INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Study cohorts for cytokine microarray analysis and validation
Sample preparation for cytokine microarray analysis
Cytokine microarray analysis
Cytokine microarray data acquisition and analysis
Bioinformatics analysis of cytokine microarray data
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Statistical analysis
RESULTS
Identification of cytokines for normoglycemia, prediabetes, and T2DM
Fig. 1
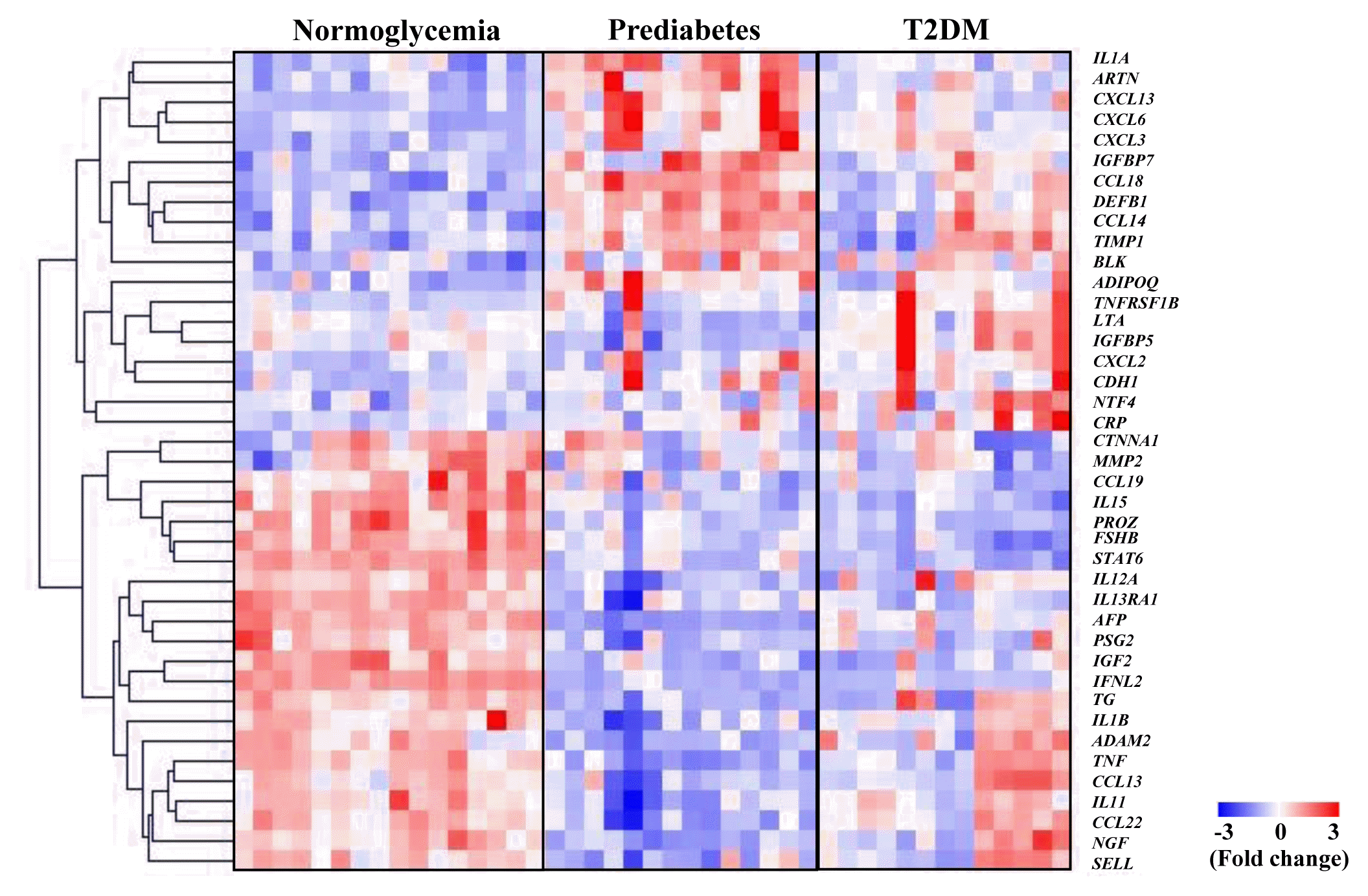
Table 1
T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; IGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2; IFNL2, interferon lambda 2; IL, interleukin; NGF, nerve growth factor; BLK, BLK proto-oncogene; PROZ, protein Z; AFP, alpha-fetoprotein; ADAM2, ADAM metallopeptidase domain 2; CA15-3, carbohydrate antigen 15-3; PSG2, pregnancy specific beta-1-glycoprotein 2; CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; CRP, C-reactive protein; FSHB, follicle stimulating hormone beta; TG, thyroglobulin; STAT6, signal transducer and activator of transcription 6.
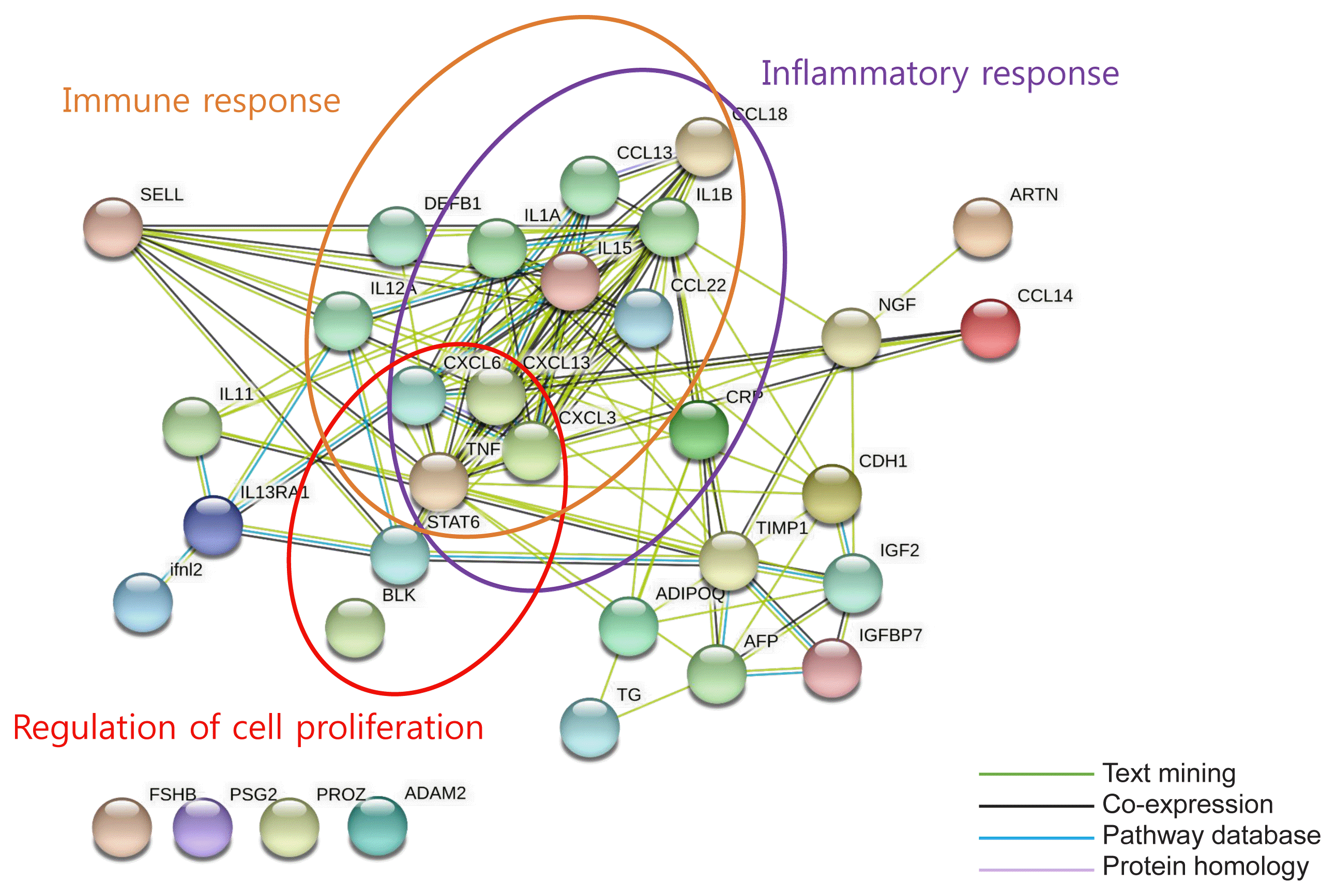
Bioinformatic analysis
Fig. 2
Validation of PROZ as a potential biomarker for prediabetes and T2DM
Fig. 3
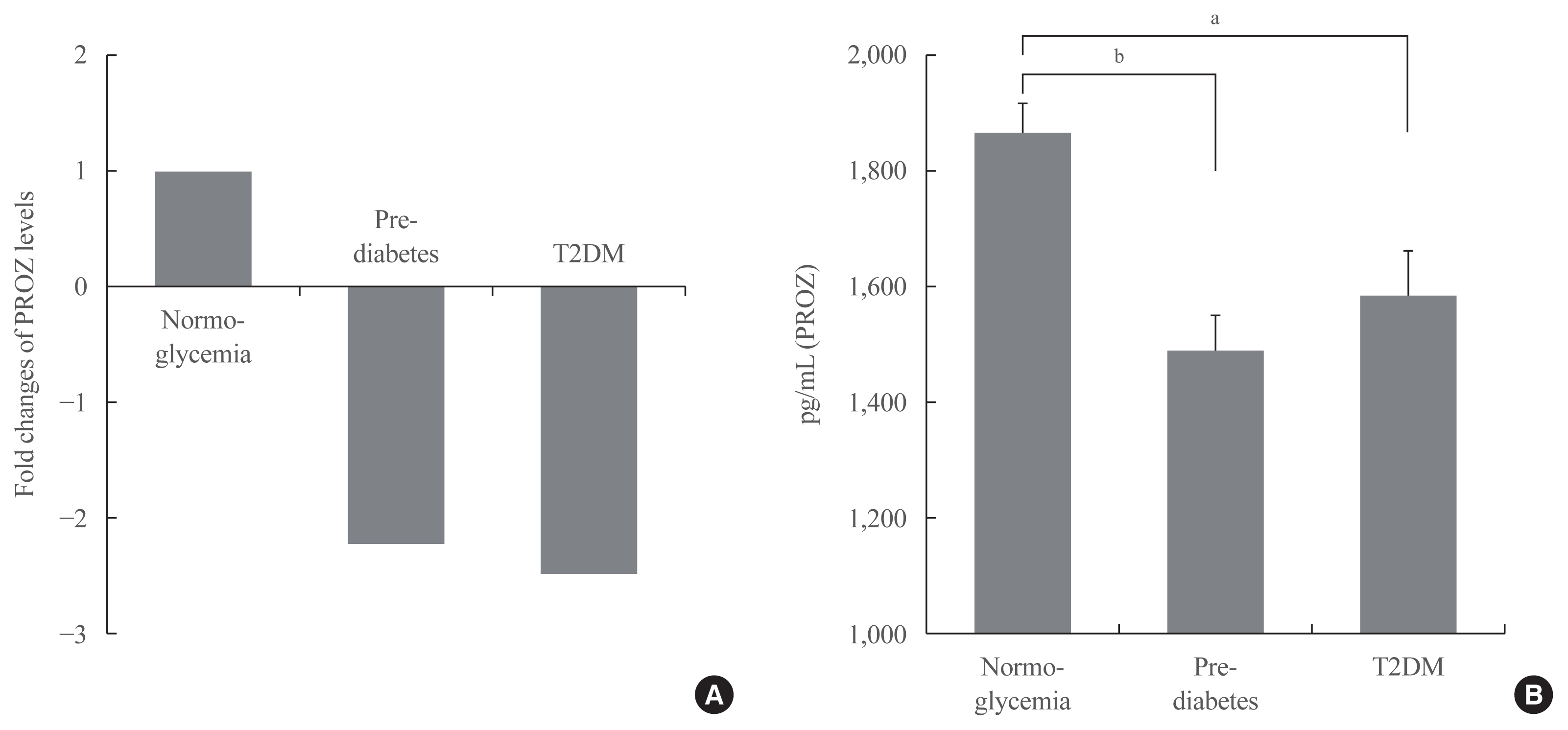
Table 2
| Characteristic | Normoglycemia (n=71) | Prediabetes (n=35) | T2DM (n=36) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male/female | 59/12 | 29/6 | 30/6 | 0.999 |
| Hypertension | 9 | 6 | 10 | 0.152 |
| Dyslipidemia | 0 | 3 | 19 | <0.001 |
| CVD | 0 | 2 | 6 | 0.001 |
| Smoking | 9 | 4 | 11 | 0.040 |
| Alcohol | 40 | 18 | 13 | 0.139 |
| Age, yr | 55.7±11.0 | 57.5±12.5 | 59.1±10.2 | 0.309 |
| Height, cm | 167.04±7.67 | 166.40±9.09 | 165.14±7.71 | 0.519 |
| Weight, kg | 62.96±7.01 | 64.15±8.20 | 63.90±8.14 | 0.702 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 22.69±1.48 | 23.22±1.24 | 23.30±1.80 | 0.079 |
| Waist, cm | 79.86±6.42 | 82.75±5.18 | 86.60±6.81 | <0.001 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 122.31±13.46 | 120.74±11.38 | 126.78±17.81 | 0.242 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 78.41±9.18 | 73.09±8.51 | 75.83±12.71 | 0.017 |
| WBC, 103/μL | 5.76±0.98a | 6.38±1.56 | 6.71±1.60 | 0.003 |
| Hb, g/dL | 14.44±1.30b | 14.37±1.12 | 14.68±1.86 | 0.691 |
| AST, U/L | 22.54±6.26 | 23.11±7.07 | 25.44±8.46 | 0.131 |
| ALT, U/L | 18.32±8.19 | 22.03±8.96 | 25.83±11.78 | 0.001 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.89±0.15 | 0.90±0.14 | 0.83±0.18 | 0.093 |
| TG, mg/dL | 138.31±99.00 | 139.85±96.98 | 178.90±102.10 | 0.116 |
| HDL, mg/dL | 51.03±14.01 | 53.78±12.43 | 44.77±10.19 | 0.010 |
| LDL, mg/dL | 109.69±25.21 | 113.74±31.17 | 113.37±50.06 | 0.766 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.29±0.20 | 5.93±0.20 | 7.29±1.49 | <0.001 |
| FPG, mg/dL | 86.77±6.01 | 107.89±7.39 | 136.83±43.09 | <0.001 |
| Insulin, μIU/mL | 2.09±1.37 | 5.45±3.48 | 7.75±5.68 | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.45±0.30 | 1.45±0.91 | 2.54±1.64 | <0.001 |
| HOMA-β | 32.62±23.30 | 44.57±30.99 | 52.08±65.20 | 0.050 |
| PROZ, pg/mL | 1,864.07±450.83 | 1,490.32±367.19 | 1,583.34±465.43 | <0.001 |
Values are expressed as number or mean±standard deviation. The definitions of smoking and alcohol are numbers of currently smoking and drinking in each group.
PROZ, protein Z; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; CVD, cardiovascular disease; BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; WBC, white blood cell; Hb, hemoglobin; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; TG, triglyceride; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HOMA-IR, homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance; HOMA-β, homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function.
Correlation analysis between PROZ and clinical parameters
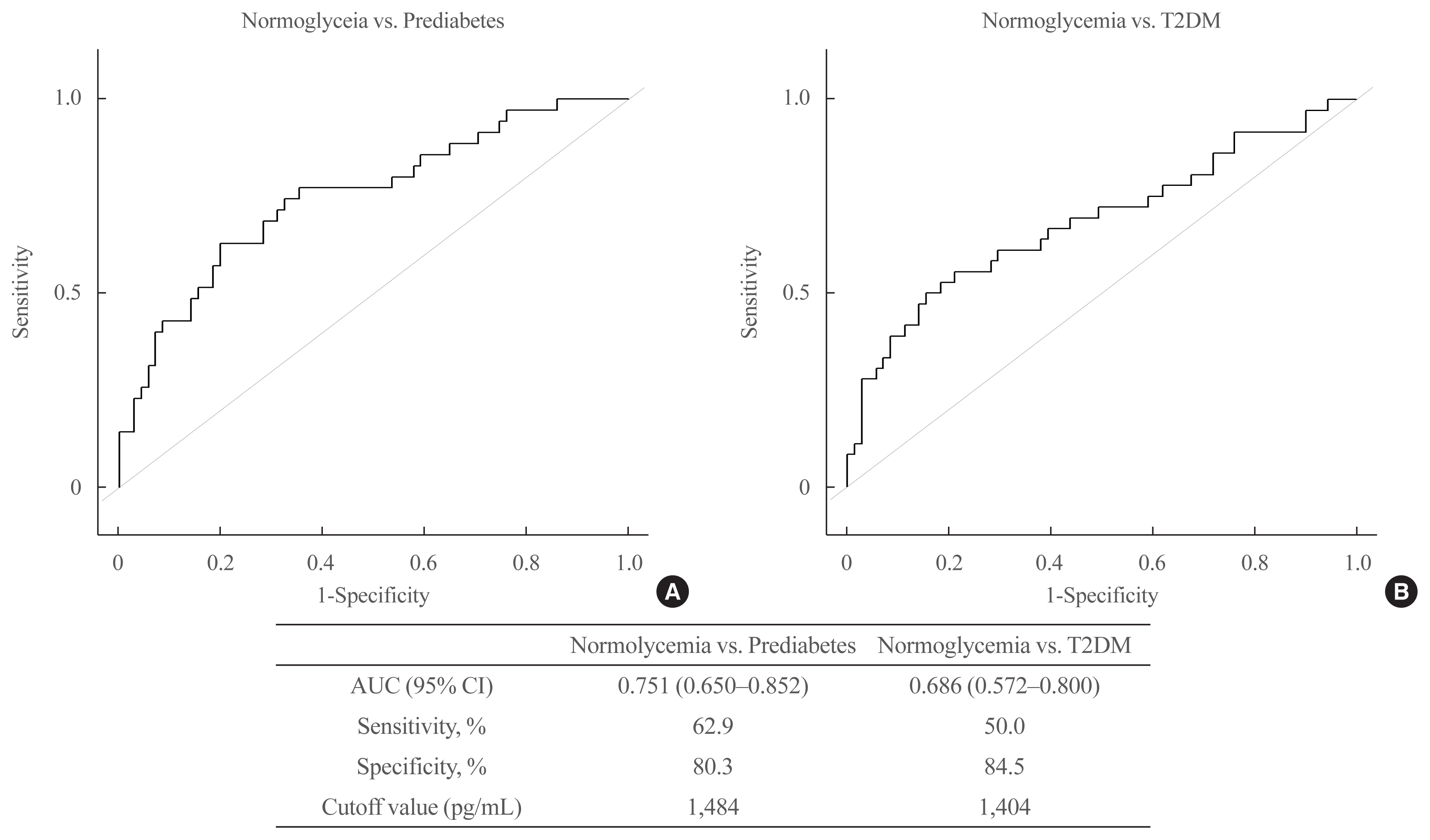
ROC curve of PROZ
Fig. 4




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download