Abstract
Background and Purpose
Methods
Results
Conclusions
Supplementary materials
Supplementary Table 1.
Notes
Disclosure
Martina B. Goeldlin: grants from SAMW/Bangerter-Rhyner-Foundation (YTCR 13/18), Stroke Society, Mittelbauvereinigung at University of Bern. Congress support from Pfizer (outside the submitted work); Davide Strambo: research grants from Swiss Heart Foundation and University of Lausanne, congress support from Bristol Myers Squibb. All fees are paid to his institution; Carlo W. Cereda: advisory board for Bayer, Ischemaview, Astra Zeneca, Medtronic, Portola/Alexion; Bastian Volbers: personal fees from Pfizer AG/Bristol-Myers Squibb SA, personal fees from Bayer AG, grants from Institutional grant (Inselspital), personal fees from Ipsen Pharma, personal fees from CSL Behring, outside the submitted work; Leo H. Bonati: grants from the Swiss National Science Foundation, the University of Basel, the Swiss Heart Foundation, and the “Stiftung zur Förderung der gastroenterologischen und allgemeinen klinischen Forschung sowie der medizinischen Bildauswertung”; an unrestricted research grant from AstraZeneca; and consultancy or advisory board fees or speaker’s honoraria from Amgen, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Claret Medical, and InnovHeart, and travel grants from AstraZeneca and Bayer; David J. Seiffge: advisory board for Bayer and Portola/Alexion, Research grant from the Bangerter-Rhyner Foundation. All other authors have nothing to disclose
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS

References
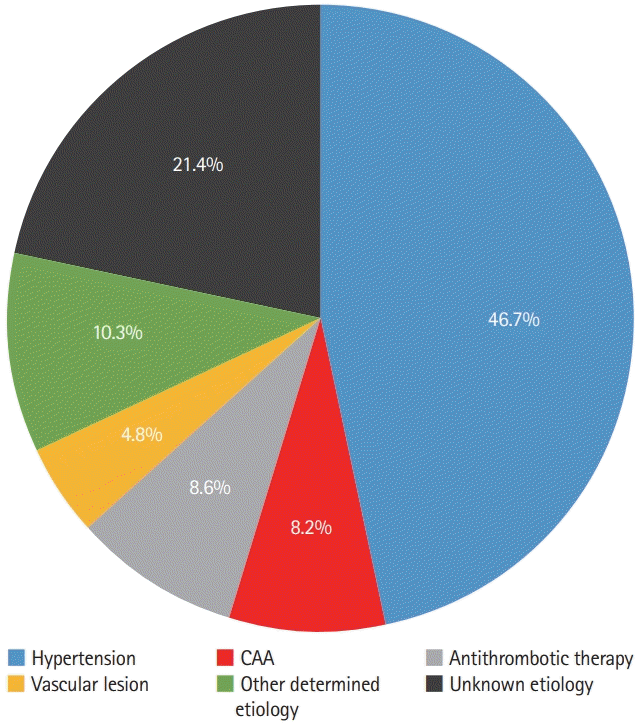
Figure 1.
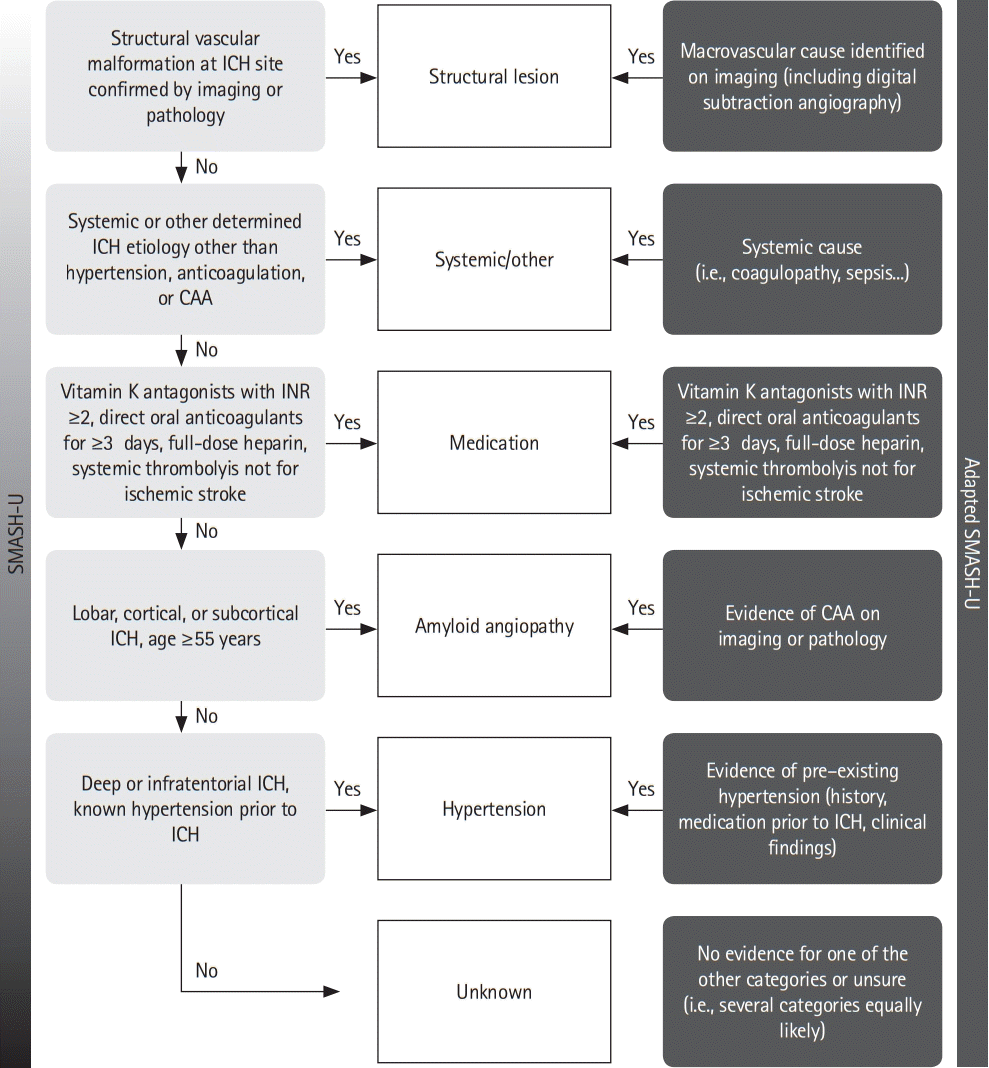
Figure 3.
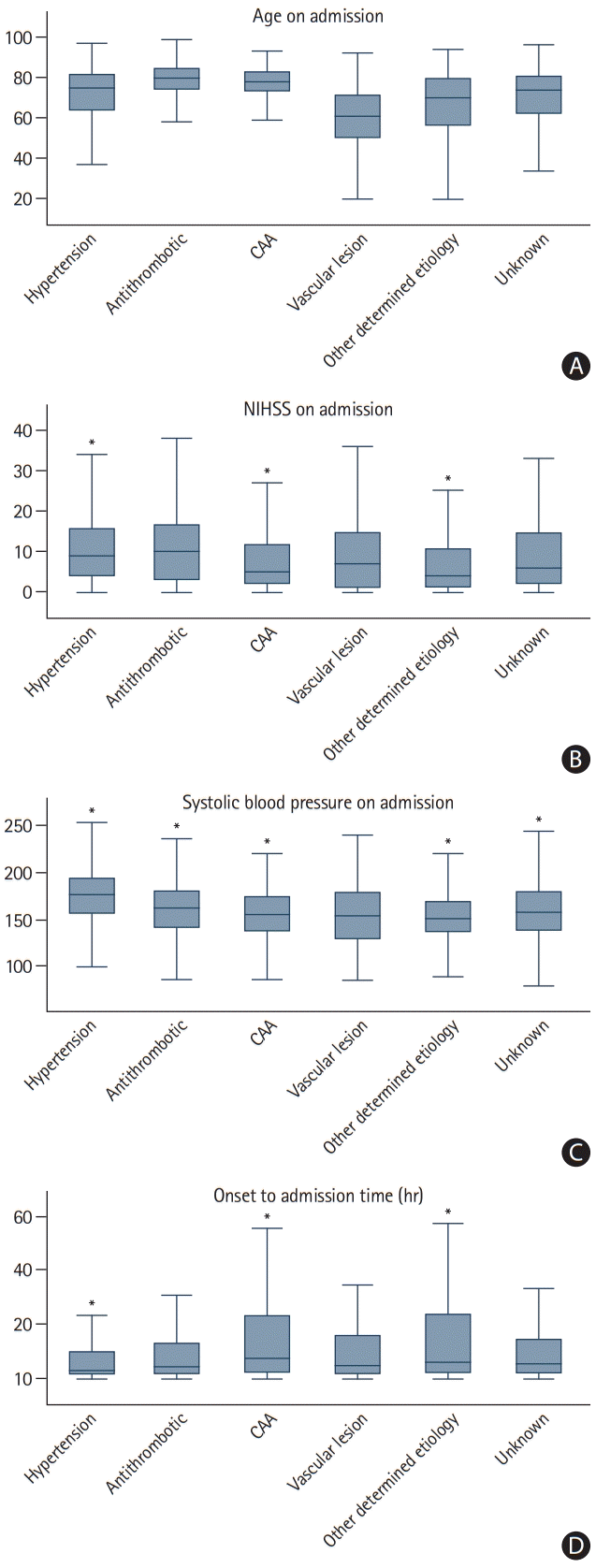
Figure 4.
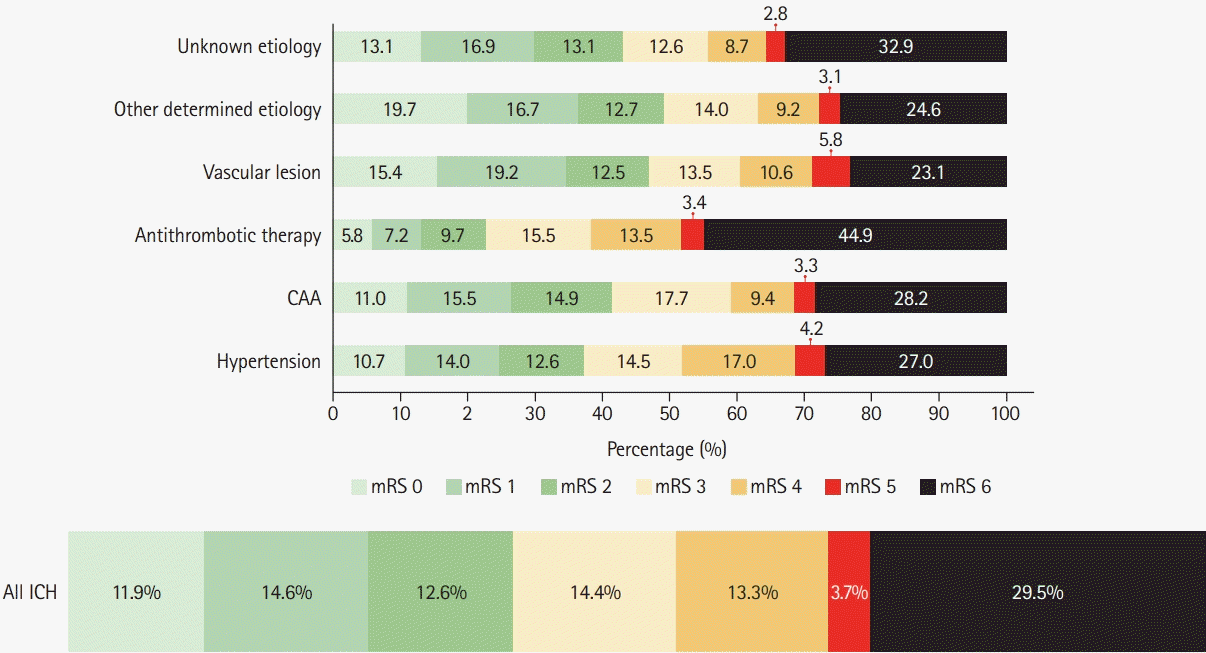
Figure 5.
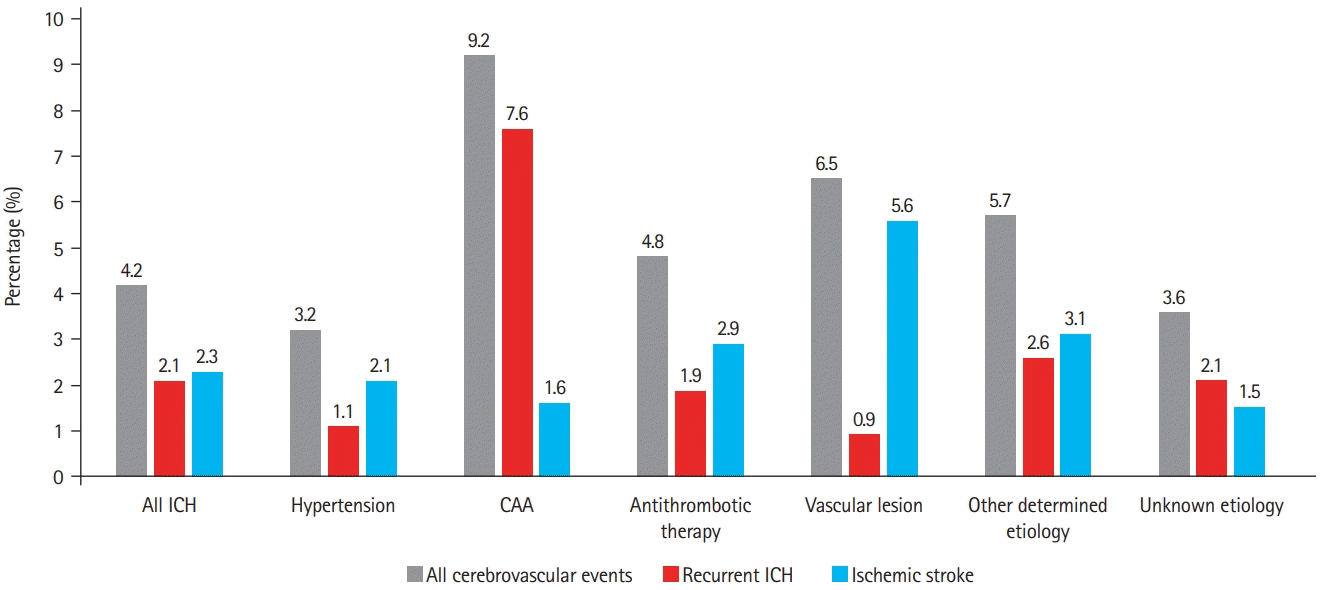
Table 1.
| Characteristic | Total (n=2,650) | Hypertension (n=1,238, 46.7%) | Antithrombotic (n=227, 8.6%) | CAA (n=217, 8.2%) | Macrovascular (n=128, 4.8%) | Other determined etiology (n=274, 10.3%) | Unknown (n=566, 21.4%) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||||||||
| Age (yr) | 71.9±14.1 | 72.6±13.0 | 78.5±9.8 | 77.1±8.2 | 59.3±17.5 | 66.1±17.6 | 70.8±14.3 | <0.001 | |
| Female sex | 1,227 (46.5) | 541 (43.9) | 95 (42.0) | 122 (56.2) | 52 (40.6) | 133 (48.5) | 284 (50.5) | 0.002 | |
| Risk factors | |||||||||
| Hypertension | 2,053 (79.9) | 1,152 (95.0) | 189 (84.8) | 147 (71.0) | 57 (46.7) | 164 (62.4) | 344 (63.4) | <0.001 | |
| Diabetes | 384 (15.0) | 198 (16.3) | 43 (19.3) | 27 (13.1) | 14 (11.4) | 40 (15.4) | 62 (11.4) | 0.033 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 1,096 (43.1) | 535 (44.5) | 105 (48.2) | 91 (44.6) | 41 (33.3) | 102 (39.7) | 222 (41.3) | 0.071 | |
| Smoking | 306 (12.0) | 142 (11.7) | 26 (11.7) | 15 (7.3) | 17 (13.9) | 40 (15.5) | 66 (12.3) | 0.154 | |
| Atrial fibrillation | 467 (18.2) | 174 (14.4) | 137 (61.4) | 22 (10.6) | 7 (5.7) | 43 (16.7) | 84 (15.5) | <0.001 | |
| Concomitant medication | |||||||||
| Antiplatelets | 729 (28.6) | 368 (31.0) | 46 (20.4) | 71 (33.8) | 28 (22.2) | 66 (25.6) | 150 (27.9) | 0.004 | |
| Anticoagulation | 568 (22.3) | 193 (16.3) | 212 (93.4) | 24 (11.4) | 8 (6.3) | 51 (19.8) | 80 (14.9) | <0.001 | |
| DOAC | 241 (42.4) | 99 (51.3) | 74 (34.9) | 12 (50.0) | 3 (37.5) | 18 (35.3) | 35 (43.8) | ||
| VKA | 296 (52.1) | 87 (45.1) | 128 (60.3) | 10 (41.6) | 5 (62.5) | 27 (52.9) | 39 (48.8) | ||
| Others* | 31 (5.4) | 7 (3.6) | 10 (4.7) | 2 (8.3) | 0 (0) | 6 (11.8) | 6 (7.5) | ||
| Medical history | |||||||||
| History of ischemic stroke | 290 (11.3) | 139 (11.5) | 38 (16.7) | 30 (14.5) | 13 (10.5) | 25 (9.6) | 45 (8.3) | 0.009 | |
| History of transient ischemic attack | 116 (4.5) | 50 (4.1) | 13 (5.8) | 14 (6.8) | 1 (0.8) | 8 (3.1) | 30 (5.5) | 0.068 | |
| History of intracerebral hemorrhage | 280 (10.9) | 97 (8.0) | 28 (12.6) | 65 (31.4) | 8 (6.5) | 23 (8.8) | 59 (10.9) | <0.001 | |
| Clinical presentation on admission | |||||||||
| NIHSS on admission | 8 (3–15) | 9 (4–16) | 10 (3–17) | 5 (2–12) | 7 (1–15) | 4 (1–11) | 6 (2–15) | <0.001 | |
| GCS on admission | 15 (12–15) | 14 (12–15) | 14 (12–15) | 15 (14–15) | 15 (10–15) | 15 (14–15) | 15 (12–15) | 0.003 | |
| Systolic blood pressure on admission (mm Hg) | 166.3±31.6 | 176.3±31.0 | 161.3±29.9 | 157.0±26.5 | 155.0±33.6 | 154.8±28.7 | 158.7±29.8 | <0.001 | |
| Diastolic blood pressure on admission (mm Hg) | 90.8±26.3 | 96.1±33.1 | 89.0±18.2 | 84.2±14.9 | 86.7±20.5 | 85.2±17.2 | 86.2±16.9 | <0.001 | |
| Management | |||||||||
| Treatment at stroke center | 2,052 (77.4) | 1,000 (80.8) | 174 (76.7) | 167 (77.0) | 92 (71.9) | 182 (66.4) | 437 (77.2) | <0.001 | |
| MRI performed | 969 (42.5) | 347 (32.3) | 55 (29.7) | 105 (57.1) | 65 (57.5) | 137 (59.6) | 260 (52.6) | <0.001 | |
| Onset-to admission time (hr) | 3.8 (1.4–13.3) | 2.8 (1.2–10.0) | 4.0 (1.3–13.3) | 7.5 (2.1–23.6) | 4.7 (1.1–16.2) | 5.6 (1.6–24.0) | 5.2 (1.6–14.8) | <0.001 | |
| Discharge destination | |||||||||
| Home | 460 (21.8) | 187 (18.4) | 18 (11.3) | 40 (22.7) | 25 (24.5) | 74 (32.7) | 116 (26.9) | <0.001 | |
| Nursing home or palliative care | 143 (6.8) | 65 (6.4) | 19 (11.9) | 21 (11.9) | 5 (4.9) | 7 (3.1) | 26 (6.0) | ||
| Other acute care hospital | 380 (18.0) | 175 (17.2) | 29 (18.2) | 22 (12.5) | 23 (22.5) | 46 (20.4) | 85 (19.7) | ||
| Rehabilitation hospital | 1,129 (53.5) | 590 (58.0) | 93 (58.5) | 93 (52.8) | 49 (48.0) | 99 (43.8) | 205 (47.5) | ||
Table 2.
Multivariable analysis adjusted for: age, sex, treatment at a stroke center (compared to treatment at a stroke unit), National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, Glasgow coma scale, systolic and diastolic blood pressure on admission, onset-to-admission time, antiplatelet and anticoagulation therapy prior to intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) onset, history of ischemic stroke or ICH, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and atrial fibrillation.
mRS, modified Rankin Scale; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; CAA, cerebral amyloid angiopathy.
Table 3.
Values are presented as number (%) or odds ratio (95% confidence interval). Multivariable analysis adjusted for: age, sex, treatment at a stroke center (compared to treatment at a stroke unit), National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale, Glasgow coma scale, systolic and diastolic blood pressure on admission, onset-to-admission time, antiplatelet and anticoagulation therapy prior to ICH onset, history of ischemic stroke or ICH, hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, smoking, and atrial fibrillation.
ICH, intracerebral hemorrhage; CAA, cerebral amyloid angiopathy.




 PDF
PDF Citation
Citation Print
Print



 XML Download
XML Download