INTRODUCTION
METHODS
Sample preparation
Total RNA isolation, RT-PCR, and semiquantitative RT-PCR
Table 1.
Immunohistochemical and western blot analyses
RESULTS
RAR mRNA expression analysis in NE, IE, and P samples via RT-PCR
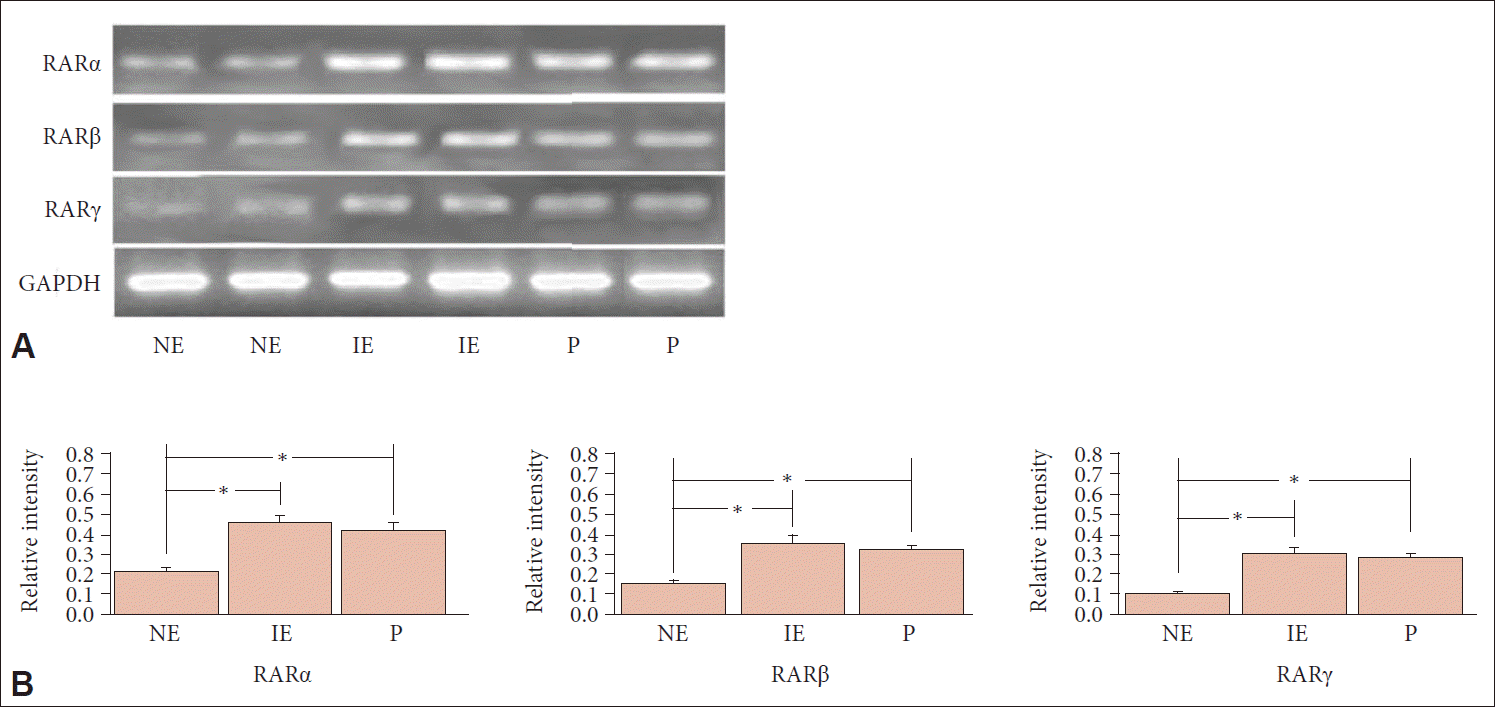 | Fig. 1.Semiquantitative RT-PCR of NE, IE and P samples. A: Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis of RAR mRNA levels in normal nasal mucosa and nasal mucosa with chronic sinusitis and polyps. B: Bands were quantified via densitometric scanning, and the expression of each gene was calculated as relative to that of the internal control GAPDH. The bar indicates mean±standard deviation. *p<0.05. RT-PCR, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; RAR, retinoic acid receptors; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; NE, normal ethmoid sinus mucosa; IE, inflammatory ethmoid sinus mucosa; P, nasal polyp. |
Immunohistochemical localization and western blotting of RARs in NE, IE, and P samples
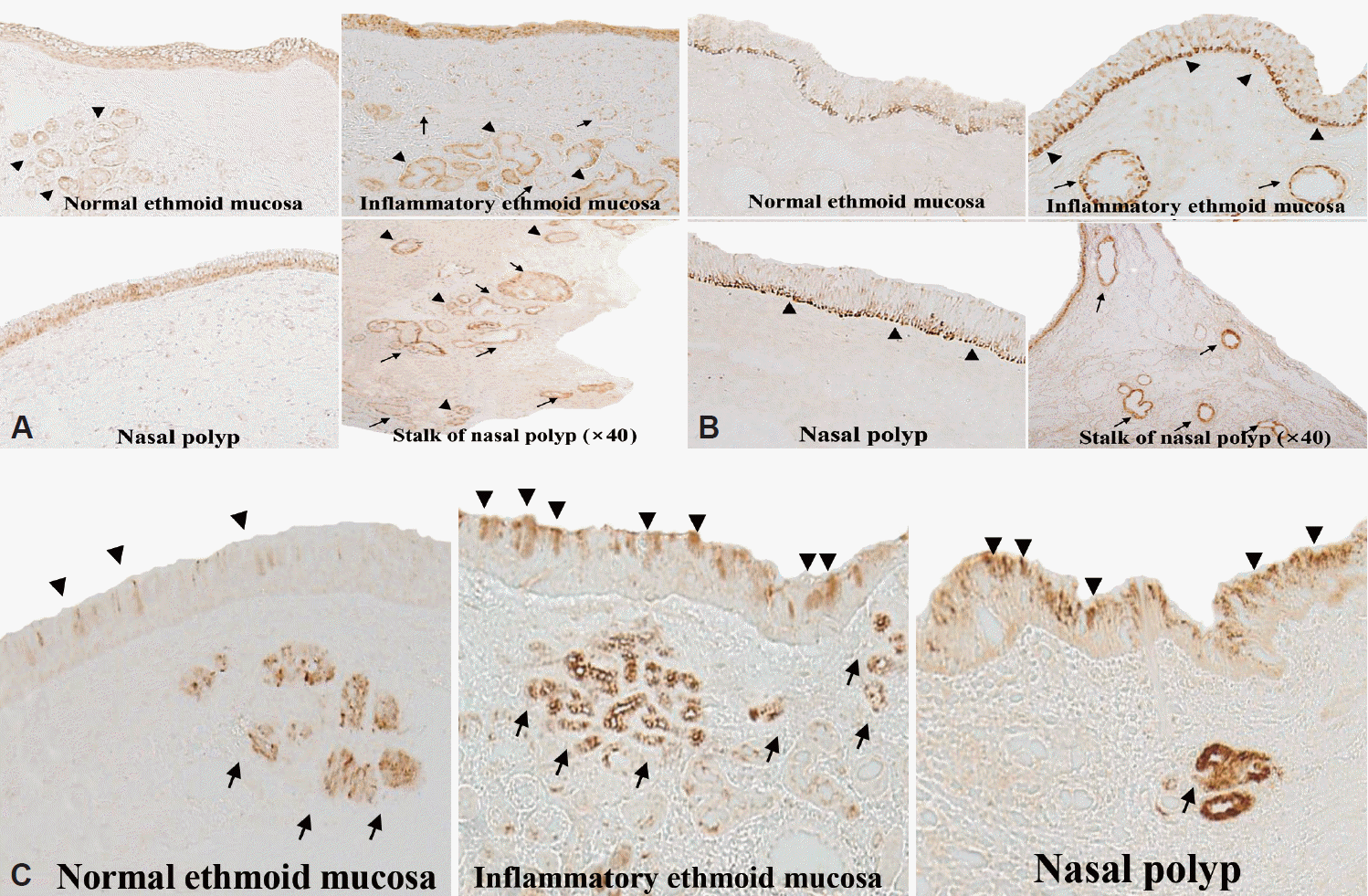 | Fig. 2.Immunohistochemical localization of RAR-α in normal mucosa, inflammatory ethmoid mucosa, and nasal polyp and its stalk. A: RAR expression was observed in epithelial cells (arrowheads) and submucosal glands (arrows) (×100). B: Expression pattern of RAR-β based on immunohistochemical analysis as shown in (A) (×100) (epithelial cells [arrowheads] and endothelial cells [arrows]). C: RAR-γ localization based on immunohistochemical analysis (×400). RAR expression in epithelial cells (arrowheads) and submucosal glands (arrows). RAR, retinoic acid receptors. |
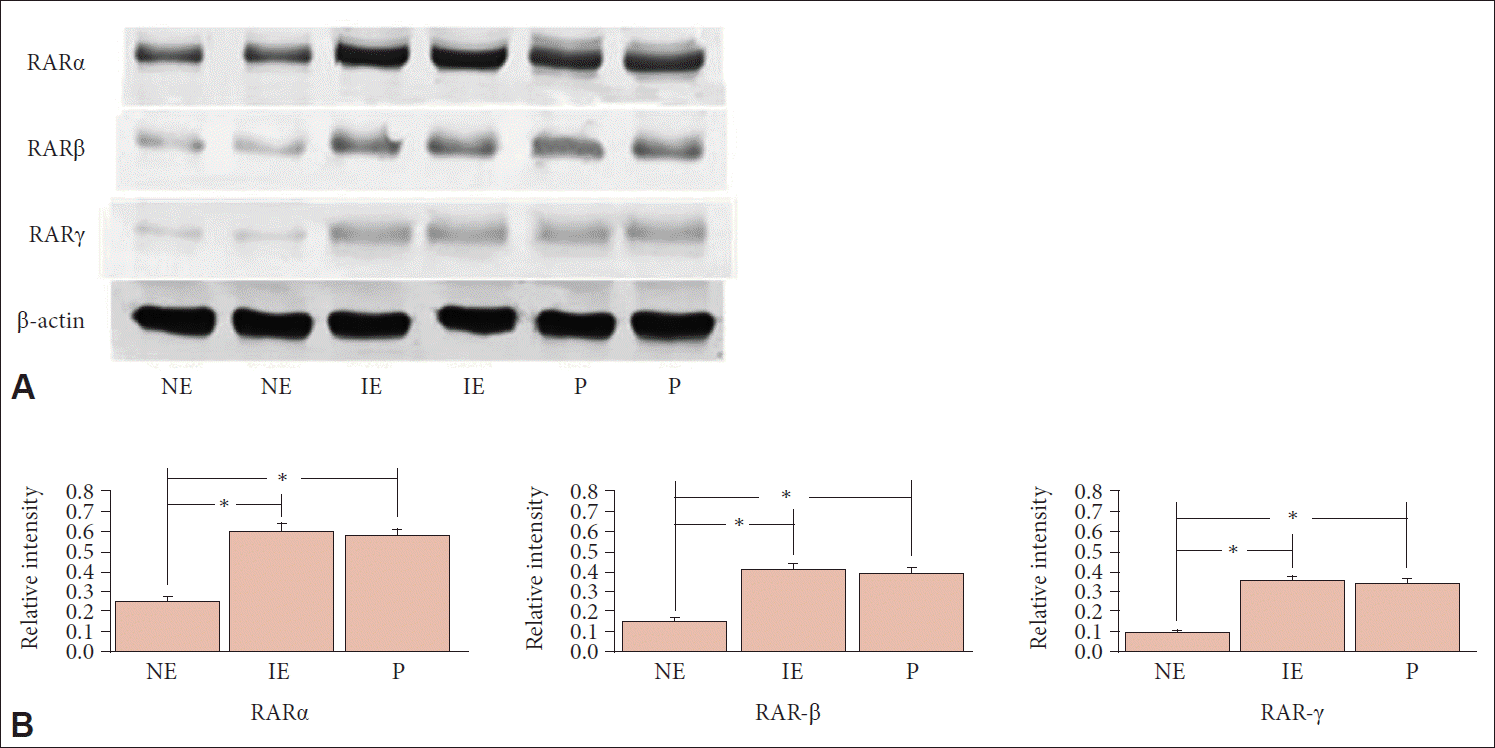 | Fig. 3.Western blot of NE, IE and P samples. A: Western blot analysis of RAR-α, -β, and -γ in normal mucosa, inflammatory nasal mucosa, and nasal polyp. B: Bands were quantified via densitometric scanning, and the expression of each gene was calculated as relative to that of the internal control β-actin. The bar indicates mean±standard deviation. *p<0.05. RAR, retinoic acid receptors; NE, normal ethmoid sinus mucosa; IE, inflammatory ethmoid sinus mucosa; P, nasal polyp. |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download