Abstract
Background
Methods
Results
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Supplemental Table S1.
Supplemental Table S2.
Supplemental Table S3.
Supplemental Fig. S1.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
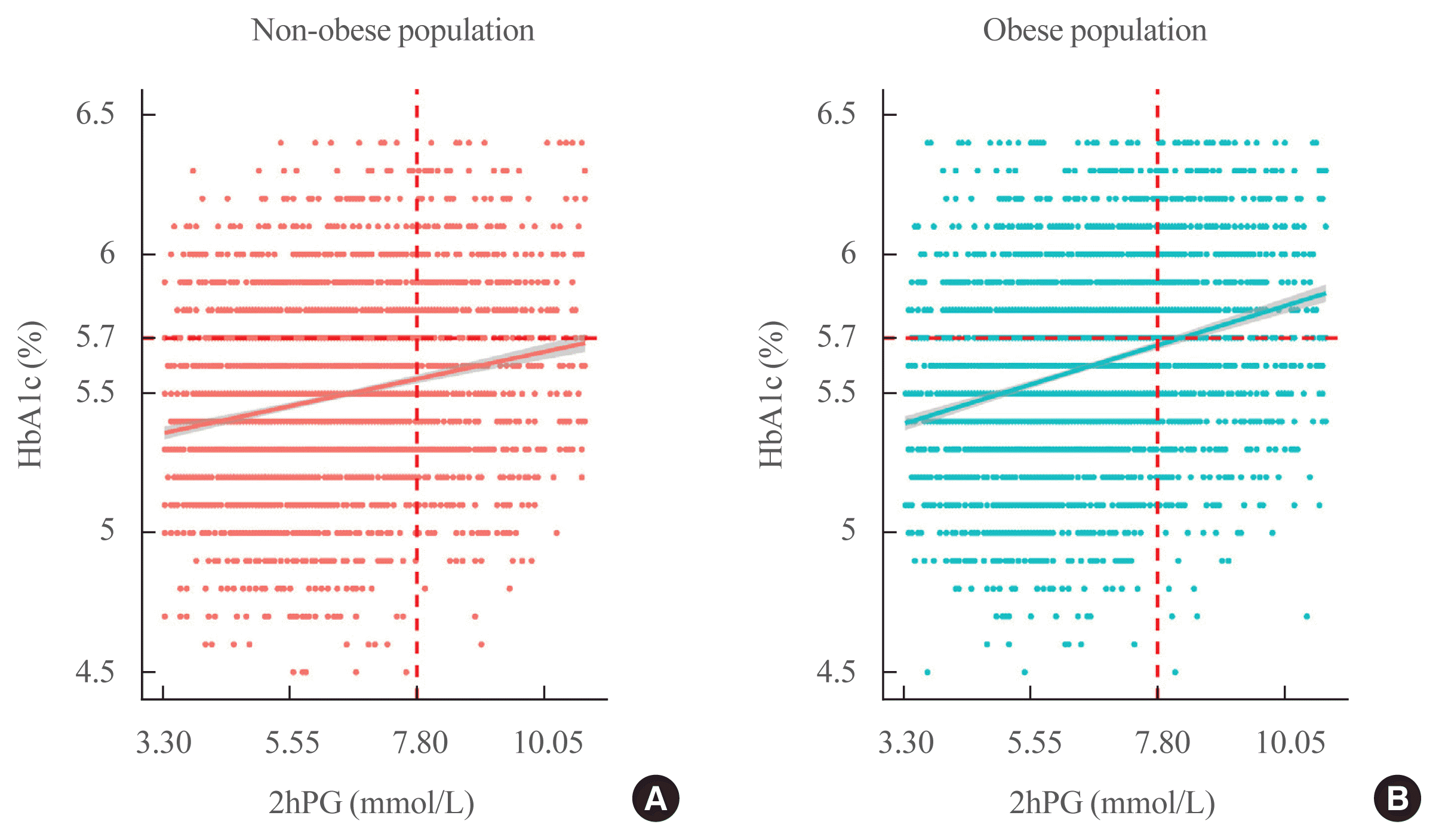
Table 1
| Characteristic | All | NGT/normal HbA1c | NGT/high HbA1c | IGT/normal HbA1c | IGT/high HbA1c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 7,512 | 4,058 | 1,886 | 692 | 876 |
|
|
|||||
| Urban area | 3,890 (51.8) | 2,129 (52.5) | 820 (43.5)a | 469 (67.8)a,b | 472 (53.9)a,b,c |
|
|
|||||
| Age, yr | 51.6±8.7 | 50.0±8.3 | 53.6±8.8a | 51.5±9.0a,b | 54.8±8.6a,b,c |
|
|
|||||
| Men | 3,526 (47.1) | 1,924 (47.4) | 962 (51.0) | 295 (42.6) | 355 (40.5) |
|
|
|||||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 24.5±3.1 | 24.2±2.9 | 24.9±3.1 | 24.3±3.0 | 25.6±3.2a,b,c |
|
|
|||||
| Waist circumference, cm | |||||
| Men | 83.5±7.5 | 82.6±7.2 | 84.4±7.6a | 83.2±7.3 | 86.2±7.5a,b,c |
| Women | 81.4±9.5 | 79.9±9.3 | 84.0±9.4a | 79.3±9.2b | 84.6±9.2a,c |
|
|
|||||
| Blood pressure, mm Hg | |||||
| Systolic | 124 (18) | 122 (18) | 125 (18)a | 125 (19)a | 130 (19)a,b,c |
| Diastolic | 82 (12) | 81 (12) | 82 (11)a | 81 (12) | 84 (11)a,b,c |
|
|
|||||
| Smoking status | |||||
| Non-smoker | 4,405 (58.6) | 2,418 (60.4) | 1,002 (53.7) | 440 (63.9) | 545 (63.4) |
| Ex-smoker | 1,106 (14.7) | 601 (15.0) | 261 (14.0) | 126 (18.3) | 128 (14.9) |
| Current smoker | 1,899 (25.3) | 985 (24.6) | 604 (32.4)a | 123 (17.9)a,b | 187 (21.7)b |
|
|
|||||
| Education status | |||||
| High school or less | 6,437 (86.4) | 3,439 (85.4) | 1,631 (87.4) | 599 (86.8) | 768 (88.5) |
| College/university or more | 1,015 (13.6) | 589 (14.6) | 235 (12.6)a | 91 (13.2) | 100 (11.5) |
|
|
|||||
| Monthly incomes | |||||
| < $1,250/mo | 3,661 (49.6) | 1,854 (46.5) | 1,034 (56.0)a | 302 (44.3)b | 471 (54.5)a,c |
| $1,250–3,300/mo | 3,159 (42.8) | 1,820 (45.6) | 687 (37.2) | 317 (46.5) | 335 (38.8) |
| ≥ $3,300/mo | 560 (7.6) | 315 (7.9) | 125 (6.8) | 62 (9.1) | 58 (6.7) |
|
|
|||||
| Physical activity | 4,317 (57.5) | 2,356 (59.0) | 1,140 (61.8) | 350 (50.9)a,b | 471 (54.8)b |
|
|
|||||
| Family history of diabetes | 762 (10.1) | 383 (9.4) | 186 (9.9) | 94 (13.6) | 99 (11.3) |
|
|
|||||
| Laboratory outcomes | |||||
| HbA1c, % | 5.5±0.3 | 5.3±0.2 | 5.9±0.2a | 5.4±0.2a,b | 5.9±0.2a,b,c |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 83 (9) | 81 (8) | 84 (9)a | 85 (9)a | 88 (10)a,b,c |
| 2-hour post-load glucose, mg/dL | 115 (30) | 102 (20) | 106 (21)a | 158 (15)a,b | 161 (16)a,c |
| Total cholesterol/HDL ratio | 4.4±1.1 | 4.3(1.0) | 4.6±1.1a | 4.4±1.1b | 4.8±1.2a,b,c |
| HOMA-IR | 1.4 (1.0–1.9) | 1.3 (1.0–1.9) | 1.5 (1.1–2.0)a | 1.4 (1.0–1.9)b | 1.6 (1.2–2.3)a,b,c |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 134 (99–186) | 125 (94–170) | 144 (108–199)a | 133 (100–187)a | 163 (120–231)a,b,c |
| C-reactive protein, mg/L | 0.14 (0.06–0.24) | 0.12 (0.05–0.21) | 0.15 (0.07–0.26)a | 0.14 (0.07–0.24)a | 0.17 (0.09–0.30)a |
| Creatinine clearance, mL/min | 92.3±13.9 | 93.7±13.6 | 91.0±13.9a | 91.2±14.9a | 89.7±13.9a |
|
|
|||||
| Cumulative incidence of diabetes | |||||
| Cumulative incidence | 1,341 (17.6) | 316 (8.4) | 390 (22.2) | 193 (32.7) | 442 (59.9) |
| Incidence density, /1,000 person-years | 22.1 | 10.1 | 24.6 | 39.1 | 86 |
Values are expressed as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range). Normal HbA1c, HbA1c <5.7%; high HbA1c, 5.7%–6.4%; Physical activity, perform moderate-intensity (≥150 minutes/week) or vigorous-intensity (≥75 minutes/week) activity. NGT, normal glucose tolerance (2-hour post-load glucose <140 mg/dL); HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; IGT, impaired glucose tolerance (2-hour post-load glucose 140–199 mg/dL); HDL, high density lipoprotein; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance.
Table 2
| Crude HR (95% CI) | Adjusted HR (95% CI)a | |
|---|---|---|
| Overall | ||
| NGT/normal HbA1c | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| NGT/high HbA1c | 2.98 (2.59–3.44)b | 2.79 (2.40–3.26)b |
| IGT/normal HbA1c | 4.41 (3.67–5.28)b,c | 4.29 (3.56–5.17)b,c |
| IGT/high HbA1c | 10.82 (9.35–12.51)b,c,d | 9.94 (8.53–11.59)b,c,d |
|
|
||
| Central obesity − | ||
| NGT/normal HbA1c | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| NGT/high HbA1c | 2.78 (2.21–3.50)b | 2.70 (2.13–3.43)b |
| IGT/normal HbA1c | 4.60 (3.58–5.93)b,c | 4.52 (3.49–5.87)b,c |
| IGT/high HbA1c | 10.61 (8.51–13.22)b,c,d | 9.65 (7.65–12.18)b,c,d |
|
|
||
| Central obesity + | ||
| NGT/normal HbA1c | 1 (reference) | 1 (reference) |
| NGT/high HbA1c | 2.99 (2.45–3.64)b | 2.82 (2.30–3.46)b |
| IGT/normal HbA1c | 4.18 (3.21–5.44)b | 3.95 (3.01–5.18)b |
| IGT/high HbA1c | 10.61 (8.71–12.91)b,c,d | 9.98 (8.13–12.26)b,c,d |
HR, hazards ratio; CI, confidence interval; NGT, normal glucose tolerance; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; IGT, impaired glucose tolerance.
a The multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression model was adjusted for area, sex, age, estimated glomerular filtration, C-reactive protein, total-to-high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio, triglycerides, systolic/diastolic blood pressure, and socioeconomic factors (education levels, monthly incomes, smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity);
Table 3
| Covariates | Obesity | AUC (model 1) | AUC (model 2) | AUC (model 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, sex, area | Non-obese | 0.69 (0.67–0.71) | 0.74 (0.72–0.76)a | 0.77 (0.76–0.79)a,b |
| Obese | 0.66 (0.63–0.69) | 0.75 (0.73–0.78)a | 0.73 (0.70–0.76)a | |
|
|
||||
| Age, sex, area+laboratory test+metabolic risk factors | Non-obese | 0.70 (0.68–0.72) | 0.75 (0.73–0.77)a | 0.78 (0.76–0.80)a,b |
| Obese | 0.67 (0.64–0.70) | 0.75 (0.73–0.78)a | 0.73 (0.71–0.76)a | |
|
|
||||
| Age, sex, area+laboratory test+metabolic risk factors+socioeconomic factors | Non-obese | 0.71 (0.69–0.73) | 0.75 (0.74–0.77)a | 0.79 (0.77–0.80)a,b |
| Obese | 0.68 (0.66–0.71) | 0.75 (0.73–0.78)a | 0.75 (0.71–0.77)a | |
Laboratory test: estimated glomerular filtration, C-reactive protein; Metabolic risk factors: the presence of dyslipidemia (triglyceride ≥2.8 mmol/L and/or high density lipoprotein [HDL] <1 mmol/L [men] or HDL <1.3 mmol/L [women] and/or taking lipid lowering drugs), hypertension (systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg and/or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg and/or taking anti-hypertensive drugs); Socioeconomic factors: education levels, monthly incomes, smoking, alcohol consumption, physical activity, and family history of diabetes. Presence of obesity: waist circumference ≥90 cm (men) or ≥85 cm (women). Model 1, fasting plasma glucose (FPG); model 2, FPG+glycated hemoglobin levels; model 3, FPG+2-hour postprandial glucose.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download