1. Spychala MS, Venna VR, Jandzinski M, Doran SJ, Durgan DJ, Ganesh BP, et al. Age-related changes in the gut microbiota influence systemic inflammation and stroke outcome. Ann Neurol. 2018; 84:23–36.

2. Blacher E, Bashiardes S, Shapiro H, Rothschild D, Mor U, Dori-Bachash M, et al. Potential roles of gut microbiome and metabolites in modulating ALS in mice. Nature. 2019; 572:474–80.

3. Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Sandhu K, Peterson V, Dinan TG. The gut microbiome in neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2020; 19:179–94.

4. Cryan JF, Dinan TG. Mind-altering microorganisms: the impact of the gut microbiota on brain and behaviour. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012; 13:701–12.

5. Cryan JF, O’Riordan KJ, Cowan CS, Sandhu KV, Bastiaanssen TF, Boehme M, et al. The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol Rev. 2019; 99:1877–2013.
6. Li N, Wang X, Sun C, Wu X, Lu M, Si Y, et al. Change of intestinal microbiota in cerebral ischemic stroke patients. BMC Microbiol. 2019; 19:191.

7. Jangi S, Gandhi R, Cox LM, Li N, von Glehn F, Yan R, et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis. Nat Commun. 2016; 7:12015.

8. Israelyan N, Margolis KG. Serotonin as a link between the gut-brain-microbiome axis in autism spectrum disorders. Pharmacol Res. 2018; 132:1–6.

9. Wallace CJ, Milev R. The effects of probiotics on depressive symptoms in humans: a systematic review. Ann Gen Psychiatry. 2017; 16:14.

10. Dono A, Patrizz A, McCormack RM, Putluri N, Ganesh BP, Kaur B, et al. Glioma induced alterations in fecal short-chain fatty acids and neurotransmitters. CNS Oncol. 2020; 9:CNS57.

11. Patrizz A, Dono A, Zorofchian S, Hines G, Takayasu T, Husein N, et al. Glioma and temozolomide induced alterations in gut microbiome. Sci Rep. 2020; 10:21002.

12. Dickson RP, Singer BH, Newstead MW, Falkowski NR, Erb-Downward JR, Standiford TJ, et al. Enrichment of the lung microbiome with gut bacteria in sepsis and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat Microbiol. 2016; 1:16113.

13. Singer BH, Dickson RP, Denstaedt SJ, Newstead MW, Kim K, Falkowski NR, et al. Bacterial dissemination to the brain in sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 197:747–56.

14. Xu R, Tan C, Zhu J, Zeng X, Gao X, Wu Q, et al. Dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota in neurocritically ill patients and the risk for death. Crit Care. 2019; 23:195.

15. Gill SR, Pop M, Deboy RT, Eckburg PB, Turnbaugh PJ, Samuel BS, et al. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science. 2006; 312:1355–9.

16. Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature. 2010; 464:59–65.

17. Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, et al. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science. 2005; 308:1635–8.

18. Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature. 2012; 486:207–14.
19. Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Dominguez-Bello MG, Contreras M, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 2012; 486:222–7.

20. Bäckhed F, Fraser CM, Ringel Y, Sanders ME, Sartor RB, Sherman PM, et al. Defining a healthy human gut microbiome: current concepts, future directions, and clinical applications. Cell Host Microbe. 2012; 12:611–22.

21. Deplancke B, Gaskins HR. Microbial modulation of innate defense: goblet cells and the intestinal mucus layer. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001; 73:1131S–1141S.

22. Chow J, Lee SM, Shen Y, Khosravi A, Mazmanian SK. Host-bacterial symbiosis in health and disease. Adv Immunol. 2010; 107:243–74.

23. Clemente JC, Ursell LK, Parfrey LW, Knight R. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view. Cell. 2012; 148:1258–70.

24. Mayer EA, Tillisch K, Gupta A. Gut/brain axis and the microbiota. J Clin Invest. 2015; 125:926–38.

25. Shafquat A, Joice R, Simmons SL, Huttenhower C. Functional and phylogenetic assembly of microbial communities in the human microbiome. Trends Microbiol. 2014; 22:261–6.

26. Turnbaugh PJ, Quince C, Faith JJ, McHardy AC, Yatsunenko T, Niazi F, et al. Organismal, genetic, and transcriptional variation in the deeply sequenced gut microbiomes of identical twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:7503–8.

27. Lloyd-Price J, Abu-Ali G, Huttenhower C. The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 2016; 8:51.

28. Turnbaugh PJ, Gordon JI. The core gut microbiome, energy balance and obesity. J Physiol. 2009; 587(Pt 17):4153–8.

29. Das B, Nair GB. Homeostasis and dysbiosis of the gut microbiome in health and disease. J Biosci. 2019; 44:117.

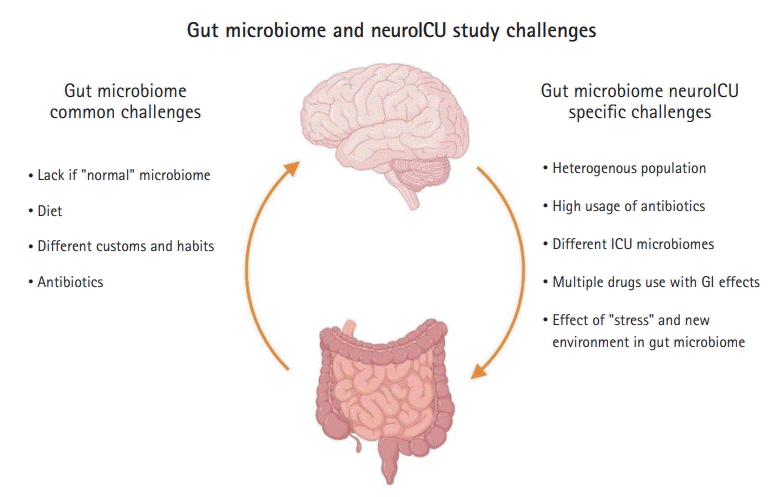
30. Clooney AG, Fouhy F, Sleator RD, O’Driscoll A, Stanton C, Cotter PD, et al. Comparing apples and oranges?: next generation sequencing and its impact on microbiome analysis. PLoS One. 2016; 11:e0148028.

31. Ranjan R, Rani A, Metwally A, McGee HS, Perkins DL. Analysis of the microbiome: advantages of whole genome shotgun versus 16S amplicon sequencing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 469:967–77.

32. Willis AD. Rarefaction, alpha diversity, and statistics. Front Microbiol. 2019; 10:2407.

33. Knight R, Vrbanac A, Taylor BC, Aksenov A, Callewaert C, Debelius J, et al. Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018; 16:410–22.

34. Kaddurah-Daouk R, Krishnan KR. Metabolomics: a global biochemical approach to the study of central nervous system diseases. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009; 34:173–86.

35. Luan H, Wang X, Cai Z. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics: targeting the crosstalk between gut microbiota and brain in neurodegenerative disorders. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2019; 38:22–33.

36. Diaz Heijtz R, Wang S, Anuar F, Qian Y, Björkholm B, Samuelsson A, et al. Normal gut microbiota modulates brain development and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:3047–52.

37. Gareau MG, Wine E, Rodrigues DM, Cho JH, Whary MT, Philpott DJ, et al. Bacterial infection causes stress-induced memory dysfunction in mice. Gut. 2011; 60:307–17.

38. Kennedy PJ, Clarke G, Quigley EM, Groeger JA, Dinan TG, Cryan JF. Gut memories: towards a cognitive neurobiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2012; 36:310–40.

39. Ma X, Mao YK, Wang B, Huizinga JD, Bienenstock J, Kunze W. Lactobacillus reuteri ingestion prevents hyperexcitability of colonic DRG neurons induced by noxious stimuli. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009; 296:G868–75.
40. Ahluwalia V, Wade JB, Heuman DM, Hammeke TA, Sanyal AJ, Sterling RK, et al. Enhancement of functional connectivity, working memory and inhibitory control on multi-modal brain MR imaging with Rifaximin in Cirrhosis: implications for the gut-liver-brain axis. Metab Brain Dis. 2014; 29:1017–25.

41. Altschuler SM, Escardo J, Lynn RB, Miselis RR. The central organization of the vagus nerve innervating the colon of the rat. Gastroenterology. 1993; 104:502–9.

42. Elenkov IJ, Wilder RL, Chrousos GP, Vizi ES. The sympathetic nerve:an integrative interface between two supersystems: the brain and the immune system. Pharmacol Rev. 2000; 52:595–638.
43. Muller PA, Schneeberger M, Matheis F, Wang P, Kerner Z, Ilanges A, et al. Microbiota modulate sympathetic neurons via a gut-brain circuit. Nature. 2020; 583:441–6.

44. Kim CH, Park J, Kim M. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain Fatty acids, T cells, and inflammation. Immune Netw. 2014; 14:277–88.

45. Banks WA. Characteristics of compounds that cross the blood-brain barrier. BMC Neurol. 2009; 9(Suppl 1):S3.

46. Chodobski A, Zink BJ, Szmydynger-Chodobska J. Blood-brain barrier pathophysiology in traumatic brain injury. Transl Stroke Res. 2011; 2:492–516.

47. Alves JL. Blood-brain barrier and traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Res. 2014; 92:141–7.

48. Archie SR, Al Shoyaib A, Cucullo L. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in CNS disorders and putative therapeutic targets: an overview. Pharmaceutics. 2021; 13:1779.

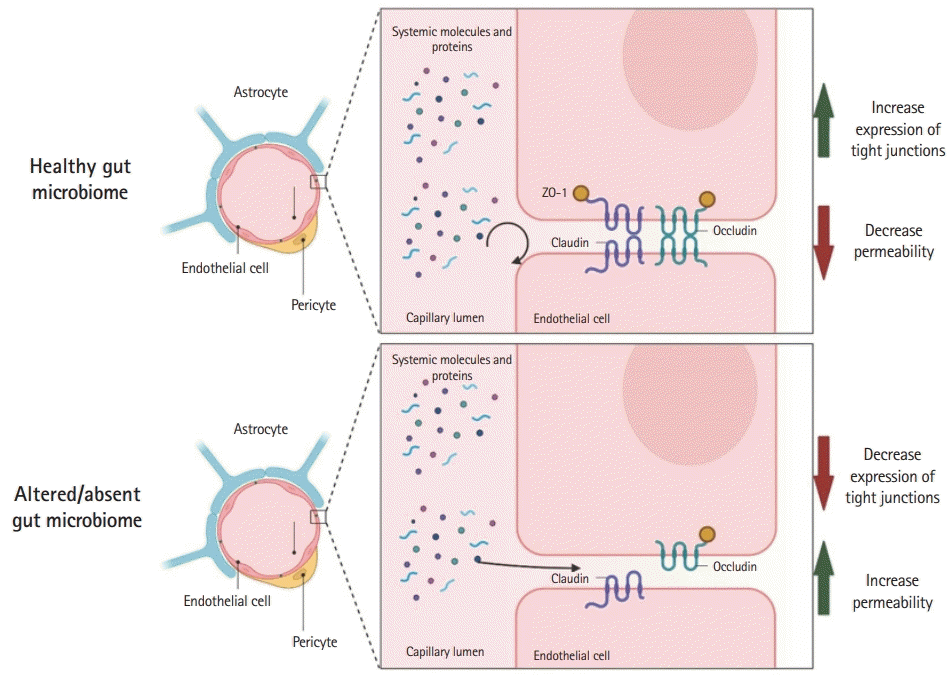
49. Braniste V, Al-Asmakh M, Kowal C, Anuar F, Abbaspour A, Tóth M, et al. The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2014; 6:263ra158.

50. Wen J, Ding Y, Wang L, Xiao Y. Gut microbiome improves postoperative cognitive function by decreasing permeability of the blood-brain barrier in aged mice. Brain Res Bull. 2020; 164:249–56.

51. Wu Q, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Xia C, Lai Q, Dong Z, et al. Potential effects of antibiotic-induced gut microbiome alteration on blood-brain barrier permeability compromise in rhesus monkeys. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2020; 1470:14–24.

52. Shahi SK, Freedman SN, Mangalam AK. Gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis: the players involved and the roles they play. Gut Microbes. 2017; 8:607–15.

53. Sgritta M, Dooling SW, Buffington SA, Momin EN, Francis MB, Britton RA, et al. Mechanisms underlying microbial-mediated changes in social behavior in mouse models of autism spectrum disorder. Neuron. 2019; 101:246–59.

54. Kang DW, Adams JB, Gregory AC, Borody T, Chittick L, Fasano A, et al. Microbiota transfer therapy alters gut ecosystem and improves gastrointestinal and autism symptoms: an open-label study. Microbiome. 2017; 5:10.

55. Grimaldi R, Gibson GR, Vulevic J, Giallourou N, Castro-Mejía JL, Hansen LH, et al. A prebiotic intervention study in children with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs). Microbiome. 2018; 6:133.

56. Cekanaviciute E, Yoo BB, Runia TF, Debelius JW, Singh S, Nelson CA, et al. Gut bacteria from multiple sclerosis patients modulate human T cells and exacerbate symptoms in mouse models. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017; 114:10713–8.

57. Kim MS, Kim Y, Choi H, Kim W, Park S, Lee D, et al. Transfer of a healthy microbiota reduces amyloid and tau pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. Gut. 2020; 69:283–94.

58. Xie G, Zhou Q, Qiu CZ, Dai WK, Wang HP, Li YH, et al. Ketogenic diet poses a significant effect on imbalanced gut microbiota in infants with refractory epilepsy. World J Gastroenterol. 2017; 23:6164–71.

59. Unger MM, Spiegel J, Dillmann KU, Grundmann D, Philippeit H, Bürmann J, et al. Short chain fatty acids and gut microbiota differ between patients with Parkinson’s disease and age-matched controls. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2016; 32:66–72.

60. Dees KJ, Koo H, Humphreys JF, Hakim JA, Crossman DK, Crowley MR, et al. Human gut microbial communities dictate efficacy of anti-PD-1 therapy in a humanized microbiome mouse model of glioma. Neurooncol Adv. 2021; 3:vdab023.

61. Benakis C, Brea D, Caballero S, Faraco G, Moore J, Murphy M, et al. Commensal microbiota affects ischemic stroke outcome by regulating intestinal γδ T cells. Nat Med. 2016; 22:516–23.

62. Zhu W, Gregory JC, Org E, Buffa JA, Gupta N, Wang Z, et al. Gut microbial metabolite TMAO enhances platelet hyperreactivity and thrombosis risk. Cell. 2016; 165:111–24.

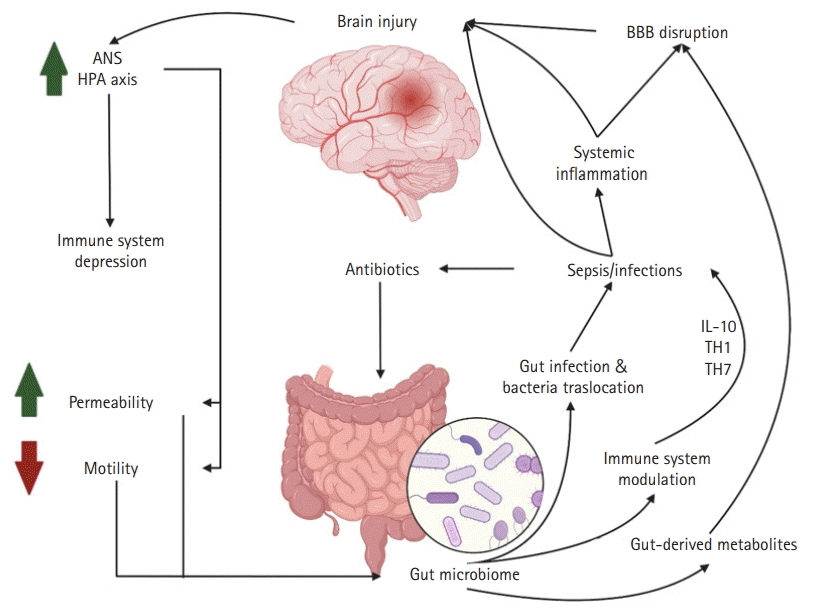
63. Shimizu K, Ogura H, Hamasaki T, Goto M, Tasaki O, Asahara T, et al. Altered gut flora are associated with septic complications and death in critically ill patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:1171–7.

64. Zaborin A, Smith D, Garfield K, Quensen J, Shakhsheer B, Kade M, et al. Membership and behavior of ultra-low-diversity pathogen communities present in the gut of humans during prolonged critical illness. mBio. 2014; 5:e01361–14.

65. Lankelma JM, van Vught LA, Belzer C, Schultz MJ, van der Poll T, de Vos WM, et al. Critically ill patients demonstrate large interpersonal variation in intestinal microbiota dysregulation: a pilot study. Intensive Care Med. 2017; 43:59–68.

66. Yeh A, Rogers MB, Firek B, Neal MD, Zuckerbraun BS, Morowitz MJ. Dysbiosis across multiple body sites in critically ill adult surgical patients. Shock. 2016; 46:649–54.

67. Ojima M, Motooka D, Shimizu K, Gotoh K, Shintani A, Yoshiya K, et al. Metagenomic analysis reveals dynamic changes of whole gut microbiota in the acute phase of intensive care unit patients. Dig Dis Sci. 2016; 61:1628–34.

68. Fontaine C, Armand-Lefèvre L, Magnan M, Nazimoudine A, Timsit JF, Ruppé E. Relationship between the composition of the intestinal microbiota and the tracheal and intestinal colonization by opportunistic pathogens in intensive care patients. PLoS One. 2020; 15:e0237260.

69. Freedberg DE, Zhou MJ, Cohen ME, Annavajhala MK, Khan S, Moscoso DI, et al. Pathogen colonization of the gastrointestinal microbiome at intensive care unit admission and risk for subsequent death or infection. Intensive Care Med. 2018; 44:1203–11.

70. Szychowiak P, Villageois-Tran K, Patrier J, Timsit JF, Ruppé É. The role of the microbiota in the management of intensive care patients. Ann Intensive Care. 2022; 12:3.

71. Ziakas PD, Thapa R, Rice LB, Mylonakis E. Trends and significance of VRE colonization in the ICU: a meta-analysis of published studies. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e75658.

72. Andremont O, Armand-Lefevre L, Dupuis C, de Montmollin E, Ruckly S, Lucet JC, et al. Semi-quantitative cultures of throat and rectal swabs are efficient tests to predict ESBL-Enterobacterales ventilator-associated pneumonia in mechanically ventilated ESBL carriers. Intensive Care Med. 2020; 46:1232–42.

73. Schuijt TJ, Lankelma JM, Scicluna BP, de Sousa e Melo F, Roelofs JJ, de Boer JD, et al. The gut microbiota plays a protective role in the host defence against pneumococcal pneumonia. Gut. 2016; 65:575–83.

74. Yin Y, Hountras P, Wunderink RG. The microbiome in mechanically ventilated patients. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2017; 30:208–13.

75. Reinhart K, Daniels R, Kissoon N, Machado FR, Schachter RD, Finfer S. Recognizing sepsis as a global health priority: a WHO resolution. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:414–7.

76. Tiru B, DiNino EK, Orenstein A, Mailloux PT, Pesaturo A, Gupta A, et al. The economic and humanistic burden of severe sepsis. Pharmacoeconomics. 2015; 33:925–37.

77. Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, et al. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis: current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016; 193:259–72.

78. Sadaka F, Cytron MA, Fowler K, Javaux VM, O’Brien J. Sepsis in the neurologic intensive care unit: epidemiology and outcome. J Clin Med Res. 2015; 7:18–20.

79. Berger B, Gumbinger C, Steiner T, Sykora M. Epidemiologic features, risk factors, and outcome of sepsis in stroke patients treated on a neurologic intensive care unit. J Crit Care. 2014; 29:241–8.

80. Rokitansky C. Handbuch der pathologischen anatomie. Vienna: Braunmueller und Seidel Wien;1842.
81. Cushing H. Peptic ulcer and the interbrain. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1932; 55:1–34.
82. Kim TJ, Torres L, Paz A, Lee JS, Park SH, Choi HA, et al. Neostigmine for treating acute colonic pseudo-obstruction in neurocritically ill patients. J Clin Neurol. 2021; 17:563–9.

83. Hui W, Li T, Liu W, Zhou C, Gao F. Fecal microbiota transplantation for treatment of recurrent C. difficile infection: an updated randomized controlled trial meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2019; 14:e0210016.

84. Baruch EN, Youngster I, Ben-Betzalel G, Ortenberg R, Lahat A, Katz L, et al. Fecal microbiota transplant promotes response in immunotherapy-refractory melanoma patients. Science. 2021; 371:602–9.

85. Davar D, Dzutsev AK, McCulloch JA, Rodrigues RR, Chauvin JM, Morrison RM, et al. Fecal microbiota transplant overcomes resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy in melanoma patients. Science. 2021; 371:595–602.





 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download