Abstract
Patients with symptomatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) typically present with gastrointestinal bleeding and abdominal pain. This report presents an unusual case of fundic GIST complicated by gastroduodenal intussusception, manifesting as acute pancreatitis. The patient presented with epigastric pain and pancreatic enzyme elevation; thus, he was diagnosed with acute pancreatitis. Computed tomography showed evidence of pancreatitis and a 4×4.7 cm well-defined hyperdense lesion in the 2nd part of the duodenum, compressing the pancreatic head and pancreatic duct. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy revealed invagination of the gastric folds into the duodenum, causing pyloric canal blockage consistent with gastroduodenal intussusception. Spontaneous reduction of the lesion during endoscopy revealed a 4 cm pedunculated subepithelial mass with central ulceration originating from the gastric fundus. Endoscopic ultrasound demonstrated a heterogeneous hypoechoic lesion originating from the 4th layer of the gastric wall. Laparoscopic-endoscopic intragastric wedge resection of the fundic lesion was subsequently performed, and surgical histology confirmed GIST.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) accounts for approximately 1% of all gastrointestinal tract neoplasms.1 GIST usually presents as an incidental gastric subepithelial lesion during upper endoscopy or abdominal radiologic studies. In symptomatic cases, abdominal pain and gastrointestinal bleeding are common manifestations. Gastrointestinal obstruction is a less frequent presentation, occurring in only 10%–30% of patients,2 while gastroduodenal intussusception and acute pancreatitis are extremely unusual presentations of gastric GIST. This report presents the case of a patient diagnosed with gastric GIST complicated by gastroduodenal intussusception, resulting in acute pancreatitis.
A 55-year-old male patient presented with worsening epigastric pain and vomiting for 10 days. He reported intermittent abdominal pain for 10 months prior to presentation. Abdominal examination revealed tenderness at the epigastrium. His serum amylase level was 320 U/L, compatible with acute pancreatitis. Abdominal computed tomography (CT) revealed a 4×4.7 cm well-defined hyperdense mass in the 2nd part of the duodenum, compressing the pancreatic head, edematous pancreatic parenchyma, peripancreatic fat stranding, and pancreatic duct dilatation (Fig. 1). Esophagogastroduodenoscopy was significant for abnormal torsion of gastric folds that originated from the gastric fundus, coursed along the lesser curvature, and invaginated into the pyloric canal, thereby blocking the passage of the scope into the duodenal bulb (Fig. 2A, B). These findings were consistent with those of gastroduodenal intussusception. The lesion spontaneously reduced back into the stomach during the procedure, allowing visualization of an approximately 4-cm sized, pedunculated subepithelial mass with inflamed mucosa and central ulceration (Fig. 2C). Endoscopic examination of the duodenal bulb, the 2nd part of the duodenum, and the ampulla were unremarkable (Supplementary Video 1). Endoscopic ultrasound was notable for a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass originating from the 4th layer of the gastric wall (Fig. 2D), highly suggestive of GIST. Given the lesion size and location, we elected to proceed with combined laparoendoscopic intragastric wedge resection. The procedure was successfully performed without any complications. The histology revealed a 5.5×4.3×4 cm-sized, intramural spindle cell tumor with a mitotic rate of <5/50 high power field (G1). Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the tumor cells were positive for CD34, CD117, and DOG-1, but not for S100 and 1A4, confirming the diagnosis of GIST (Fig. 3). Therefore, the final diagnosis was gastric fundal GIST complicated by gastroduodenal intussusception, triggering acute pancreatitis. The patient remained asymptomatic without evidence of recurrence after 2 years of follow-up.
Gastroduodenal intussusception, first described by Hobbs and Cohen, and also known as ball valve syndrome, is an uncommon condition in which a part of the stomach invaginates into the pylorus and duodenum.3 This condition accounts for less than 10% of all intussusceptions in adults.4 The possible etiologies of this condition include adenomatous polyps, lipomas, hamartomas, leiomyomas, leiomyosarcomas, adenocarcinomas, and GISTs. Among the gastrointestinal tract mesenchymal tumors, GIST is the most common, with the stomach being the most predominant location, accounting for 60% of cases.5 The presentations of GIST generally include abdominal pain, gastrointestinal bleeding, and, to a lesser extent, bowel obstruction, although cases can also be asymptomatic.5 In contrast, gastroduodenal intussusception caused by GIST is incredibly infrequent; only 17 case reports of GIST complicated by gastroduodenal intussusception have been identified thus far. Most reported patients present with acute or intermittent episodes of epigastric pain and vomiting that are compatible with clinical gastric outlet obstruction for a day to months leading up to diagnosis. The most common tumor location is the antrum and fundus, with sizes ranging from 2.5 cm to 8 cm in maximum dimension. All patients underwent surgical resection.6
Our patient developed acute pancreatitis, which is an exceedingly peculiar complication of gastroduodenal intussusception. This condition was believed to be triggered by pancreatic duct distortion or compression secondary to the duodenal wall traction or direct obstruction of the pancreatic duct orifice by the intussusceptum.7 Extensive literature search to date only yielded reports of 11 cases of such exceptional circumstances, and only five cases of acute pancreatitis secondary to gastroduodenal intussusception of gastric GIST (Table 1).8-18 The mean age of these five patients was 71 years, with a slight female predilection. Three patients had pedunculated GISTs dangling from the fundus, causing intussusception, while the remaining two patients had GISTs located in the antrum. Tumor size ranged from 6 cm to 8.8 cm. All patients underwent successful surgical resection.
Endoscopically, GIST appears as a smooth bulge of subepithelial lesions covered by normal overlying mucosa, with or without central ulceration, and with a firm consistency when probed with biopsy forceps.19 Endoscopic ultrasound usually demonstrates hypoechoic homogeneous lesions arising from either the 2nd or 4th layer, although heterogeneous lesions with anechoic spaces and calcifications may also be found.19 Contrast-enhanced CT scans can help evaluate lesion extension, evidence of malignant metastasis, and complications such as intussusception and obstruction. As in our case, endoscopy and CT helped in the diagnosis.
Reduction of the intussusception can be performed endoscopically; however, this technique may not always be feasible in cases with totally obliterated lumens. In such a scenario, open surgical reduction may be required unless spontaneous reduction occurs, as demonstrated in our case. Resection by either laparoscopic or open surgery remains the only definitive treatment for GIST to date. Endoscopic submucosal dissection, submucosal tunnel resection, and full-thickness resection are viable options for 2 to 4 cm GIST.19
In conclusion, gastric GIST complicated by gastroduodenal intussusception is uncommon. Here, we present a case of acute pancreatitis secondary to gastroduodenal intussusception from a pedunculated gastric GIST at the fundus. Our patient subsequently underwent successful combined laparoscopic and endoscopic intragastric wedge resection. This diagnosis should be considered in patients presenting with acute pancreatitis and gastric outlet obstruction.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Video 1. Upper endoscopy demonstrated gastroduodenal intussusception with spontaneous reduction of the pedunculated subepithelial mass originating from the gastric fundus (https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.073.v001).
Supplementary materials related to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2021.073.
Notes
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: PN, SN, NP; Data curation: PN, SN, TP, NP; Formal analysis: PN, SN, NP; Investigation: PN, TP, NP; Project administration: NP; Supervision: NP; Validation: SN, NP; Visualization: PN, SN, TP, NP; Writing-original draft: PN, SN; Writing-review & editing: SN, TP, NP.
REFERENCES
1. Chandrasekhara V, Ginsberg GG. Endoscopic management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011; 13:532–539.
2. Lehnert T. Gastrointestinal sarcoma (GIST): a review of surgical management. Ann Chir Gynaecol. 1998; 87:297–305.
3. Hobbs WH, Cohen SE. Gastroduodenal invagination due to a submucous lipoma of the stomach. Am J Surg. 1946; 71:505–518.
4. Stubenbord WT, Thorbjarnarson B. Intussusception in adults. Ann Surg. 1970; 172:306–310.
5. Søreide K, Sandvik OM, Søreide JA, et al. Global epidemiology of gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST): a systematic review of population-based cohort studies. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016; 40:39–46.
6. Đokić M, Novak J, Petrič M, et al. Case report and literature review: patient with gastroduodenal intussusception due to the gastrointestinal stromal tumor of the lesser curvature of the gastric body. BMC Surg. 2019; 19:158.
7. Fuchizaki U, Nishitani M, Ueda Y. A rare cause of acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2018; 155:e8–e10.
8. White PG, Adams H, Sue-Ling HM, et al. Case report: gastroduodenal intussusception--an unusual cause of pancreatitis. Clin Radiol. 1991; 44:357–358.
9. Herman LL, Kurtz RC, Brennan MF, et al. Acute pancreatitis from intussusception of a gastric polyp in a patient with Gardner’s syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1992; 37:955–960.
10. Senadhi V, Arora D, Jani N. Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) presenting with acute pancreatitis. Endoscopy. 2011; 43 Suppl 2 UCTN:E76.
11. Jones O, Monk D, Balling T, et al. Acute pancreatitis secondary to a prolapsed gastric fundal GIST. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2012; 3:82–85.
12. Sun J, Shen X, Li Z, et al. A rare case of acute pancreatitis induced by a gastrointestinal stromal tumor arising from the gastric fundus. Endoscopy. 2012; 44 Suppl 2 UCTN:E426–E427.
13. Chahla E, Kim MA, Beal BT, et al. Gastroduodenal intussusception, intermittent biliary obstruction and biochemical pancreatitis due to a gastric hyperplastic polyp. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2014; 8:371–376.
14. Prakash M, Kumar S, Sharma V, et al. Gastro-gastric and gastro-duodenal intussusception with pancreatitis due to GIST. Tropical Gastroenterology. 2017; 37:305–307.
15. Yildiz MS, Doğan A, Koparan IH, et al. Acute pancreatitis and gastroduodenal intussusception induced by an underlying gastric gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a case report. J Gastric Cancer. 2016; 16:54–57.
16. Salazar-Alarcón JL, Arones-Collantes RA, León-Estrella MÁ, et al. Pancreatitis aguda debido a intususcepción gastroduodenal. Rev Chil Cir. 2017; 69:259–263.
17. Jetha Z, Lisi M. Prolapsed fundic gastric polyp causing gastroduodenal intussusception and acute pancreatitis. J Surg Case Rep. 2018; 2018:rjy139.
18. Bejjani LE, Hasbany G, Assaker R, et al. Gastric adenocarcinoma presenting as gastroduodenal intussusception and acute pancreatitis. Med Sci Case Rep. 2018; 5:21–26.
19. Faulx AL, Kothari S, Acosta RD, et al. The role of endoscopy in subepithelial lesions of the GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017; 85:1117–1132.
Fig. 1.
(A) Computed tomography scan of the abdomen revealed a 4×4.7 cm well-defined hyperdense tumor in the 2nd part of the duodenum, edematous change of the pancreatic parenchyma, and peripancreatic fat stranding. (B) The mass was originated from the gastric fundus.
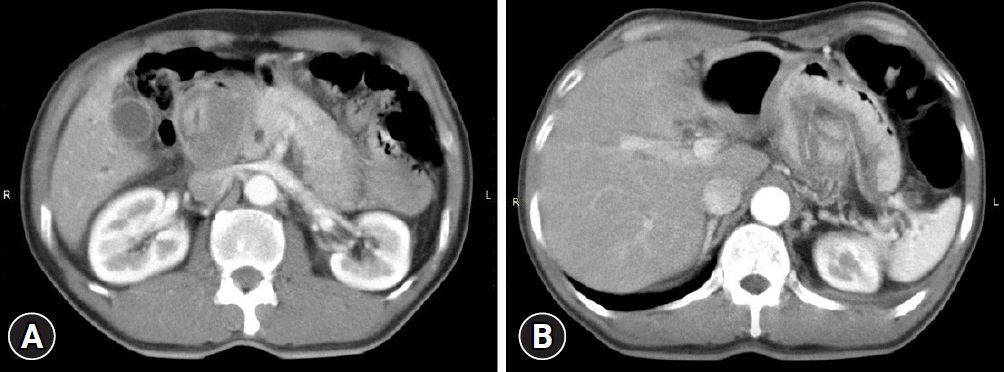
Fig. 2.
Endoscopic images of the lesion. (A) Twisting of the gastric folds in the gastric cardia and fundus. (B) Torsion of the gastric folds running across the incisura into the pyloric canal. (C) A 4-cm sized, pedunculated subepithelial lesion arising from the fundus was visualized after spontaneous reduction of the intussuscepted gastric folds. (D) Endoscopic ultrasound of the subepithelial lesion demonstrating a heterogeneous hypoechoic mass originating from the 4th layer of the gastric wall.
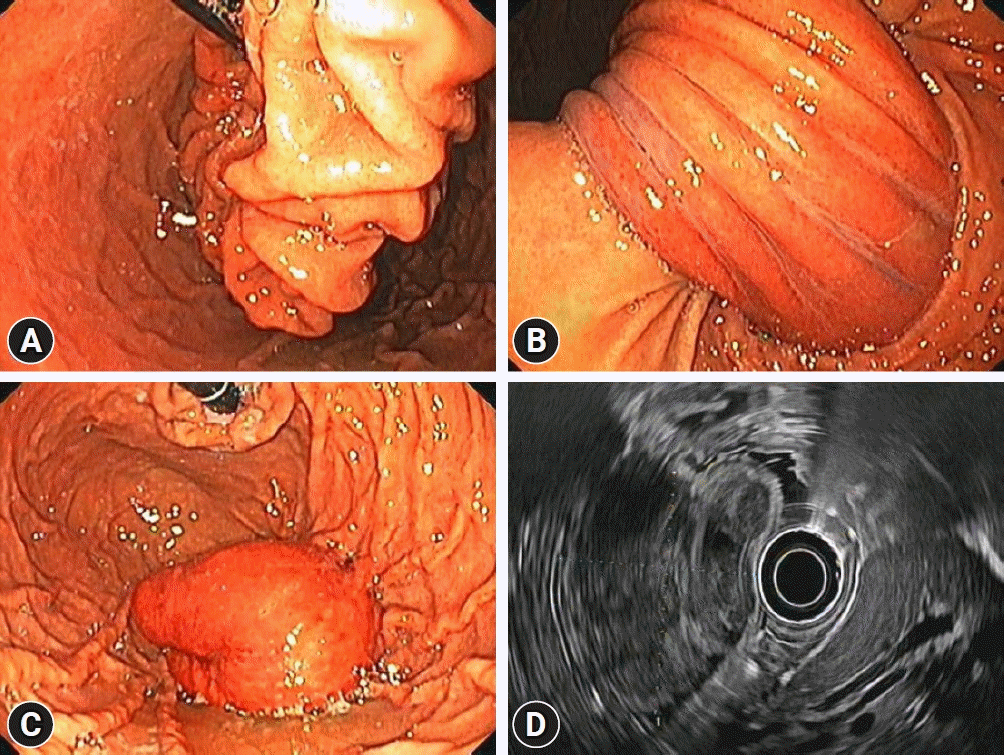
Fig. 3.
(A) Pathologic examination showed spindle-shape cells on hematoxylin & eosin stain. Immunohistochemical staining of the specimen was positive for (B) CD117, (C) CD34, and (D) DOG-1, respectively. All images were taken in high-power-field magnification (x400).
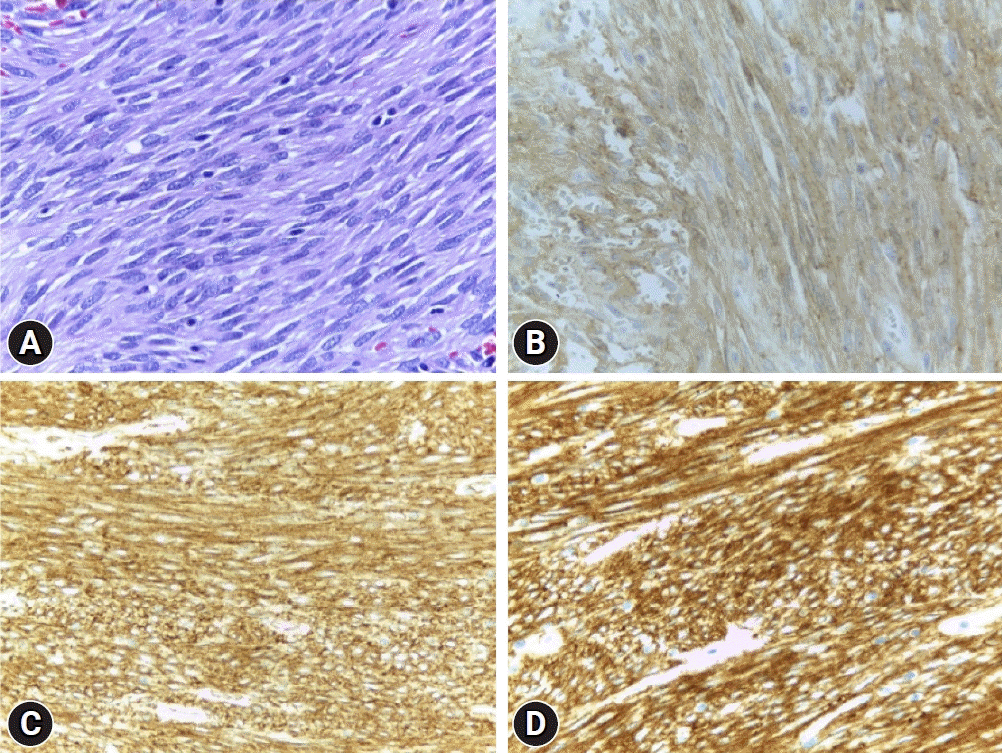
Table 1.
Case reports of gastroduodenal intussusception causing acute pancreatitis
| Study | Age (yr) | Sex | Etiology | Location | Size (cm) | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White (1991)8 | 67 | Male | Leiomyoma | Body | 3.5 | Gastrostomy excision |
| Herman (1992)9 | 44 | Female | Adenomatous polyp | Body | 6 | Gastrostomy excision |
| Senadhi (2011)10 | 58 | Female | GIST | Antrum | 6 | Partial anterior gastric resection |
| Jones (2012)11 | 65 | Male | GIST | Fundus | 8.2 | Laparoscopic wedge resection |
| Sun (2012)12 | 82 | Female | GIST | Fundus | 8 | Surgical resection |
| Chahla (2014)13 | 76 | Male | Hyperplastic polyp | Antrum | 12 | Partial endoscopic resection |
| Prakash (2017)14 | 65 | Male | GIST | Antrum | - | Subtotal gastrectomy |
| Yildiz (2016)15 | 85 | Female | GIST | Fundus | 6 | Subtotal gastrectomy |
| Salazar-Alarcón (2017)16 | 68 | Male | Adenocarcinoma | Antrum | 7 | Subtotal gastrectomy |
| Jetha (2018)17 | 86 | Female | Adenomatous polyp | Fundus | 8.8 | Laparoscopic resection |
| Bejjani (2018)18 | 84 | Female | Adenocarcinoma | Antrum | 7.5 | Partial lateral gastrectomy |




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print




 XML Download
XML Download