Dear Editor,
Therapy-related myeloid neoplasia (t-MN) describes leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome in people who have undergone chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy for malignant tumors or non-malignant disorders [
1].
t-MNs are divided into two categories based on the type of previous therapy. The first subtype usually occurs after the use of an alkylating agent and/or radiation therapy, and the second subtype occurs in patients taking topoisomerase II inhibitors or after radiation alone. Balanced translocations involving
KMT2A (also known as MLL) or
RUNX1 are common in the second subtype. Approximately 104 different chromosomal rearrangements associated with
KMT2A have been described to date, with 64 translocation partner genes characterized at the molecular level [
2]. Therapy-related t(11;22)(q23;q13) involving a rare partner gene,
EP300, has been reported in four different cases globally (
Table 1) [
1-
4]. All four patients had a history of malignancy and chemotherapy, and three of them suffered from hematologic malignancies.
Here, we report the first case of a rearrangement involving EP300, in Korea. The patient had prostate cancer and subsequently developed AML with t(11;22)(q23;q13)/KMT2A-EP300 fusion after receiving local palliative radiation therapies from March 2010 to May 2021. The Institutional Review Board of Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea, approved this study (IRB No. 4-2021-1453) and waived the need for informed consent.
A 76-year-old male diagnosed as having prostate adenocarcinoma, who had undergone five radiotherapy treatments (55 Gy of tomotherapy to the pelvis, prostate, and L4-sacrum; 40 Gy of three-dimensional conformal radiation therapy to the cervical, thoracic, and sacrum vertebrae; and three rounds of intensity-modulated radiation therapy [60, 35, and 37.5 Gy, respectively]), was admitted five months after completing the last radiotherapy session, complaining of general weakness and fever. Regular hormonal treatments were administered, and no chemotherapy was initiated. The complete blood count showed pancytopenia: white blood cell count, 0.81×10
9/L; hemoglobin, 42 g/L; and platelet count, 51×10
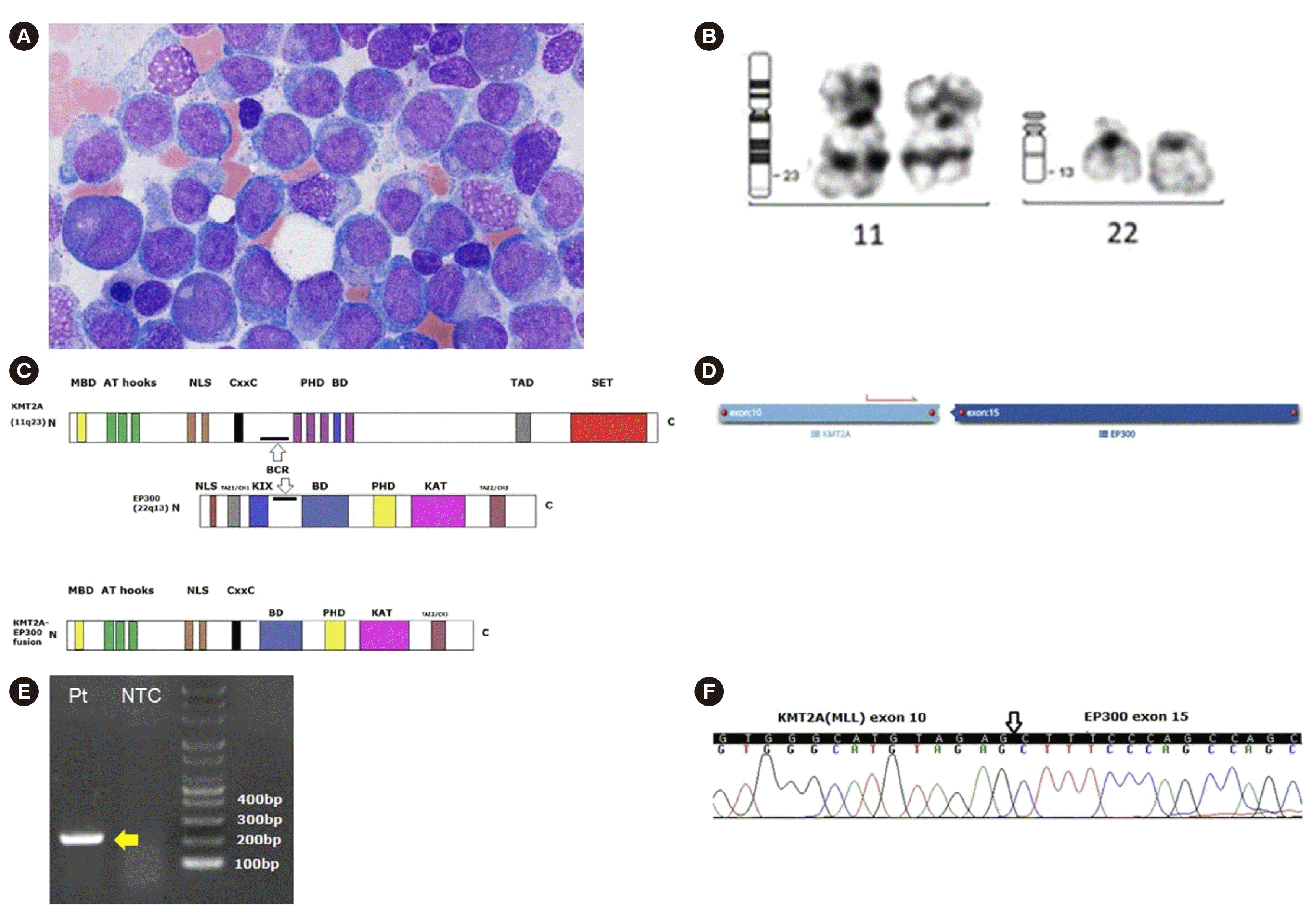
9/L. Monocytosis was noted and nucleated red blood cells were frequently seen in the peripheral smear. The bone marrow biopsy showed h–ypercellularity (60%–80%) with markedly decreased number of megakaryocytes. Leukemic blasts up to 21.1% were observed in the bone marrow aspirate (
Fig. 1A). Flow cytometry analysis showed that the blasts were positive for CD117, cMPO, CD38, CD11c, HLA-DR, CD33, CD13, CD64, and CD123, indicating AML with monocytic differentiation. G-banding analysis using the bone marrow sample revealed a 46,XY,t(11;22)(q23;q13)[13]/46,XY[
7] karyotype (
Fig. 1B). A schematic representation of the
KMT2A-
EP300 fusion is provided in
Fig. 1C. A next-generation sequencing (NGS) RNA fusion panel detected the fusion between exon 10 of
KMT2A and exon 15 of
EP300 in 42.58% reads (
Fig. 1D). To validate the
KMT2A-
EP300 fusion transcripts, reverse transcription-PCR and direct sequencing were performed using
KMT2A- and
EP300-specific primers (
Fig. 1E and
1F).
An NGS panel targeting 531 genes associated with myeloid malignancy detected variants of
BCOR (c.4717+1G>A; 89.2% variant allele frequency [VAF]) and
PPM1D (p.Arg572Ter; 44.3% VAF). Loss of
BCOR can enhance the self-renewal of myeloid progenitors and promote leukemogenesis [
5].
PPM1D is mutated in ~20% of patients with therapy-related AML or myelodysplastic syndrome and is associated with prior chemotherapy or radiotherapy [
6]. In our case, a nonsense mutation in exon 6 of
PPM1D produces a C-terminal-truncated protein resulting in the loss of the degradation motif [
6]. A truncated form of
PPM1D confers overexpression, resulting in chronic suppression of
p53 activity and tumorigenesis [
7]. Induction chemotherapy with decitabine was administered for five days. No further bone marrow examination was conducted, and the patient was eventually sent to a hospital close to his hometown.
KMT2A-rearranged leukemia accounts for ~10% of acute leukemias in all age categories, which can occur de novo or after chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy [
4]. A bimodal distribution is seen in patients with
KMT2A rearrangements. The first peak typically manifests as ALL in newborns under the age of 12 months, and the second manifests as AML in older children and adults [
8].
KMT2A and
EP300 are transcriptional co-activators involved in epigenetic chromatin remodeling, which induce leukemogenesis by transcriptional upregulation of target genes such as
HOXA9 and its cofactor
MEIS1. The overexpression of
HOXA9 and
MEIS1 promotes the expansion of hematopoietic progenitor cells and self-renewal of stem cells [
9]. The
MENIN-LEDGF complex anchors and stabilizes KMT2A fusion proteins to their target genes [
10]. The bromodomain of
EP300 transfers acetyl groups to lysine 27 of histone 3 (H3K27Ac)—an active transcription marker in hematopoietic epigenetics [
1].
We represent the first worldwide report of
KMT2A-
EP300 therapy-related leukemia following radiation-only therapy. Comprehensive molecular tests can help determine and characterize the rare gene rearrangements associated with leukemogenesis [
11].




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download