1. Kris MG, Johnson BE, Berry LD, Kwiatkowski DJ, Iafrate AJ, Wistuba II, et al. Using multiplexed assays of oncogenic drivers in lung cancers to select targeted drugs. JAMA. 2014; 311:1998–2006.

2. Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, et al. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9:154–62.

3. Hsu KH, Ho CC, Hsia TC, Tseng JS, Su KY, Wu MF, et al. Identification of five driver gene mutations in patients with treatment-naive lung adenocarcinoma in Taiwan. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0120852.
4. Kuan FC, Kuo LT, Chen MC, Yang CT, Shi CS, Teng D, et al. Overall survival benefits of first-line EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2015; 113:1519–28.

5. Lee CK, Davies L, Wu YL, Mitsudomi T, Inoue A, Rosell R, et al. Gefitinib or erlotinib vs chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung cancer: individual patient data meta-analysis of overall survival. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2017; 109:djw279.

6. Park K, Tan EH, O’Byrne K, Zhang L, Boyer M, Mok T, et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment of patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (LUX-Lung 7): a phase 2B, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016; 17:577–89.

7. Wu YL, Cheng Y, Zhou X, Lee KH, Nakagawa K, Niho S, et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017; 18:1454–66.

8. Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113–25.

9. Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:41–50.

10. Ito K, Morise M, Wakuda K, Hataji O, Shimokawaji T, Takahashi K, et al. A multicenter cohort study of osimertinib compared with afatinib as first-line treatment for EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer from practical dataset: CJLSG1903. ESMO Open. 2021; 6:100115.

11. Chen DS, Mellman I. Oncology meets immunology: the cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity. 2013; 39:1–10.

12. Stinchcombe TE, Janne PA, Wang X, Bertino EM, Weiss J, Bzhenova L, et al. Effect of erlotinib plus bevacizumab vs erlotinib alone on progression-free survival in patients with advanced EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer: a phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019; 5:1448–55.

13. Seto T, Kato T, Nishio M, Goto K, Atagi S, Hosomi Y, et al. Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014; 15:1236–44.

14. Saito H, Fukuhara T, Furuya N, Watanabe K, Sugawara S, Iwasawa S, et al. Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:625–35.

15. Maemondo M, Fukuhara T, Saito H, Furuya N, Watanabe K, Sugawara S, et al. NEJ026: final overall survival analysis of bevacizumab plus erlotinib treatment for NSCLC patients harboring activating EGFR-mutations. J Clin Oncol. 2020; 38(15 Suppl):9506.

16. Nakagawa K, Garon EB, Seto T, Nishio M, Ponce Aix S, Paz-Ares L, et al. Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019; 20:1655–69.
17. Zhou Q, Wu YL, Cheng Y, Liu Y, Chen G, Cui J, et al. CTONG 1509: phase III study of bevacizumab with or without erlotinib in untreated Chinese patients with advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC. Ann Oncol. 2019; 30(Suppl 5):v603.

18. Ninomiya T, Ishikawa N, Inoue K, Kubo T, Yasugi M, Shibayama T, et al. Phase 2 study of afatinib alone or combined with bevacizumab in chemonaive patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations: AfaBev-CS study protocol. Clin Lung Cancer. 2019; 20:134–8.

19. Hsu PC, Huang CY, Wang CC, Kuo SC, Chu CH, Tung PH, et al. The combination of afatinib and bevacizumab in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced lung adenocarcinoma: a multicenter observational study. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020; 13:331.

20. Wang CC, Chiu LC, Tung PH, Kuo SC, Chu CH, Huang AC, et al. A real-world analysis of patients with untreated metastatic epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-mutated lung adenocarcinoma receiving first-line erlotinib and bevacizumab combination therapy. Oncol Ther. 2021; 9:489–503.

21. Tsai JS, Su PL, Yang SC, Chang CC, Lin CY, Yen YT, et al. EGFR-TKI plus bevacizumab versus EGFR-TKI monotherapy for patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a propensity score matching analysis. J Formos Med Assoc. 2021; 120:1729–39.
22. Tsai TH, Su KY, Wu SG, Chang YL, Luo SC, Jan IS, et al. RNA is favourable for analysing EGFR mutations in malignant pleural effusion of lung cancer. Eur Respir J. 2012; 39:677–84.

23. Su KY, Chen HY, Li KC, Kuo ML, Yang JC, Chan WK, et al. Pretreatment epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation predicts shorter EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor response duration in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:433–40.
24. Ninomiya T, Nogami N, Kozuki T, Harada D, Kubo T, Ohashi K, et al. A phase I trial of afatinib and bevacizumab in chemonaive patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations: Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group Trial 1404. Lung Cancer. 2018; 115:103–8.

25. Ninomiya T, Nogami N, Kozuki T, Harada D, Kubo T, Ohashi K, et al. Updated analysis of a phase I trial of afatinib (Afa) and bevacizumab (Bev) in chemo-naïve patients (pts) with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) harboring EGFR-mutations: OLCSG1404. Ann Oncol. 2019; 30(Suppl 5):v626.

26. Ko R, Shukuya T, Imamura CK, Tokito T, Shimada N, Koyama R, et al. Phase I study of afatinib plus bevacizumab in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR mutations. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021; 10:183–92.

27. Harrison PT, Vyse S, Huang PH. Rare epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in non-small cell lung cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020; 61:167–79.

28. Hong S, Gao F, Fu S, Wang Y, Fang W, Huang Y, et al. Concomitant genetic alterations with response to treatment and epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018; 4:739–42.

29. Jiao XD, He X, Qin BD, Liu K, Wu Y, Liu J, et al. The prognostic value of tumor mutation burden in EGFR-mutant advanced lung adenocarcinoma, an analysis based on cBioPortal data base. J Thorac Dis. 2019; 11:4507–15.

30. Kim Y, Lee SH, Ahn JS, Ahn MJ, Park K, Sun JM. Efficacy and safety of afatinib for EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer, compared with gefitinib or erlotinib. Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 51:502–9.

31. Yu HA, Paz-Ares LG, Yang JC, Lee KH, Garrido P, Park K, et al. Phase I study of the efficacy and safety of ramucirumab in combination with osimertinib in advanced T790M-positive EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2021; 27:992–1002.

32. Akamatsu H, Toi Y, Hayashi H, Fujimoto D, Tachihara M, Furuya N, et al. Efficacy of osimertinib plus bevacizumab vs osimertinib in patients with EGFR T790M-mutated non-small cell lung cancer previously treated with epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor: West Japan Oncology Group 8715L phase 2 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021; 7:386–94.

33. Yu HA, Schoenfeld AJ, Makhnin A, Kim R, Rizvi H, Tsui D, et al. Effect of osimertinib and bevacizumab on progression-free survival for patients with metastatic EGFR-mutant lung cancers: a phase 1/2 single-group open-label trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020; 6:1048–54.

34. Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS, Zakowski MF, Pao W, et al. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2013; 19:2240–7.
35. Huang YH, Hsu KH, Tseng JS, Chen KC, Hsu CH, Su KY, et al. The association of acquired T790M mutation with clinical characteristics after resistance to first-line epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. 2018; 50:1294–303.

36. Hochmair MJ, Morabito A, Hao D, Yang CT, Soo RA, Yang JC, et al. Sequential afatinib and osimertinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: final analysis of the GioTag study. Future Oncol. 2020; 16:2799–808.
37. Reck M, von Pawel J, Zatloukal P, Ramlau R, Gorbounova V, Hirsh V, et al. Phase III trial of cisplatin plus gemcitabine with either placebo or bevacizumab as first-line therapy for non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer: AVAil. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:1227–34.

38. Mok TS, Hsia TC, Tsai CM, Tsang K, Chang GC, Chang JW, et al. Efficacy of bevacizumab with cisplatin and gemcitabine in Asian patients with advanced or recurrent non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer who have not received prior chemotherapy: a substudy of the Avastin in Lung trial. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2011; 7(Suppl 2):4–12.

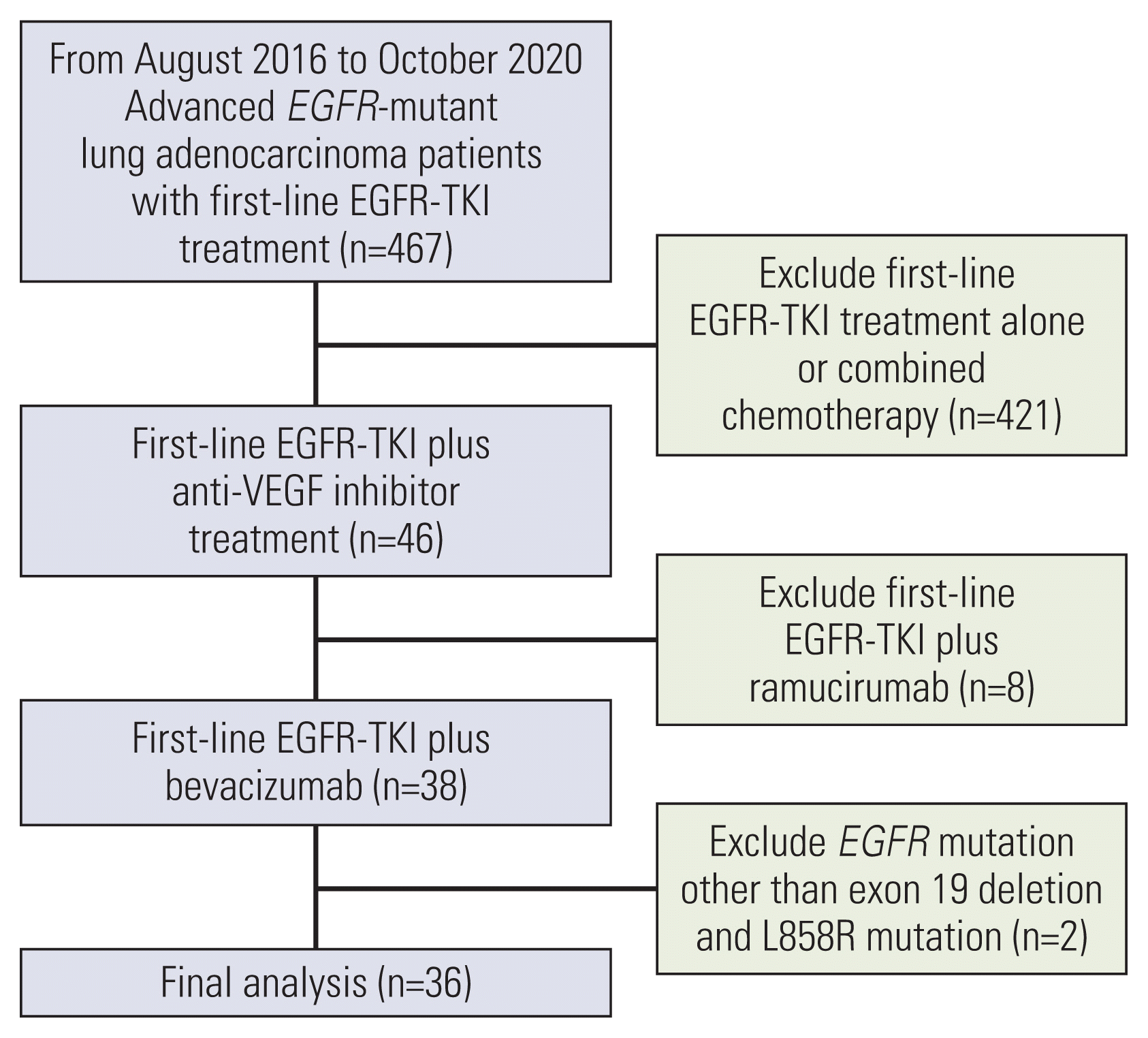
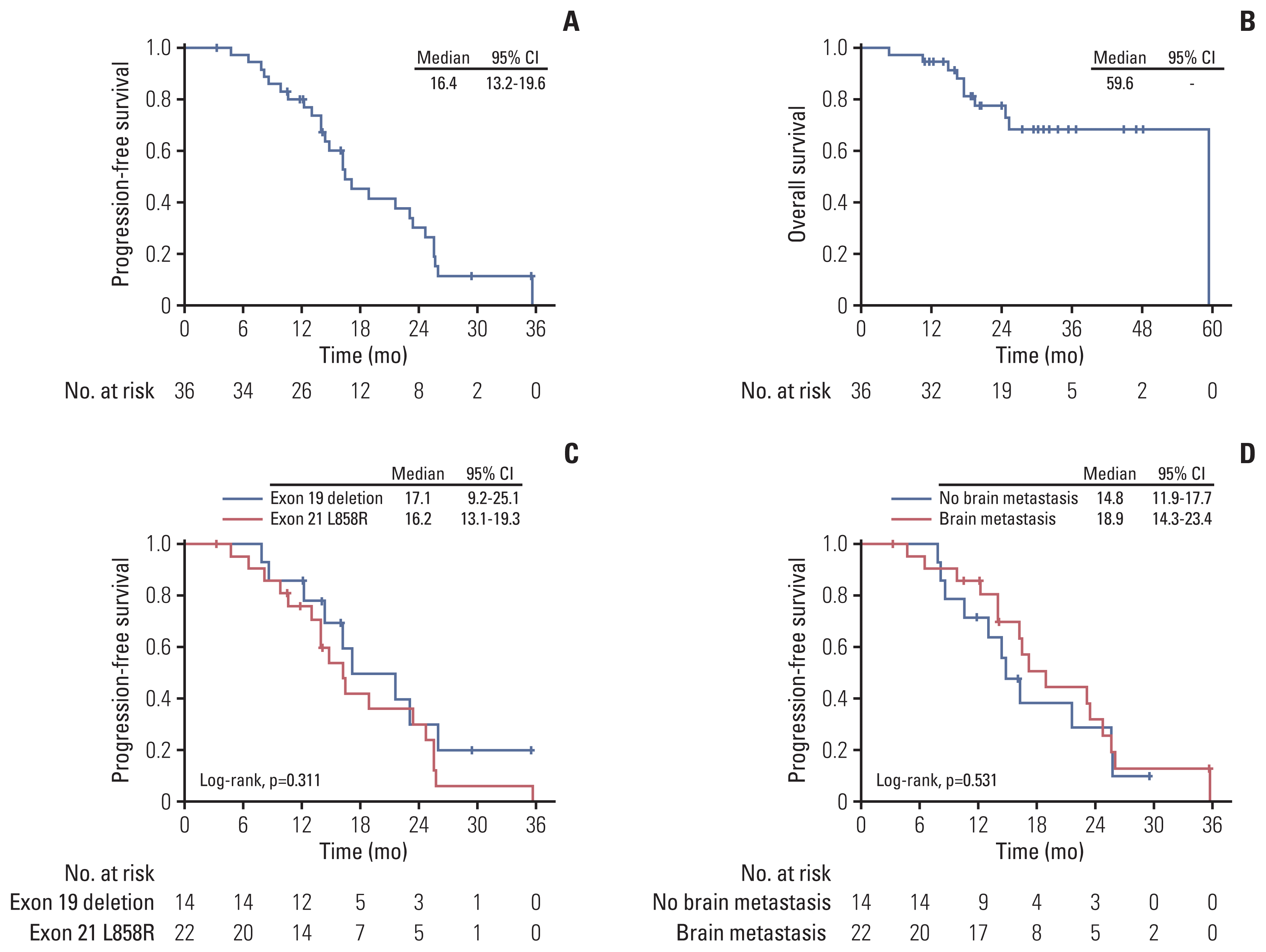
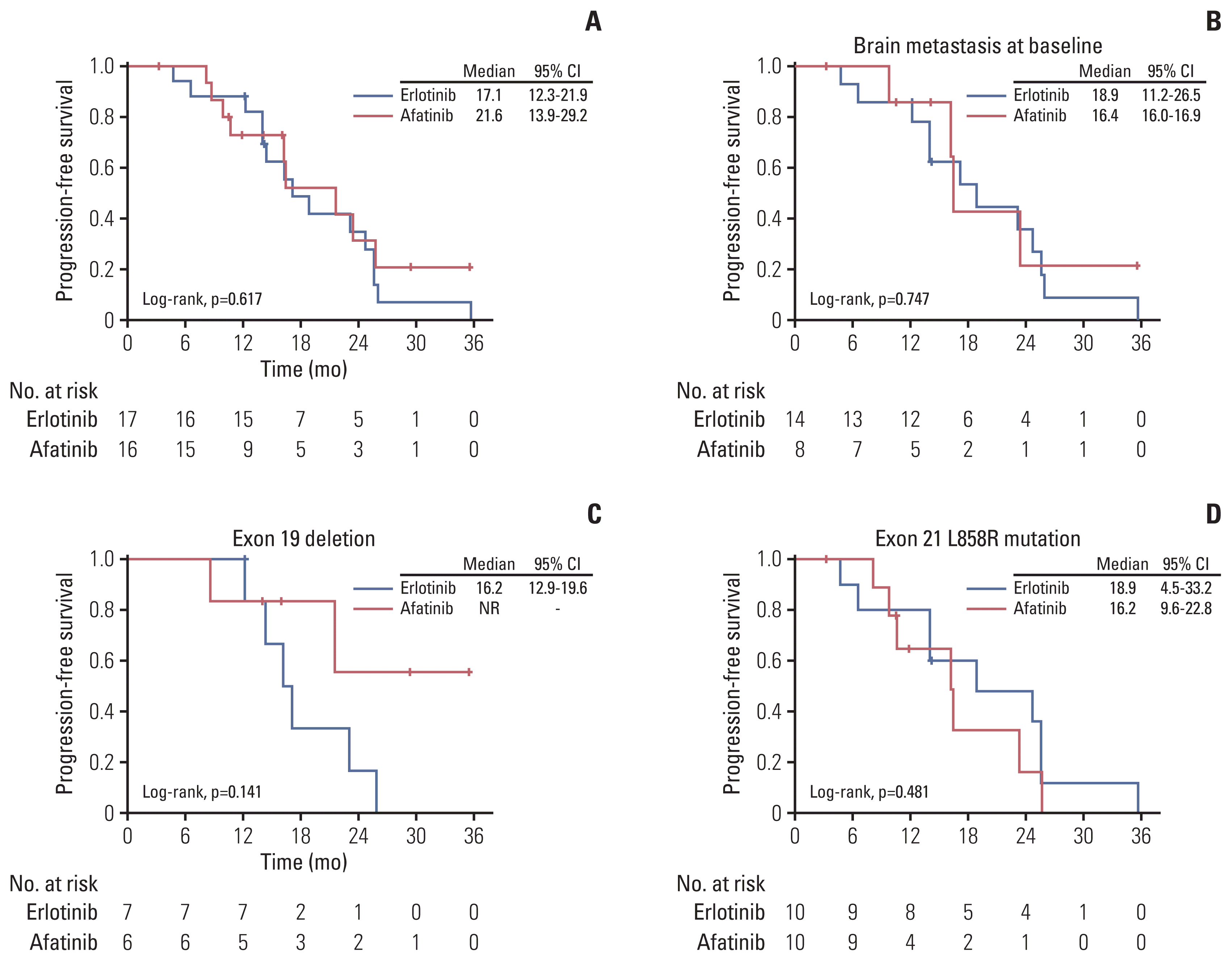




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print


 XML Download
XML Download