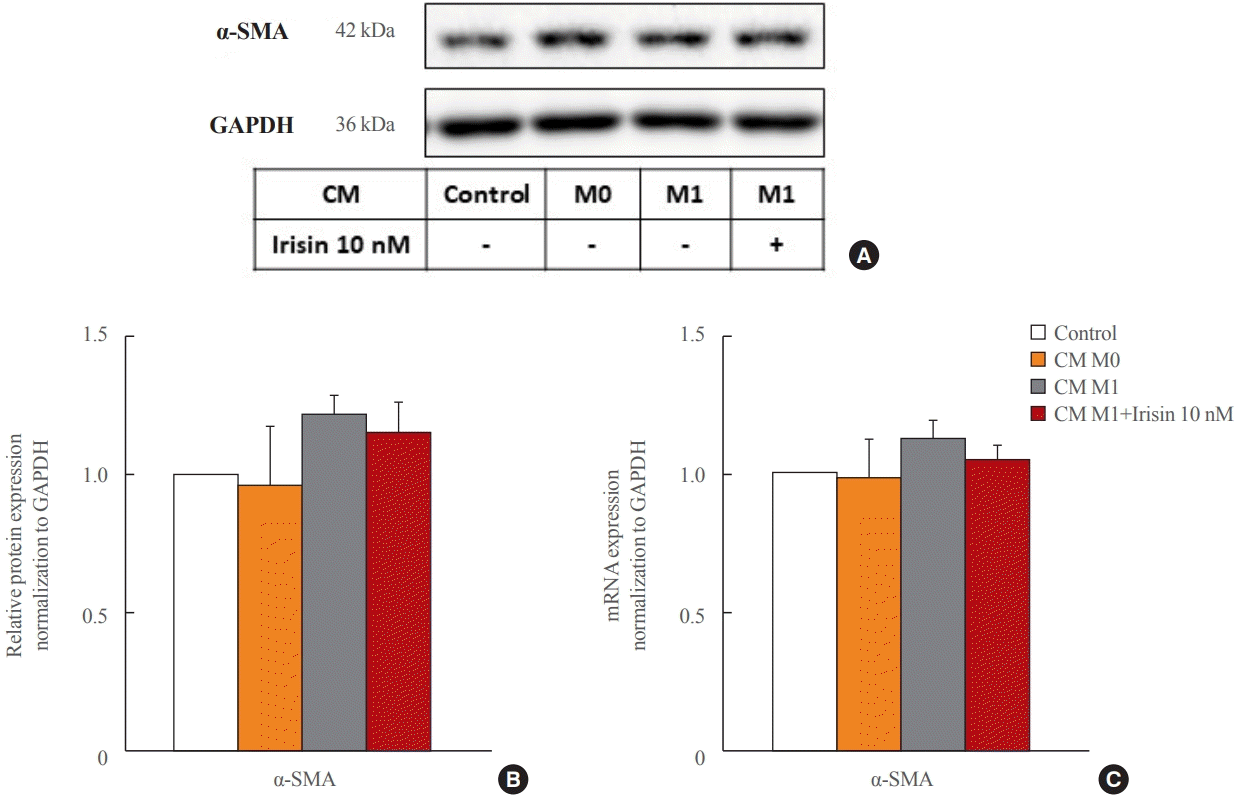
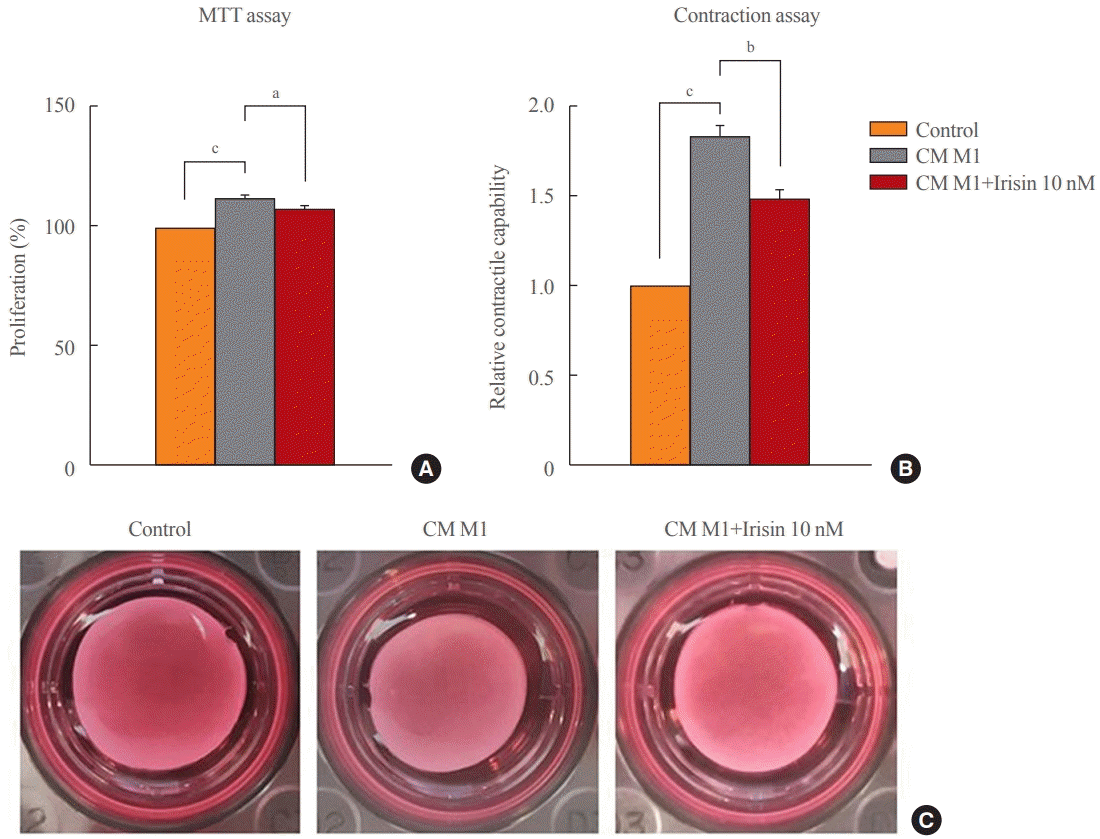
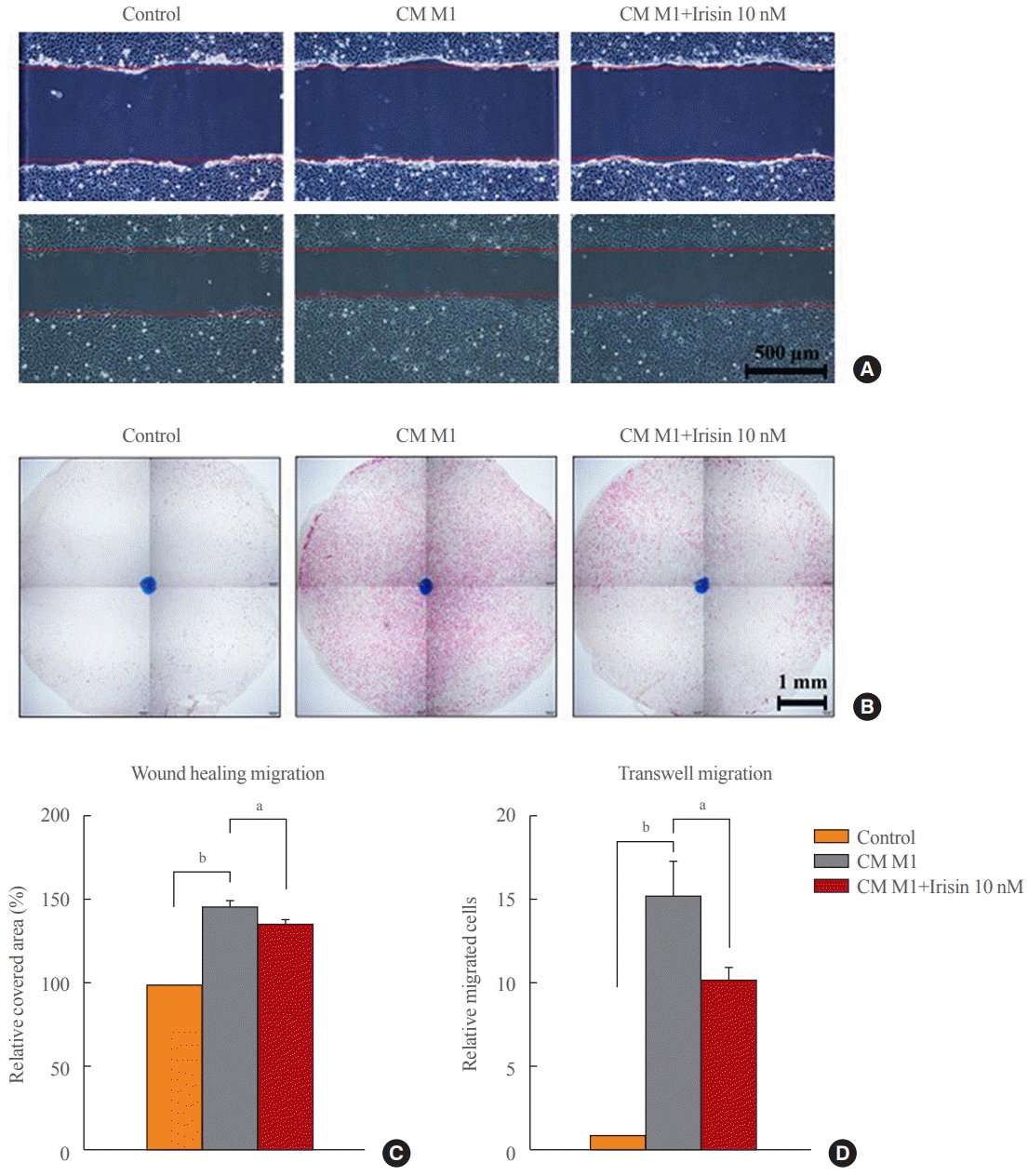
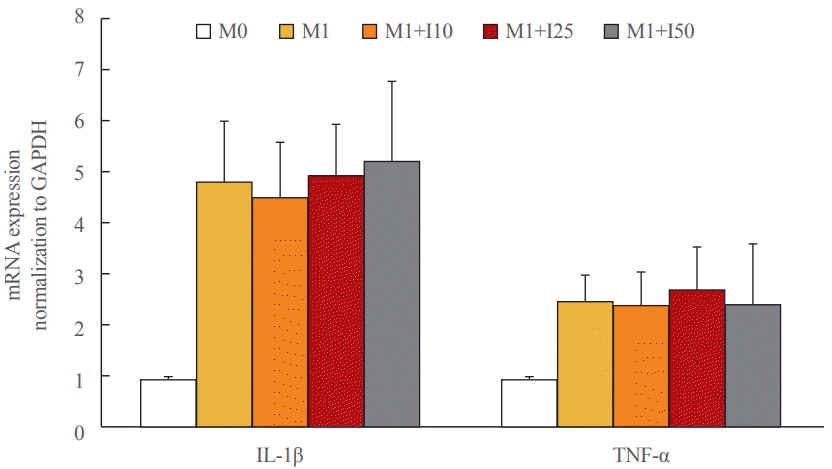
15. Dong HN, Park SY, Le CT, Choi DH, Cho EH. Irisin regulates the functions of hepatic stellate cells. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2020; 35:647–55.

16. Duffield JS, Forbes SJ, Constandinou CM, Clay S, Partolina M, Vuthoori S, et al. Selective depletion of macrophages reveals distinct, opposing roles during liver injury and repair. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115:56–65.

17. Han J, Zhang X, Lau JK, Fu K, Lau HC, Xu W, et al. Bone marrow-derived macrophage contributes to fibrosing steatohepatitis through activating hepatic stellate cells. J Pathol. 2019; 248:488–500.

18. Cheng D, Chai J, Wang H, Fu L, Peng S, Ni X. Hepatic macrophages: key players in the development and progression of liver fibrosis. Liver Int. 2021; 41:2279–94.

19. Tacke F. Targeting hepatic macrophages to treat liver diseases. J Hepatol. 2017; 66:1300–12.

20. Mazur-Bialy AI, Pochec E, Zarawski M. Anti-inflammatory properties of irisin, mediator of physical activity, are connected with TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway activation. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18:701.

21. Mazur-Bialy AI, Pochec E. The time-course of antioxidant irisin activity: role of the Nrf2/HO-1/HMGB1 axis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021; 10:88.

22. Li Q, Tan Y, Chen S, Xiao X, Zhang M, Wu Q, et al. Irisin alleviates LPS-induced liver injury and inflammation through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB signaling. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2021; 41:294–303.

23. Naim A, Baig MS. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8) regulates the activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) through the ERK-mediated pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020; 467:107–16.

24. Chen L, Yao X, Yao H, Ji Q, Ding G, Liu X. Exosomal miR-103-3p from LPS-activated THP-1 macrophage contributes to the activation of hepatic stellate cells. FASEB J. 2020; 34:5178–92.

25. Robert S, Gicquel T, Bodin A, Fautrel A, Barreto E, Victoni T, et al. Influence of inflammasome pathway activation in macrophages on the matrix metalloproteinase expression of human hepatic stellate cells. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019; 72:12–20.

26. Hu M, Wang Y, Liu Z, Yu Z, Guan K, Liu M, et al. Hepatic macrophages act as a central hub for relaxin-mediated alleviation of liver fibrosis. Nat Nanotechnol. 2021; 16:466–77.

27. Ying HZ, Chen Q, Zhang WY, Zhang HH, Ma Y, Zhang SZ, et al. PDGF signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis pathogenesis and therapeutics (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2017; 16:7879–89.
28. Dewidar B, Meyer C, Dooley S, Meindl-Beinker AN. TGF-β in hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrogenesis: updated 2019. Cells. 2019; 8:1419.

29. Rabiee F, Lachinani L, Ghaedi S, Nasr-Esfahani MH, Megraw TL, Ghaedi K. New insights into the cellular activities of Fndc5/Irisin and its signaling pathways. Cell Biosci. 2020; 10:51.

30. Tsiani E, Tsakiridis N, Kouvelioti R, Jaglanian A, Klentrou P. Current evidence of the role of the myokine irisin in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13:2628.

31. Song H, Wu F, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Wang F, Jiang M, et al. Irisin promotes human umbilical vein endothelial cell proliferation through the ERK signaling pathway and partly suppresses high glucose-induced apoptosis. PLoS One. 2014; 9:e110273.

32. Hemmann S, Graf J, Roderfeld M, Roeb E. Expression of MMPs and TIMPs in liver fibrosis: a systematic review with special emphasis on anti-fibrotic strategies. J Hepatol. 2007; 46:955–75.
33. Gong J, Han J, He J, Liu J, Han P, Wang Y, et al. Paired related homeobox protein 1 regulates PDGF-induced chemotaxis of hepatic stellate cells in liver fibrosis. Lab Invest. 2017; 97:1020–32.

34. Locklear CT, Golabi P, Gerber L, Younossi ZM. Exercise as an intervention for patients with end-stage liver disease: systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e12774.
35. Kisseleva T, Brenner D. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021; 18:151–66.






 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download