1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018; 68:7–30.

2. Shro ff GS, Viswanathan C, Carter BW, Benveniste MF, Truong MT, Sabloff BS. Staging lung cancer: metastasis. Radiol Clin North Am. 2018; 56:411–8.
3. Bates JE, Milano MT. Prognostic significance of sites of extrathoracic metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 2017; 9:1903–10.

4. Morgensztern D, Waqar S, Subramanian J, Gao F, Govindan R. Improving survival for stage IV non-small cell lung cancer: a surveillance, epidemiology, and end results survey from 1990 to 2005. J Thorac Oncol. 2009; 4:1524–9.

5. Morgensztern D, Ng SH, Gao F, Govindan R. Trends in stage distribution for patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a National Cancer Database survey. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:29–33.

6. Chang YP, Chen YM, Lai CH, Lin CY, Fang WF, Huang CH, et al. The impact of de novo liver metastasis on clinical outcome in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0178676.

7. Hess KR, Varadhachary GR, Taylor SH, Wei W, Raber MN, Lenzi R, et al. Metastatic patterns in adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 2006; 106:1624–33.

8. Ren Y, Dai C, Zheng H, Zhou F, She Y, Jiang G, et al. Prognostic effect of liver metastasis in lung cancer patients with distant metastasis. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:53245–53.

9. Wang X, Wang Z, Pan J, Lu ZY, Xu D, Zhang HJ, et al. Patterns of extrathoracic metastases in different histological types of lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:715.

10. Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR, Steins M, Ready NE, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:1627–39.

11. Brahmer J, Reckamp KL, Baas P, Crino L, Eberhardt WE, Poddubskaya E, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373:123–35.

12. Herbst RS, Baas P, Kim DW, Felip E, Perez-Gracia JL, Han JY, et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016; 387:1540–50.

13. Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017; 389:255–65.

14. Putzu C, Cortinovis DL, Colonese F, Canova S, Carru C, Zinellu A, et al. Blood cell count indexes as predictors of outcomes in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with Nivolumab. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018; 67:1349–53.

15. Pirker R. Is smoking history the truly best biomarker for immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer? ESMO Open. 2018; 3:e000421.

16. Tumeh PC, Hellmann MD, Hamid O, Tsai KK, Loo KL, Gubens MA, et al. Liver metastasis and treatment outcome with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody in patients with melanoma and NSCLC. Cancer Immunol Res. 2017; 5:417–24.

17. Funazo T, Nomizo T, Kim YH. Liver metastasis is associated with poor progression-free survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. J Thorac Oncol. 2017; 12:e140–1.

18. Schmid S, Diem S, Li Q, Krapf M, Flatz L, Leschka S, et al. Organ-specific response to nivolumab in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2018; 67:1825–32.

19. Bilen MA, Shabto JM, Martini DJ, Liu Y, Lewis C, Collins H, et al. Sites of metastasis and association with clinical outcome in advanced stage cancer patients treated with immunotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2019; 19:857.

20. Sasaki A, Nakamura Y, Mishima S, Kawazoe A, Kuboki Y, Bando H, et al. Predictive factors for hyperprogressive disease during nivolumab as anti-PD1 treatment in patients with advanced gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2019; 22:793–802.

21. West H, McCleod M, Hussein M, Morabito A, Rittmeyer A, Conter HJ, et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin plus nab-paclitaxel chemotherapy compared with chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for metastatic non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower130): a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:924–37.

22. Nishio M, Barlesi F, West H, Ball S, Bordoni R, Cobo M, et al. Atezolizumab plus chemotherapy for first-line treatment of nonsquamous NSCLC: results from the randomized phase 3 IMpower132 trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2021; 16:653–64.

23. Reck M, Mok TS, Nishio M, Jotte RM, Cappuzzo F, Orlandi F, et al. Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer (IMpower150): key subgroup analyses of patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver metastases in a randomised, open-label phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2019; 7:387–401.

24. Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000100.

25. Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011; 343:d5928.

26. Dias S, Welton NJ, Sutton AJ, Ades AE. NICE decision support unit technical support documents. NICE DSU technical support document 2 a generalised linear modelling framework for pairwise and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE);2014.
27. Lu G, Ades AE. Combination of direct and indirect evidence in mixed treatment comparisons. Stat Med. 2004; 23:3105–24.

28. Jotte R, Cappuzzo F, Vynnychenko I, Stroyakovskiy D, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Hussein M, et al. Atezolizumab in combination with carboplatin and nab-paclitaxel in advanced squamous NSCLC (IMpower131): results from a randomized phase III trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2020; 15:1351–60.
29. Gadgeel S, Rodriguez-Abreu D, Speranza G, Esteban E, Felip E, Domine M, et al. Updated analysis from KEYNOTE-189: pembrolizumab or placebo plus pemetrexed and platinum for previously untreated metastatic nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38:1505–17.

30. Vokes EE, Ready N, Felip E, Horn L, Burgio MA, Antonia SJ, et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 017 and CheckMate 057): 3-year update and outcomes in patients with liver metastases. Ann Oncol. 2018; 29:959–65.

31. Paz-Ares L, Ciuleanu TE, Cobo M, Schenker M, Zurawski B, Menezes J, et al. First-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab combined with two cycles of chemotherapy in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 9LA): an international, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021; 22:198–211.

32. Hellmann MD, Paz-Ares L, Bernabe Caro R, Zurawski B, Kim SW, Carcereny Costa E, et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019; 381:2020–31.

33. Steven A, Fisher SA, Robinson BW. Immunotherapy for lung cancer. Respirology. 2016; 21:821–33.

34. Yang K, Li J, Bai C, Sun Z, Zhao L. Efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small-cell lung cancer patients with different metastatic sites: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:1098.

35. Li S, Sun S, Xiang H, Yang J, Peng M, Gao Q. Liver metastases and the efficacy of the PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors in cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Oncoimmunology. 2020; 9:1746113.

36. Kitadai R, Okuma Y, Hakozaki T, Hosomi Y. The efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with liver metastases. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020; 146:777–85.

37. Qin BD, Jiao XD, Liu J, Liu K, He X, Wu Y, et al. The effect of liver metastasis on efficacy of immunotherapy plus chemotherapy in advanced lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2020; 147:102893.

38. Tournoy KG, Thomeer M, Germonpre P, Derijcke S, De Pauw R, Galdermans D, et al. Does nivolumab for progressed metastatic lung cancer fulfill its promises? An efficacy and safety analysis in 20 general hospitals. Lung Cancer. 2018; 115:49–55.

39. Nishino M, Ramaiya NH, Chambers ES, Adeni AE, Hatabu H, Janne PA, et al. Immune-related response assessment during PD-1 inhibitor therapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients. J Immunother Cancer. 2016; 4:84.

40. Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, et al. Five-year survival and correlates among patients with advanced melanoma, renal cell carcinoma, or non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab. JAMA Oncol. 2019; 5:1411–20.

41. Shiroyama T, Suzuki H, Tamiya M, Tamiya A, Tanaka A, Okamoto N, et al. Clinical characteristics of liver metastasis in nivolumab-treated patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018; 38:4723–9.

42. Gettinger SN, Horn L, Gandhi L, Spigel DR, Antonia SJ, Rizvi NA, et al. Overall survival and long-term safety of nivolumab (anti-programmed death 1 antibody, BMS-936558, ONO-4538) in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:2004–12.

43. Wong WB, Wu N, Yang E, Davies J, Chae YK. Real-world clinical and economic outcomes and the role of bevacizumab in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer with liver metastases. J Oncol Pract. 2019; 15:e878–87.

44. Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, et al. Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:2542–50.

45. Kwilas AR, Ardiani A, Donahue RN, Aftab DT, Hodge JW. Dual effects of a targeted small-molecule inhibitor (cabozantinib) on immune-mediated killing of tumor cells and immune tumor microenvironment permissiveness when combined with a cancer vaccine. J Transl Med. 2014; 12:294.

46. Shi S, Wang R, Chen Y, Song H, Chen L, Huang G. Combining antiangiogenic therapy with adoptive cell immunotherapy exerts better antitumor effects in non-small cell lung cancer models. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e65757.

47. Yasuda S, Sho M, Yamato I, Yoshiji H, Wakatsuki K, Nishiwada S, et al. Simultaneous blockade of programmed death 1 and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2) induces synergistic anti-tumour effect in vivo. Clin Exp Immunol. 2013; 172:500–6.
48. Hegde PS, Wallin JJ, Mancao C. Predictive markers of anti-VEGF and emerging role of angiogenesis inhibitors as immunotherapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018; 52:117–24.

49. Chen DS, Hurwitz H. Combinations of Bevacizumab with cancer immunotherapy. Cancer J. 2018; 24:193–204.

50. Xu C, Chen YP, Du XJ, Liu JQ, Huang CL, Chen L, et al. Comparative safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer: systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ. 2018; 363:k4226.

51. Liu T, Ding S, Dang J, Wang H, Chen J, Li G. First-line immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with wild-type epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) or anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK): a systematic review and network meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 2019; 11:2899–912.

52. Herbst RS, Arkenau HT, Santana-Davila R, Calvo E, Paz-Ares L, Cassier PA, et al. Ramucirumab plus pembrolizumab in patients with previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer, gastro-oesophageal cancer, or urothelial carcinomas (JVDF): a multicohort, non-randomised, open-label, phase 1a/b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:1109–23.

53. Hodi FS, Lawrence D, Lezcano C, Wu X, Zhou J, Sasada T, et al. Bevacizumab plus ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014; 2:632–42.

54. Amin A, Plimack ER, Ernstoff MS, Lewis LD, Bauer TM, McDermott DF, et al. Safety and efficacy of nivolumab in combination with sunitinib or pazopanib in advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: the CheckMate 016 study. J Immunother Cancer. 2018; 6:109.

55. Dudek AZ, Liu LC, Gupta S, Logan TF, Singer EA, Joshi M, et al. Phase Ib/II clinical trial of pembrolizumab with bevacizumab for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: BTCRC-GU14–003. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38:1138–45.

56. Golden EB, Chhabra A, Chachoua A, Adams S, Donach M, Fenton-Kerimian M, et al. Local radiotherapy and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to generate abscopal responses in patients with metastatic solid tumours: a proof-of-principle trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:795–803.

57. Golden EB, Frances D, Pellicciotta I, Demaria S, Helen Barcellos-Hoff M, Formenti SC. Radiation fosters dose-dependent and chemotherapy-induced immunogenic cell death. Oncoimmunology. 2014; 3:e28518.

58. Twyman-Saint Victor C, Rech AJ, Maity A, Rengan R, Pauken KE, Stelekati E, et al. Radiation and dual checkpoint blockade activate non-redundant immune mechanisms in cancer. Nature. 2015; 520:373–7.

59. Shaverdian N, Lisberg AE, Bornazyan K, Veruttipong D, Goldman JW, Formenti SC, et al. Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: a secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017; 18:895–903.

60. Tagliamonte M, Petrizzo A, Tornesello ML, Ciliberto G, Buonaguro FM, Buonaguro L. Combinatorial immunotherapy strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016; 39:103–13.

61. Rebuzzi SE, Facchinetti F, Tiseo M. Anti-angiogenesis boosts chemo-immunotherapy in patients with EGFR mutations or baseline liver metastases: insights from IMpower150 study. Transl Cancer Res. 2019; 8(Suppl 6):S612–7.

62. McGranahan N, Swanton C. Clonal heterogeneity and tumor evolution: past, present, and the future. Cell. 2017; 168:613–28.

63. Duan J, Cui L, Zhao X, Bai H, Cai S, Wang G, et al. Use of immunotherapy with programmed cell death 1 vs program-med cell death ligand 1 inhibitors in patients with cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2020; 6:375–84.

64. Homet Moreno B, Ribas A. Anti-programmed cell death protein-1/ligand-1 therapy in different cancers. Br J Cancer. 2015; 112:1421–7.

65. George S, Papanicolau-Sengos A, Lenzo FL, Conroy JM, Nesline M, Pabla S, et al. PD-L2 amplification and durable disease stabilization in patient with urothelial carcinoma receiving pembrolizumab. Oncoimmunology. 2018; 7:e1460298.

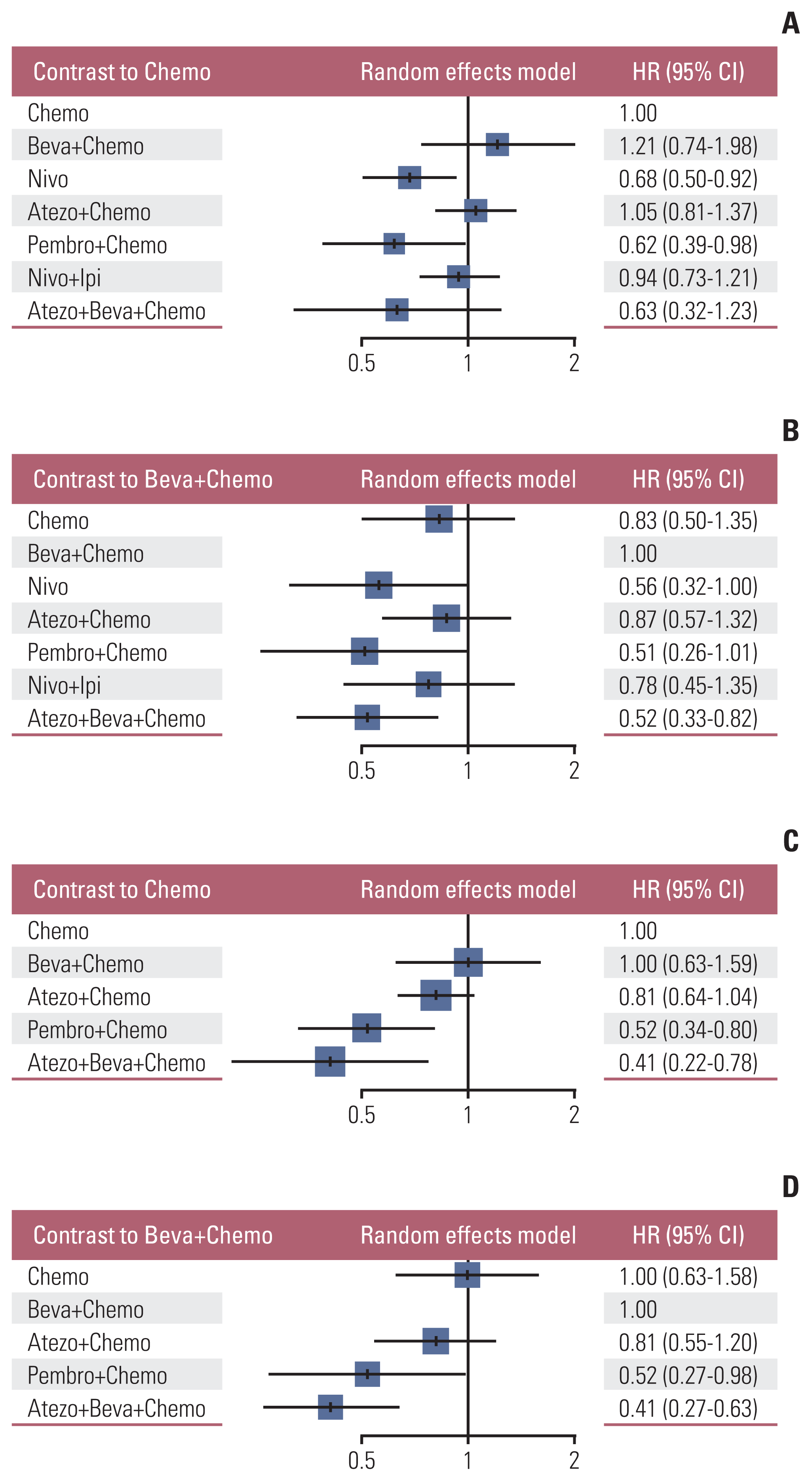
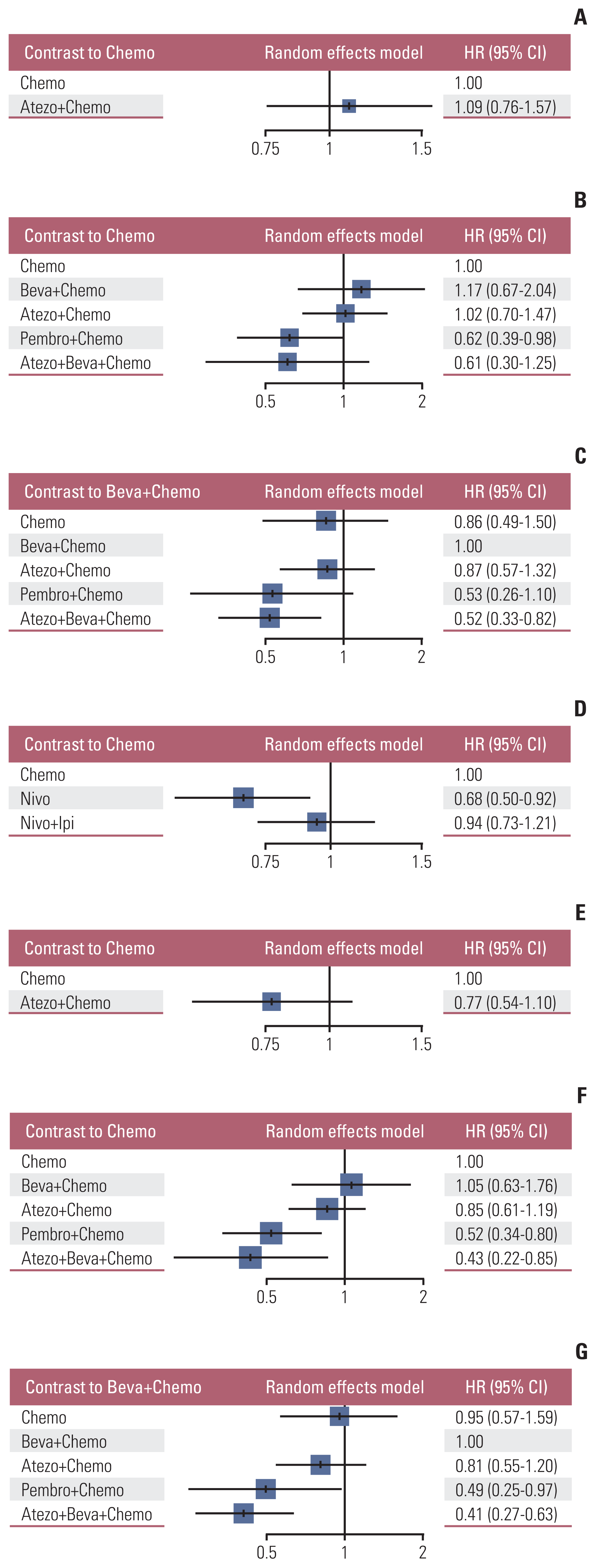
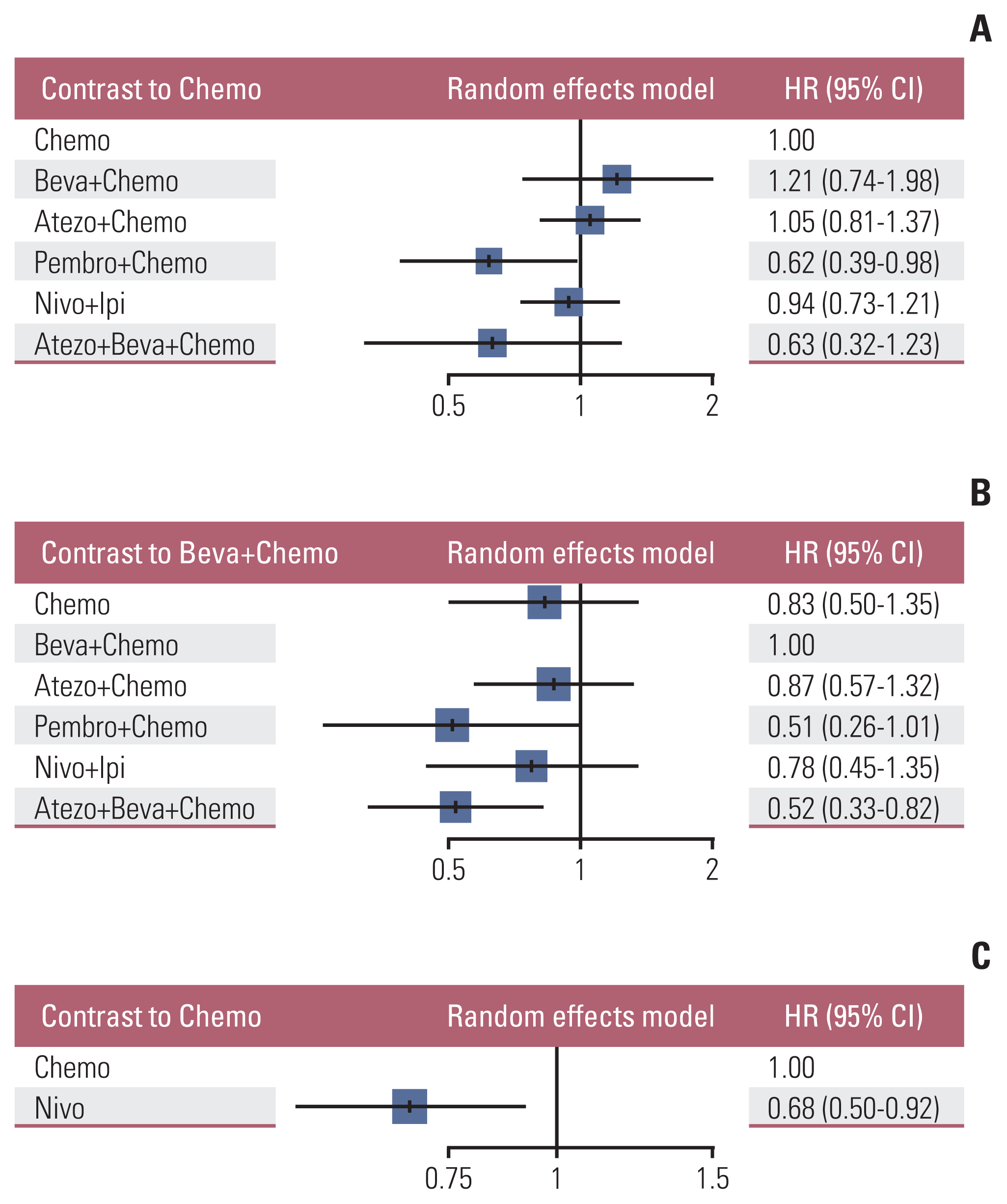




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download